SBI4U - U1 Water and Macromolecules Practice Test
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
U1 flashcard set 1/2 --> other one for this unit test is U1 Enzymes l *questions are extra that H hinted we would have to know
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
1. A hydrogen bond is
a. | a sharing of a pair of electrons between a hydrogen and an oxygen nucleus. |
b. | a sharing of a pair of electrons between a hydrogen nucleus and either an oxygen or a nitrogen nucleus. |
c. | an attractive force that involves a hydrogen atom and an oxygen or a nitrogen atom that are either in two different molecules or within the same molecule. |
d. | none of these |
e. | all of these |
c. | an attractive force that involves a hydrogen atom and an oxygen or a nitrogen atom that are either in two different molecules or within the same molecule. |
2. Which of the following is NOT true of hydrogen bonds?
a. | They are quite weak. |
b. | The hydrogen is slightly positive. |
c. | They are common in macromolecules. |
d. | They form in salts such as NaCl. |
e. | They always involve hydrogen. |
d. | They form in salts such as NaCl. |
3. Hydrophobic molecules are __________ water.
a. | attracted to |
b. | absorbed by |
c. | repelled by |
d. | mixed with |
e. | polarized by |
c. | repelled by |
no affinity for water
4. Which of the following is true of water?
a. | The oxygen end is slightly electropositive. |
b. | Hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together. |
c. | Water covers about one-half of the earth's surface. |
d. | Hydrophobic interactions attract water molecules. |
e. | Solvent properties are greatest with nonpolar molecules. |
b. | Hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together. |
5. Water is an excellent solvent because
a. | it forms spheres of hydration around charged substances and can form hydrogen bonds with many substances. |
b. | it has a high heat-containing property. |
c. | of its cohesive properties. |
d. | it is a liquid at room temperature. |
e. | all of these |
e. | all of these |
6. In a lipid bilayer, the __________ phospholipid tails point inward and form a region that excludes water.
a. | acidic | c. | hydrophilic | e. | none of these | |
b. | basic | d. | hydrophobic |
d. | hydrophobic |
7. Glucose dissolves in water because it
a. | ionizes. |
b. | is a polysaccharide. |
c. | is polar and forms many hydrogen bonds with the water molecules. |
d. | has a very reactive primary structure. |
e. | none of these |
c. | is polar and forms many hydrogen bonds with the water molecules. |
8. Water has the ability to retain heat gain and loss due to its
a. | hydrophilic interactions. | d. | crystal structure. | |
b. | evaporation. | e. | liquidity. | |
c. | hydrogen bonds. | |||
c. | hydrogen bonds. |
9. The column of water extending in tubes from plant roots to leaves is due mostly to
a. | cohesion. | d. | hydrophobic interactions. | |
b. | evaporation. | e. | all of these | |
c. | ionization. | |||
cohesion |
10. Water's surface tension and heat storage capacity is accounted for by its
a. | orbitals | c. | H bonds | e. | size | |
b. | weight. | d. | mass |
c. | H bonds |
11. As ice melts,
a. | hydrogen bonds are broken. |
b. | water molecules become less tightly packed. |
c. | the water becomes less dense. |
d. | covalent bonds form. |
e. | All of the choices are true. |
a. | hydrogen bonds are broken. |
12. The hydrogen atoms of a water molecule are bonded to the oxygen atom by __________ bonds, whereas neighboring water molecules are held together by __________ bonds.
a. | hydrogen . . . ionic |
b. | hydrogen . . . polar covalent |
c. | polar covalent . . . hydrogen |
d. | ionic . . . covalent |
e. | polar covalent . . . ionic |
c. | polar covalent . . . hydrogen |
13. The temperature of evaporation is much higher for water than for alcohol. Without knowing more about the chemistry of alcohol, which of the following is the most logical chemical explanation for this phenomenon?
a. | Ionic bonds form between alcohol molecules. These are the weakest type of bond and are easier to break than the hydrogen bonds between water molecules. |
b. | Alcohol has a higher surface tension than water. This means that alcohol molecules can easily break away from other alcohol molecules and evaporate at a lower temperature. |
c. | Alcohol molecules are more cohesive than water molecules. This means that as alcohol molecules evaporate, they pull other alcohol molecules into the air along with them. |
d. | Fewer hydrogen bonds form between alcohol molecules. As a result, less heat is needed for alcohol molecules to break away from solution and enter the air. |
e. | None of the choices is a logical chemical explanation for this phenomenon. |
d. | Fewer hydrogen bonds form between alcohol molecules. As a result, less heat is needed for alcohol molecules to break away from solution and enter the air. |
14. The oxygen atom of a water molecule
a. | is more positively charged than the hydrogen atoms. |
b. | attracts electrons less strongly than the hydrogen atoms. |
c. | is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms. |
d. | is electrically neutral. |
e. | is attracted to the negatively charged atoms of other molecules. |
c. | is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms. |
15. Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface tension of water?
a. | Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures. |
b. | A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond. |
c. | Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions. D) Water can act as a solvent. |
d. | The pH of water remains exactly neutral. |
b. | A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond. |
16. Water's high specific heat is mainly a consequence of the
a. | small size of the water molecules. |
b. | high specific heat of oxygen and hydrogen atoms. |
c. | absorption and release of heat when hydrogen bonds break and form. |
d. | fact that water is a poor heat conductor. |
e. | inability of water to dissipate heat into dry air. |
c. | absorption and release of heat when hydrogen bonds break and form. |
17. At what temperature (oC) is water at its densest?
a. 0
b. 4
c. 32
d. 100
e. 312
b. 4
18. Why does ice float in liquid water?
a. | The liquid water molecules have more kinetic energy and thus support the ice. |
b. | The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking. |
c. | Ice always has air bubbles that keep it afloat. |
d. | Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of liquid water. |
e. | The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water. |
d. | Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of liquid water. |
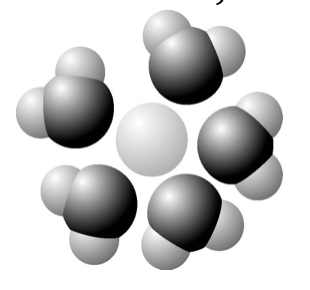
19. Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule is most likely
a. | positively charged. | d. | hydrophobic. | |
b. | negatively charged. | e. | nonpolar. | |
c. | without charge. | |||
a. | positively charged. |
20. Nitrogen (N) is much more electronegative than hydrogen (H). Which of the following statements is correct about the atoms in ammonia (NH3)?
a. | Each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge. |
b. | The nitrogen atom has a strong positive charge. |
c. | Each hydrogen atom has a slight negative charge. |
d. | The nitrogen atom has a partial positive charge. |
e. | There are covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms. |
a. | Each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge. |
21. What results from an unequal sharing of e-s between atoms?
a. | a nonpolar covalent bond |
b. | a polar covalent bond |
c. | an ionic bond |
d. | a hydrogen bond |
e. | a hydrophobic interaction |
b. | a polar covalent bond |
22. Isomers are molecules that
a. | react readily with one another |
b. | have the same molecular formula |
c. | have different molecular masses |
d. | differ in the number of unsaturated bonds |
e. | must contain the same functional group |
b. | have the same molecular formula |
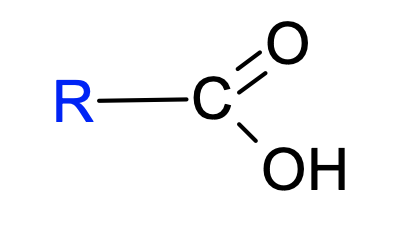
23. The following structural formula is representative of which functional group:
a. | sulfhydryl | c. | carbonyl | e. | amino | |
b. | hydroxyl | d. | carboxyl |
d. | carboxyl |
24. What name is given to compounds in which a carbon atom only bonds to hydrogen and other carbon atoms?
a. | fatty acids | d. | nucleic acids | |
b. | hydrocarbons | e. | carbohydrates | |
c. | lipids | |||
b. | hydrocarbons |
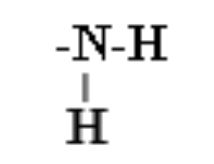
25. The following structural formula is representative of which functional group?
a. | sulfhydryl | c. | carbonyl | e. | amino | |
b. | hydroxyl | d. | carboxyl |
e. | amino |
from the N
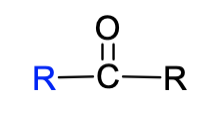
26. The following structural formula is representative of which functional group?
a. | sulfhydryl | c. | carboxyl | e. | amino | |
b. | hydroxyl | d. | carbonyl |
d. | carbonyl |
27. An amino acid always has an amino group, as its name suggests. What other group is also present in all amino acids?
a. | a methyl group | d. | a carboxyl group | |
b. | an aldehyde group. | e. | a hydroxyl group | |
c. | a carbonyl group | |||
d. | a carboxyl group |
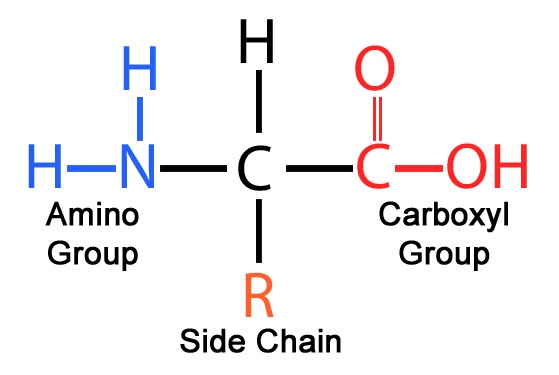
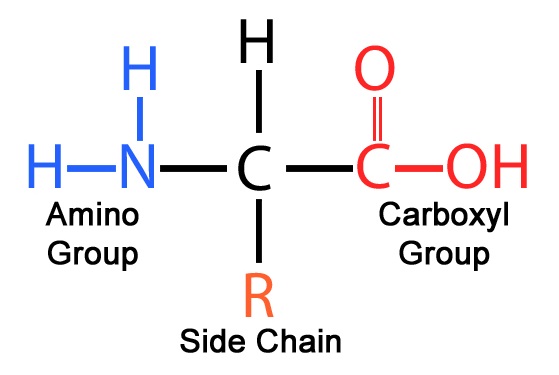
28. Which of the following functional groups would be found in a monosaccharide?
a. | carbonyl and hydroxyl | d. | carboxyl and carbonyl | |
b. | glycosidic and hydroxyl | e. | hydroxyl and sulfhydryl | |
c. | carboxyl and amino | |||
a. | carbonyl and hydroxyl |
note C double bond O and OH
29. Of the following, which is not considered to by a polymer?
a. cellulose
b. RNA
c. starch
d. protein
e. fat
e. fat
30. There are four elements that make up all amino acids. Two of these are carbon and hydrogen. The other two are
a. | sulfur and nitrogen | d. | nitrogen and oxygen | |
b. | phosphorus and nitrogen | e. | phosphorus and oxygen | |
c. | sulfur and oxygen | |||
d. | nitrogen and oxygen |
31. When digested, which of the following substances would yield a mixture of amino acids?
a. | carbohydrate | c. | sugar | e. | fat | |
b. | nucleic acids | d. | protein |
d. | protein |
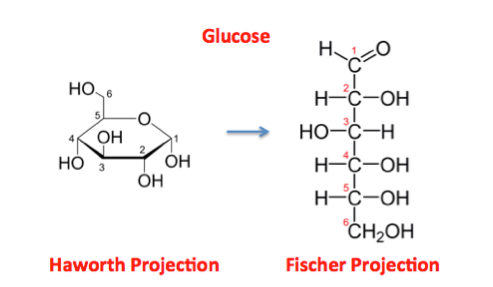
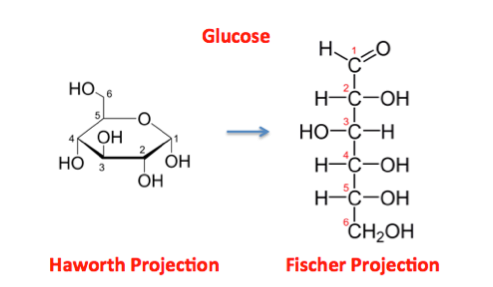
32. From the following list, which is an example of a monosaccharide?
a. maltose
b. glycogen
c. cellulose
d. glucose
e. sucrose
d. glucose
33. When a molecule of glycerol reacts with one or more fatty acids an ester linkage results. The formation of this linkage is a result of a reaction between
a. | an amino acid and a carboxylic acid |
b. | two alcohols |
c. | an alcohol and a carboxylic acid |
d. | two carboxylic acids |
e. | two amino acids |
c. | an alcohol and a carboxylic acid |
34. When two organic molecules are joined together and a water molecule is removed, the reaction is called which of the following?
a. | condensation | c. | hydrolysis | e. | reduction | |
b. | hydrogenation | d. | oxidation |
a. | condensation |
35. The production, or synthesis, of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates involves the
a. | production of ATP | d. | hydrogen bonding | |
b. | addition of water | e. | removal of nitrogen | |
c. | removal of water | |||
c. | removal of water |
dehydation synthesis
36. Many people are aware that water is the most abundant substance in all organisms. However, next to water, what is the major component of living cells?
a. | nucleotides | c. | proteins | e. | lipids | |
b. | carbohydrates | d. | vitamins |
c. | proteins |
37. Carbon usually forms how many bonds with other atoms?
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 5
e. 6
c. 4
38. An -OH group is a(n) __________ group.
a. carboxyl
b. hydroxyl
c. amino
d. methyl
e. ketone
b. hydroxyl
39. A -COOH group is a(n) __________ group.
a. carboxyl
b. hydroxyl
c. amino
d. methyl
e. ketone
a. carboxyl
40. The addition of water is an example of what kind of reaction?
a. | oxidation | c. | condensation | e. | decarboxylation | |
b. | reduction | d. | hydrolysis |
d. | hydrolysis |
41. Which is a monomer of carbohydrates?
a. | glycogen | c. | simple sugar | e. | Both c) & d) | |
b. | nculeotide | d. | monosaccharide |
e. | Both c) & d) |
c. | simple sugar |
d. | monosaccharide |
42. A macromolecule is composed of smaller units called
a. polymers
b. isomers
c. monomers
d. isotopes
e. dimers
c. monomers
43. Which of the following is composed of a 1:2:1 ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen?
a. | carbohydrate | c. | lipid | e. | steroid | |
b. | protein | d. | nucleic acid |
a. | carbohydrate |
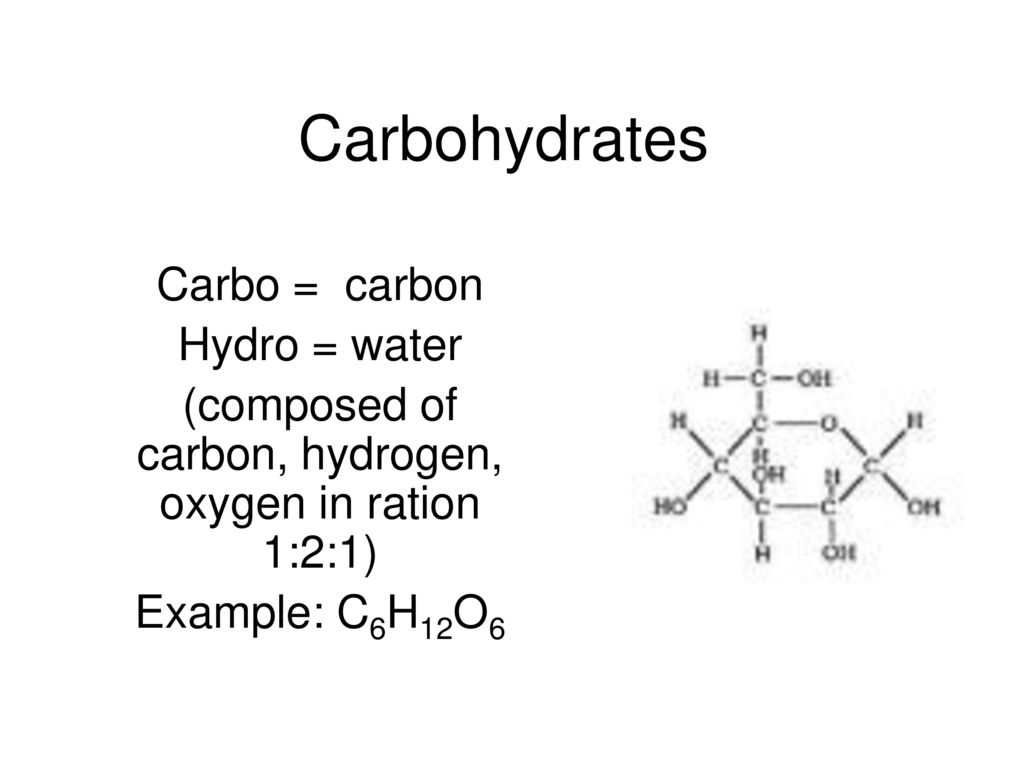
44. Fructose and glucose are
i. isomers.
ii. monosaccharides.
iii. disaccharides.
iv. six-carbon sugars
v. enantiomers
a. | i. and ii. only | d. | i., ii., and iv. only | |
b. | ii. and iv. only | e. | all of i., ii., iii., iv., and v. | |
c. | iii. and iv. only | |||
d. | i., ii., and iv. only |
45. Glucose and fructose
a. | form rings with the same number of carbon atoms. |
b. | both have an oxygen atom as part of their ring structure. |
c. | are alike in that both are aldehydes. |
d. | contain the same number of hydrogens and hydroxyl groups. |
e. | are disaccharides. |
d. | contain the same number of hydrogens and hydroxyl groups. |
46. Plants store their excess carbohydrates in the form of
a. starch
b. glycogen
c. glucose
d. cellulose
e. fats
a. starch
47. Glycogen is a polysaccharide used for energy storage by
a. | animals. | c. | protistans. | e. | Both a) & c) | |
b. | plants. | d. | prokaryotes |
a. | animals. |
48. Cellulose is
a. | a material found in cell walls. |
b. | a component of cell membranes. |
c. | a plant protein. |
d. | formed by photosynthesis. |
e. | the most complex of the organic compounds. |
a. | a material found in cell walls. |
49. Which is NOT a monosaccharide?
a. glucose
b. fructose
c. deoxyribose
d. starch
e. ribose
d. starch
50. Triglycerides are
a. | carbohydrate | c. | proteins. | e. | amino acids. | |
b. | nucleotides. | d. | neutral fats. |
d. | neutral fats. |
51. Oils are
a. | liquid at room temperatures. |
b. | unsaturated fats. |
c. | found only in animals. |
d. | complex carbohydrates. |
e. | both liquid at room temperature and unsaturated fats. |
e. | both liquid at room temperature and unsaturated fats. |
52. Which of the following are lipids?
a. | sterols | c. | oils | e. | all of these | |
b. | triglycerides. | d. | waxes |
e. | all of these |
53. An example of a saturated fat is
a. | olive oil. | c. | butter. | e. | soybean oil | . |
b. | corn oil. | d. | oleo. |
c. | butter. |
54. Lipids
a. | serve as food reserves in many organisms. |
b. | include cartilage and chitin. |
c. | include fats consisting of one fatty acid molecule and three glycerol molecules. |
d. | are composed of monosaccharides. |
e. | none of these |
a. | serve as food reserves in many organisms. |
55. All sterols have
a. | the same number of double bonds. |
b. | double bonds in the same positions. |
c. | four rings of carbon to which are attached other atoms. |
d. | the same functional groups. |
e. | the same number and positions of double bonds. |
c. | four rings of carbon to which are attached other atoms. |
56. Proteins may function as
a. | structural units. | d. | transport molecules. | |
b. | hormones. | e. | All of these. | |
c. | storage molecules. | |||
e. | All of these. |
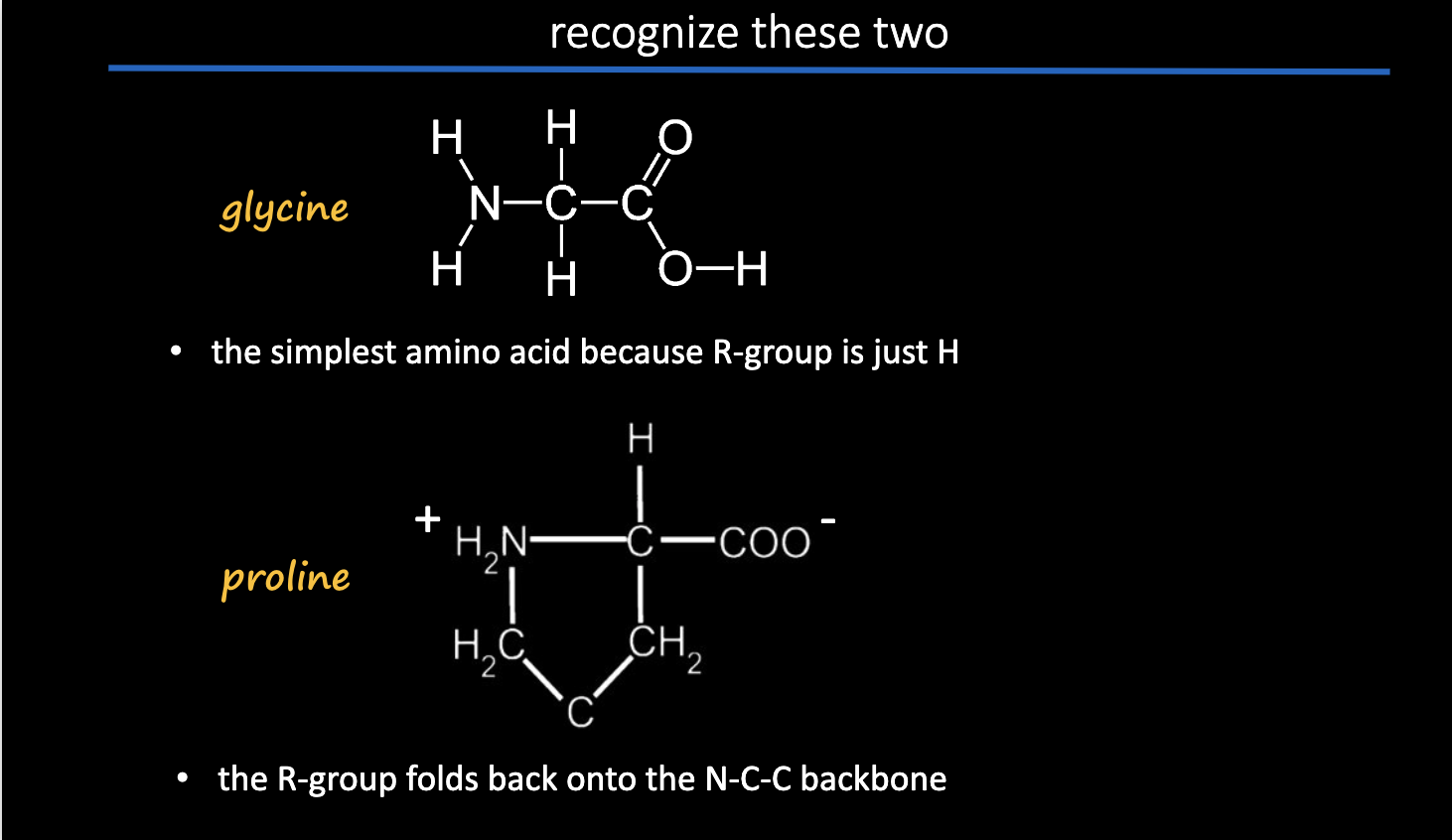
57. Which of the following is structurally the simplest of the amino acids?
a. proline
b. serine
c. tryptophan
d. cysteine
e. glycine
e. glycine
58. Amino acids are the building blocks for
a. | proteins. | c. | lipids. | e. | carbohydrates. | |
b. | steroids. | d. | nucleic acid |
a. | proteins. |
59. What kind of bond exists between two amino
acids in a protein?
a. | peptide | c. | hydrogen | e. | sulfhydroxyl | |
b. | ionic | d. | amino |
a. | peptide |
60. The sequence of amino acids is the __________ structure of proteins.
a. | primary | c. | tertiary | e. | stereo | |
b. | secondary | d. | quaternary |
a. | primary |
61. Amino acids are linked by what kind of bonds
to form the primary structure of a protein?
a. | disulfide | c. | ionic | e. | none of these | |
b. | hydrogen | d. | peptide |
d. | peptide |
62. The secondary structure of proteins is
a. | helical. | d. | sequence of amino acids. | |
b. | sheetlike. | e. | Both a) & b) | |
c. | globular. | |||
e. | Both a) & b) |
63. The interaction of four polypeptide chains in a hemoglobin molecule is __________ structure.
a. quaternary
b. secondary
c. primary
d. tertiary
e. quintineary
a. quaternary
64. Denaturation of proteins may result in all but one of the following. Which one is it?
a. | breakage of hydrogen bonds |
b. | loss of three-dimensional structure |
c. | removal of R groups from amino acids |
d. | alteration of enzyme activity |
e. | endangerment of cell's life |
c. | removal of R groups from amino acids |
65. The nucleotide most closely associated with energy is
a. | cyclic AMP. | c. | NAD+. | e. | all of these | |
b. | FAD. | d. | ATP. |
d. | ATP. |
66. Nucleotides contain what kind of sugars?
a. 3-
b. 4-
c. 5-C
d. 6-C
e. 7-
c. 5-C
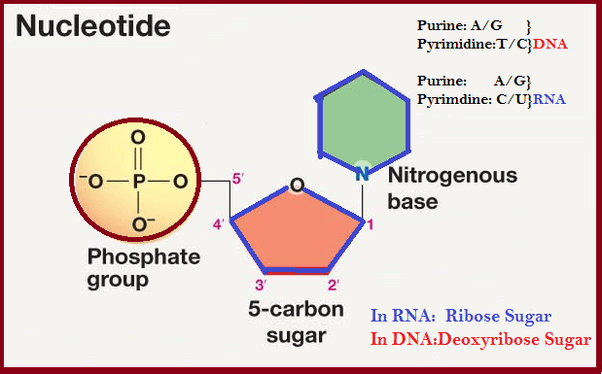
67. DNA
a. | is one of the adenosine phosphates. |
b. | is one of the nucleotide coenzymes. |
c. | contains protein-building instructions. |
d. | translates protein-building instructions into actual protein structures. |
e. | none of these |
c. | contains protein-building instructions. |
68. Which molecule is incorrectly matched with its component parts?
a. | fat: fatty acids | d. | glycogen: glucoses | |
b. | starch: riboses | e. | nucleic acids: nucleotides | |
c. | protein: amino acids | |||
b. | starch: riboses |
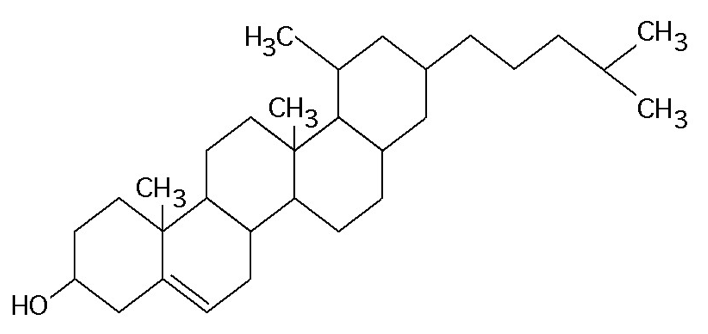
69. What is the structure shown?
a. | starch molecule | d. | cellulose molecule | |
b. | protein molecule | e. | phospholipid molecule | |
c. | steroid molecule | |||
c. | steroid molecule cholesterol |
70. Which three of the following are characteristics of H-bonds?
I. responsible for the surface tension properties of water.
II. responsible for the relatively high boiling point of water.
III. stronger than ionic bonds.
IV. present in all substances.
V. weaker than covalent bonds.
a. | III, IV and V |
b. | I, II and V |
c. | I, III and IV |
d. | II, III and IV |
e. | I, III, and IV |
b. | I, II and V |
I. responsible for the surface tension properties of water.
II. responsible for the relatively high boiling point of water.
V. weaker than covalent bonds.
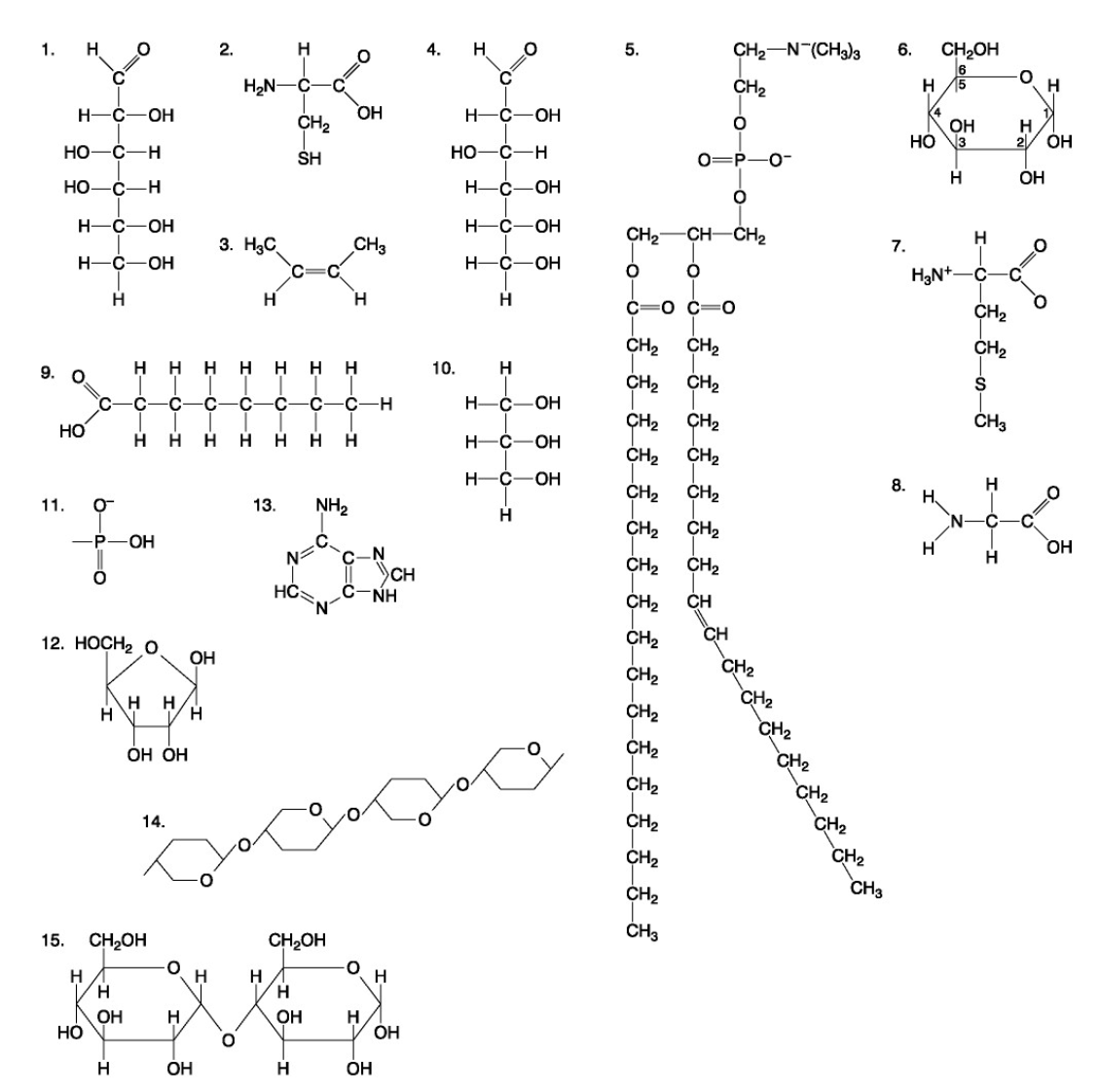
The following questions are based on the 15 molecules illustrated below. Each molecule may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
71. Which molecule has hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties and would be found in plasma membranes?
a. 1
b. 5
c. 6
d. 12
e. 14
b. 5
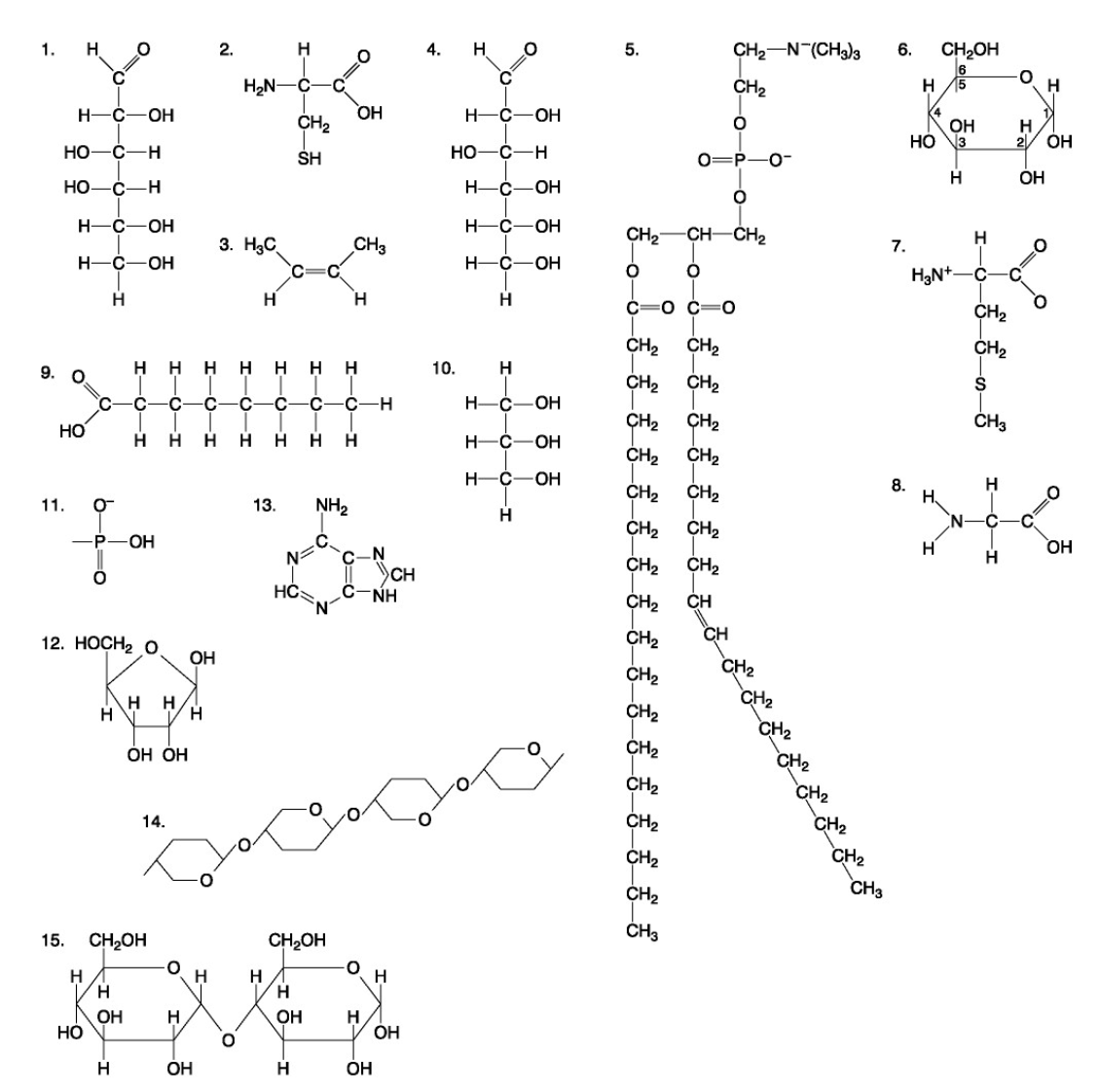
72. Which of the following combinations could be linked together to form a nucleotide?
a. | 1, 2, and 11 | c. | 5, 9, and 10 | e. | 12, 14, and 15 | |
b. | 3, 7, and 8 | d. | 11, 12, and 13 |
d. | 11, 12, and 13 |
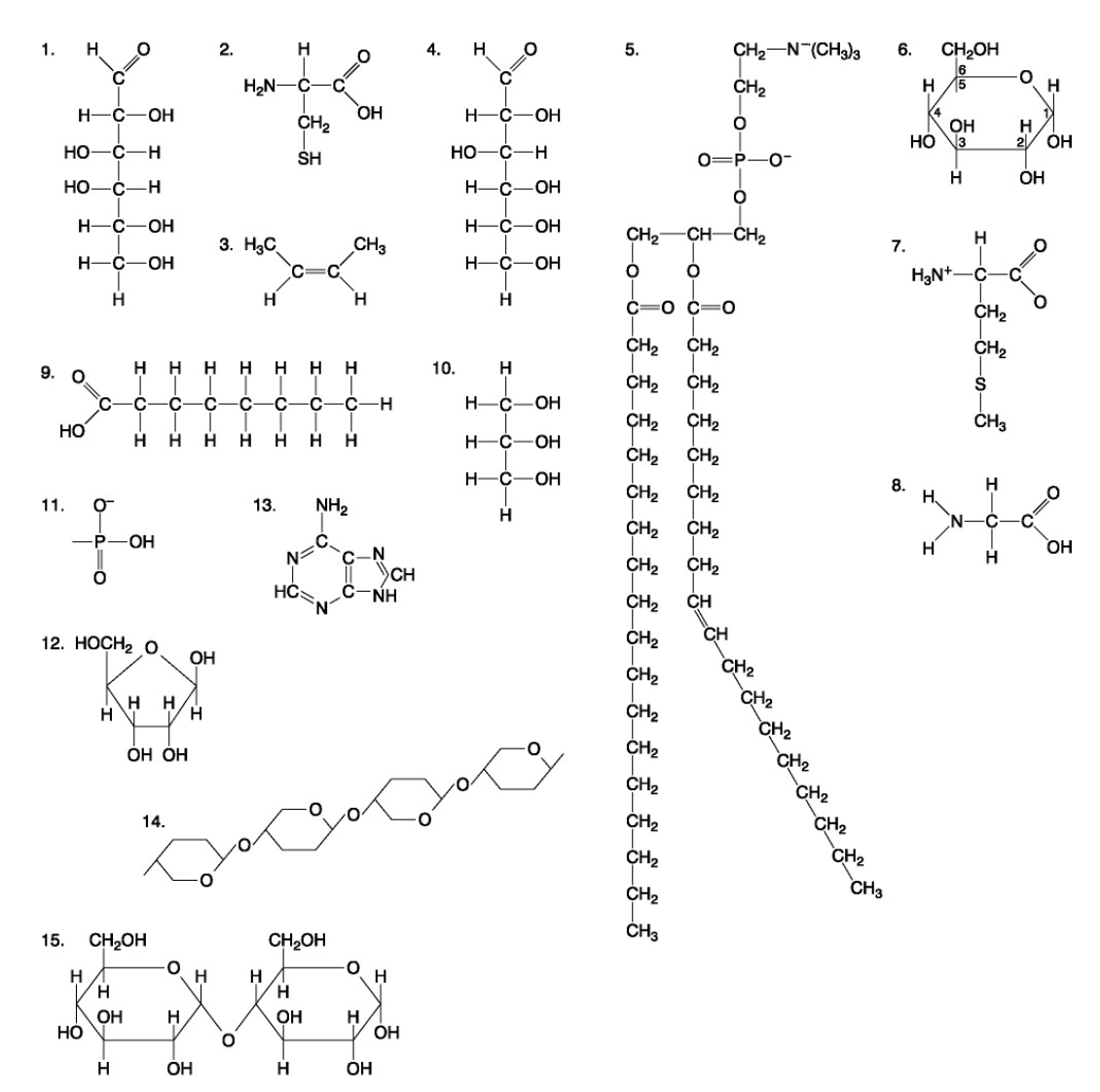
Which of the following molecules contain(s) an aldehyde type of carbonyl functional group
a. 1
b. 4
c. 8
d. 10
e. 1+4
e. 1+4
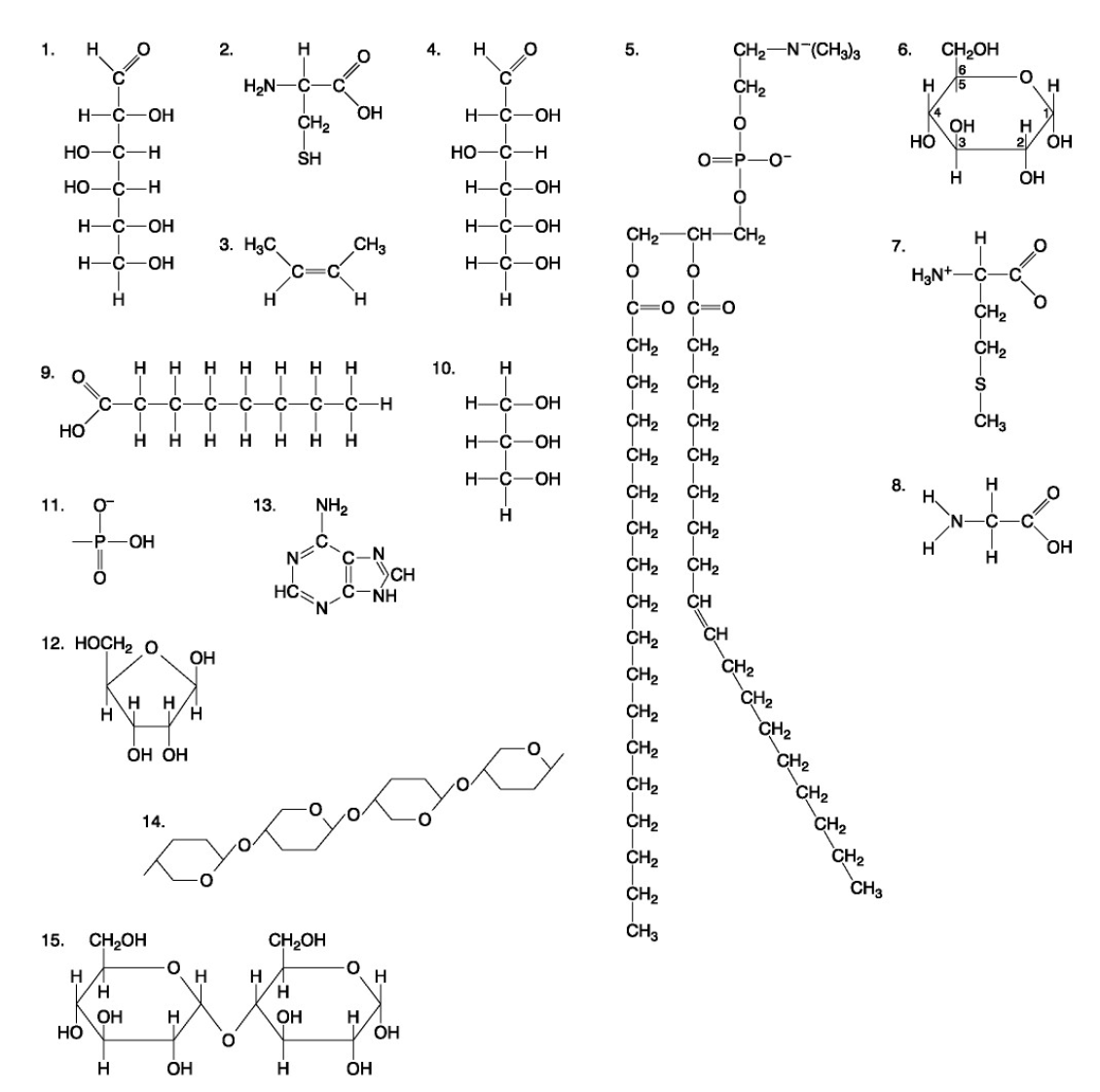
Which molecule is glycerol?
a. 1
b. 6
c. 10
d. 16
e. 15
c. 10
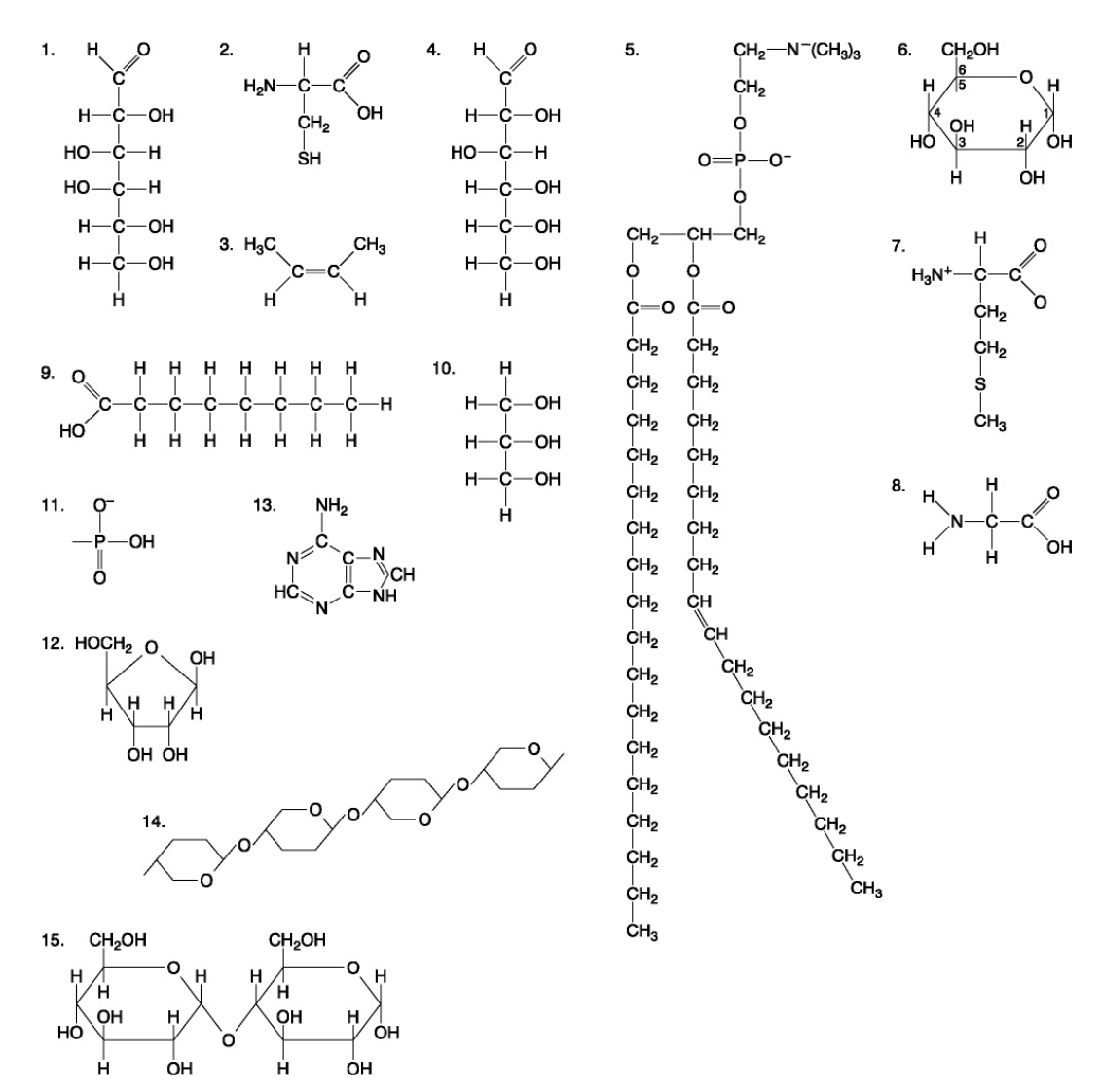
Which molecule is a saturated fatty acid?
a. 1
b. 5
c. 6
d. 8
e. 9
e. 9
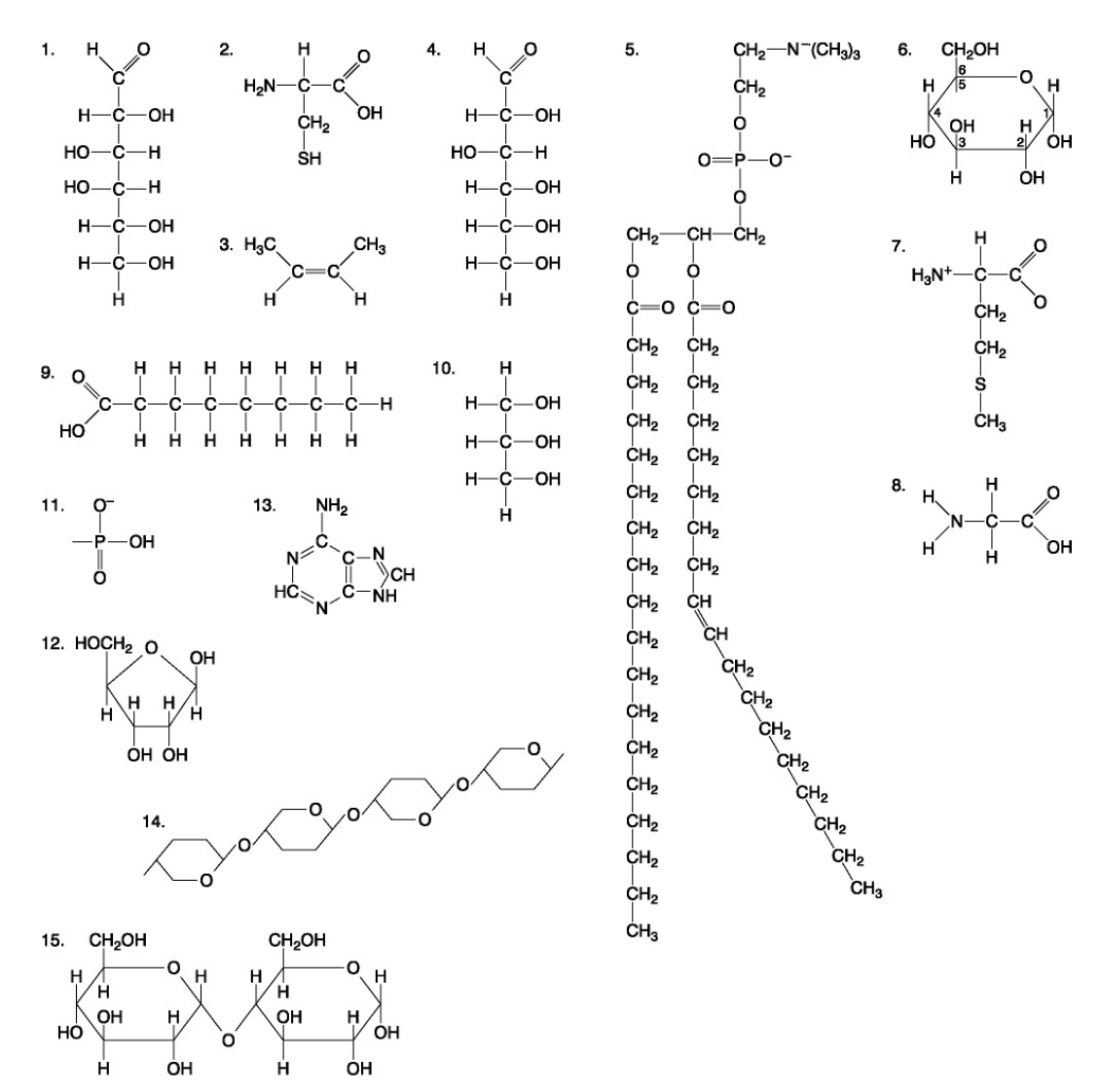
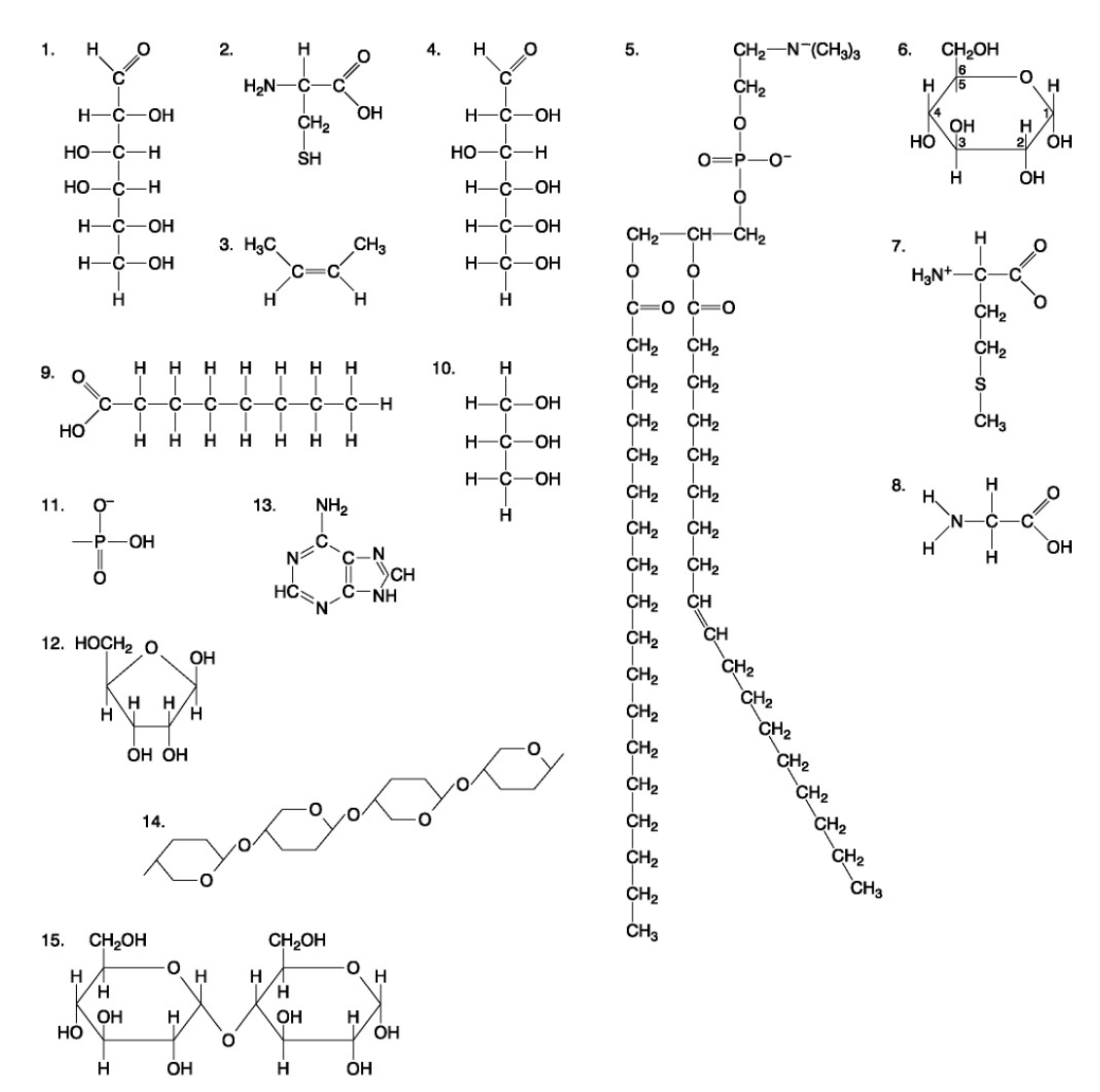
Which of the following molecules is a purine type of nitrogenous base?
a. 2
b. 3
c. 5
d. 12
e. 13
e. 13
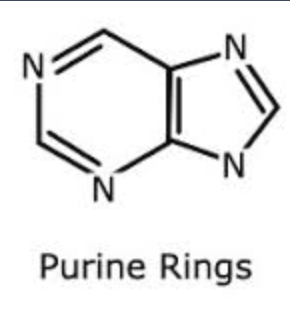
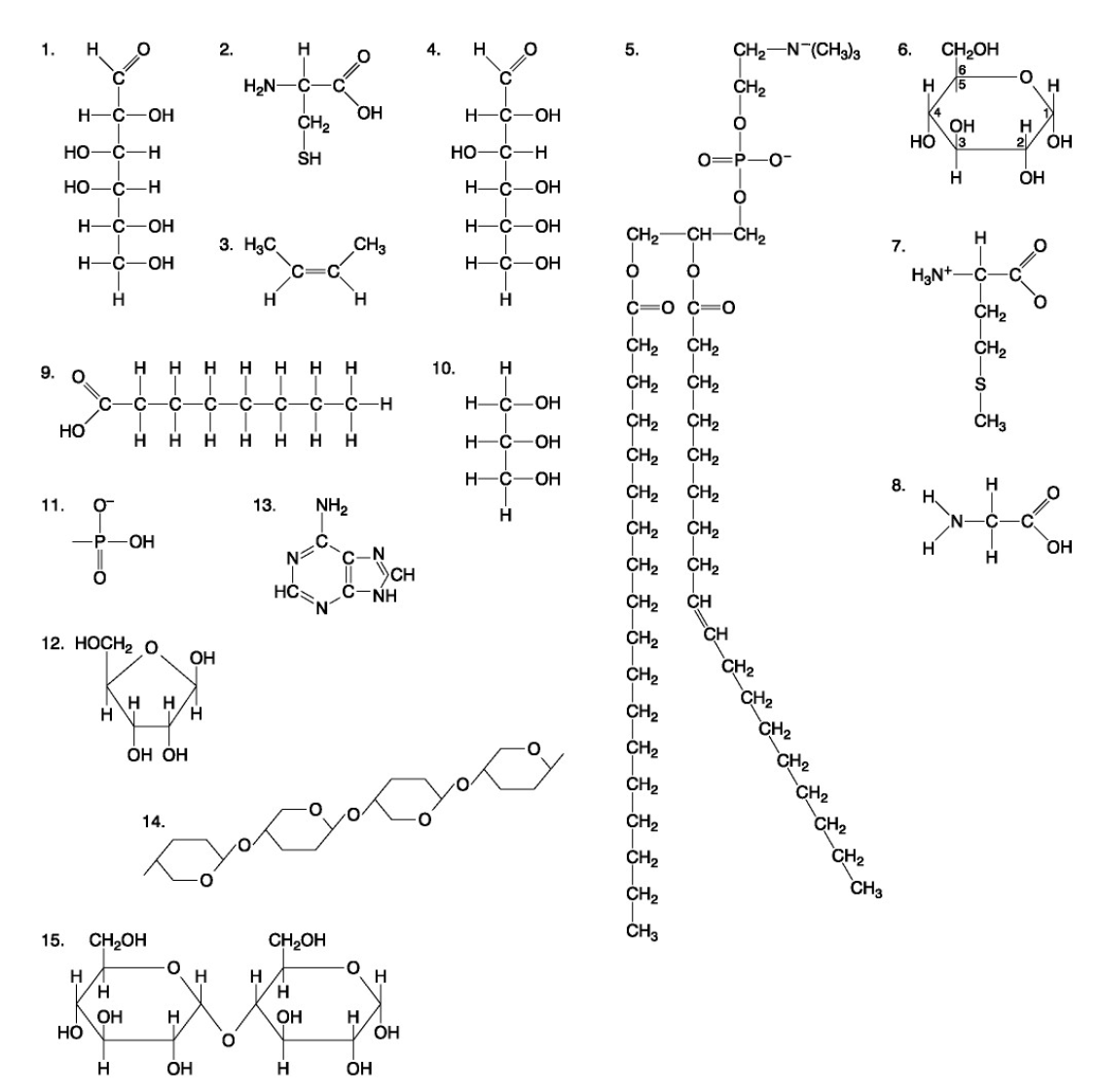
77. Which of the following molecules could act as building blocks (monomers) of polypeptides?
a. | 1, 4, and 6 | c. | 7, 8, and 13 | e. | 12, 13, and 15 | |
b. | 2, 7, and 8 | d. | 11, 12, and 13 |
b. | 2, 7, and 8 |
78. Which of the following molecules is an amino acid with a hydrophobic R group or side chain?
a. 3
b. 7
c. 8
d. 12
b. 7
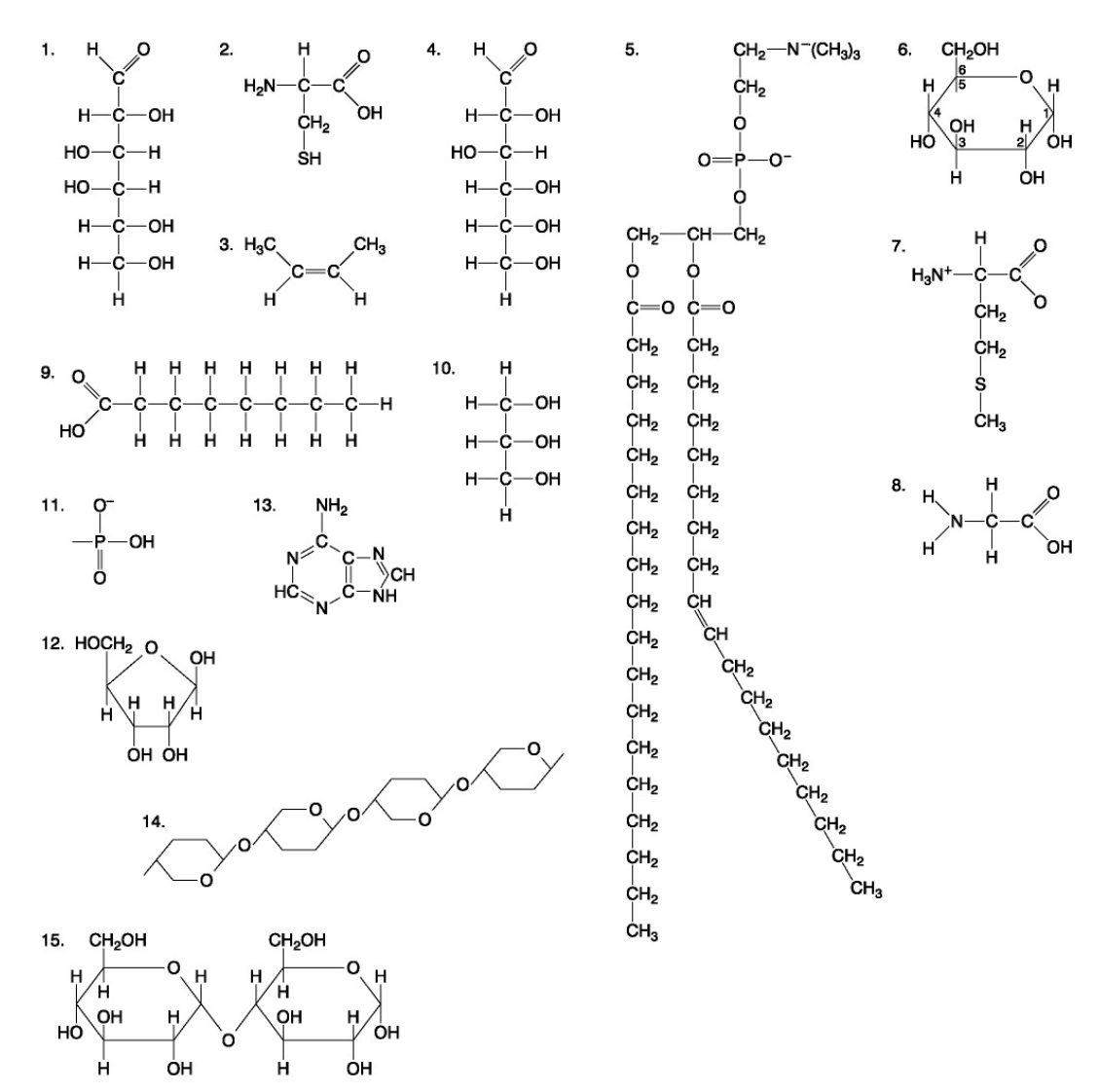
79. Which of the following molecules could be joined together by a peptide bond as a result of a dehydration reaction?
a. 2,3
b. 3,7
c. 7,8
d. 8,9
e. 12,13
c. 7,8
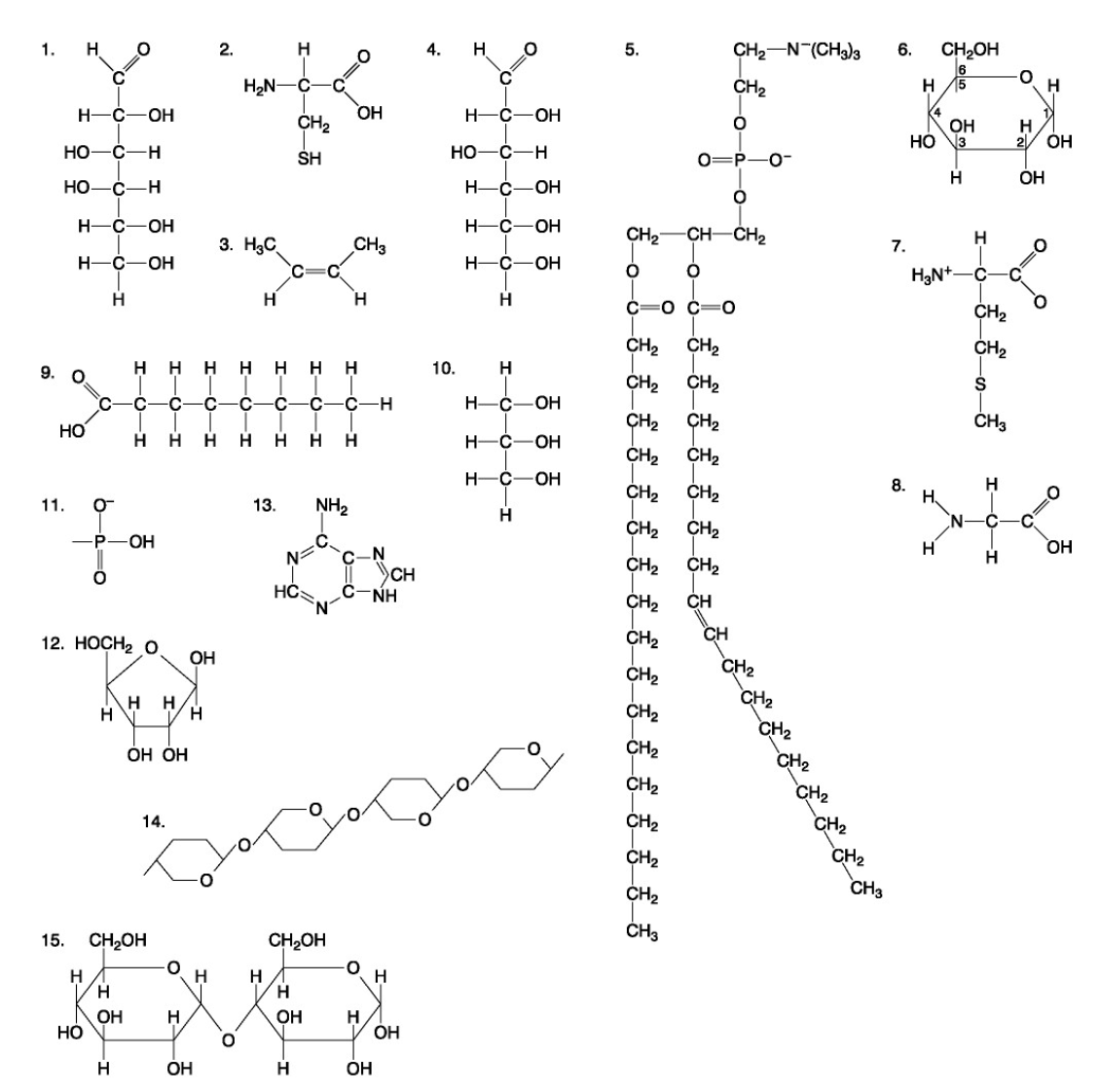
80. A fat (or triacylglycerol) would be formed as a result of a dehydration reaction between
a. | one molecule of 9 and three molecules of 10. |
b. | three molecules of 9 and one molecule of 10. |
c. | one molecule of 5 and three molecules of 9. |
d. | three molecules of 5 and one molecule of 9. |
e. | one molecule of 5 and three molecules of 10. |
b. | three molecules of 9 and one molecule of 10. |
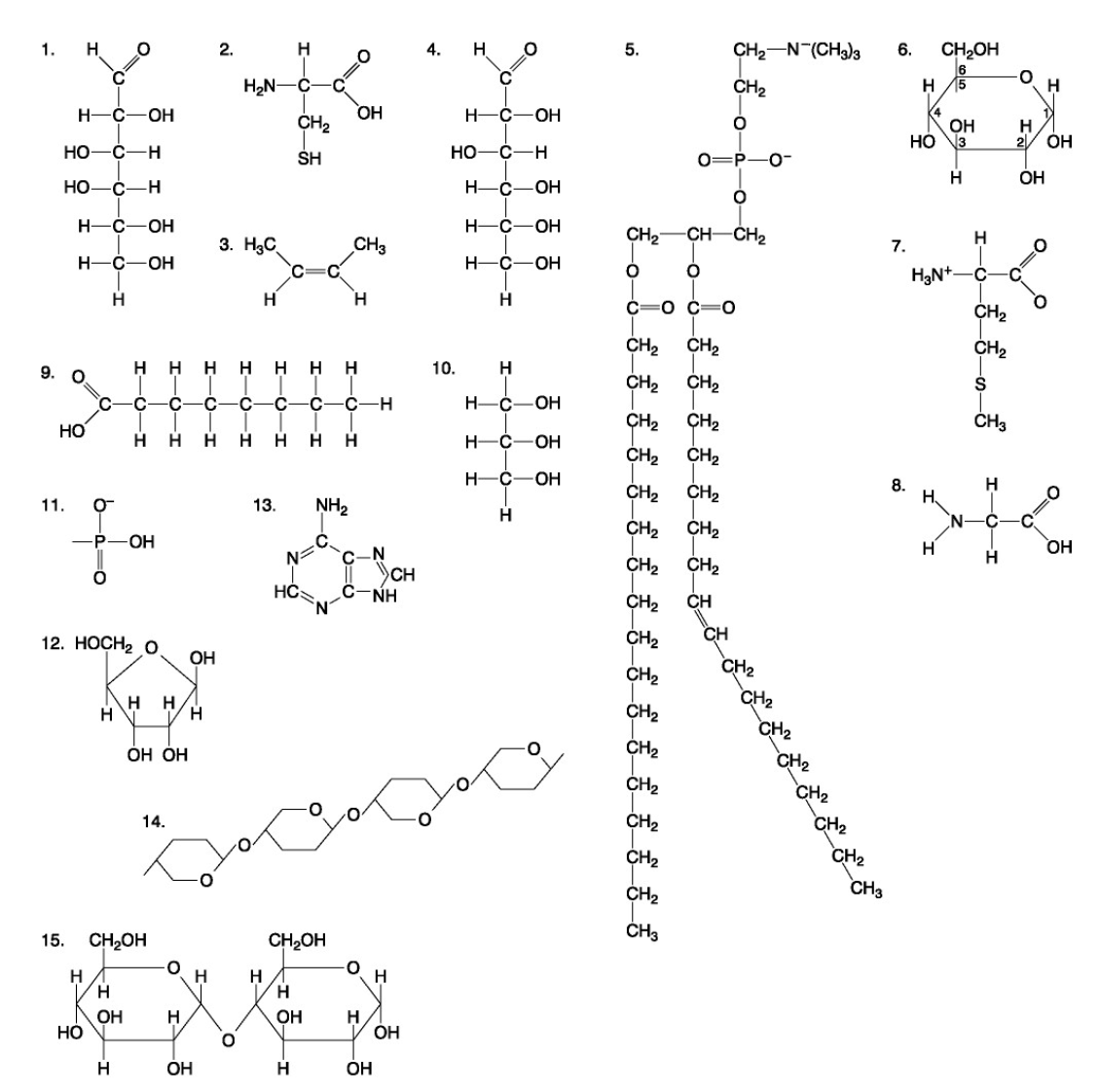
81. Which of the following molecules could be joined together by a phosphodiester type of covalent bond?
a. | 3 and 4 | c. | 6 and 15 | e. | 11 and 13 | |
b. | 3 and 8 | d. | 11 and 12 |
d. | 11 and 12 |
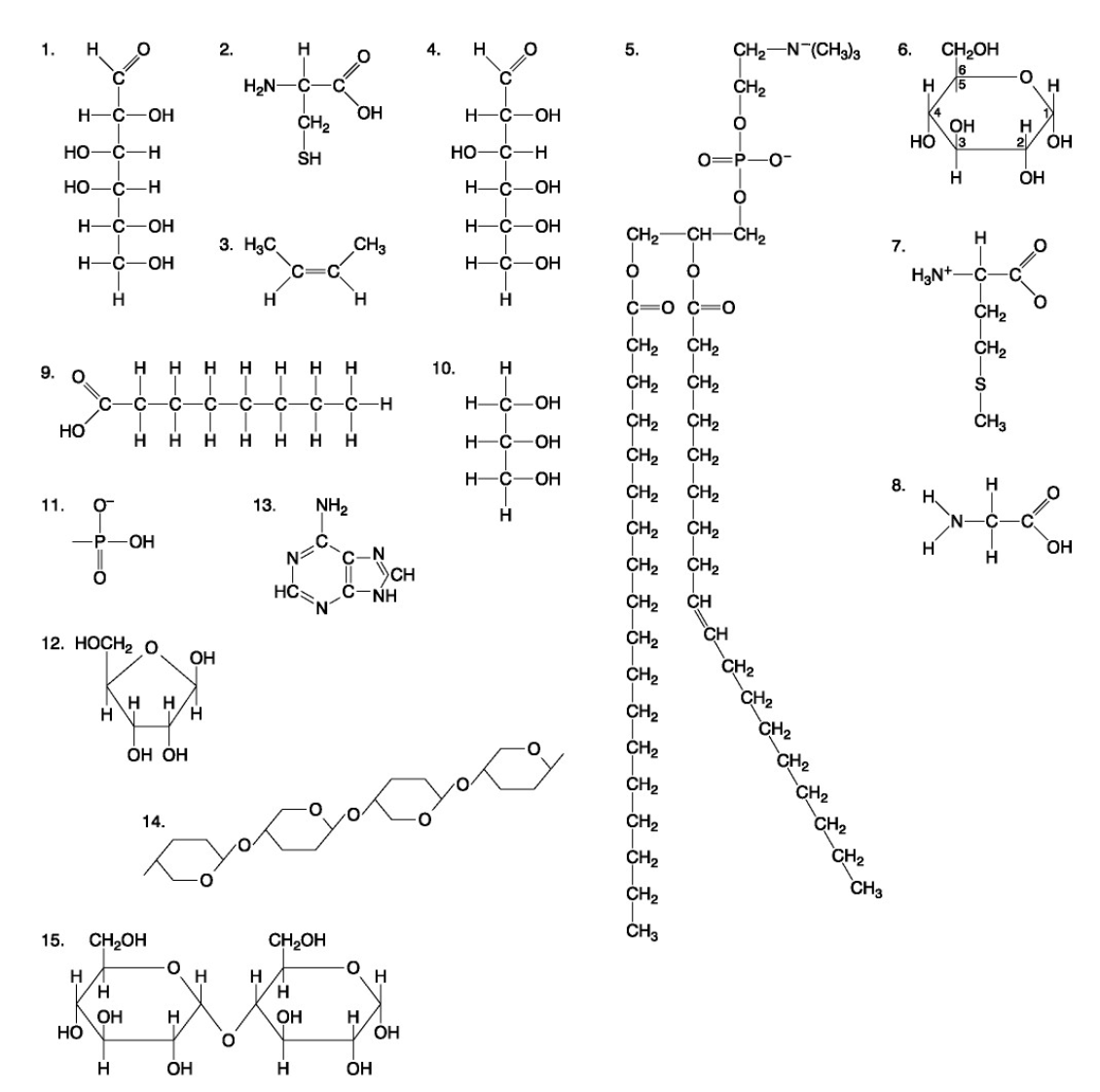
82. Which of the following molecules is the pentose sugar found in RNA?
a. 1
b. 4
c. 6
d. 12
e. 13
d. 12
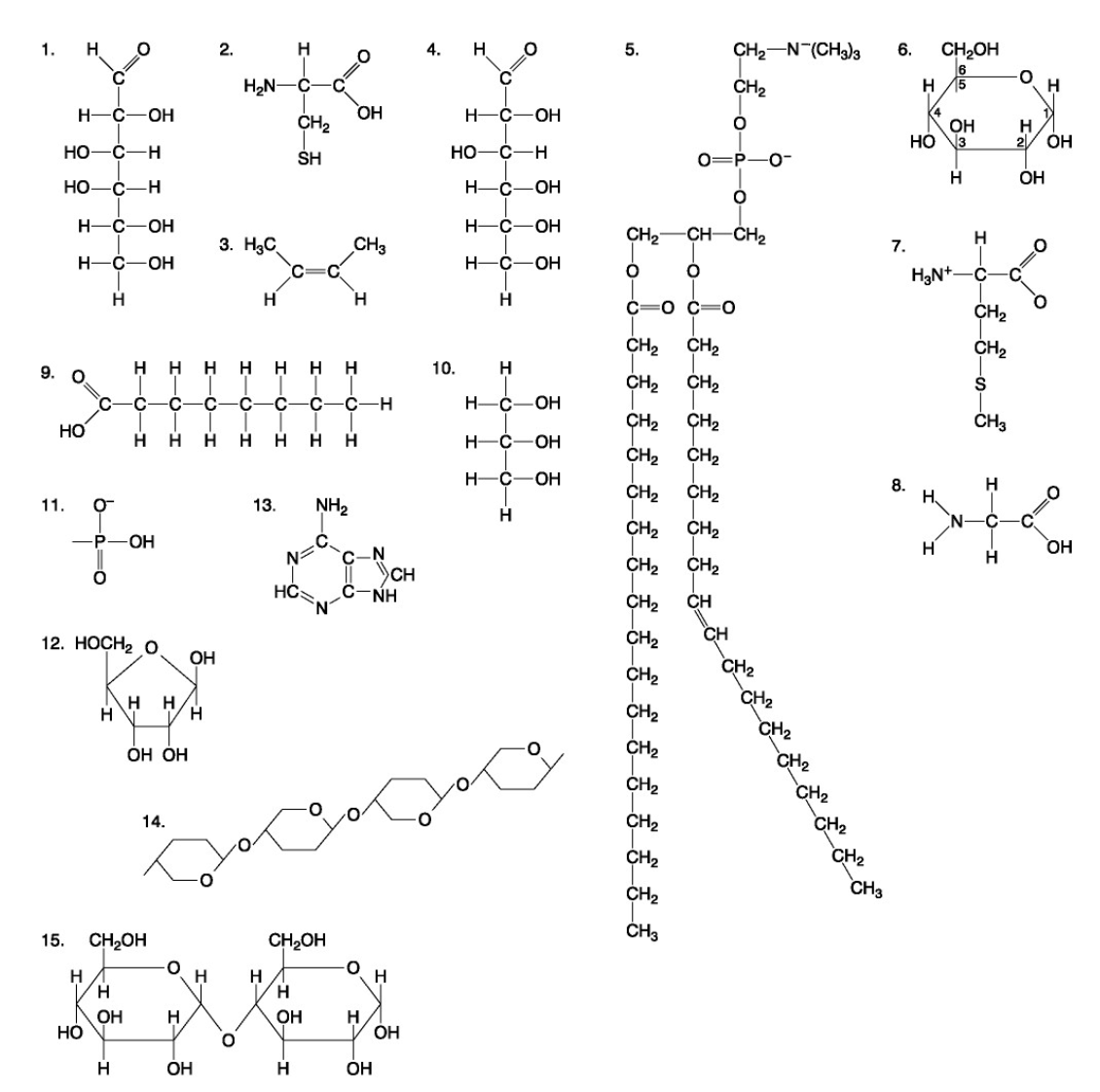
83. Which of the following molecules contains a glycosidic linkage type of covalent bond?
a. 4
b. 6
c. 12
d. 13
e. 15
e. 15
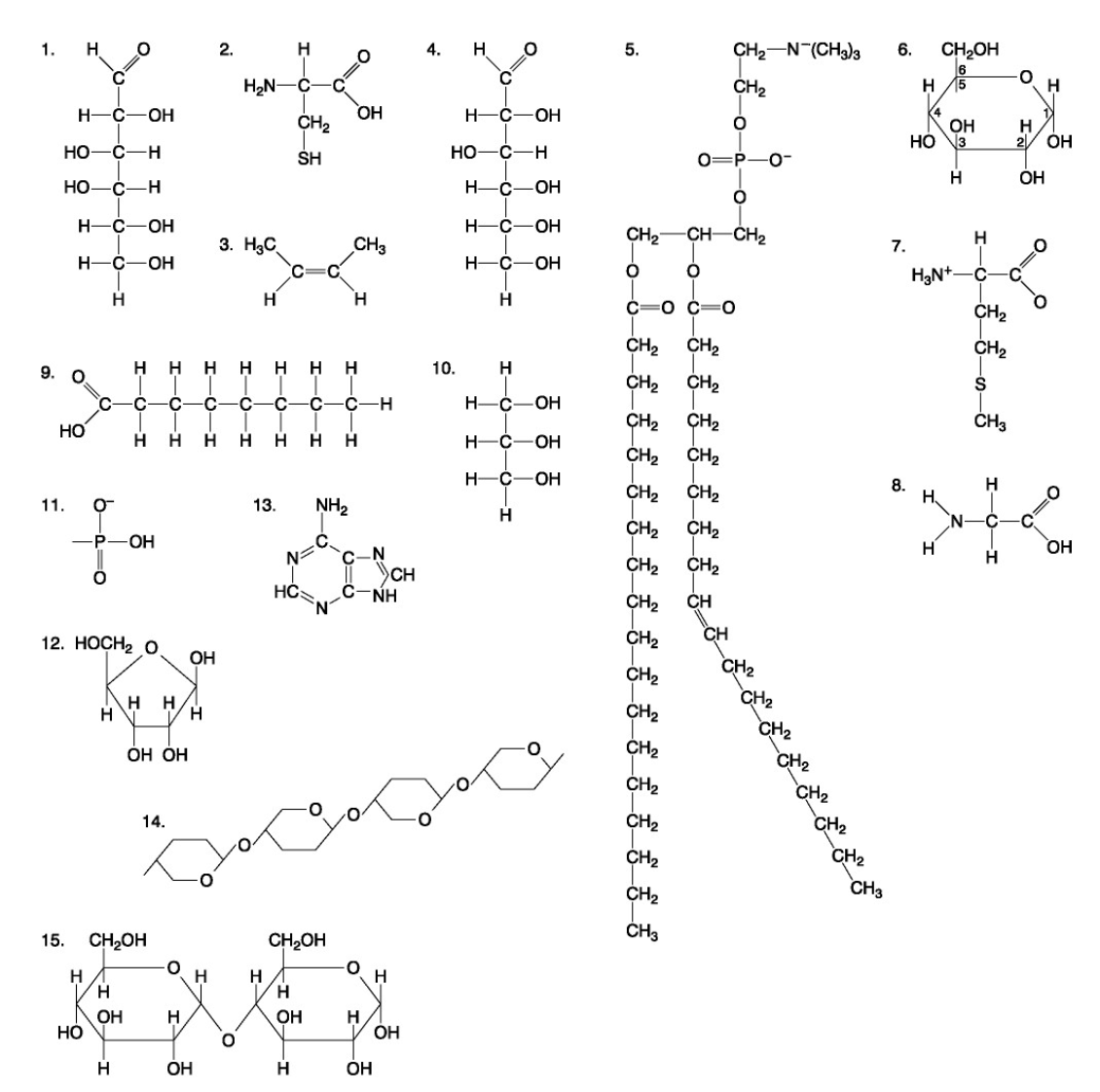
84. Which of the following molecules consists of a hydrophilic "head" region and a hydrophobic "tail" region?
a. 2
b. 5
c. 7
d. 9
e. 11
b. 5
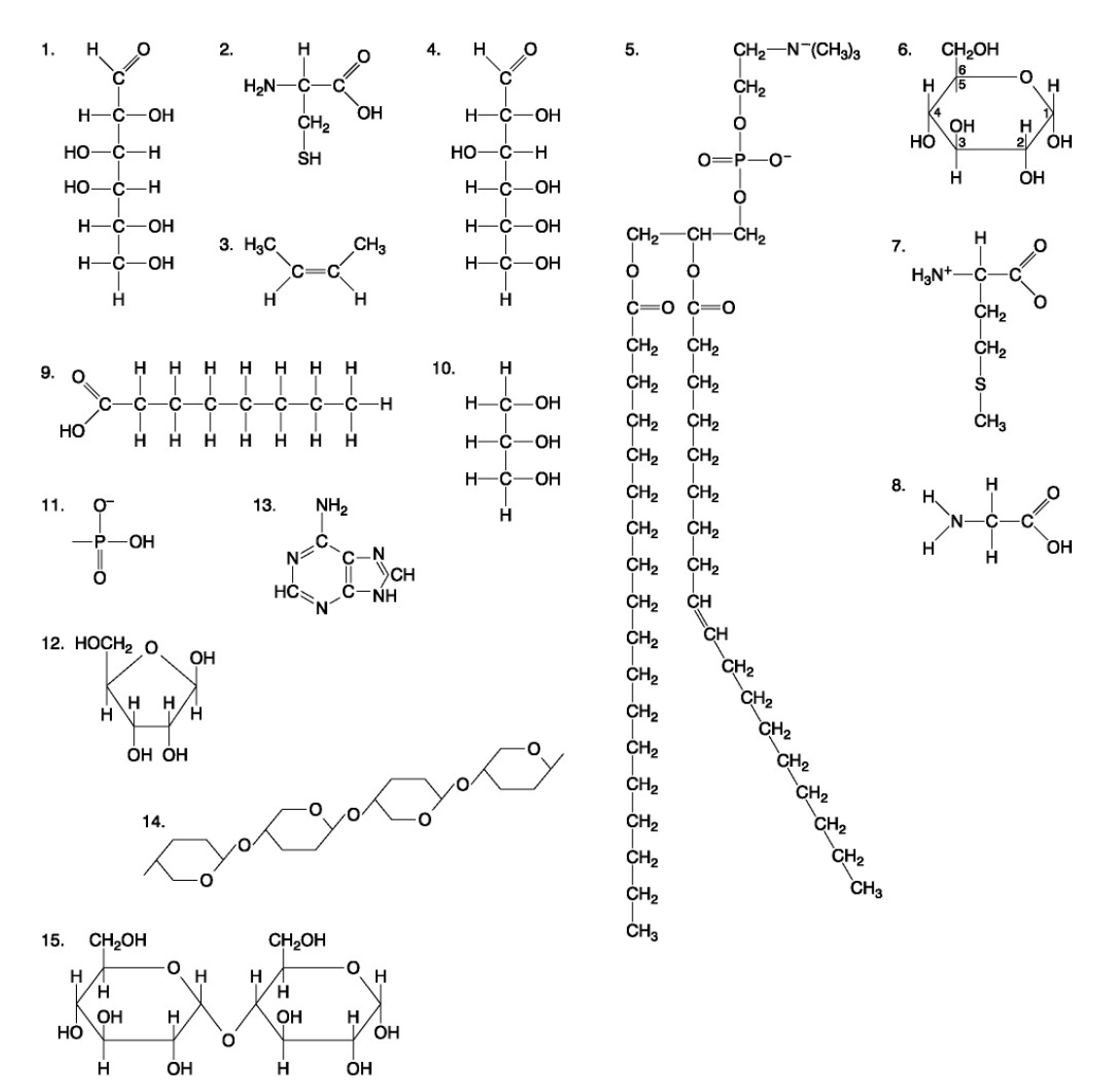
85. Which of the following statements is false?
a. | 1 and 4 could be joined together by a glycosidic linkage to form a disaccharide. |
b. | 9 and 10 could be joined together by ester bonds to form a triacylglycerol. |
c. | 2 and 7 could be joined together to form a short peptide. |
d. | 2, 7, and 8 could be joined together to form a short peptide. |
e. | 14 and 15 could be joined together to form a polypeptide. |
e. | 14 and 15 could be joined together to form a polypeptide. |
*what is the specific heat of water?
1 cal / g * (°C)
*what does hydrophilic mean?
one that has an affinity for water
cis vs trans
cis: two functional groups on the same side, straight, stronger intermolecular forces
trans: two functional groups on opposite sides, bent/kinked, don’t pack together well, weaker intermolecular forces
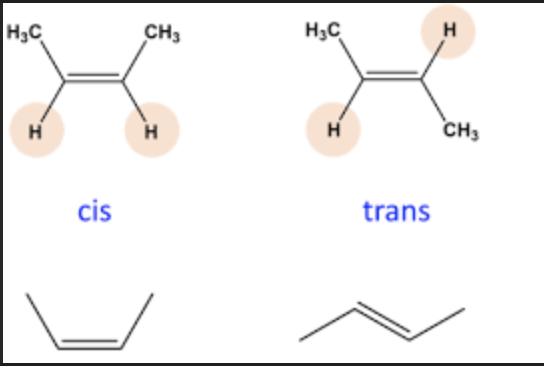
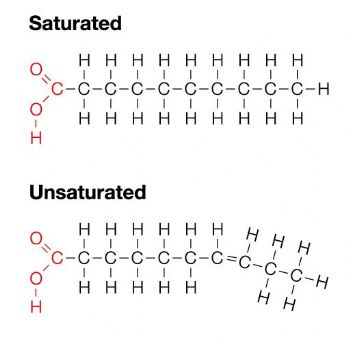
saturated vs unsaturated
saturated: only single C-C bonds, meaning hydrocarbons can sit closely parallel to each other and be tightly packed together (ie. animal fat)
unsaturated: contain at least one C=C bond (monounsaturated fats: olive oil)(2+ C=C bonds are polyunsaturated fats: canola oil)
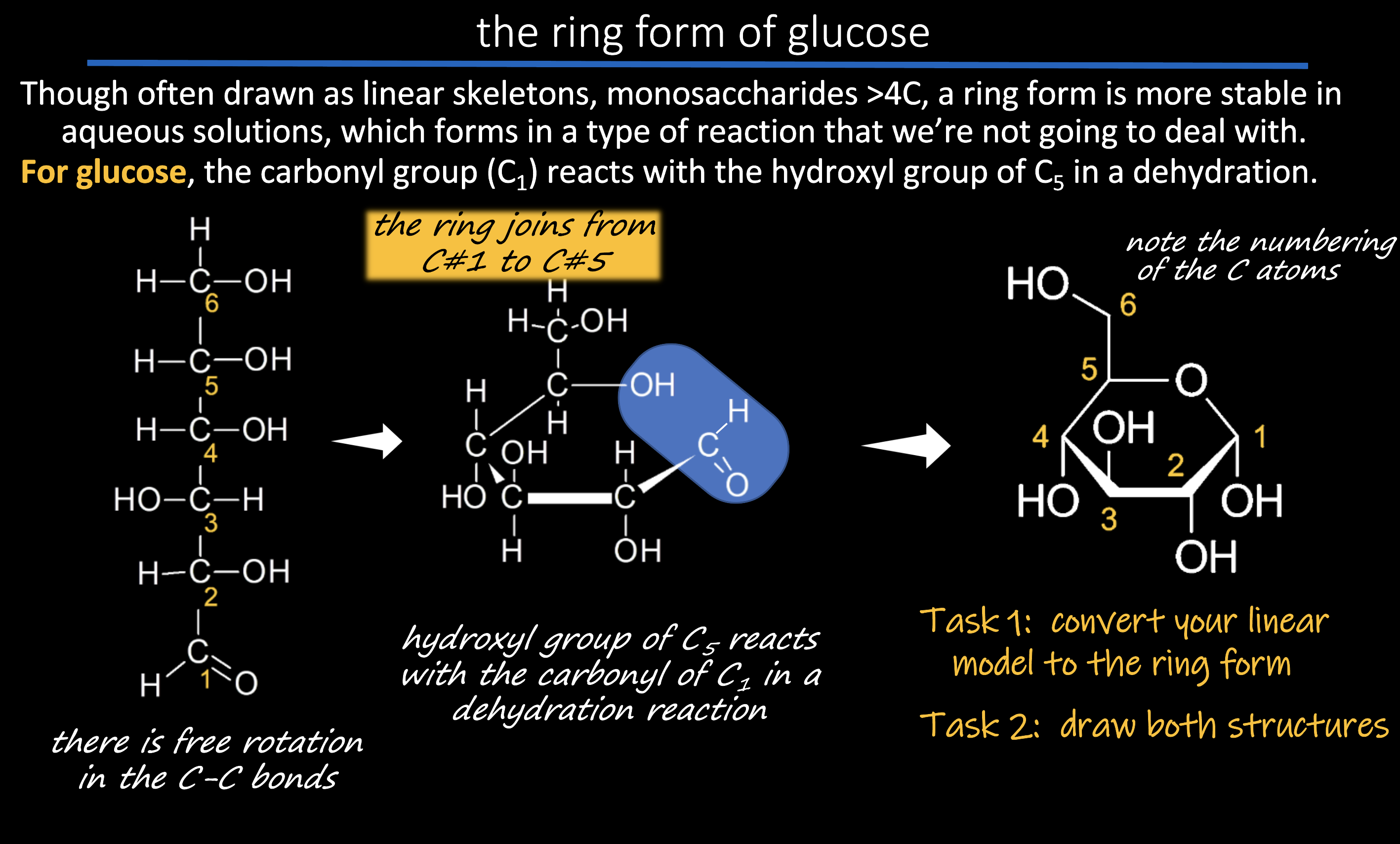
*whats the formula of glucose, + draw it
C6H12O6
recognize cholesterol and nucleotide.
*Classifying different functional groups
Hydroxyl
Carbonyl
Carboxyl
Amino
Phosphate
Sulfhydryl
Hydroxyl: R-OH
Carbonyl: C=O
Carboxyl: R-COOH
Amino: R-NH2 , NCC Backbone, ( a.a: amino end and carbonyl end)
phosphate: R-PO4
Sulfhydryl: R-SH
Methyl: R-CH3
*whats the difference between glucose and fructose?
Glucose: 6 Carbon Frame
Fructose: 5 Carbon Frame
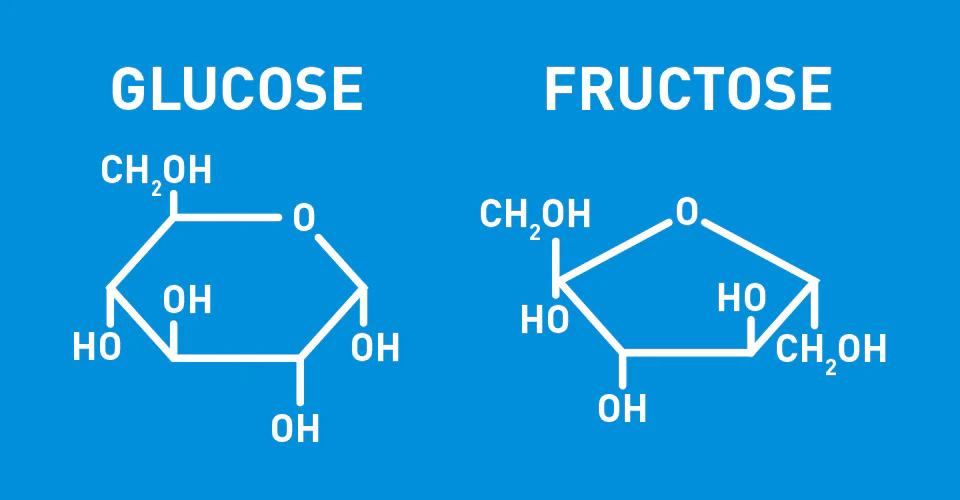
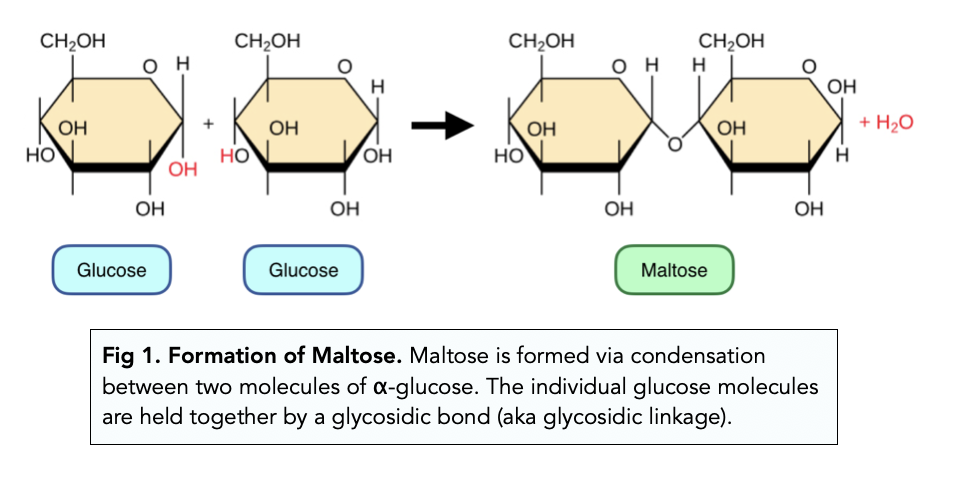
*what is maltose?
two glucose
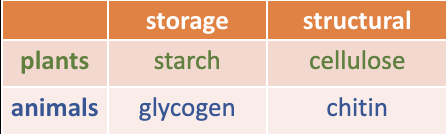
*Plants vs Animals: Structure and Storage
(need to know how to fill in that chart)
Plants: Cellulose and starch
Animals: Glycogen and Chitin
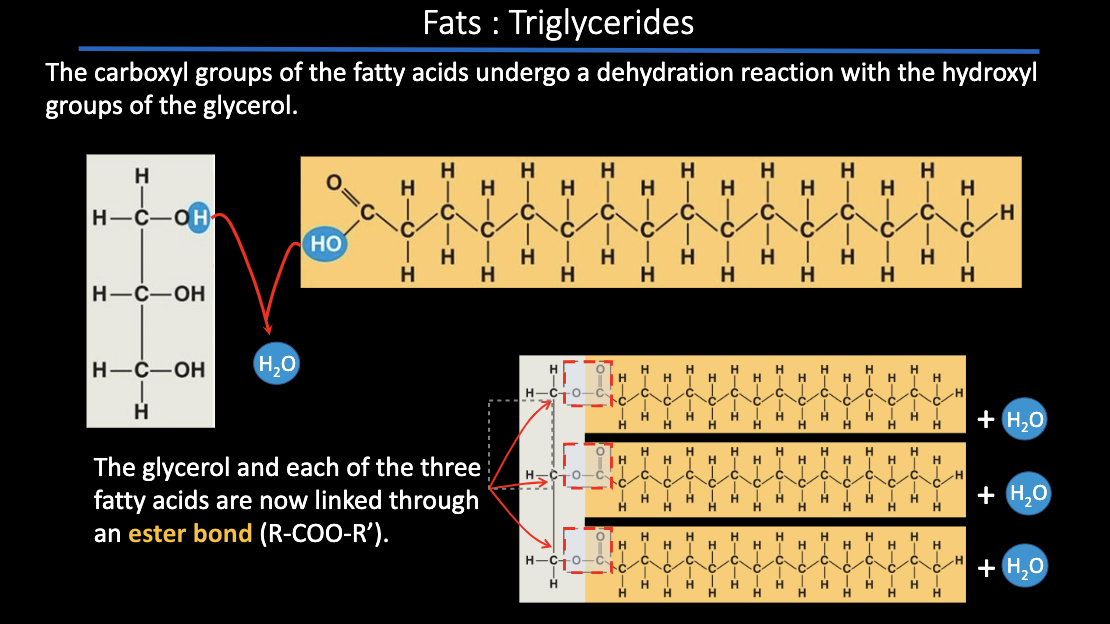
*draw a dehydration of fat + glycerol
idk if we really have to know this i didn’t specify on my note
Matching
The following are types of chemical bonds. Answer the questions by matching the descriptions with the most appropriate bond type. Answers may be used more than once.
a. | hydrogen | d. | disulfide |
b. | ionic | e. | peptide |
c. | covalent | ||
1. The bond between the atoms of table salt
2. The bond type holding several molecules of water together
3. The bond between the oxygen atoms of gaseous oxygen
4. The bond that breaks when salts dissolve in water
5. Atoms connected by this kind of bond share electrons.
B
A
C
B
C