[ 1MID ] CHEMISTRY
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Atom
smallest unit of matter that retains the identity and properties of an element
Molecule
a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded
0.0005
The atomic mass of an electron
1
The atomic mass of a proton
1
The atomic mass of a neutron
-1
Charge of an electron
+1
Charge of a proton
0
Charge of a neutron
Isotopic Symbol
allows for the mass number, atomic number, and charge to be easily known.
Mass Number
the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus.
Atomic Number
the charge number of an atomic nucleus. This is equal to the proton number (np) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element.
The number of protons tells the identity of the element and the arrangement of the elements in the periodic table.
Ion
is formed when an atom gains or loses electrons.
Cation
positively charged, formed when a metal loses electrons.
Anion
negatively charged, formed when a nonmetal gains electrons.
Isotopes
atoms of the same element with different mass numbers
Monatomic
only one atom
Polyatomic
multiple atoms
Nucleons
The name for the protons and neutrons together
Identity
What does the proton tell about the element?
Hydrated Salts
Some ionic compounds with water molecules incorporated in their structure
Arrhenius Acid
Substance that yields H+ in aqueous solution
Arrhenius Base
a compound that increases the OH− ion concentration in aqueous solution.
Covalent Compounds
combination of two or more NONMETALS covalently bonded (involves sharing of electrons)
Law of Conservation of Mass
This states that in an (ordinary) chemical reaction, the mass of the substances produced is equal to the mass of the substances reacted.
Antoine Lavoisier
He is known as the father of modern chemistry.
Law of Definite Proportions
This states that any sample of a given compound will always be composed of the same elements in the same proportion by mass.
Nitrous Oxide
This is known as the laughing gas
Law of Multiple Proportions
This states that for elements that can form different compounds, the masses of the second element that can combine with a fixed mass of the first element are in a ratio of small whole numbers
John Dalton
He published a book called “A New System of Chemical Philosophy” where he proposed an atomic theory of matter that can explain chemical observations as predicted by the three fundamental laws.
Joseph John Thomson
He discovered the electron while studying the nature of cathode rays.
Cathode Ray Tube
a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen.
Ernest Rutherford
He performed the gold foil experiment and observed that some alpha rays were deflected at a regular pattern, some bounced back to the alpha particle source, and other passed through the foil. He then concluded that the atom has a very tiny positive nucleus at its center, an idea that led to the emergence of the nuclear model of an atom.
He discovered the proton.
James Chadwick
A former student of Rutherford, discovered the other type of particle in the nucleus—the neutron.
Ionic Compounds
Results from an attraction between a cation and an anion.
Gold Foil Experiment
What did Rutherford perform that led to his discovery of the proton.
John Dalton
He made the Solid Sphere model
J.J. Thomson
He made the Plum Pudding model
Ernest Rutherford
He made the Nuclear Model
Niels Bohr
He made the Planetary Model
Erwin Schrodinger
He made the Quantum Model
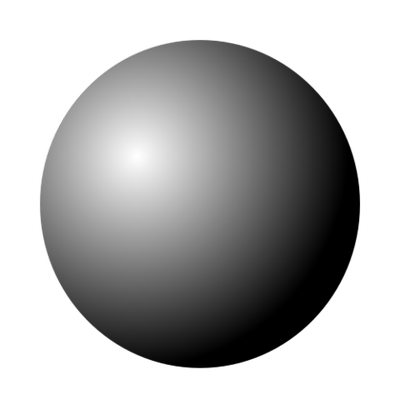
Solid Sphere Model
an atomic model proposed by John Dalton in 1803. It states that all objects are made of particles called atoms and that they are solid spheres that cannot be divided further into smaller particles. This is similar to the model made by the Greeks in the fifth century BCE.
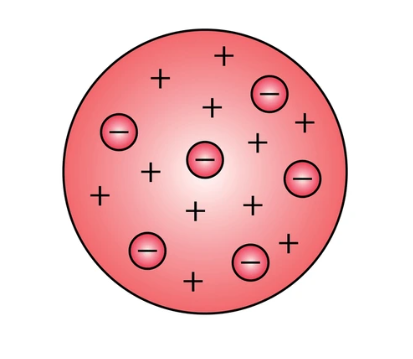
Plum Pudding Model
the first scientific model of the atom to describe an internal structure. It was first proposed by J. J. Thomson in 1904 following his discovery of the electron in 1897, and was rendered obsolete by Ernest Rutherford's discovery of the atomic nucleus in 1911.
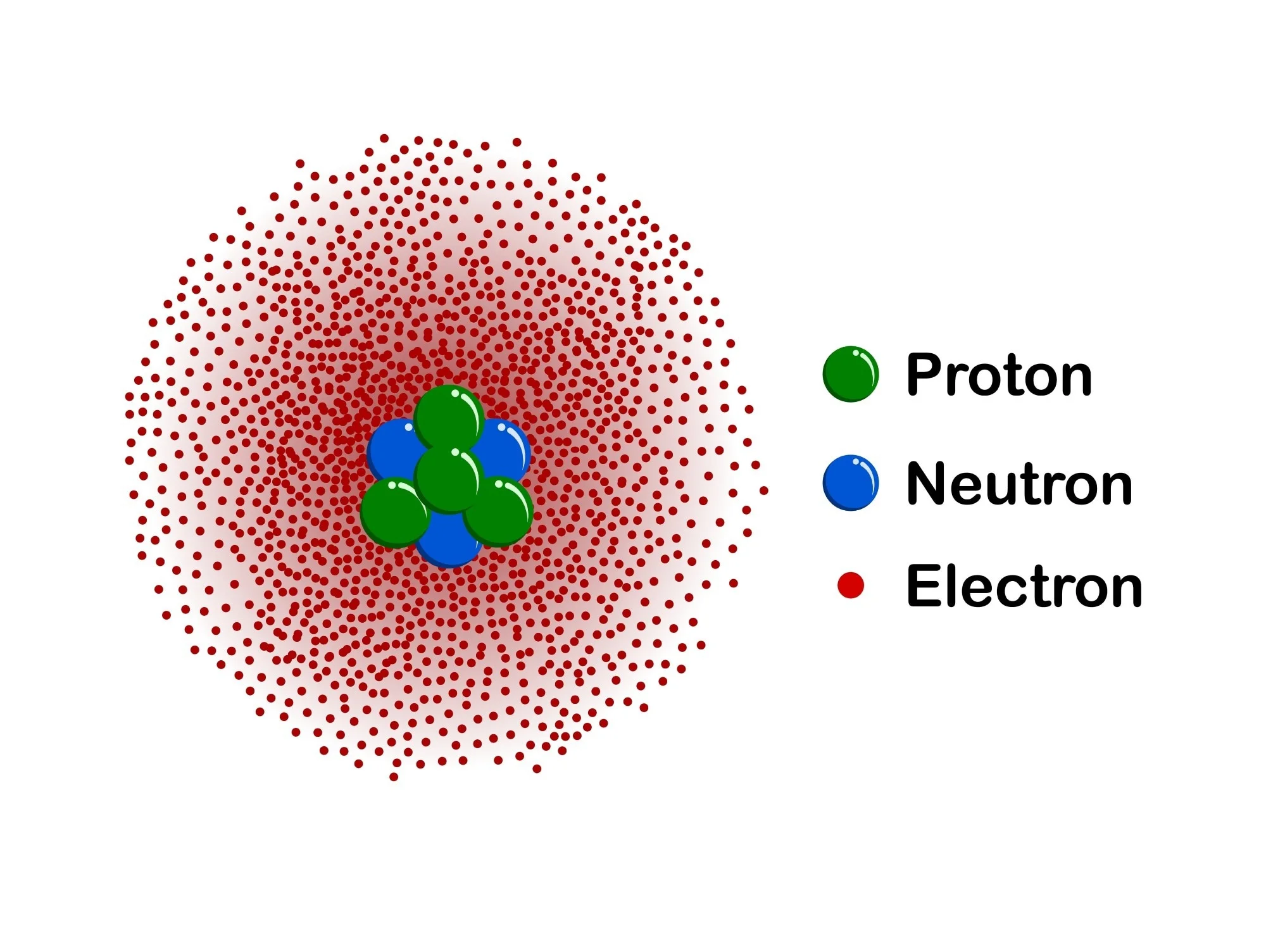
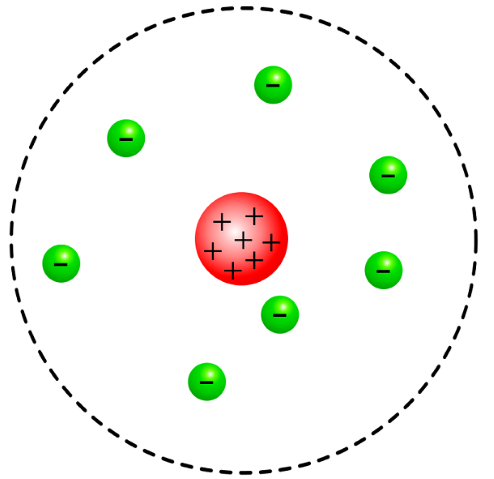
Nuclear Model
refers to a theoretical framework used in nuclear physics to describe the structure and behavior of atomic nuclei. It is based on the understanding obtained from studying nuclei near the β-stability line, incorporating concepts such as magic numbers and nuclear matter incompressibility.
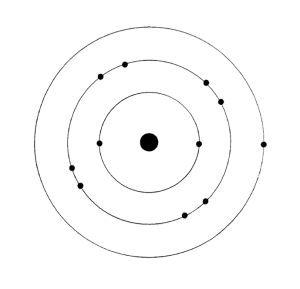
Planetary Model
electrons are arranged in concentric circular orbits around the nucleus. This model is patterned on the solar system and is known as the _________
Quantum Model
describes the probability of finding electrons within given orbitals, or three-dimensional regions of space, within an atom. The properties of each electron within the quantum atom can be described using a set of four quantum numbers.
Solid Sphere Model

Plum Pudding Model
Nuclear Model
Planetary Model
Quantum Model