intro to transition metals
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
what is a transition metal?
a metal that can form one or more stable ions w/ an incomplete d sub level
by definition, which 2 elements in the d block of the periodic table are not transition metals?
Sc
Zn
when figuring out e- configurations of the transition metals, in which order do we fill the orbitals? what does this mean for the ionisation of transition metals?
4s before 3d
so when transition metals become ions, they lose 4s e- before 3d e-
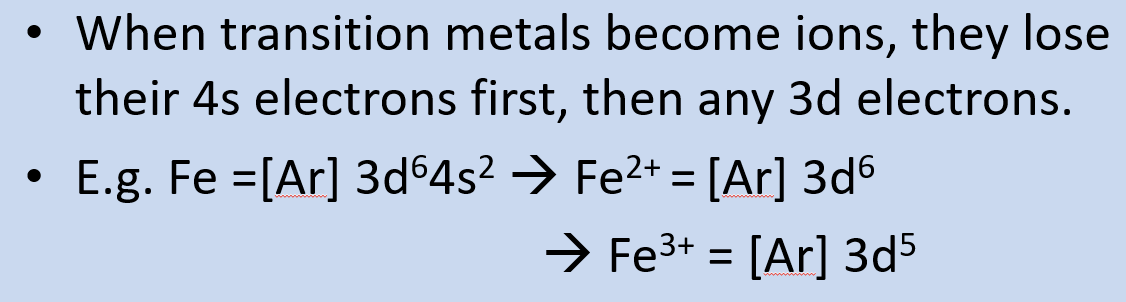
give and explain the two exceptions to the electron configuration rule:
Cr - [Ar] 4s1 3d5
Cu - [Ar] 4s1 3d10
as a half or fully filled subshell is more stable than a partially filled one
give 2 physical properties of transition metals:
high densities
high mpts/bpts
what is a physical property?
a characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing its chemical composition
give 4 chemical properties of transition metals:
form coloured ions
very good catalysts
have variable oxidation states
form complex ions
what is a chemical property?
properties which can only be observed or measured during a chemical reaction
give a transition metal with a variable oxidation state and explain why it has this:
Fe2+ and Fe3+ as the 4s and 3d orbitals are very similar in energy so different nos. of e- can be lost/gained