SL22107: Formulation of liposomes and gels
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is a gel
A viscoelastic solid-like material
Made of cross-linked network and a solvent put together by physical or chemical forces
What causes the appearance of a gel
entrapment and adhesion of a liquid in the large surface area of solid 3D matrix
How is a gel classified, give the 5 factors
Hydrophile-lipophile balance of polymer (HLB)
regularity of structure
polymer solvent interaction
molecular weight of polymer
flexibility of polymer chain
How can we describe gel characteristics
Large increase in viscosity above gel point
Appearance of rubber like elasticity
Gels typically retain their shape, until high stress = deformation
Describe wet soft solid gels
soap
shampoo
toothpaste
hair gel
contact lenses
ALL MADE FROM POLYMERIC COMPOUNDS
Describe what is meant by supramolecular gels and some uses
Low molecular mass compounds
Function: energy transfer, hybrid materials, tissue engineering, regenerative medicine
Describe what is meant by macromolecular gels and some uses
Large molecular mass compounds formed by hydrogen bond cross linking
Uses: Gelatin, collagen, agar, starch, gellan gum
What is a smart gel
Gels which respond to their environment e.g. pH change, difference in light
Describe the classification of gels
Natural or Artificial
Supramolecular or Macromolecular
Physical or Chemical
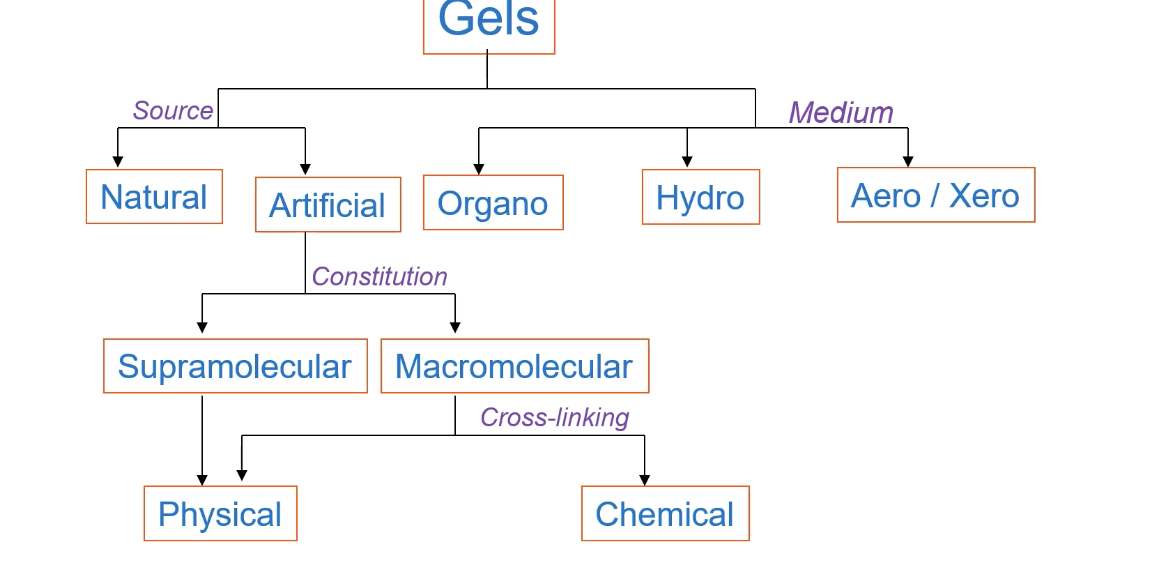
Physical vs chemical gels
Physical gels are reversible. Chemical gels irreversible
What are hydrogels
Water molecules trapped within 3D network
e.g. gelatin
What are some characteristics of hydrogels
Can retain significant amounts of water
Water insoluble
Used in topical drug delivery, wound healing, soft contact lenses, implant coating
Organic liquid gels: organogels
Organic liquids trapped in 3D matrix
e.g. petroleum
Jelly gel
When coherent matrix is rich in liquid
e.g. ephedrine sulphate jelly
Xerogel/Aerogel
When the liquid from the coherent matrix is removed and only the 3D network remains
e.g. gelatin sheet
How does diffusion in hydrogel occur
If a gel is highly hydrated it occurs through the pores
If a gel is low hydrated it occurs through dissolving in the polymer and is transported between the chains
What effect does cross linking have on diffusion rate
Increases hydrophobicity of a gel
Decreases the diffusion rate of the drug
What happens when hydrogels swell
Swelling characteristic of polymeric gel can be changed by heat, pH or application of electrical current
swollen at low temperature allows for drug delivery
shrunken at high temperature doesn’t allows for drug delivery
How are macromolecules formed
From irreversible thermal chemical reactions e.g. strong chemical bonds
From reversible physical reactions e.g. weak non-covalent interactions
Type 1 gels
Irreversible systems
3D network formed by covalent bonds between macromolecules
Formed by polymerisation of monomers of water soluble polymers in presence of X-linker
Type 2 gels
Held together by intermolecular bonds
Form a gel by cooling below gel point (T)
Very viscous
Why are type 2 gels suitable for topical skin applications
Has gelling properties
Dries rapidly
leaves a plastic film with the drug after contact with the skin
What happens when water soluble polymer chains are covalently cross linked into a 3D structure
A gel forms when the dry material interacts with water
How do cross linked polymeric gels behave in water
They swell but cannot dissolve due to cross links
Used for expanding implants and antibiotic-loaded gels for treating middle ear infections
What are SAFIN’s formed from (Self-Assembled Fibrillar Network)
Combination of non-covalent interactions
H bonds
PI-PI stacking
donor acceptor interaction
metal coordination
van der waals
these interactions are weak so they can be transformed = thermally reversible
How are supramolecular gels made
LMMC heated to isotropic supersaturated solution then condense
Highly ordered aggregation give rise to crystals = crystallisation
Random aggregation results in amorphous precipitate
An intermediate between crystallisation and amorphous precipitate creates a gel
What are some uses of supramolecular gels
cosmetic formulation
media for tissue engineering as its similar composition to body
controlled release of molecules
model antigens for immunogenicity studies
Wound dressing