6.1 and 6.2 Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
Last updated 11:16 PM on 12/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
atomic radii down a grp
increases
2
New cards
Electronegativity down a grp
Decreases
3
New cards
Ionization energy down a grp
Decreases
4
New cards
Electron Affinity down a grp
Decreases
5
New cards
Zeff down a grp
Constant
6
New cards
Shielding down a grp
increases
7
New cards
atomic radii across a period
decreases
8
New cards
Electronegativity across a period
increases
9
New cards
Ionization energy across a period
increases
10
New cards
Electron affinity across a period
increases
11
New cards
Zeff across a period
Increases
12
New cards
Shielding across a period
constant
13
New cards
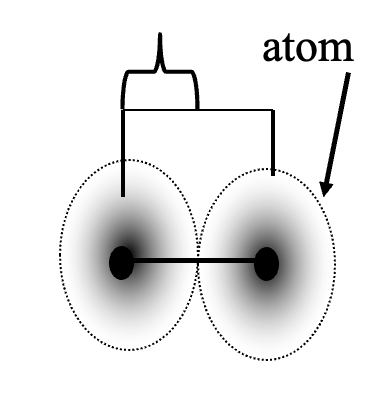
What is Atomic Radius
The radius of an atom .... (how big)
14
New cards
What is electronegativity
the tendency of an atom to attract an electron towards itself

15
New cards
What is ionization energy
the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom

16
New cards
What is electron affinity
the change in energy (kj) when an electron is added (the atom's likeliness of gaining an electron)
17
New cards
Zeff
effective nuclear charge ( Zeff = Z-S .... z= # of protons .... s= # of core electrons)

18
New cards
Sheilding
a reduction in effective nuclear charge (zeff), due to energy levels blocking the valence electrons from feeling the charge of the nucleus
19
New cards
Johann Doberereiner
Lived from : 1780 - 1849
1829; Classified elements into grps of 3 .... triads.
Each triad had similar chemical properties and orderly physical properties (Chlorine, Bromine and Iodine)
1829; Classified elements into grps of 3 .... triads.
Each triad had similar chemical properties and orderly physical properties (Chlorine, Bromine and Iodine)
20
New cards
John Newlands
Lived from 1838 -1898
1863; Suggested elements be arranged in "octaves"
He noticed that the properties repeat every 8 elements
(law of octaves)
Law of octaves failed past calcium
Ridiculed by chemical society XDDD (L Bozo)
1863; Suggested elements be arranged in "octaves"
He noticed that the properties repeat every 8 elements
(law of octaves)
Law of octaves failed past calcium
Ridiculed by chemical society XDDD (L Bozo)
21
New cards
Mendeleev
Lived 1834-1907
Created the first periodic table
Arranged elements according to atomic mass, similarities and chemical properties
1871; he predicted the properties of elements that would fill up gaps in his table ..... in 1886 the three elements he predicted were found 🤯
remember ms tujauge screaming MENDELEEV!!!!
Created the first periodic table
Arranged elements according to atomic mass, similarities and chemical properties
1871; he predicted the properties of elements that would fill up gaps in his table ..... in 1886 the three elements he predicted were found 🤯
remember ms tujauge screaming MENDELEEV!!!!
22
New cards
Henry Moseley
Lived 1887 -1915
English Physicist who worked with Rutherford
Figured out the acc nuclear charge (atomic number) of elements
English Physicist who worked with Rutherford
Figured out the acc nuclear charge (atomic number) of elements
23
New cards
Periodic Law
States that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number.... THERE IS A PATTERN !!!!
24
New cards
Glenn T. Seaborg (YEAAAAA)
1912-1999
Co-Discovered 10 new elements
1844; Moved 14 elements out of the main body of the periodic table and created the Actinide series (under the Lanthanides)
Had an element named after him while he was still alive
Co-Discovered 10 new elements
1844; Moved 14 elements out of the main body of the periodic table and created the Actinide series (under the Lanthanides)
Had an element named after him while he was still alive
25
New cards
WHere are the metals
Generally to the left of the periodic table
26
New cards
Where are the metalloids
The diagonal line starting with Boron
27
New cards
WHere are the nonmetals
Generally to the right of the periodic table (+ hydrogen)
28
New cards
List the grp names left to right
- Alkali metals
- Alkaline earth metals
- Transition Metals
- Inner transition metals (Lanthanides top, and Actanides bottom)
- Main grp elements
- Halogens
- Noble gases
- Alkaline earth metals
- Transition Metals
- Inner transition metals (Lanthanides top, and Actanides bottom)
- Main grp elements
- Halogens
- Noble gases
29
New cards
What are the properties of metals
- Good heat and electricity conductors
- Usually solid at room temp
- Malleable
- Ductile
- SHiny Luster
Mercury is the only liquid metal
- Usually solid at room temp
- Malleable
- Ductile
- SHiny Luster
Mercury is the only liquid metal
30
New cards
What are the properties of nonmetals
- Poor heat and electricity conductors
- Can be solids, liquids or gases at room temp
- Solids are usually brittle and dull
bromine is the only nonmetallic element in liquid state
- Can be solids, liquids or gases at room temp
- Solids are usually brittle and dull
bromine is the only nonmetallic element in liquid state
31
New cards
What are the properties of metalloids
- Have properties of metals and nonmetals
- Mostly brittle solids
- Intermediate conductors of electricity - AKA emiconductors
- Mostly brittle solids
- Intermediate conductors of electricity - AKA emiconductors
32
New cards
Properties of alkali metals
Extemely reactive (water, or air)
silvery appearance
soft
lower density
low melting points
not found freely in nature
silvery appearance
soft
lower density
low melting points
not found freely in nature
33
New cards
properties of alkaline earth metals
harder and stronger that alkali metals
high density, melting point than alkali metals
less reactive than alkali
not found freely in nature
high density, melting point than alkali metals
less reactive than alkali
not found freely in nature
34
New cards
Properties of halogens
Most reacitve nonmetals
react with most metals to form salts
most electronegative
react with most metals to form salts
most electronegative
35
New cards
properties of noble gases
least reactive because valence shell is compeltely filled
36
New cards
properties of transition metals (d block)
high density
high melting point
good conductor of heat and electricity
high luster
less reactive than the alkali or alkaline metals
Birght colors
high melting point
good conductor of heat and electricity
high luster
less reactive than the alkali or alkaline metals
Birght colors
37
New cards
Properties of p block metals
Harder and more dense than s block
softer and less dense than d block
softer and less dense than d block