Chemistry topic 4-Chemical changes
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
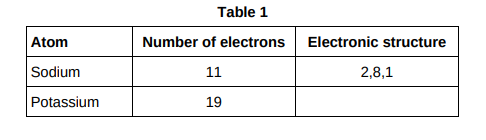
Complete Table 1 to show the electronic structure of a potassium atom.(1)
2,8,8,1

Why do Group 1 elements have similar chemical properties?(1)
They have the same number of outer shell electrons.

What is the type of bonding in sodium?(1)
Metallic
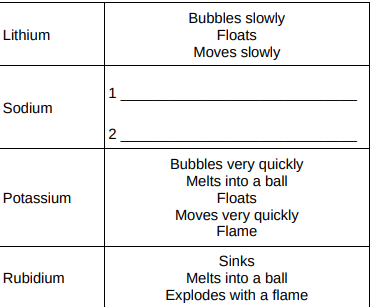
Give two observations you could make when sodium reacts with water. Write your answers in Table 2. (2)
Bubbles quickly, melts quickly
How does the reactivity of the elements change going down Group 1?(1)
It increases
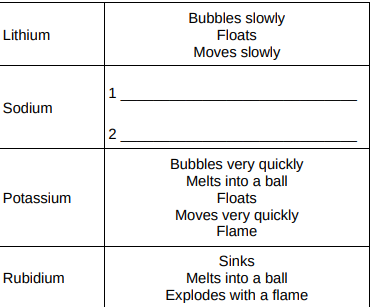
Give two ways in which the observations in Table 2 show the change in reactivity going down Group 1.(2)
Increasing speed of movement, doesn’t melt—>melt

Which gas is produced when Group 1 elements react with water?(1)
Hydrogen
(3)

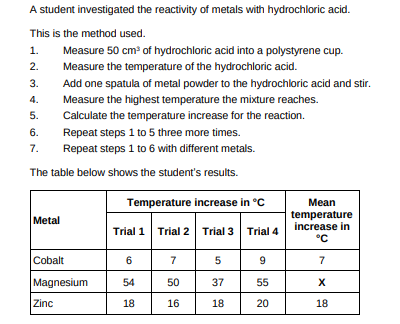
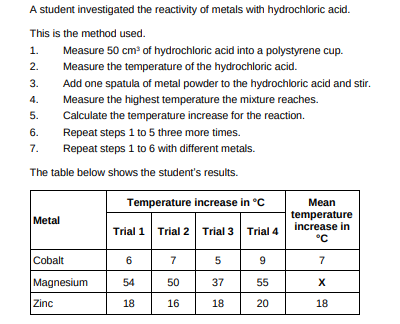
Calculate the mean temperature increase X for magnesium in the table above. Do not include the anomalous result in your calculation.(2)
54+50+55/3 = 53
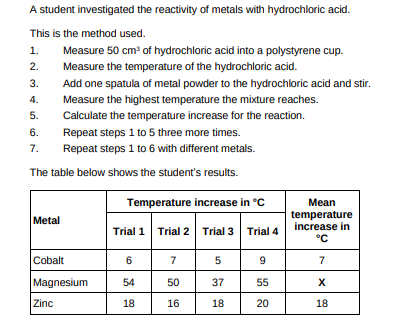
Determine the order of reactivity for the metals cobalt, magnesium and zinc. Use the table above. Most reactive __________________________ _____________________________________ Least reactive __________________________(1)
magnesium, zinc, cobalt
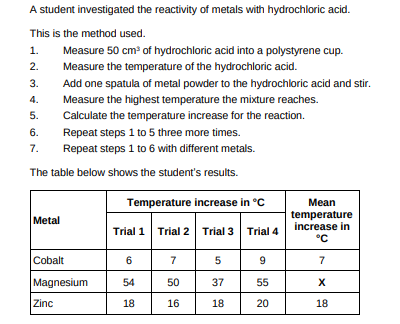
The range of measurements either side of the mean shows the uncertainty in the mean temperature increase. Complete the sentence. Use the table above. The mean temperature increase for zinc is 18 ± __________°C (1)
2
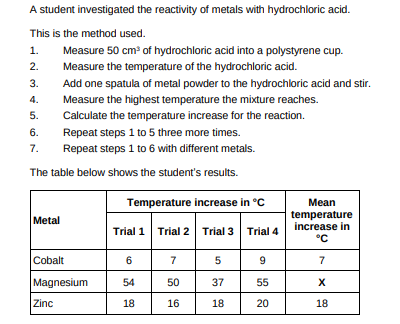
What type of variable is the volume of hydrochloric acid in this investigation?(1)
control
Suggest one way of improving step 3 in the method to give results which are more repeatable.(1)
Use the same mass of metal powder
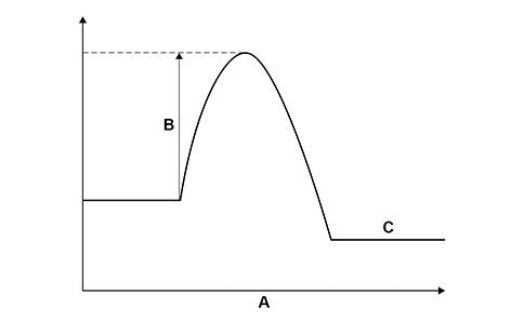
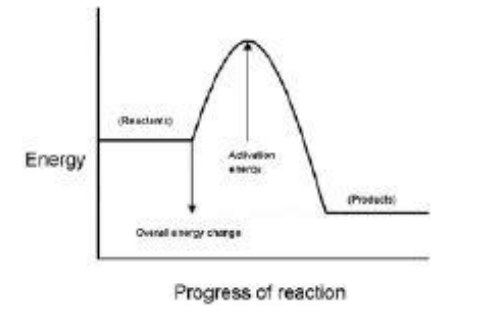
What do labels A, B and C represent on the figure above? Choose answers from the box. (activation energy, energy, overall energy change, products, progress of reaction, reactants)
A _________________________________________________________
B _________________________________________________________
C _________________________________________________________(3)
progress of reaction, activation energy, products
The sum of the relative formula masses (Mr) of the reactants (3 H2 + RO3) is 150 Calculate the relative atomic mass (Ar) of R. Relative atomic masses (Ar): H = 1 O = 16(2)
(3*(2×1))+(16×3)=54, 150-54 = 96
Identify element r which has Ar of 96(1)
Molybdenum
Carbon is used to extract tin (Sn) from tin oxide (SnO2). The equation for the reaction is: SnO2 + C → Sn + CO2. Calculate the percentage atom economy for extracting tin in this reaction. Relative atomic masses (Ar): C = 12 O = 16 Sn = 119.(3)
119/163×100 = 73%
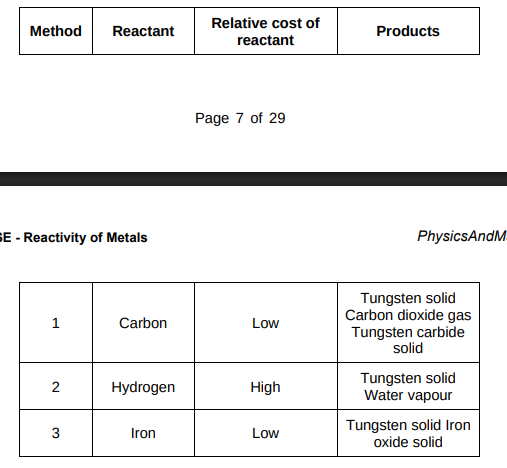
Evaluate the three possible methods for extracting tungsten from tungsten oxide.(4)
Carbon and iron are the cheapest reactants while hydrogen is the most expensive reactant. In method one, tungsten needs to be separated from tungsten carbide while method 3 consists of separating tungsten from tungsten oxide but there is no separation of solids required in method 2.
This question is about Group 1 elements. Give two observations you could make when a small piece of potassium is added to water.(2)
Floats, melts
Complete the equation for the reaction of potassium with water. You should balance the equation.K + H2O → + (2)
K + H2O → + 2KOH+H2
Explain why the reactivity of elements changes going down Group 1. (4)
Reactivity increases because the outer shell is further away from the nucleus so there is less attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons so the atom loses an electron more easily.
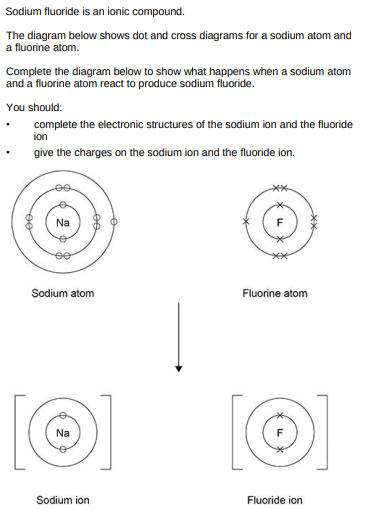
Sodium reacts with oxygen to produce the ionic compound sodium oxide. Oxygen is a Group 6 element. Draw a dot and cross diagram to show what happens when atoms of sodium and oxygen react to produce sodium oxide.(6)
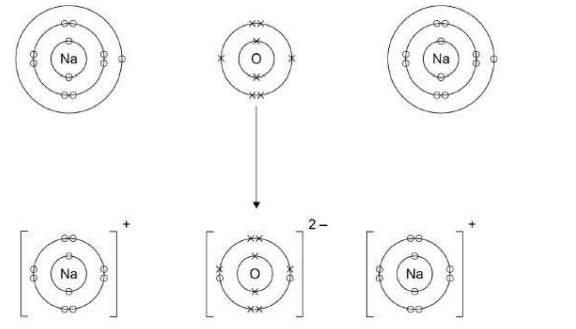
Why is oxygen described as being reduced in the reaction between sodium and oxygen?(1)
Because it gains electrons
Explain why sodium oxide has a high melting point.(3)
Sodium oxide is a giant structure with strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions meanign large amounts of energy are needed to break the bonds.
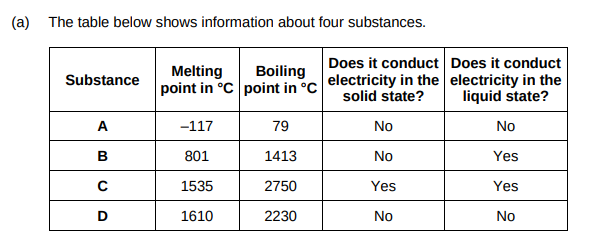
Which substance could be a metal?(1)
C
Explain why alloys are harder than pure metals.(3)
An alloy has atoms of different sizes so the layers in an alloy are distorted meaning the layers slide over each other less easily.
A student wants to compare the reactivity of an unknown metal, Q, with that of zinc. Both metals are more reactive than silver. The student is provided with:
• silver nitrate solution
• metal Q powder
• zinc powder
• a thermometer
• normal laboratory equipment.
No other chemicals are available. Describe a method the student could use to compare the reactivity of metal Q with that of zinc. Your method should give valid results.(4)
Measure the temperature change when each metal is added to the silver nitrate solution using the same volume of solution. The greater the temperature change, the more reactive.

Which two statements are properties of most transition metals?(2)
They form ions with different charges, they have high melting point
A student added copper metal to colourless silver nitrate solution. The student observed:
• pale grey crystals forming
• the solution turning blue.
Explain how these observations show that silver is less reactive than copper.
The grey crystals are silver and the copper ions are blue because copper displaces silver.
A student is given three metals, X, Y and Z to identify. The metals are magnesium, iron and copper. Plan an investigation to identify the three metals by comparing their reactions with dilute hydrochloric acid. Your plan should give valid results.(4)
1)Set up by taking 3 test tubes and pouring the same amount of hydrochloric acid in each one
2)Take a thermometer and measure temperature of one of the test tubes, then add a small amount of metal X
3)Wait for 5 mins and measure the temperature. Calculate the temperature change
4)Repeat again with the other metals using other test tubes. Make sure to add the same amount of metal.
Here are valid results: copper should not have had a reaction meaning no temperature change. Magnesium should have had the greatest temperature change followed by iron.
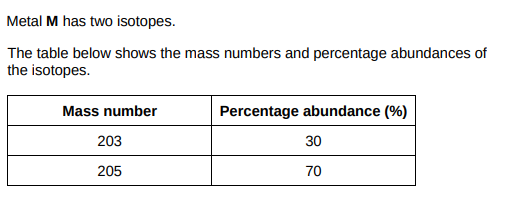
Calculate the relative atomic mass (Ar) of metal M. Give your answer to 1 decimal place.(2)
(203×30)+(205×70)/1 = 204.4
What is meant by ‘activation energy’?(1)
The minimun energy needed for a reaction to occur
A mixture contains 1.00 kg of aluminium and 3.00 kg of iron oxide. The equation for the reaction is: 2 Al + Fe2O3 → 2 Fe + Al2O3. Show that aluminium is the limiting reactant. Relative atomic masses (Ar): O = 16 Al = 27 Fe = 56 (4)
Moles Al:1000/27 = 37, Moles Fe2O3:3000/160 = 18.75, Aluminium is limiting because 37/2 = 18.5<18.75
Complete the ionic equation for the reaction. You should include state symbols. Mg(s) + Zn2+(aq) → _________ + _________(2)
Mg(s) + Zn2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Zn(s)
Explain why the reaction between magnesium atoms and zinc ions is both oxidation and reduction.(2)
Because magnesium is oxidised because it loses electrons and zinc is reduced as it gains electrons
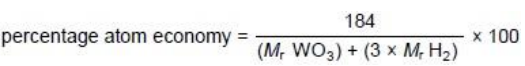
Tungsten is a metal. The symbol of tungsten is W Tungsten is produced from tungsten oxide by reaction with hydrogen. The equation for the reaction is:
WO3 + 3 H2 → W + 3 H2O
Calculate the percentage atom economy when tungsten is produced in this reaction. Relative formula masses (Mr): WO3 = 232 H2 = 2 (2)
(184/232+6)*100=77%[
38% of a rock sample is aluminium oxide. Calculate the mass of aluminium oxide in 40 kg of the rock sample.(2)
38/100×40=15kg
The formula of aluminium oxide is Al2O3 Calculate the relative formula mass (Mr) of aluminium oxide. Relative atomic masses (Ar): O = 16 Al = 27 (2)
(2×27)+(3×16)=102

60.0 kg of aluminium oxide produces a maximum of 31.8 kg of aluminium. In an extraction process only 28.4 kg of aluminium is produced from 60.0 kg of aluminium oxide. Calculate the percentage yield. Give your answer to 3 significant figures.(3)
28.4/31.8×100=89.3081761%=89.3%
Extracting metals by electrolysis is a very expensive process. Explain why aluminium is extracted using electrolysis and not by reduction with carbon.(2)
Aluminium is more reactive than carbon so carbon cannot displace aluminium.

State the dependent then the independent variable in the practical.(2)
Temperature change, type of metal
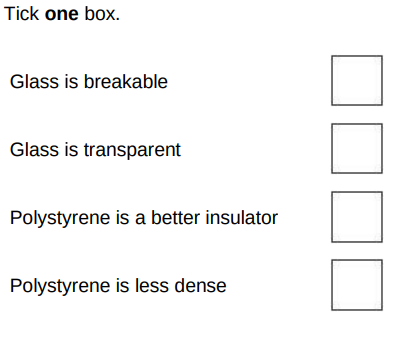
The student used a polystyrene cup and not a glass beaker. Why did this make the investigation more accurate?(1)
Polystyrene is less dense
The student concluded that the reactions between the metals and copper sulfate solution are endothermic. Give one reason why this conclusion is not correct. (1)
Temperature does not decrease
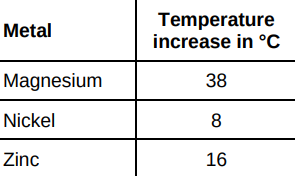
The temperature increase depends on the reactivity of the metal. Write the metals magnesium, nickel and zinc in order of reactivity. Use the table above. (1)
Magnesium, Zinc, Nickel
Y is an unknown metal. Describe a method to find the position of Y in the reactivity.(3)
Add the unknown metal to copper sulfate solution and measure temperature change. Then place the metals in order of temperature change.
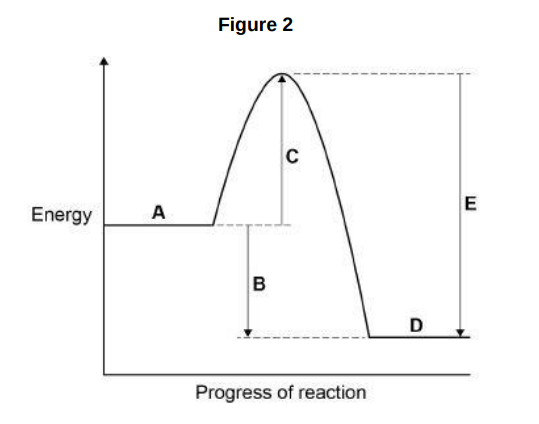
Which letter represents the products of the reaction?(1)
D
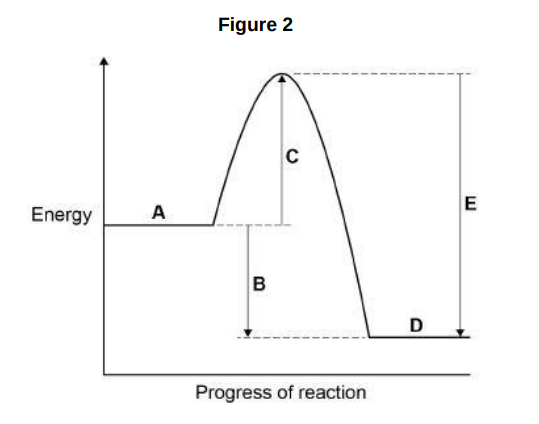
Which letter represents the activation energy?(1)
C
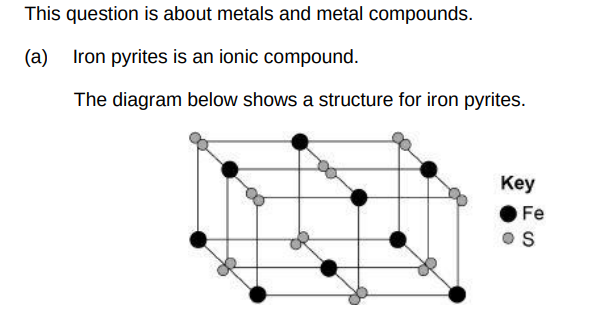
Determine the formula of iron pyrites. Use the diagram above.(1)
FeS2
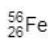
Give the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in this atom of iron. (3)
26,30,26
Iron is a transition metal. Sodium is a Group 1 metal. Give two differences between the properties of iron and sodium.(2)
Iron is less reactive, iron is stronger
Nickel is extracted from nickel oxide by reduction with carbon. Explain why carbon can be used to extract nickel from nickel oxide. (2)
Carbon is more reactive than nickel so carbon will displace it.
An equation for the reaction is: NiO + C ⟶ Ni + CO. Calculate the percentage atom economy for the reaction to produce nickel. Relative atomic masses (Ar): C = 12 Ni = 59. Relative formula mass (Mr): NiO = 75. Give your answer to 3 significant figures. (3)
59/87×100 =67.8%
Draw a fully labelled reaction profile for the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate solution on Figure 2.(3)

Suggest one hazard associated with Stage 1. (1)
Chlorine is toxic

Water must be kept away from the reaction in Stage 2. Give one reason why it would be hazardous if water came into contact with sodium (1)
Very violent reaction
Suggest why the reaction in Stage 2 is carried out in an atmosphere of argon and not in air.(2)
Argon is unreactive and oxygen would react with the sodium.
Titanium chloride is a liquid at room temperature. Explain why you would not expect titanium chloride to be a liquid at room temperature.(3)
Metal chlorides are usually ionic so they are solid at solid at room temperature because they have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between ions.
Sodium atoms are oxidised to sodium ions in this reaction. Why is this an oxidation reaction?(1)
Because sodium loses electrons
Complete the half equation for the oxidation reaction. Na ⟶ ____________ + ____________(1)
Na ⟶ Na+ + e−
In Stage 2, 40 kg of titanium chloride was added to 20 kg of sodium. The equation for the reaction is:
TiCl4 + 4 Na ⟶ Ti + 4 NaCl
Relative atomic masses (Ar): Na = 23 Cl = 35.5 Ti = 48
Explain why titanium chloride is the limiting reactant. You must show your working.(4)
Mr TiCl = 90, moles Na: 20000/23 = 870, Moles TiCl4 = 40000/190=211, 870/4 = 217.5 so TiCl4 is the limiting reactant as 211<217.5
For a Stage 2 reaction the percentage yield was 92.3% The theoretical maximum mass of titanium produced in this batch was 13.5 kg. Calculate the actual mass of titanium produced.(2)
92.3/100× 13.5 = 12.5
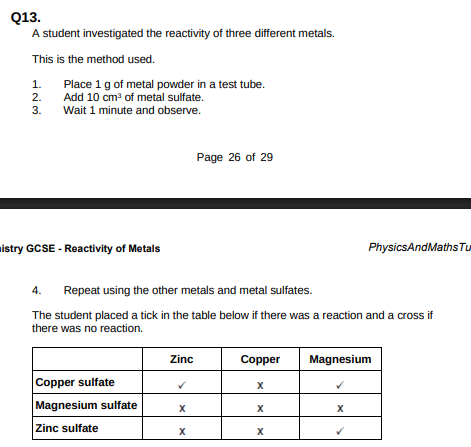
What is the dependent variable in the investigation?(1)
Whether there was a reaction or not
Give one observation the student could make that shows there is a reaction between zinc and copper sulfate.(1)
Brown deposit on zinc
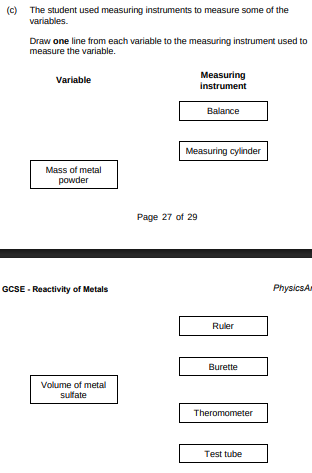
The student used measuring instruments to measure some of the variables. Draw one line from each variable to the measuring instrument used to measure the variable.(2)
Balance, measuring cylinder
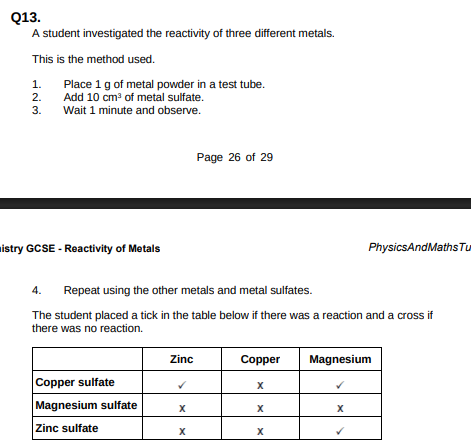
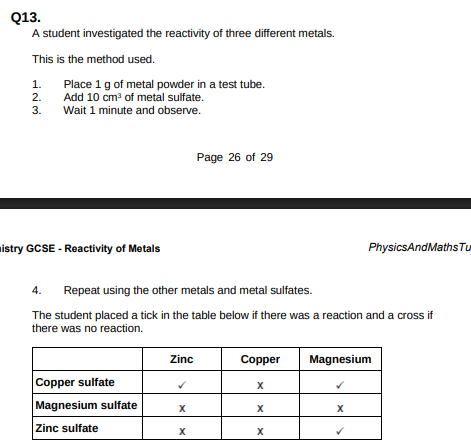
Use the results shown in table above to place zinc, copper and magnesium in order of reactivity.(1)
Magnesium, zinc, copper
Suggest one reason why the student should not use sodium in this investigation.(1)
Sodium is too reactive
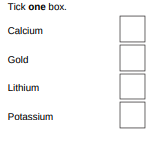
Which metal is found in the Earth as the metal itself?
gold
Balance the equation for the reaction. ___Fe2O3 + ___C → ___Fe + ___CO2 (1)
2Fe2O3 + 3C → 4Fe + 3CO2
What is meant by reduction?(1)
Loss of oxygen
Name the element used to reduce iron oxide.(1)
carbon