Organic - Chapter 3: Alcohols, Phenols, & Ethers
5.0(3)
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1
New cards
Hydroxy Group
The -OH functional group.
2
New cards
R Groups
Indicate carbon groups; R&R can be the same or different groups.
3
New cards
Alcohols
Have an -OH group attached to an aliphatic carbon (C-OH).
4
New cards
R-OH
General Formula of Alcohols
5
New cards
Phenols
Have an -OH group on a benzene ring (an aromatic alcohol).
6
New cards
C6H5OH
General Formula of Phenol
7
New cards
Ethers
Have the functional group C-O-C.
8
New cards
R-O-R
General Formula of Ether
9
New cards
large
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers are important organic compounds that occur naturally and are produced synthetically in ____ amounts.
10
New cards
Ethanol
(drinking alcohol) has been used since ancient times.
11
New cards
peppermint oil
Menthol is a ten-carbon alcohol found in __________; it is used widely as a flavoring agent.
12
New cards
Cholesterol
An important biological molecule and has been implicated in some forms of heart disease.
13
New cards
H2O
Alcohols, phenols, and ethers may be considered to be derived from ____.
14
New cards
alkyl group
In alcohols one of water's hydrogens is replaced with an ______.
15
New cards
aromatic ring
In phenols one of water's hydrogens is replaced with an _________.
16
New cards
both
In ethers ______ of water's hydrogens are replaced with alkyl groups.
17
New cards
Alcohol Nomenclature
1.) Name the longest carbon chain to which the -OH group is attached. Use the hydrocarbon name of the chain, drop the final -e and replace it with -ol.
2.) Number the longest carbon chain to give the lowest number to the carbon with the attached -OH.
3.) Locate the -OH position and locate/name any other groups attached to the longest chain.
4.) Combine the name and location of other groups, the location of the -OH, and the longest chain into the final name.
2.) Number the longest carbon chain to give the lowest number to the carbon with the attached -OH.
3.) Locate the -OH position and locate/name any other groups attached to the longest chain.
4.) Combine the name and location of other groups, the location of the -OH, and the longest chain into the final name.
18
New cards
common names
Some of the simpler alcohols are often known by ________; in these names the alkyl group is followed by the word alcohol.
19
New cards
Phenol Nomenclature
Substituted are usually named as derivatives of the parent compound phenol.
20
New cards
chemistry
The ______ of alcohols often depends on the groups bonded to the carbon with the hydroxy on it.
21
New cards
attached group
There are three classifications of alcohols; these classifications are based on the alcohol's ________.
22
New cards
Primary Alcohols
The carbon with the hydroxy group is attached to one other carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms.
23
New cards
Secondary Alcohols
The carbon with the hydroxy group is attached to two other carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
24
New cards
Tertiary Alcohols
The carbon with the hydroxy group is attached to three other carbon atoms and no hydrogens.
25
New cards
polar
The -OH group of alcohol is ______ and capable of hydrogen bonding.
26
New cards
True
T or F: Hydrogen bonding in alcohols makes low molecular weight alcohols highly soluble in water.
27
New cards
alkane
As the size of the alkyl group in an alcohol increases, the physical properties become less water-like and more _____-like.
28
New cards
hydrophobic
Larger alkanes have greater _______ regions and are less soluble or insoluble in water.
29
New cards
Solubility Ratio
1 hydroxy for every 5 carbons.
30
New cards
carbon
The number of _____ atoms per hydroxy group determines the solubility in water.
31
New cards
boiling point
Hydrogen bonding can affect __________.
32
New cards
high
The -OH group in alcohol can hydrogen bond between alcohol molecules leading to relatively _____ boiling points.
33
New cards
alcohols
When compared to molecules of similar molecular weight, ______ have much higher boiling points.
34
New cards
Dehydration
The removal of water from an alcohol.
35
New cards
Dehydration to Produce an Alkene
(180 degrees C) An elimination reaction, uses Markovnikov's rule.
36
New cards
Elimination Reaction
A reaction when two or more bonds are broken to form a new multiple bond.
37
New cards
False
T or F: Only one product can be formed in dehydration to produce an alkene.
38
New cards
principle
The major/______ alkene produced is the one in which the higher number of carbon groups is bonded to the double-bonded carbon atoms.
39
New cards
living systems
Alcohol dehydration is important in __________.
40
New cards
Enzymes
_______ (rather than sulfuric acid) are the catalysts in alcohol dehydration.
41
New cards
Dehydration to Produce an Ether
(140 degree C) A dehydration reaction occurs between two alcohol molecules where an -H is removed from one alcohol, an -OH group is removed from the other and they combine to make water. Leaving the two remaining fragments to bond.
42
New cards
Primary Alcohols
Ether-forming reactions are useful mainly with _________.
43
New cards
living organisms
Dehydration synthesis is important in ________ because it is part of the formation of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and other essential substances.
44
New cards
temperature
The type of dehydration is controlled by ________.
45
New cards
Oxidation Reactions
When a molecule gains oxygen atoms or loses hydrogen atoms.
46
New cards
two
Alcohols can be oxidized by removing ____ hydrogen atoms.
47
New cards
oxidizing agents
Alcohol oxidations can be accomplished with an __________ (O) such as K2Cr2O7 or KMnO4.
48
New cards
carboxylic acid
Primary alcohols --> aldehyde --> __________
49
New cards
ketone
Secondary alcohols --> _________
50
New cards
no reaction
Tertiary alcohols --> __________
51
New cards
useful
Alcohols can be converted by chemical reactions into a wide variety of other ______ products.
52
New cards
False
T or F: Most alcohols occur naturally in commercial quantities therfore they are prepared from alkenes.
53
New cards
Nature
_______ also employs multistep reactions to carry out processes essential to life.
54
New cards
protonated alcohol
During alcohol dehydration mechanism, the H+ ion becomes bonded to the oxygen resulting in a _________.
55
New cards
Methanol
(methyl alcohol) known as wood alcohol because historically it was produced by the distillation of wood. Useful as a solvent and industrial starting material due to its oxidation product formaldehyde. Highly toxic, can cause blindness.
56
New cards
CH3OH
Formula of Methanol
57
New cards
Ethanol
(ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol) the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages. Produced commercially from ethylene and through biological fermentation of carbohydrates. Used in pharmaceuticals as a solvent and in aftershave lotions as an antiseptic and skin softener. It is an important industrial starting material and used in fuels such as gasohol.
58
New cards
Gasohol
Mixture of gasoline and ethanol.
59
New cards
CH3CH2OH
Formula of Ethanol
60
New cards
2-Propanol
(isopropyl alcohol) the main component of rubbing alcohol. Acts as an astringent on the skin causing the skin tissue to contract, harden, and limit secretions. Lowers skin temperature by rapidly evaporating from the skin. It is extremely poisonous and shouldn't be taken internally.
61
New cards
1,2,3-Propanetriol
(glycerol or glycerin) has three hydroxy groups making it useful for many things. The hydrogen bonding resulting from the three hydroxy groups causes it to a syrupy/high-boiling point liquid with an affinity for water. Used as a food moistening agent, good for soaps, and to retain water that maintains the freshness of cut flowers.
62
New cards
1,2-Ethanediol
(ethylene glycol) high-boiling point liquid that is completely miscible with water (hydrogen bonding). Used as antifreeze and a starting material for the manufacture of polyester fibers.
63
New cards
1,2-Propanediol
(propylene glycol) high-boiling point liquid that is completely miscible with water (hydrogen bonding). Used as antifreeze and a starting material for the manufacture of polyester fibers.
64
New cards
colorless
Phenol is a ______, low-melting-point solid with a medicinal odor.
65
New cards
carbolic acid
Adding a small amount of water to Phenol causes the solid to liquefy (this mixture is commonly called _________).
66
New cards
weak acids
Unlike alcohols, phenols behave as _________ in water (these acids can chemically burn the skin).
67
New cards
salts
Phenols can also react with bases to form ______.
68
New cards
Joseph Lister
In the late 1800's an English surgeon named _________ introduced phenols as a hospital antiseptic (before that time antiseptics were not used and few patients survived even minor surgeries).
69
New cards
4-chloro-3,5-dimethylphenol
Nonirritating topical antiseptic
70
New cards
4-hexylresorcinol
Used in mouthwashes and throat lozenges.
71
New cards
disinfectants
Some phenol derivatives are used as ________.
72
New cards
Lysol
O-phenylphenol and 2-benzyl-4-chlorophenol are the active ingredients in ______.
73
New cards
food
Some phenol derivatives are used as antioxidants in _____.
74
New cards
Antioxidants
Agents that interfere with oxidizing reactions, protect food from spoilage and other unwanted reactions.
75
New cards
BHA & BHT
_________ are widely used in the packaging materials for foods that might turn rancid (they are listed as food ingredient that "will maintain freshness").
76
New cards
Naming Ethers
Name the smaller of the two R groups as an alkoxy group attached to the parent chain by replacing the -yl ending of the R group with -oxy.
77
New cards
Common Names of Ethers
Name the groups attached to the oxygen alphabetically and add the word ether. If the groups are the same use the prefix di-.
78
New cards
Heterocyclic Rings
Contain atoms of elements other than carbon in the ring (many biological molecules have these rings).
79
New cards
carbohydrates
Many ________ contain cyclic ethers.
80
New cards
Cyclic Ethers
Rings containing oxygen
81
New cards
Furan
Common cyclic ether:
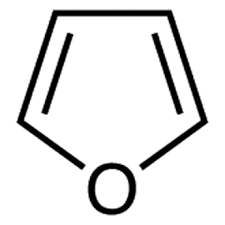
82
New cards
Pyran
Common cyclic ether:
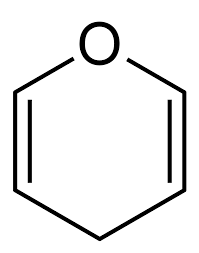
83
New cards
less
Ethers are much _____ polar than alcohols because oxygen is bonded to two carbons rather than a hydrogen.
84
New cards
alkanes
Ethers can hydrogen bond to water, making them more soluble than _____.
85
New cards
low
Ethers cannot hydrogen bond with other ethers, therefore they have ____ boiling and melting points and are less soluble in water than alcohols.
86
New cards
inert
Ethers are ____ and do not react with most reagents (like alkanes) making them a useful solvent.
87
New cards
flammable
Ethers are highly ______ (like alkanes).
88
New cards
Thiols
Contain a sulfhydryl group (-SH).
89
New cards
6A
Sulfur and oxygen belong to the same group (___) on the periodic table so they react similarly.
90
New cards
analogous
The sulfhydryl group in thiols is ________ to the hydroxy group in alcohols.
91
New cards
Disulfides
Compounds containing an -S--S- linkage.
92
New cards
odor
The most distinguishing characteristic of thiols is their strong and offensive _____. Ex.) skunks, stink bugs, onions, garlic, etc.
93
New cards
flavors
Some thiols have less offensive odors and some are _____.
94
New cards
1-propanethiol
The odor in freshly chopped onions.
95
New cards
1-propane-3-thiol
Responsible for the odor and flavor of garlic.
96
New cards
3,3-di-(1-propenyl)
______disulfide is responsible for the odor and flavor of garlic.
97
New cards
Ethanethiol
(CH3CH2-SH) added to natural gas (methane) to make it possible to detect a gas leak.
98
New cards
Oxidizing Thiols
Forms disulfide (-S--S-) linkage.
General Formula: 2R -- SH + (O) ----> R--S--S--R + H2O
General Formula: 2R -- SH + (O) ----> R--S--S--R + H2O
99
New cards
Disulfide Reduction
Oxidation reactions can be reversed with a reducing agent (H). The disulfides are uncoupled to produce thiols.
General Reaction: R--S--S--R + 2(H) ------> 2R--SH
General Reaction: R--S--S--R + 2(H) ------> 2R--SH
100
New cards
Heavy Metal Reaction
Metal ions react with the sulfhydryl group.
General Reaction: 2R--SH + M2+ ------> R--S--M--S--R + 2H+
General Reaction: 2R--SH + M2+ ------> R--S--M--S--R + 2H+