Meiosis and Mitosis
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Chromosome
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
Chromatin
Lose clusters of DNA
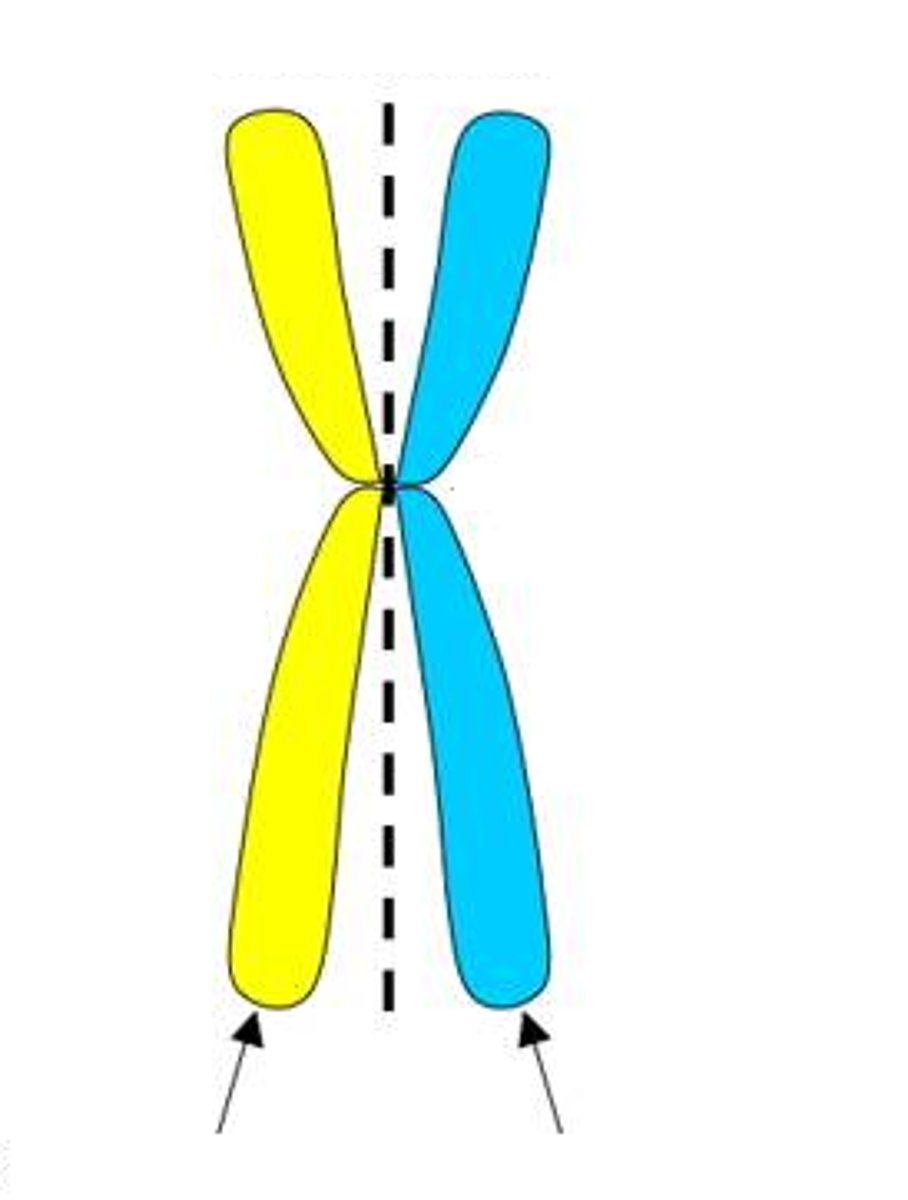
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
Chromatids
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
Haploid
n
Diploid
2n
Autosomes
Non-sex chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size and same genes.
Spindle fiber
help pull apart the cell during mitosis and meiosis
Centriole
What does DNA wind itself around?
Histones (protein)
What phase does a cell spend most of its time in?
Interphase (90-95%)
Gap 1
The first part of interphase: the cell grows and functions takes place
Synthesis
DNA replication
Gap 2
additional growth and normal functions
Parts of interphase
G1 --> S --> G2 --> Mitosis/Meiosis
How do you count chromosomes?
by centromeres
Mitosis
Cell division where a parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells
Mitosis function
Growth and repair
Meiosis
Cell division that produces four daughter reproductive cells each with half the of chromosomes as the parent cells
Meiosis function
sexual reproduction
Crossover
Exchange of genetic information between a homologous pair
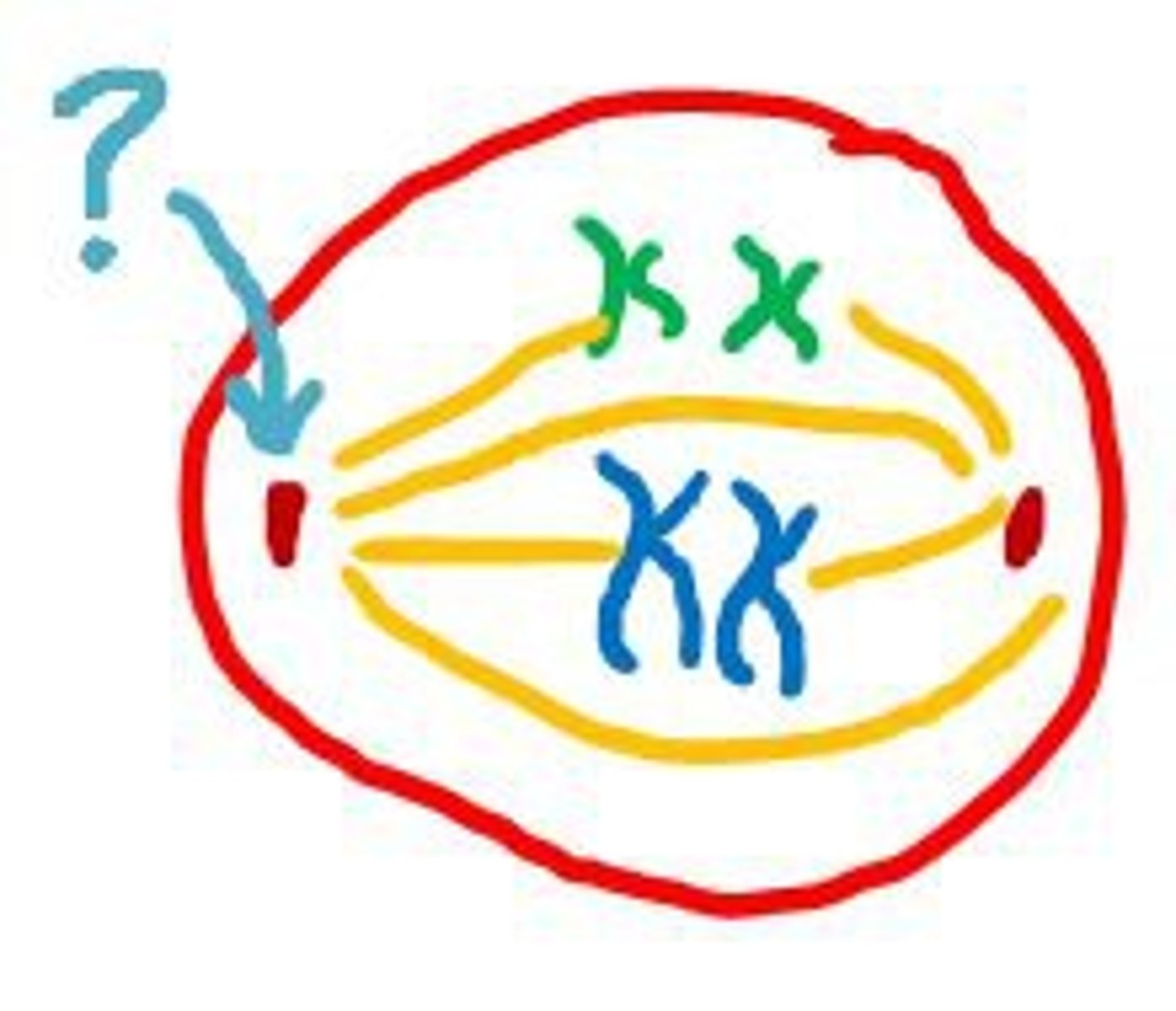
Nondisjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate causing to many or too few chromosomes in daughter cells
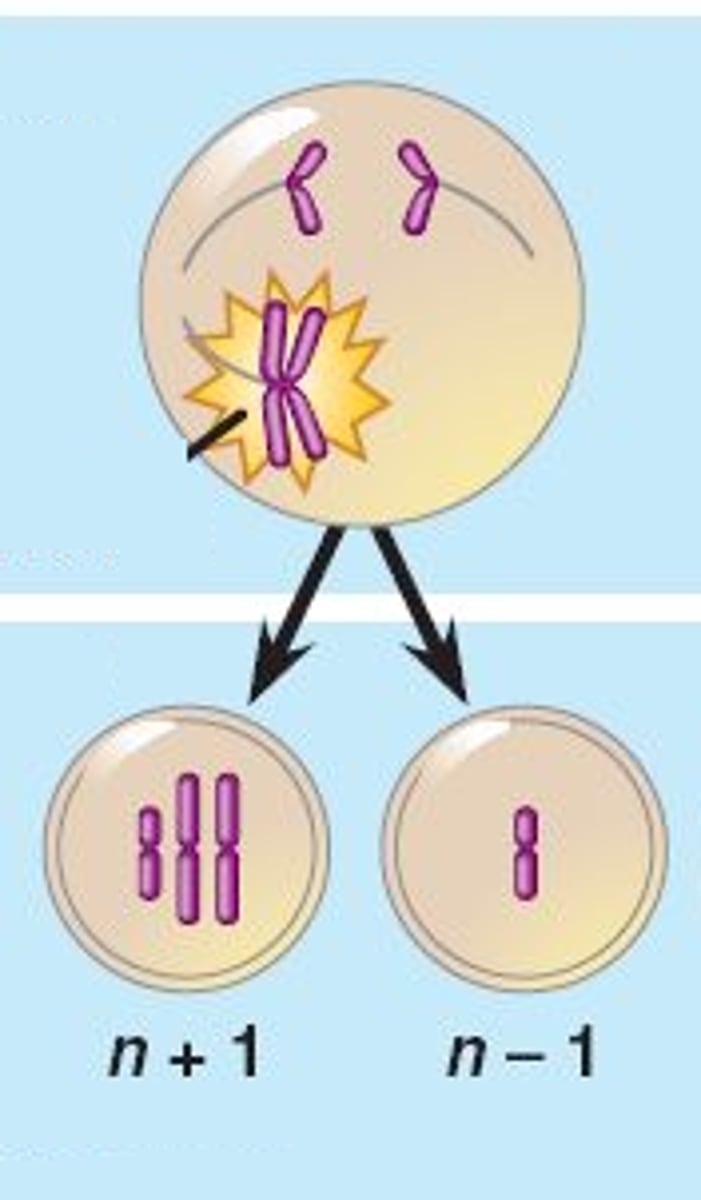
What causes down syndrome?
an extra chromosome 21
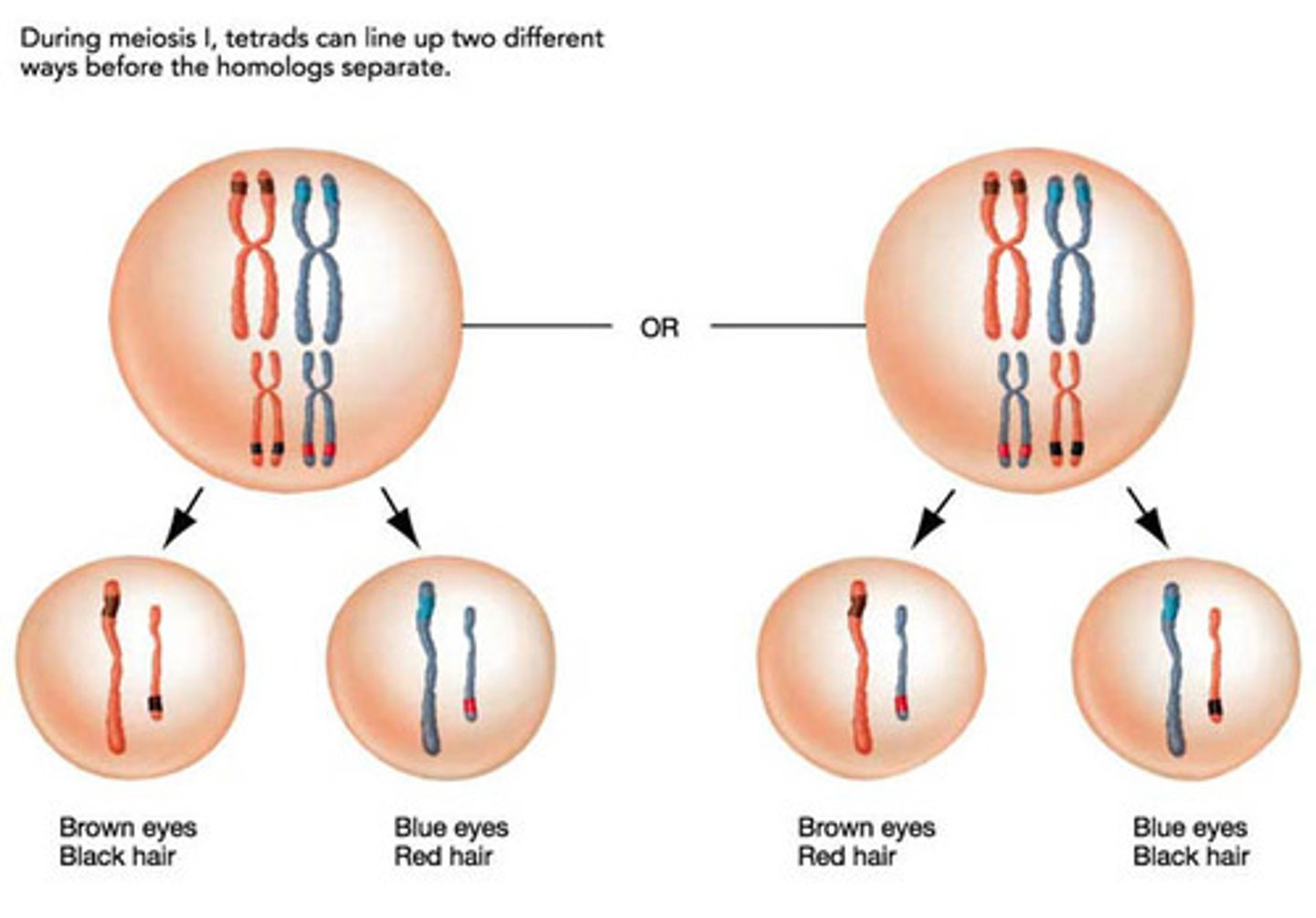
law of independent assortment
Each member of a pair of homologous chromosomes separates independently of the members of other pairs so the results are random
Prophase (mitosis)
chromosomes condense and spindle fibers begins to form
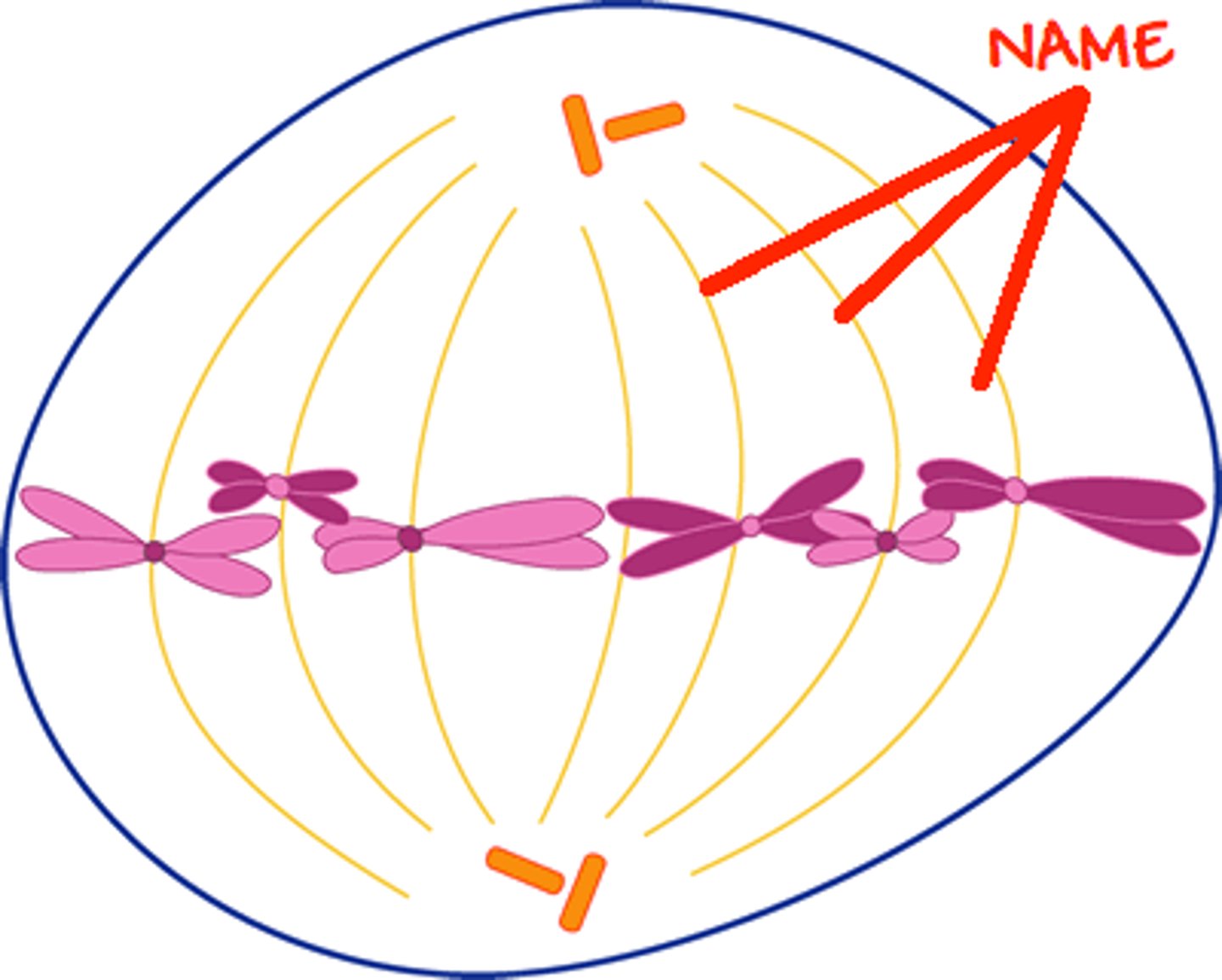
Metaphase (mitosis)
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell (m for middle)
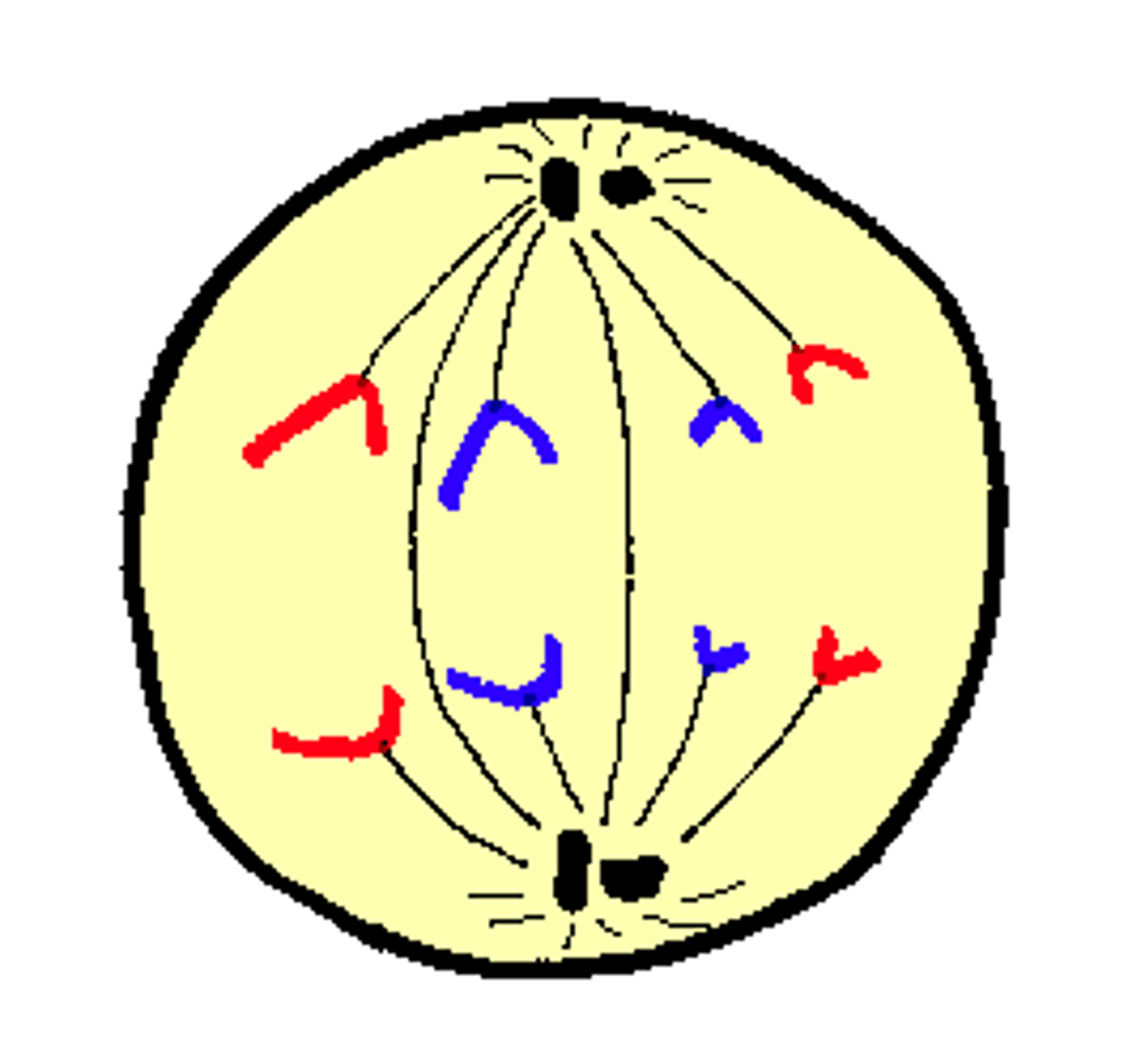
Anaphase (mitosis)
sister chromatids are pulled apart (A for away)
Telophase (Mitosis)
Separation the duplicated genetic material into two identical daughter cells. Nucleus reforms and chromosomes de-condense forming chromatin
Cytokenisis (Mitosis)
division of the cytoplasm
Prophase 1
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibres begins to form; chromosomes find their homologous pairs and crossing over occurs!!
Metaphase 1
Paired homologous chromosomes line up randomly across the middle of the cell
Anaphase 1
Homologous chromosome pairs separate
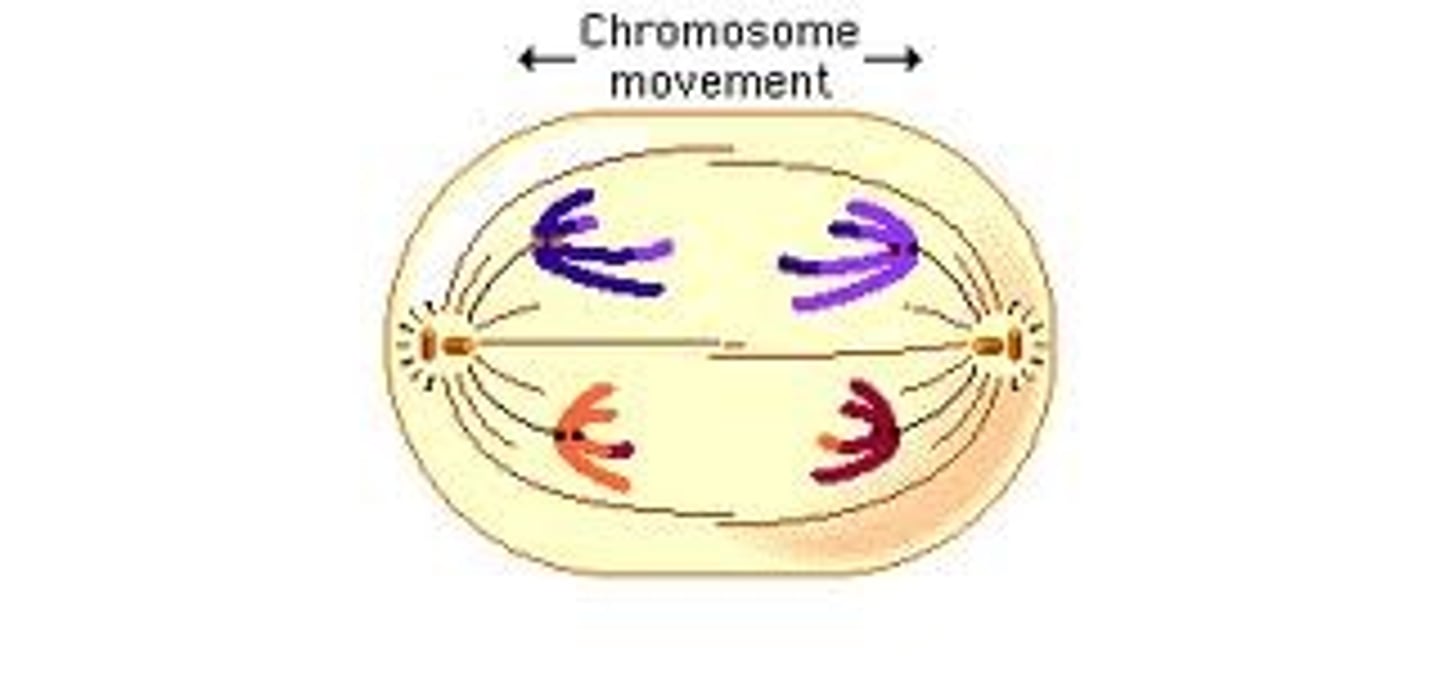
Telophase 1
Cytoplasm divides, 2 daughter cells are formed
Prophase 2
Chromosomes condense and spindles form in each new cell. (No crossover or homologous pairs)
Metaphase 2
Centromeres of chromosomes line up at the middle of each cell
Anaphase 2
sister chromatids separate
Telophase