FDA - Data Mining Methods, week 4
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Data mining categories - Supervised method
Uses labeled data to predict the output for new, unseen data
→ Example: data= customer financial info, whether they defaulted on a loan
task= predict if new applicant is likely to default
Data mining categories - Unsupervised method
Uses unlabeled data to find hidden patterns, groupings or structures.
→ Example: data= shopping transactions
task= identify patterns like: ‘people who buy bread often buy butter’
Data mining categories - Global method
Creates information applicable to all data.
Data mining categories - Local method
Creates information only applicable to some of the data.
Data mining method - Linear regression, goal
Supervised and global
Goal= to create a linear model to relate an output variable to one or more input variables
Data mining method - Linear regression, SSD
SSD= Sum of Squared Deviations
The lower the SSD of a model the better the model.
→ SSD expresses variation relative to the model. Small SSD shows you that the prediction is close to the real data
Always look at the outcome of SSD in relation to the y-value to see if it is large or small
→ small: SSD= 0,8 and y-value= around 10
→ large: SSD= 3,6 and y-value= ranges 0-5
Data mining method - Linear regression, R2
Explains how well the regression line fits the data.
→ - R²= a slope down from left to right
→ + R²= a slope going up from left to right
The closer the R² to 0, the regression line has little to no predictive power.
→ -1 = perfect predictive power
→ -0.2 = little predictive power
→ 1 = perfect predictive power
→ 0.3 = little predictive power
Data mining method - Linear regression, residual plot
Used to check the linear regression plot.
→ Good plot= residual plot centered around 0, no pattern
→ Bad plot= residual plot with patterns, clusters and extreme plots(outliers)
Data mining method - Clustering, goal
Unsupervised and global
Goal= partition all locations in geographically meaningful groups.
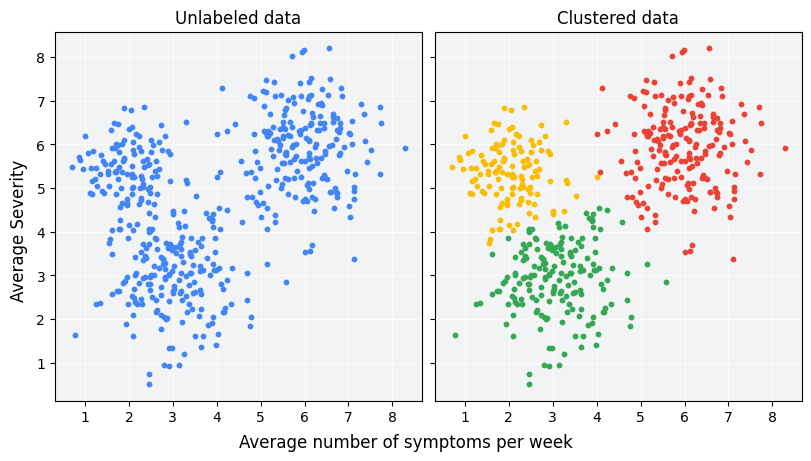
Data mining method - Clustering, k-means
This is clustering by algorithms.
Pick random centroids of clusters.
Assign points to nearest centroid.
Recompute centroids until clusters are stable
→ The smaller the distance between centroids the better
Data mining method - Decision tree, goal
Supervised and global
Goal= Learn a tree to separate ‘quit’ and ‘non-quit’ cases.
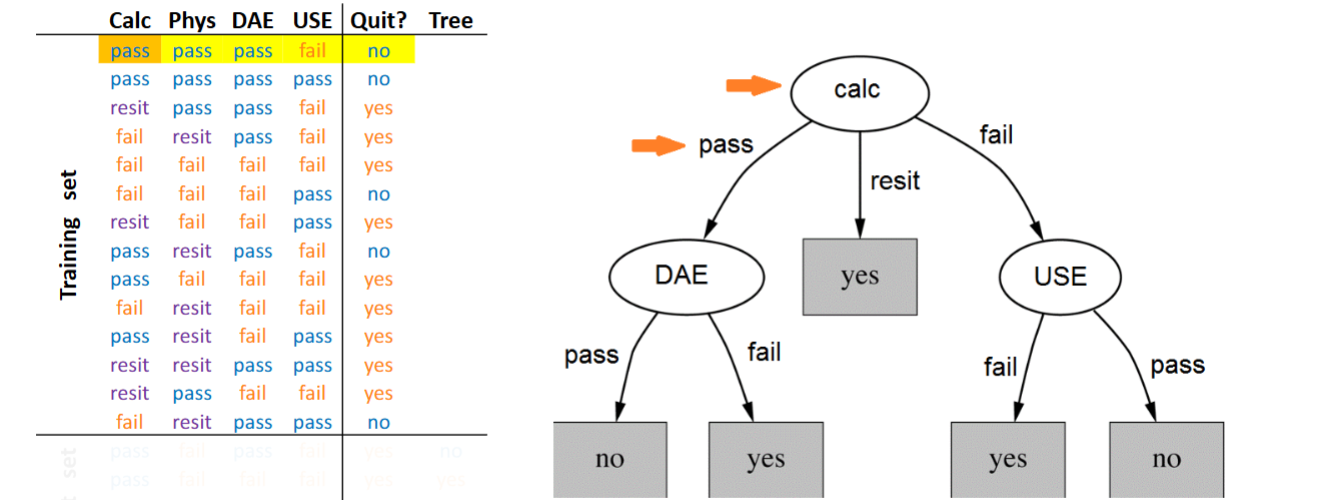
Data mining method - Decision tree, structure
Branches= the lines in between the ovals and cubes
Nodes= the ovals, the ‘topics’
Tree’s leaves= the cubes, the eventual outcome
→ Branches connect the nodes and the tree’s leaves
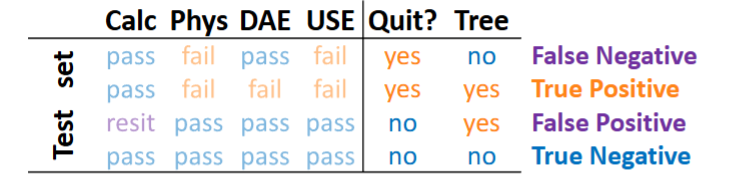
Data mining method - Decision tree, confusion matrix
Used to check the quality of the decision tree.
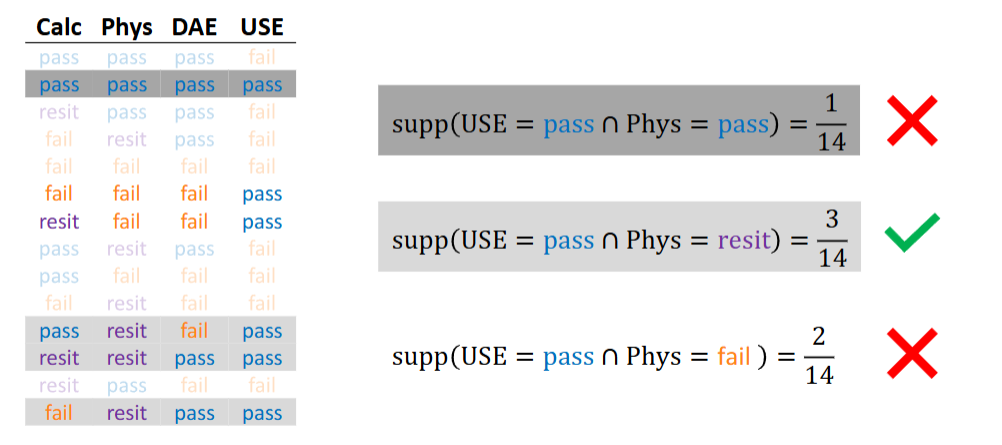
Data mining method - Association rules, goal
Unsupervised and local
Goal= to find high-confidence associations between frequently occurring (exam outcomes)