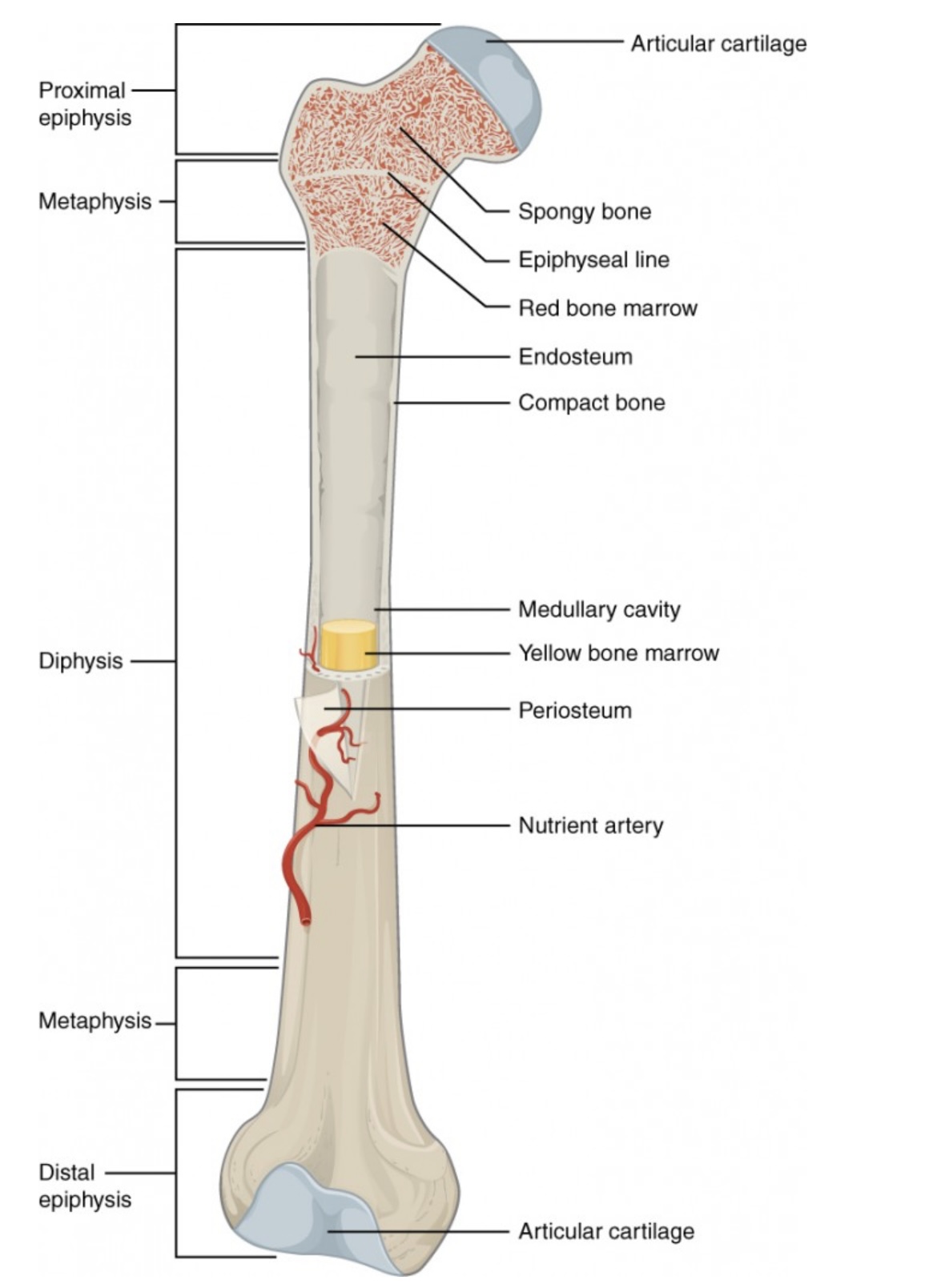
Anatomy of a Long Bone
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Proximal Epiphysis
End of the long bone closest to the body’s trunk.
Contains spongy bone and red bone marrow for blood cell production.
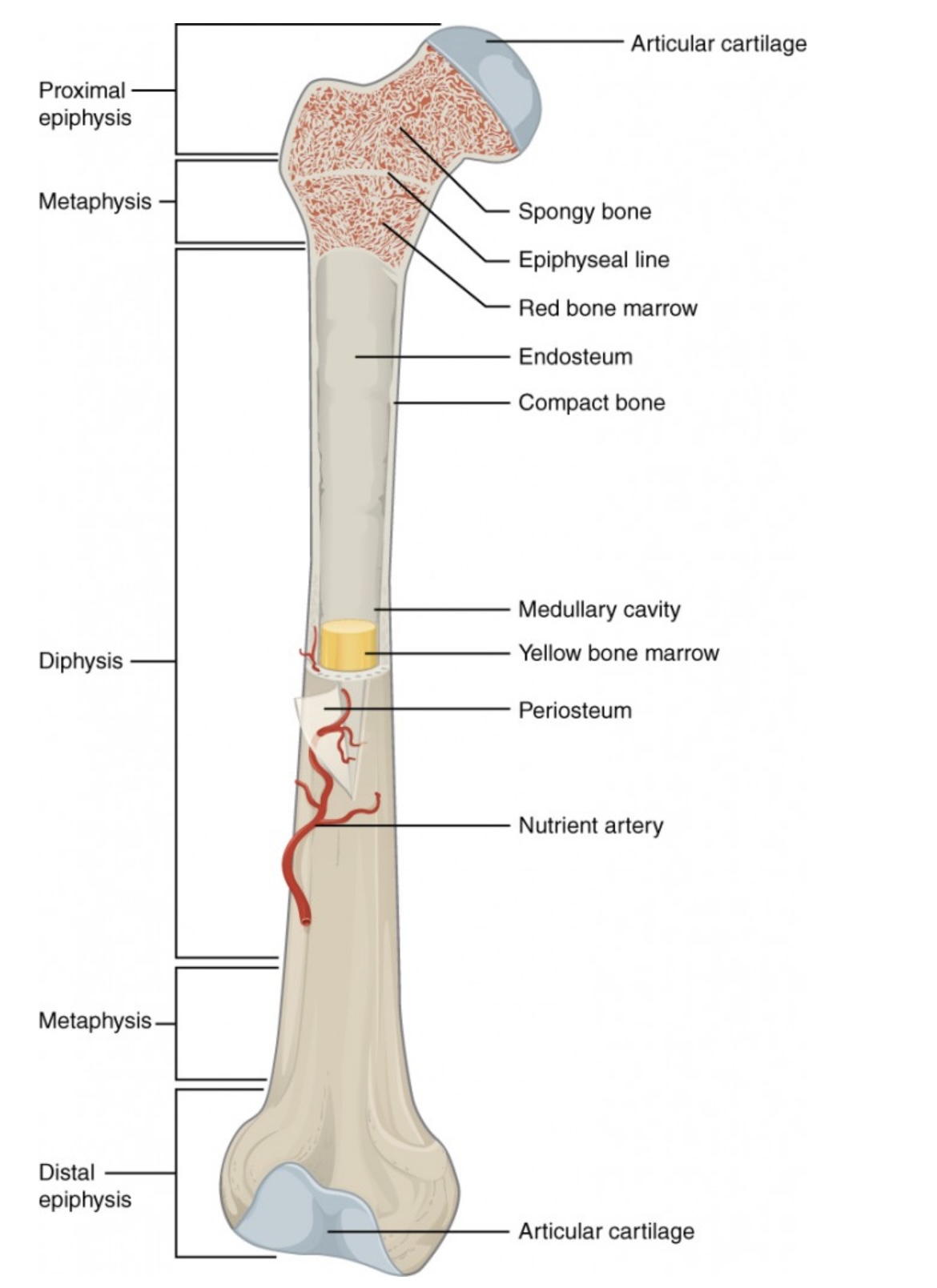
Distal Epiphysis
End of the bone farthest from the body’s trunk.
Also made of spongy bone; forms joints with other bones.
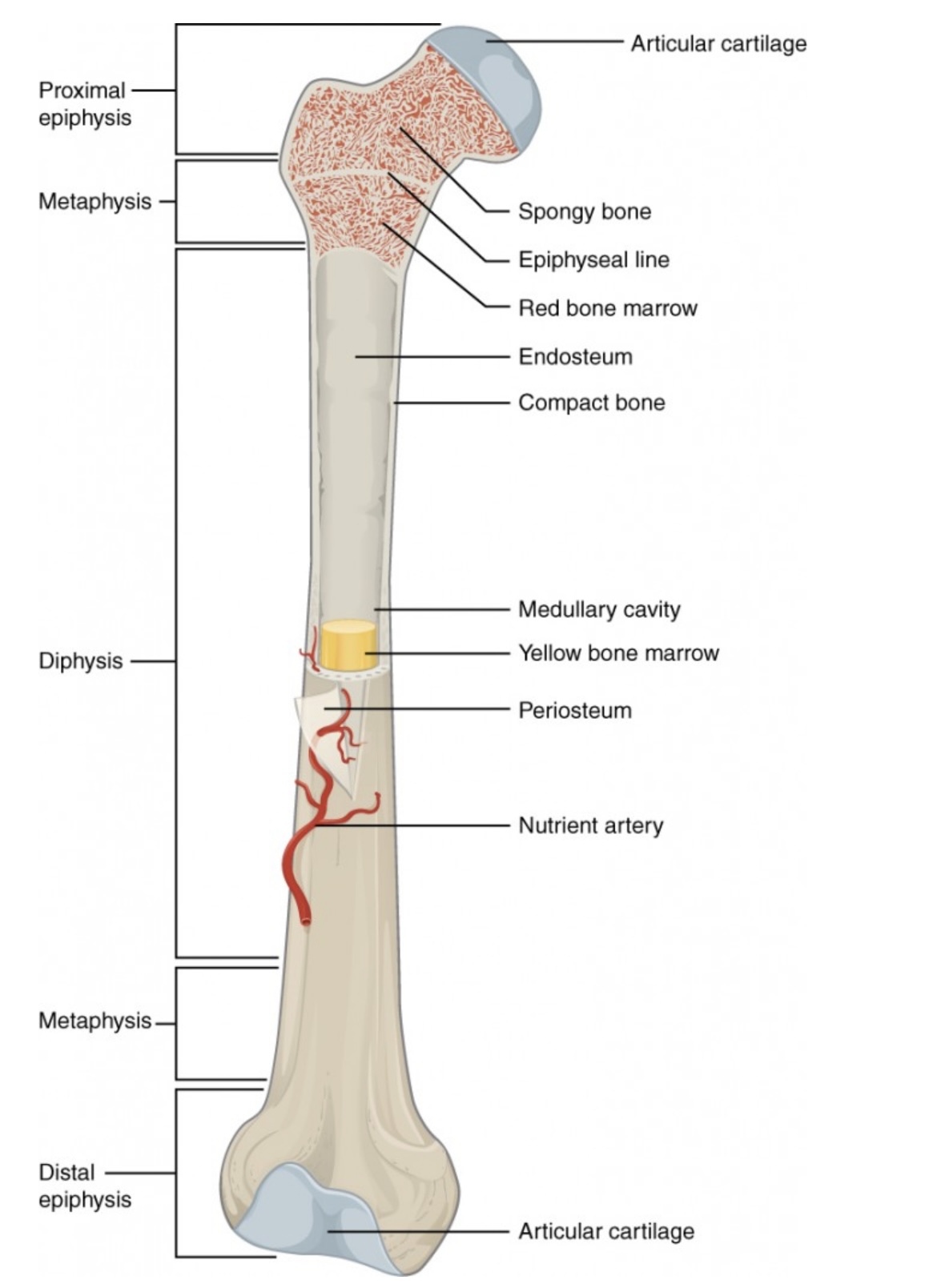
Metaphysis
Between the epiphysis and diaphysis.
Contains the growth plate (epiphyseal line) in adults; allows bone growth during youth.
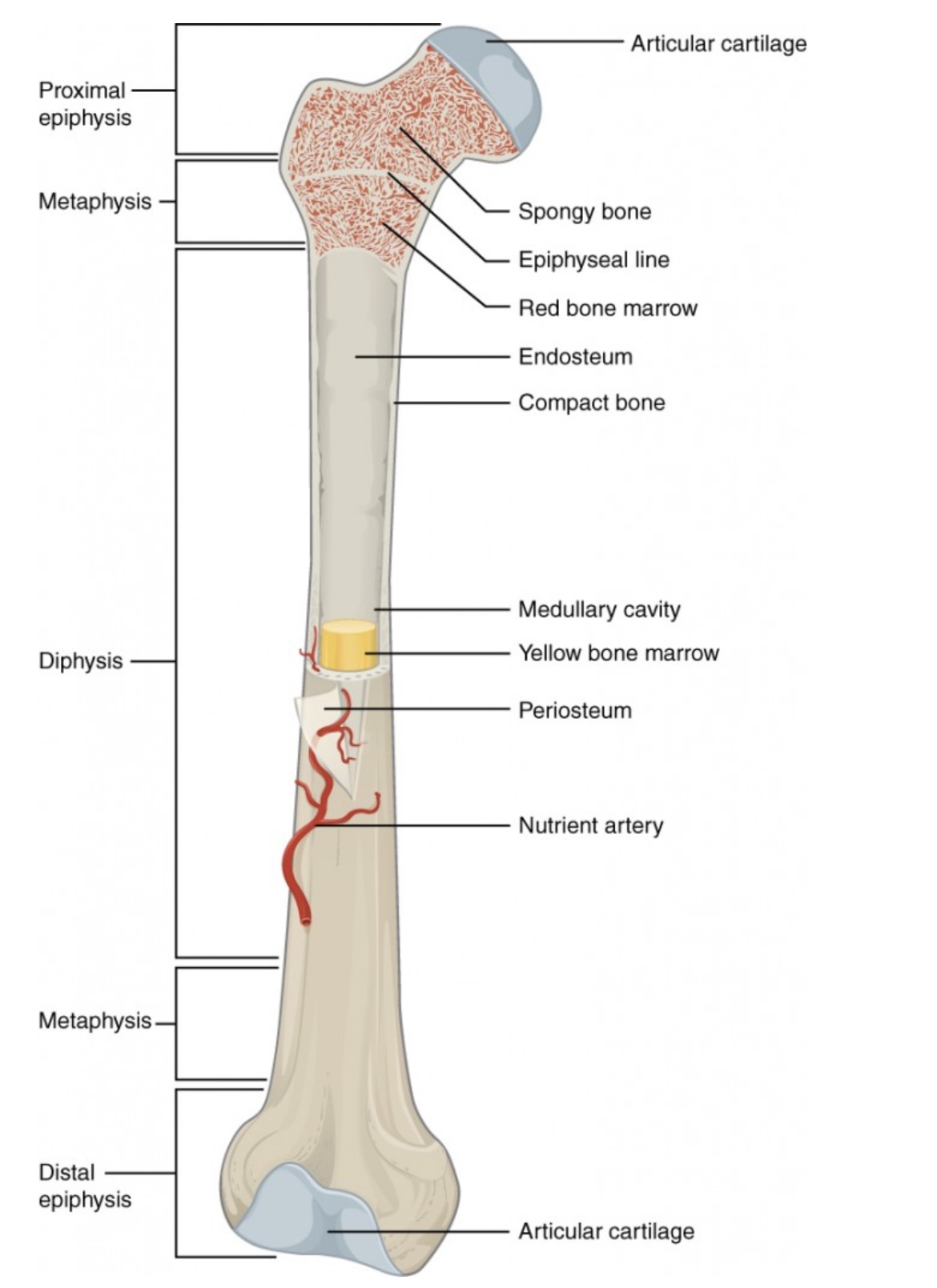
Diaphysis
The long, central shaft of the bone.
Provides support, strength, and leverage; made mostly of compact bone.
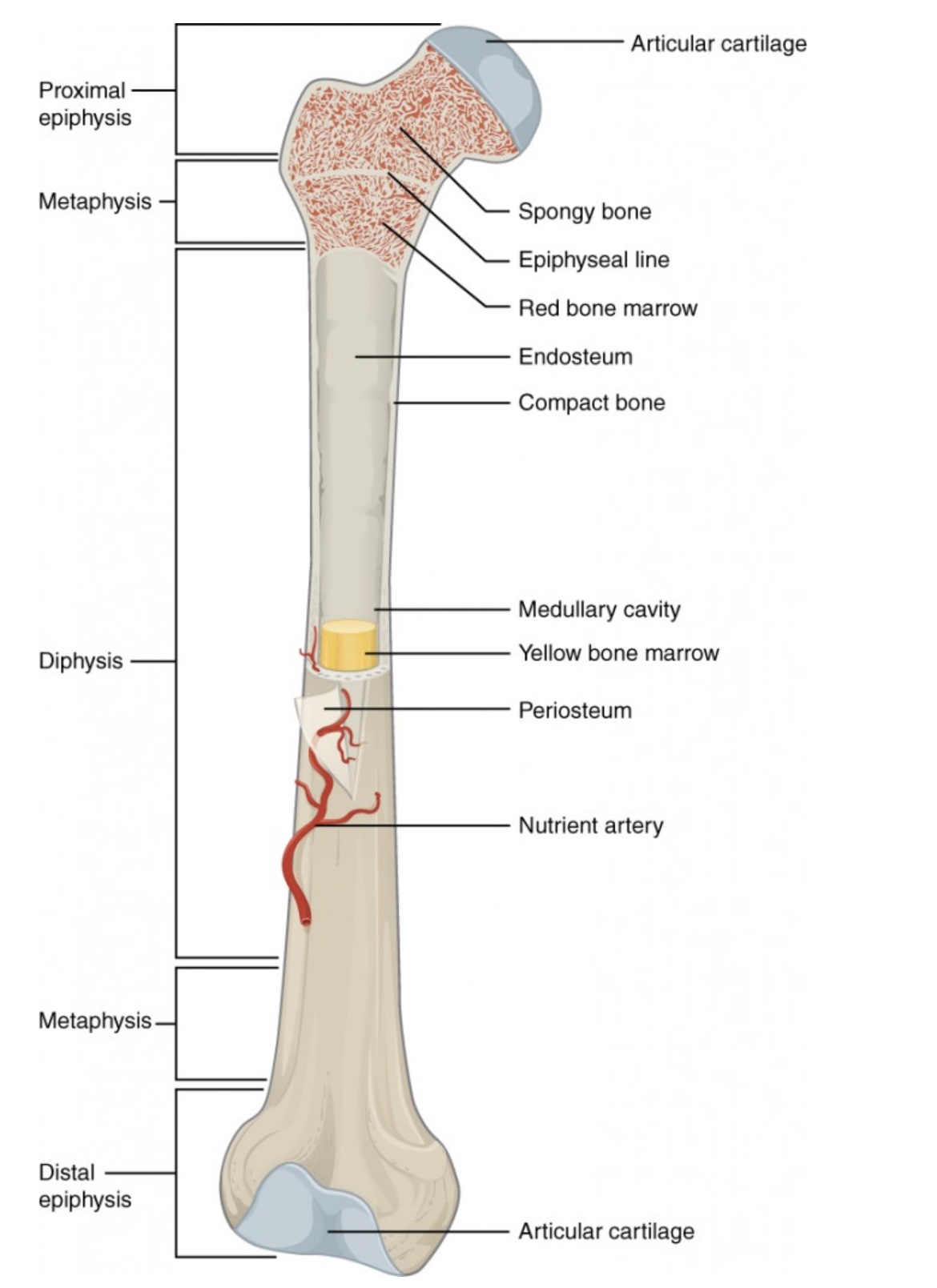
Articular Cartilage
Smooth cartilage covering the ends of bones at joints.
Reduces friction and absorbs shock during movement.
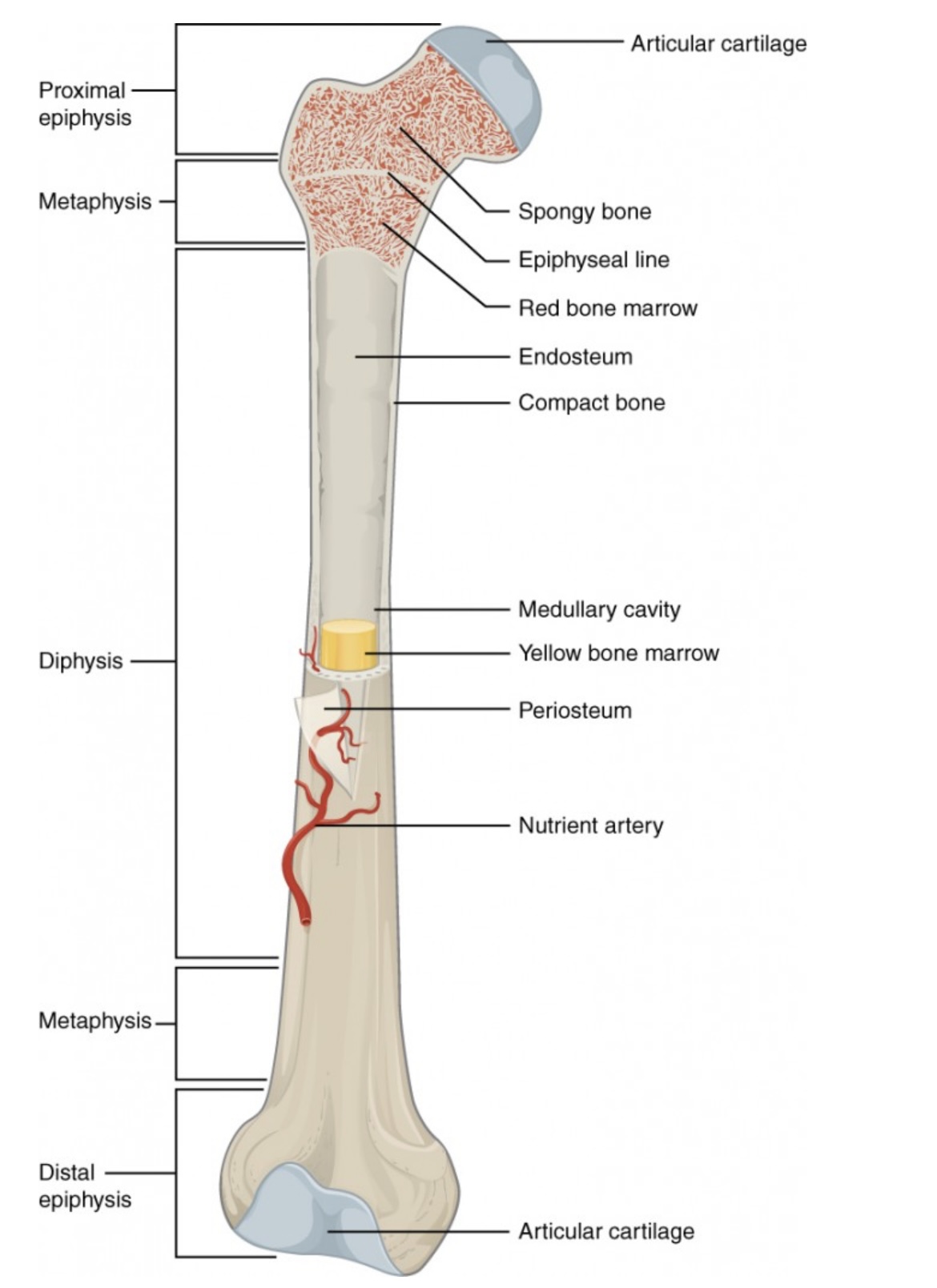
Spongy Bone (Cancellous Bone)
Porous bone tissue inside the epiphyses.
Houses red bone marrow for making blood cells.
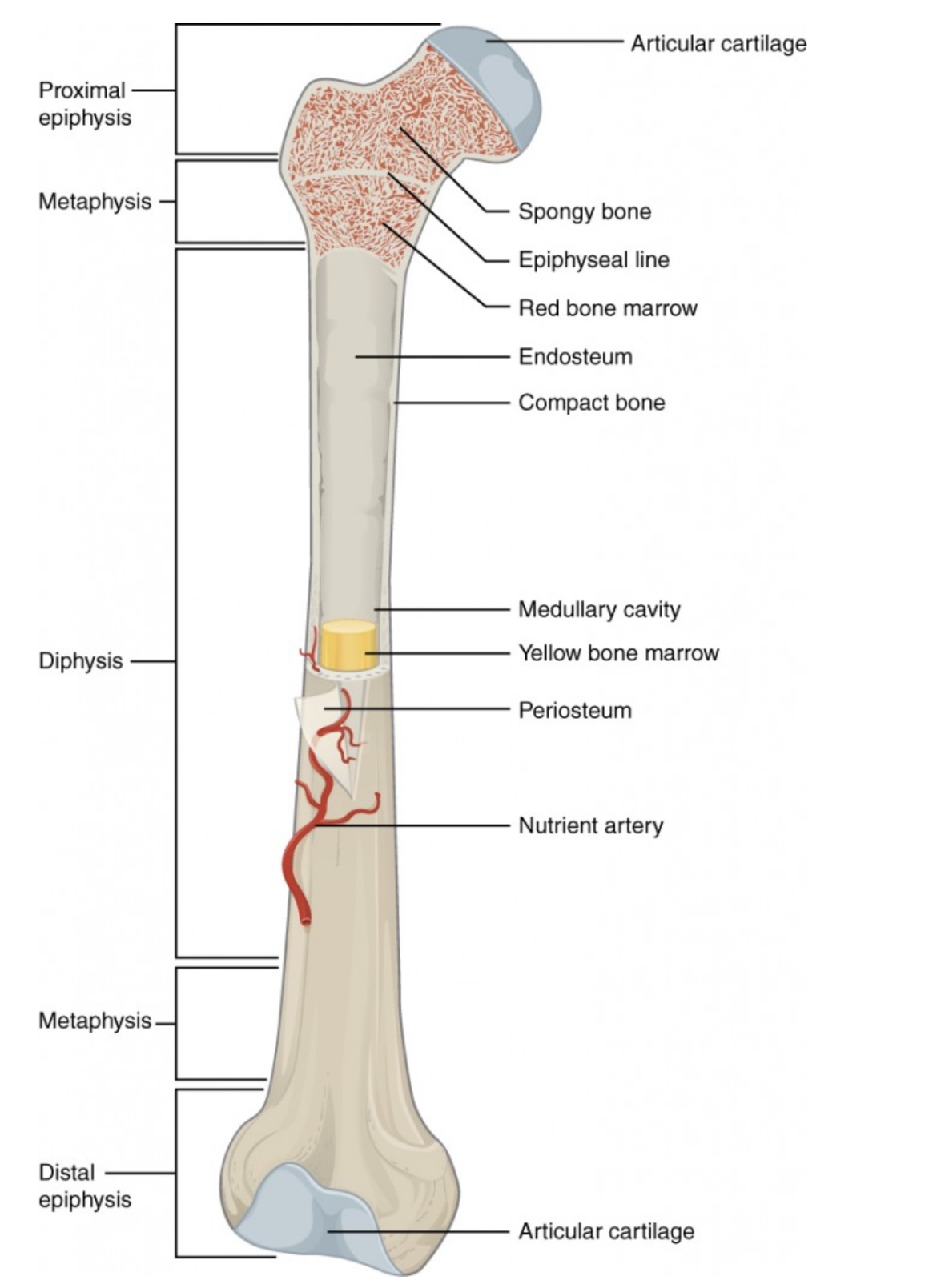
Compact Bone
Dense outer layer of the bone shaft.
Gives strength and protection; supports weight.
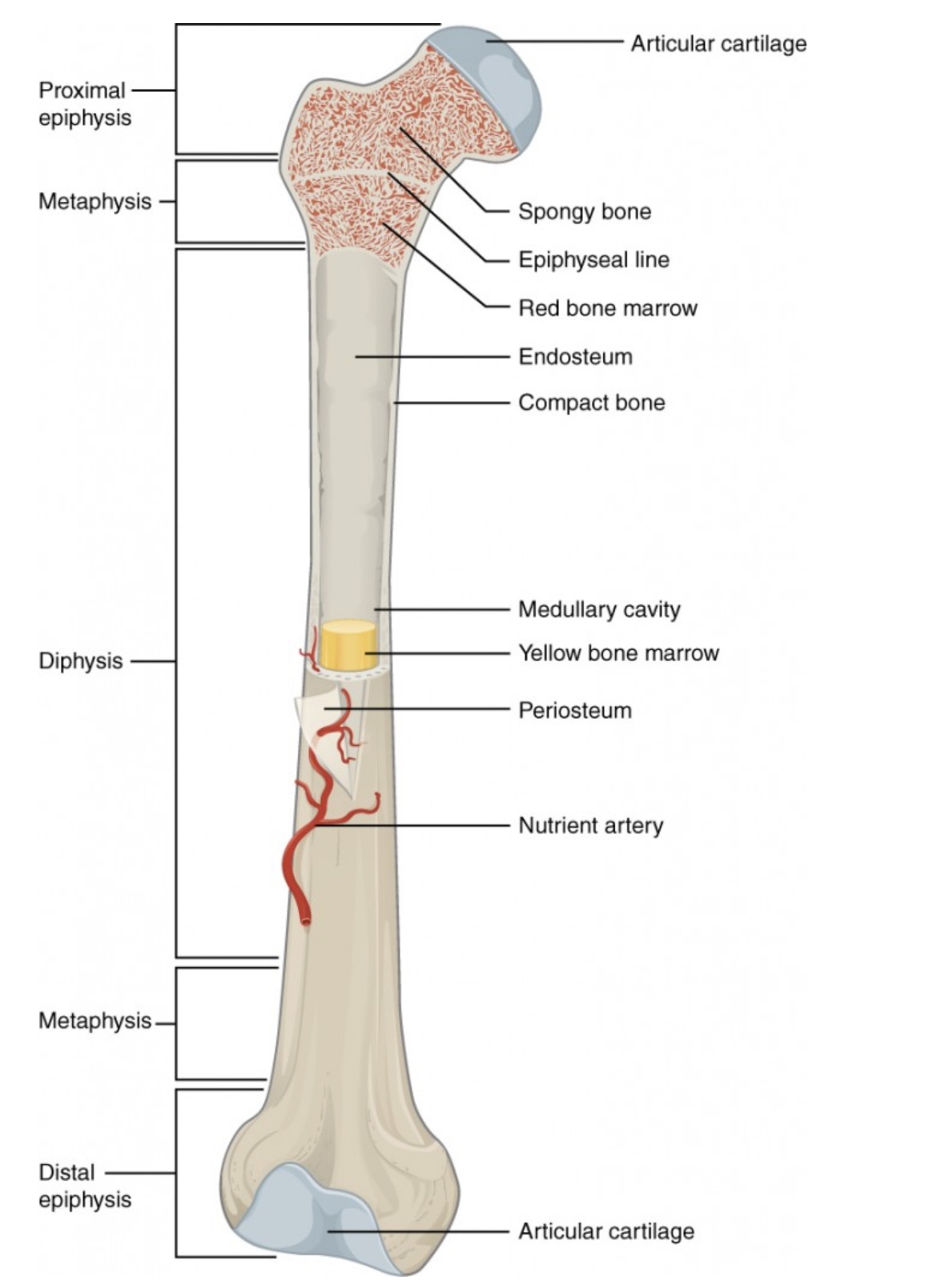
Epiphyseal Line (Plate)
Line between epiphysis and diaphysis.
Marks where growth occurred (growth plate in children).
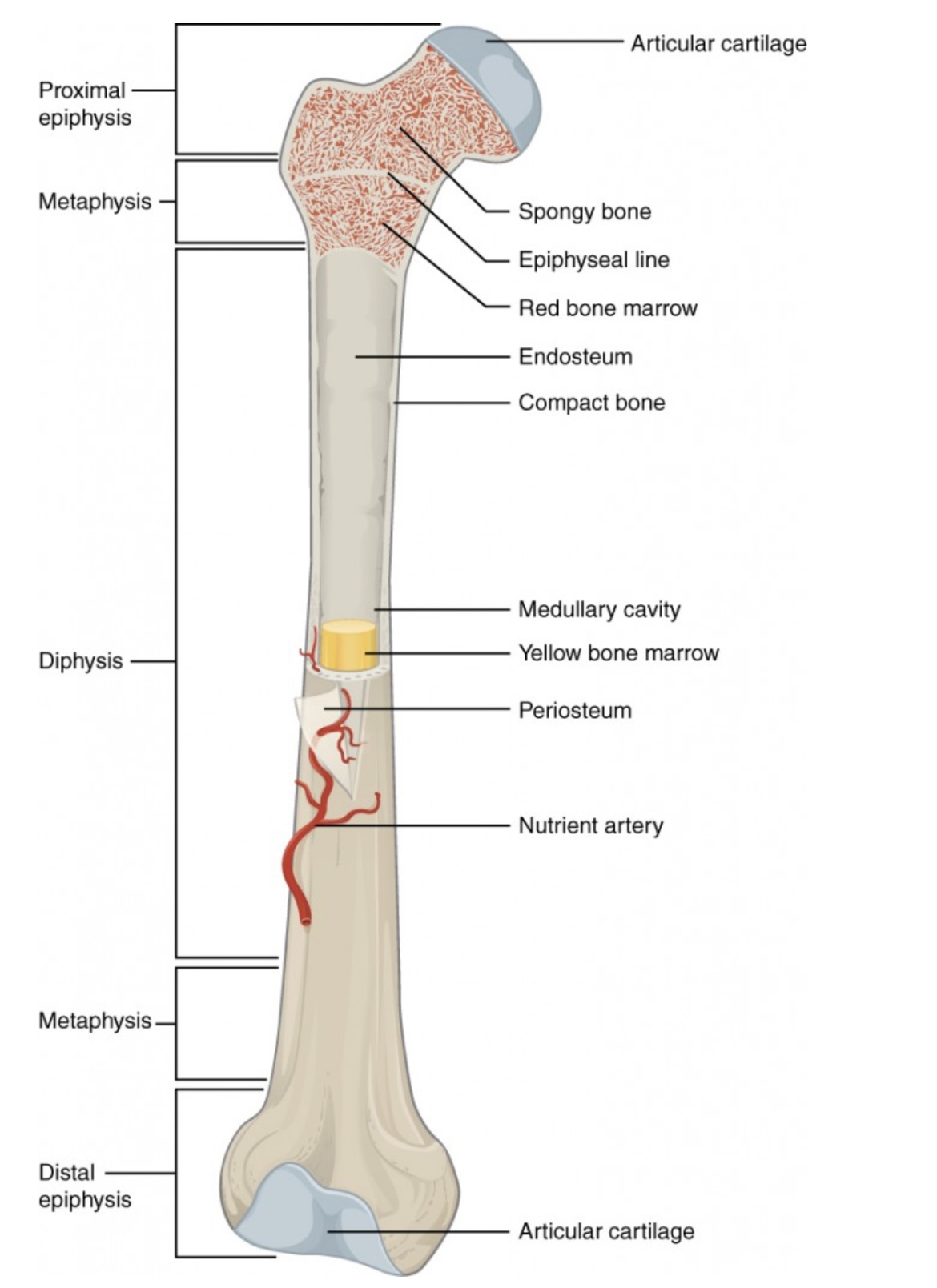
Red Bone Marrow
Found in spongy bone.
Produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
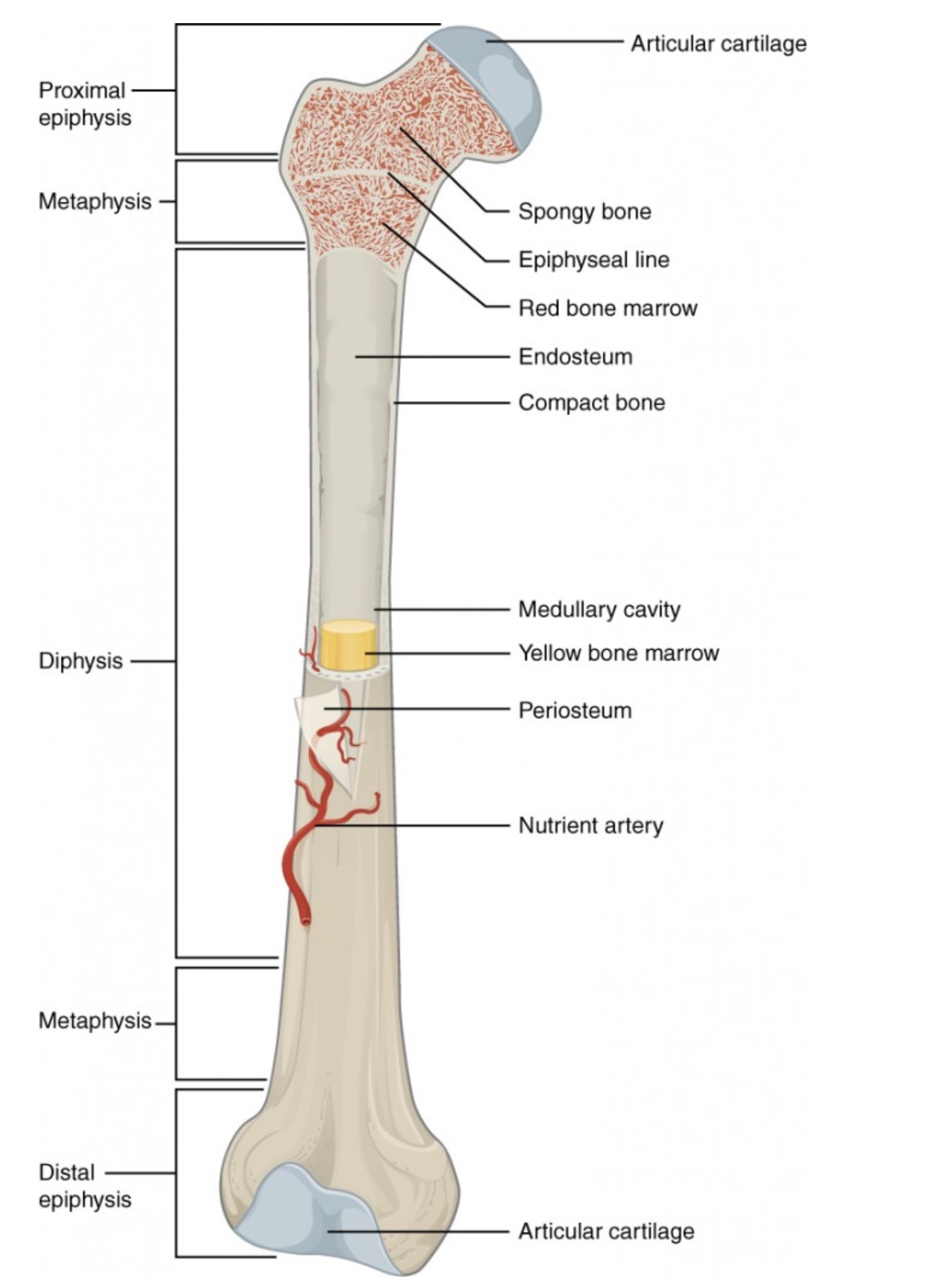
Yellow Bone Marrow
Inside the medullary cavity.
Stores fat and can convert to red marrow if blood loss occurs.
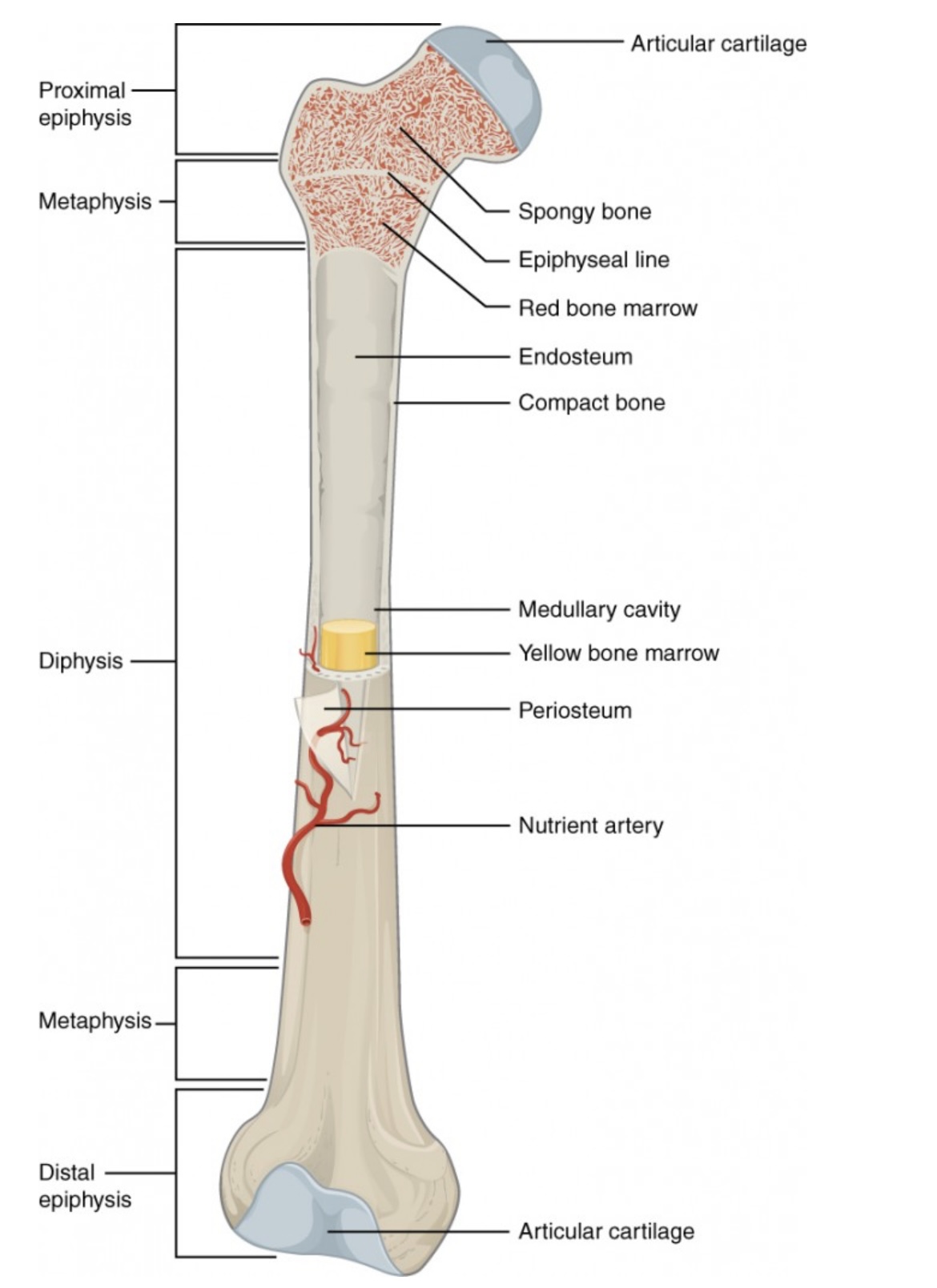
Medullary Cavity
Hollow center of the diaphysis.
Holds yellow marrow and lightens bone weight.
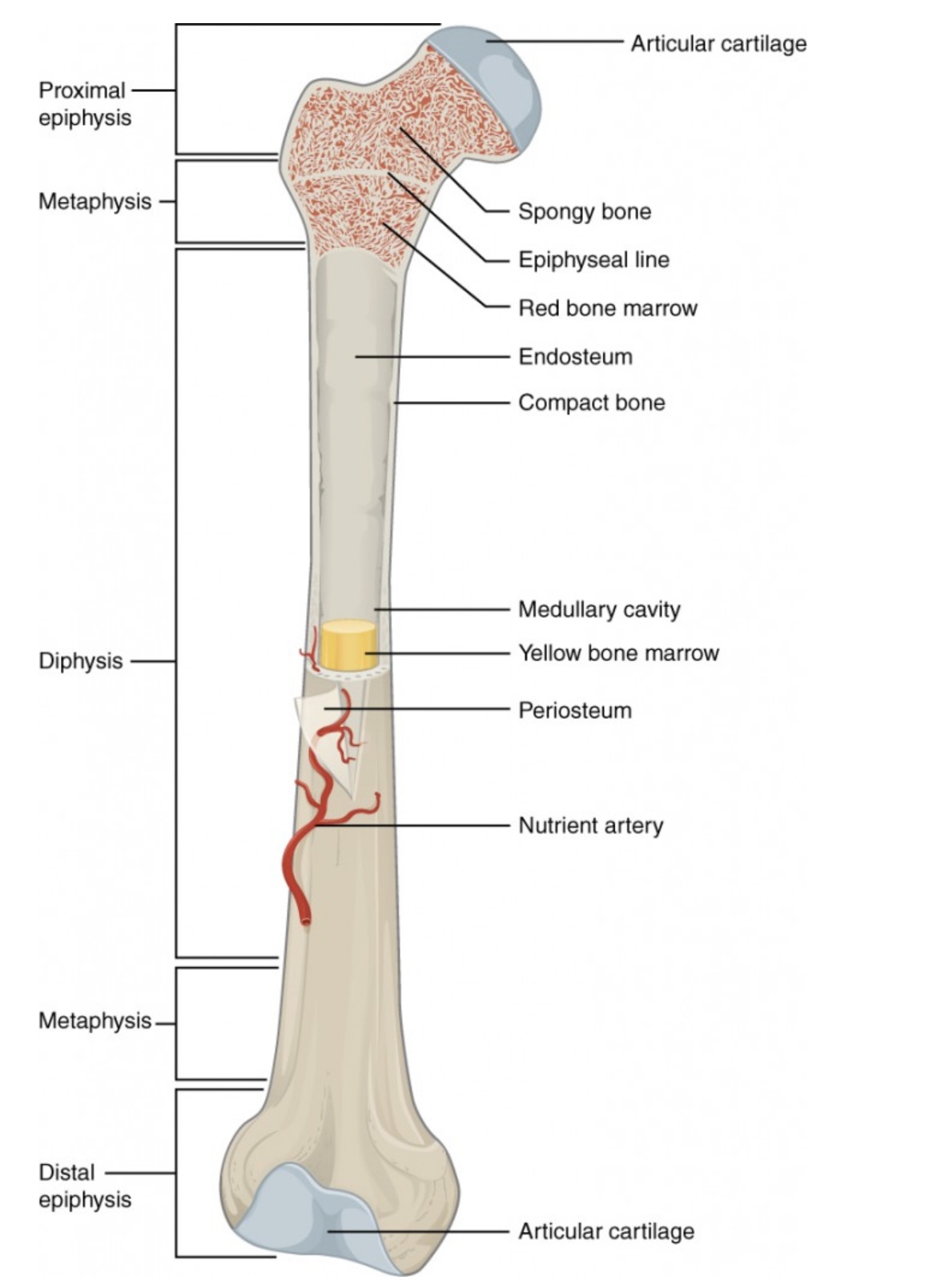
Endosteum
Thin membrane lining the medullary cavity.
Contains bone-forming and bone-destroying cells for growth and repair.
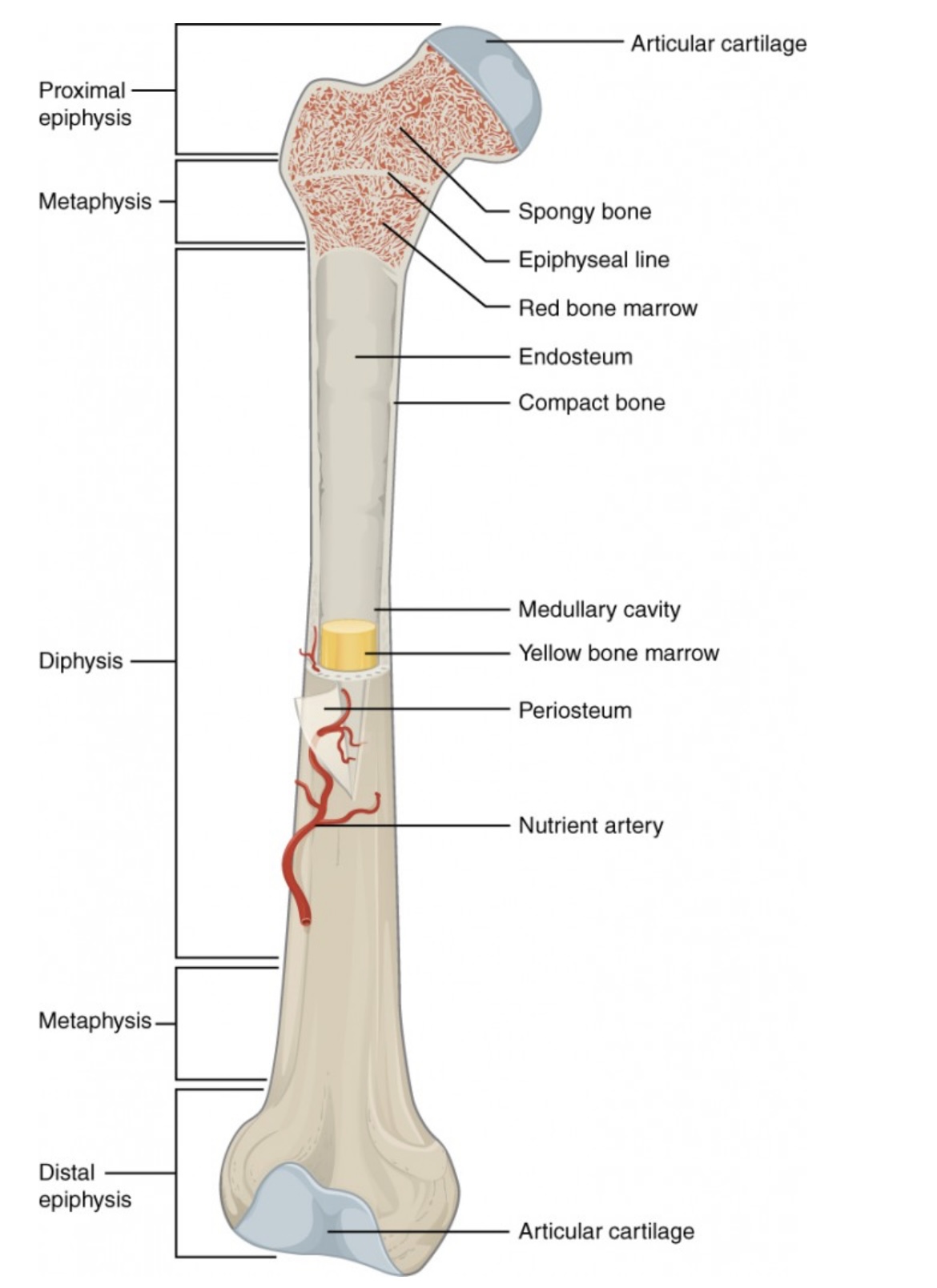
Periosteum
Tough outer covering of the bone.
Protects bone surface and helps with attachment of tendons and ligaments.
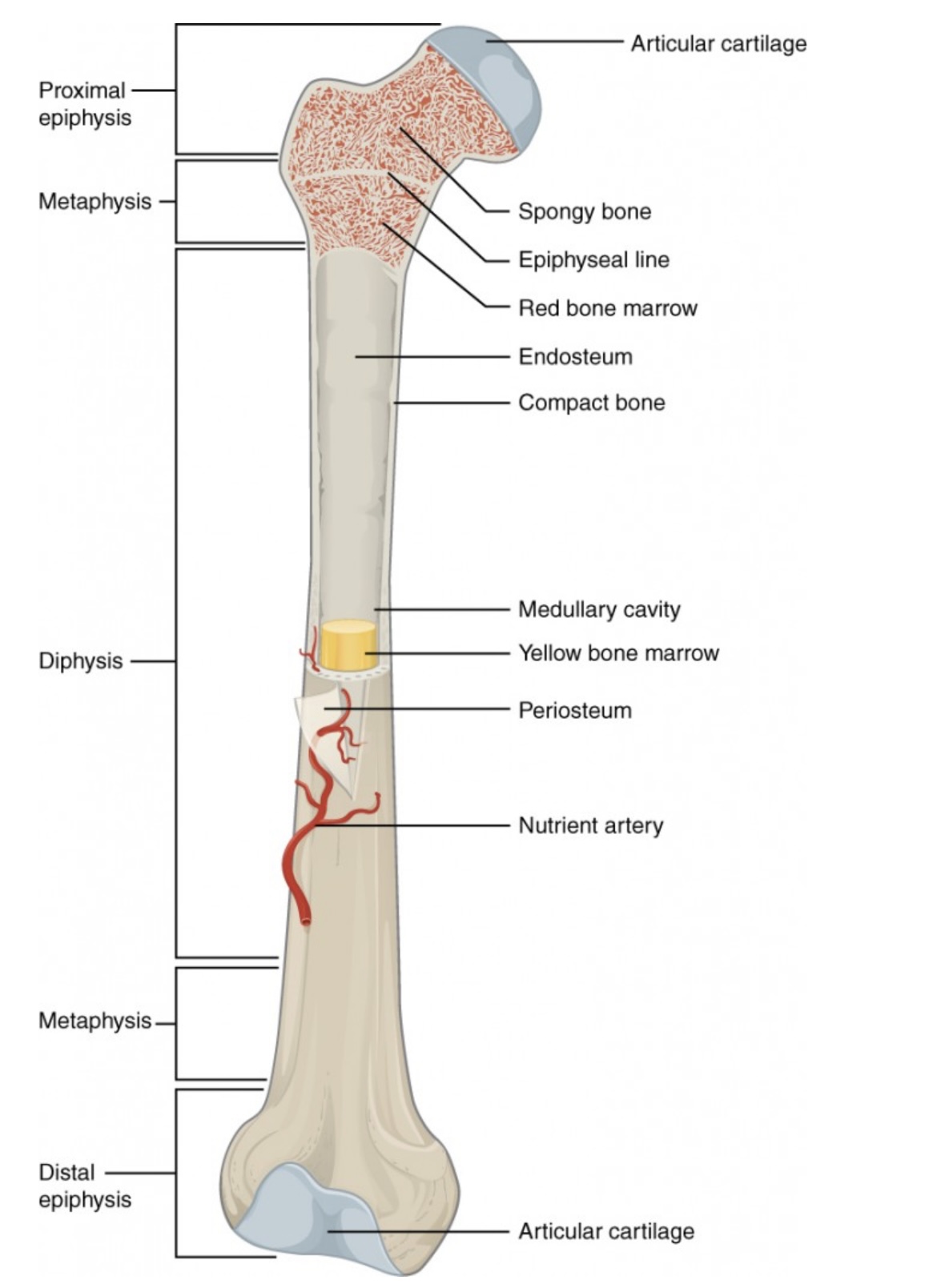
Nutrient Artery
Main blood vessel entering through the diaphysis.
Supplies oxygen and nutrients to bone cells.