Micro Bio Lab 9 More differential stains
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
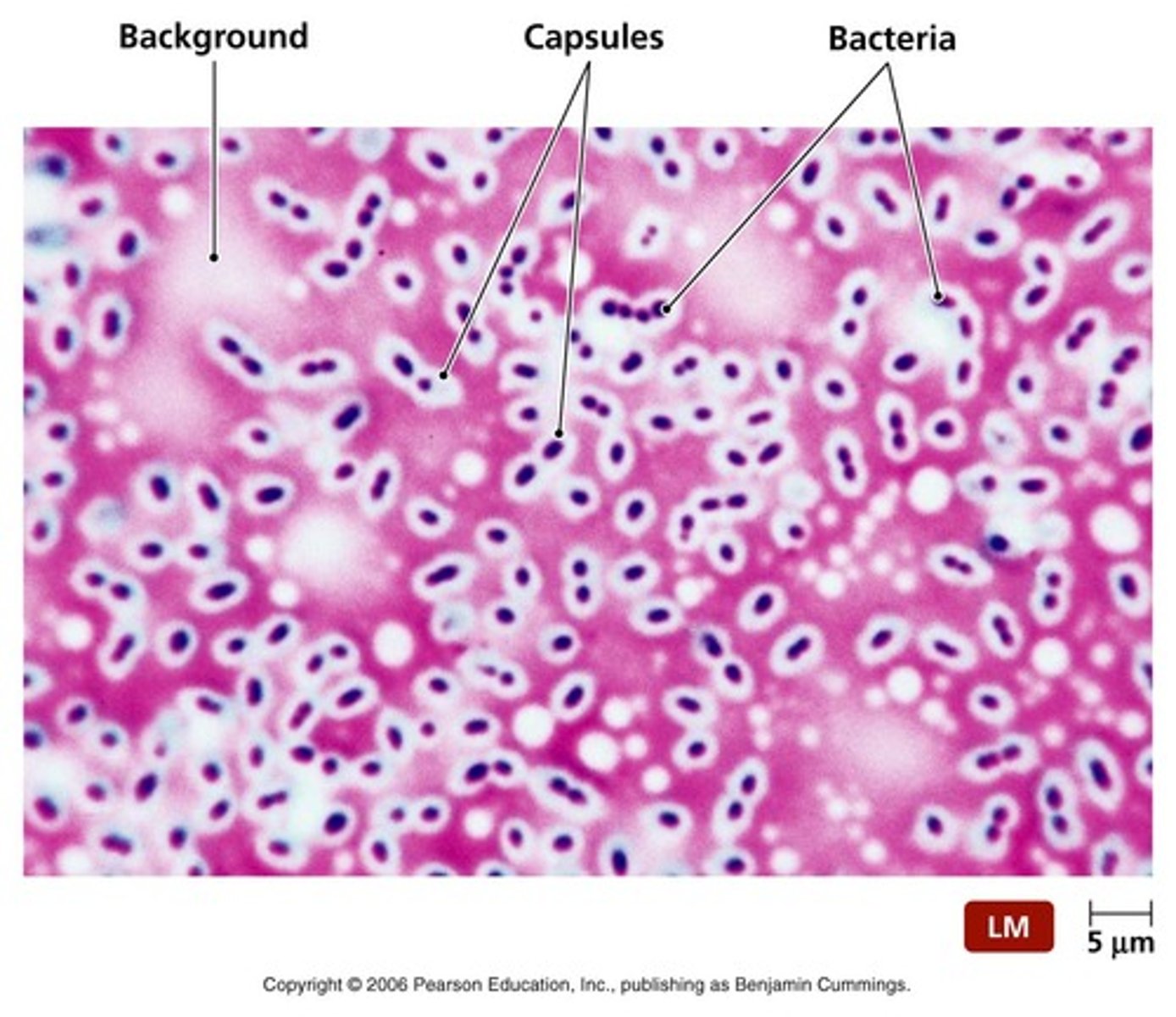
Overview of the capsule stain
Step 1: india ink repels capsule
Step 2: Crystal violet counterstains the cell inside the capsule
Procedure of the capsule stain
1. Drop of india ink on clean slide
2. add bacteria
3. Use a second glass slide as a spreader in the following manner (45 degree angle and spread: feather spread)
4. Allow to air dry
5. heat fix
6. Crystal violet for one minute
7. Rinse with water
8. Dry in bibulous paper and view under microscope
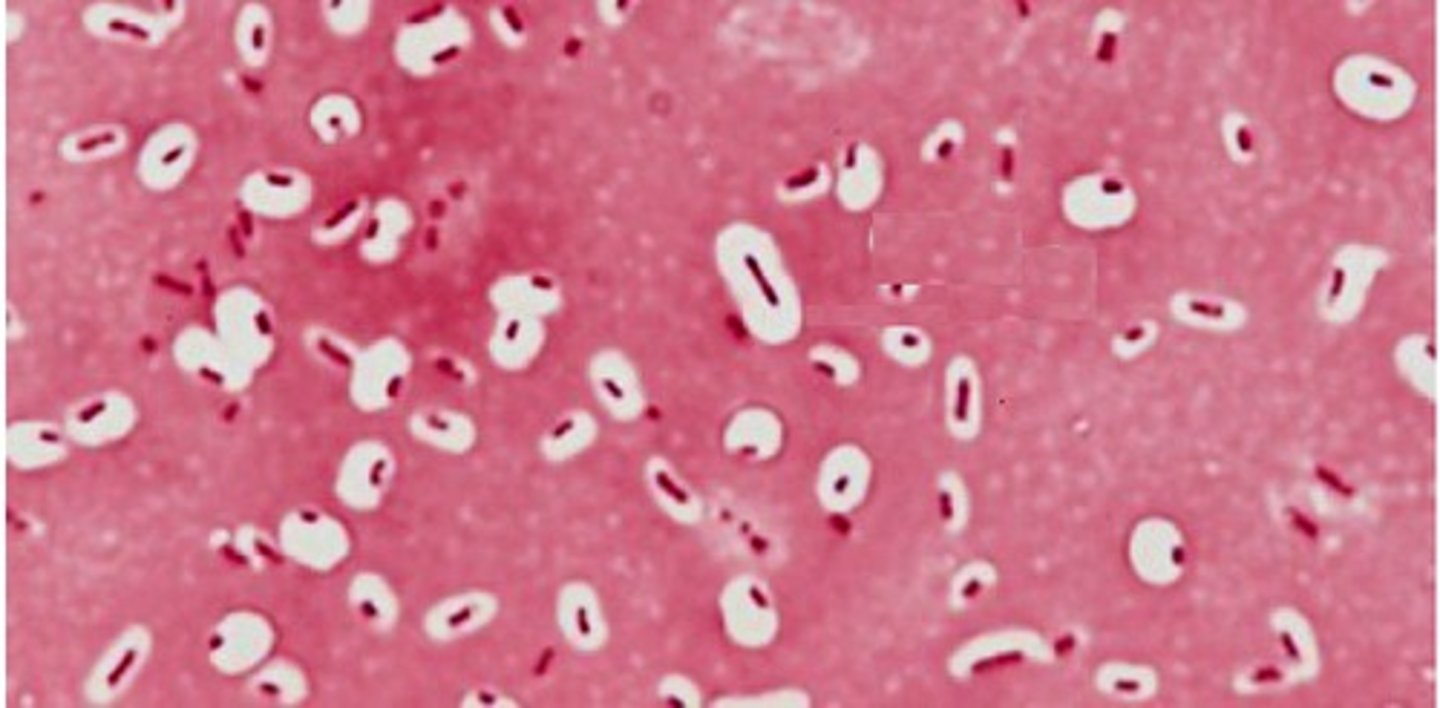
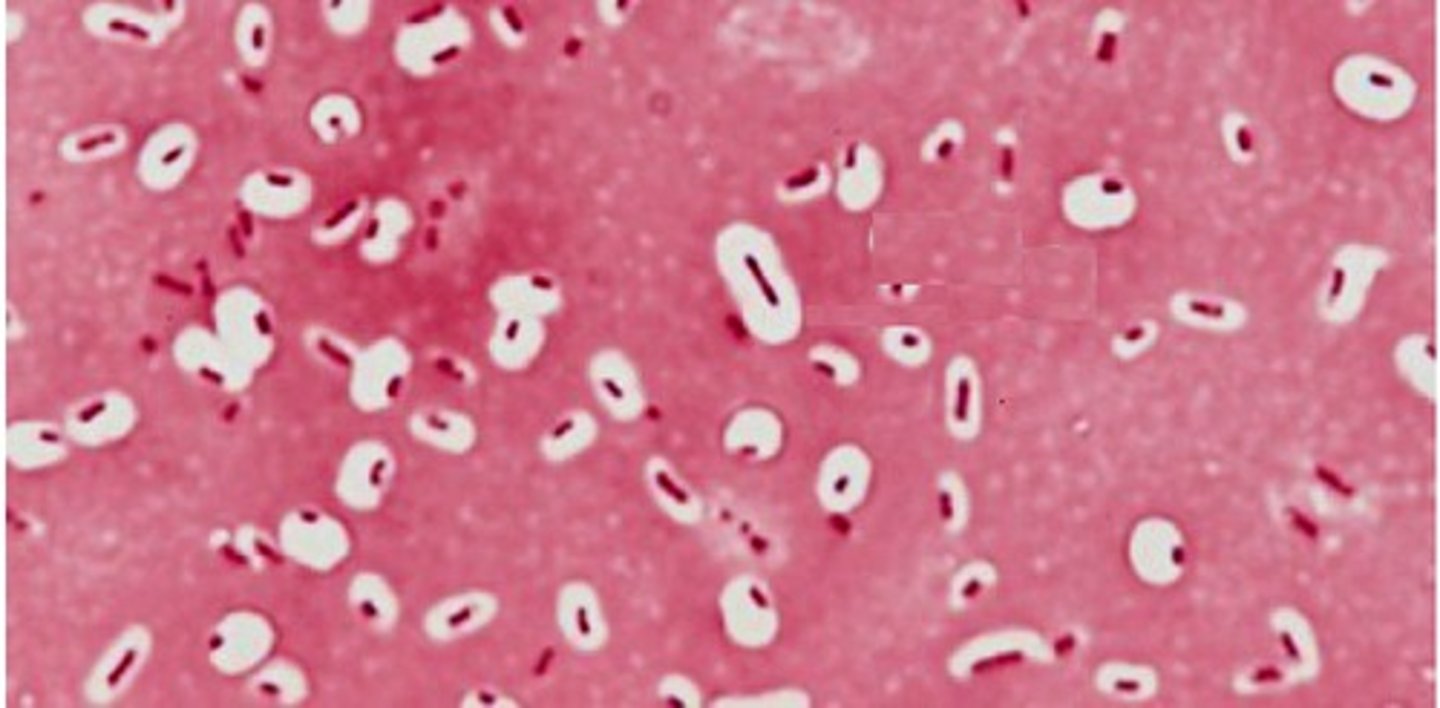
In a capsule stain is the capsule actually stained?
No — in a capsule stain, the capsule itself is not actually stained. it appears clear
Standard terminology for a capsule stain
State capsule present or capsule not present
Standard terminology for spore stain
State positive for spore formation or negative for spore formation
- include if its central, terminal(protruding at end), or subterminal (near end)
Standard terminology for acid fast stain
State acid fast or non acid fast
Standard terminology for flagella stain
State flagella present or flagella not present
and where flagella are present
- amphitrichous ( one at both ends)
- lophotrichous (tufts multiple at one end)
- peritrichous (flagella all over)
- monotrichous (1 flagella)

State the function of a bacterial capsule. Describe the role of a capsule in determining an organism's level of virulence
The capsule protects the bacterium from host defenses and environmental stress. Also provides defense agaisnt human immune system
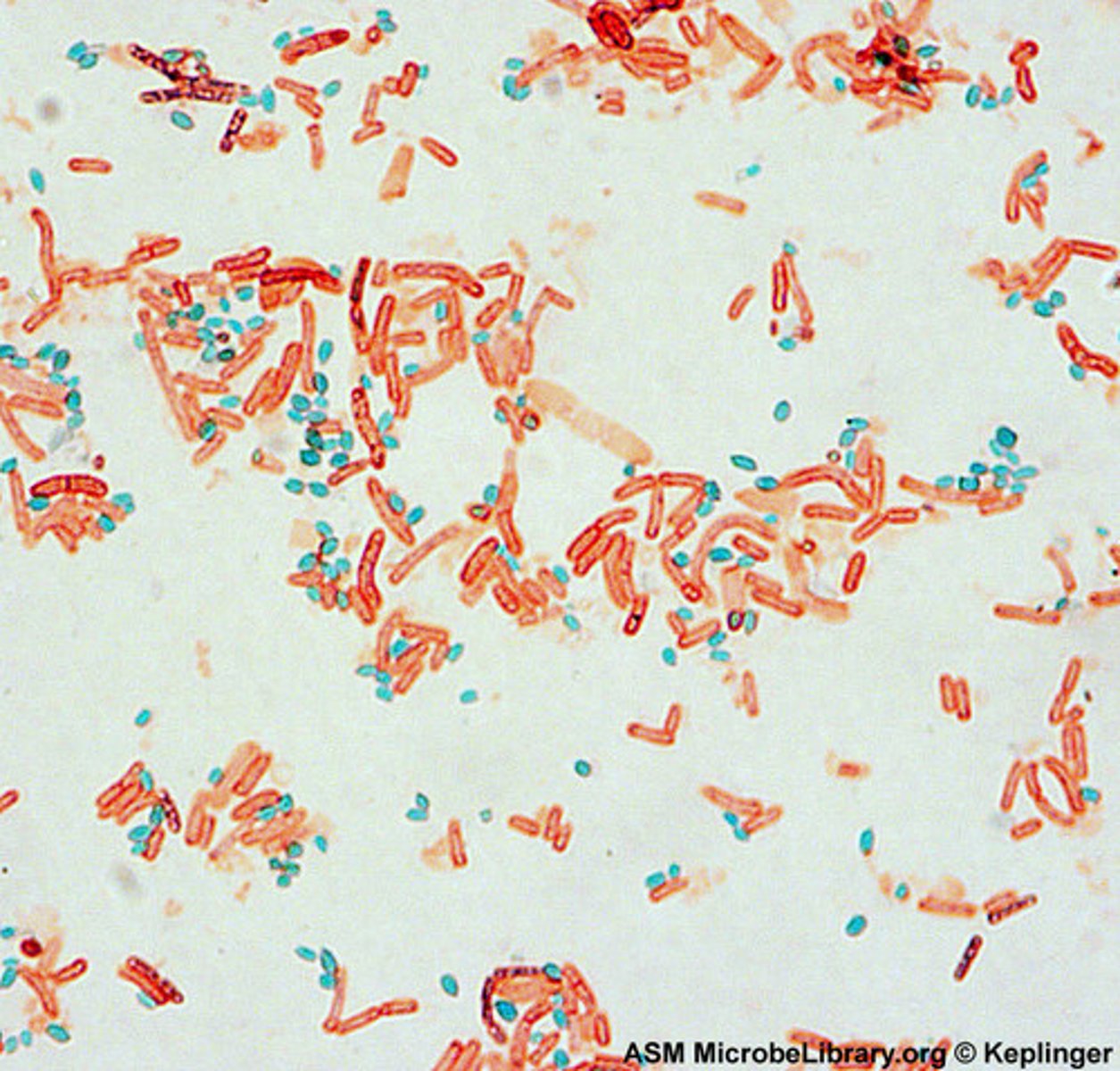
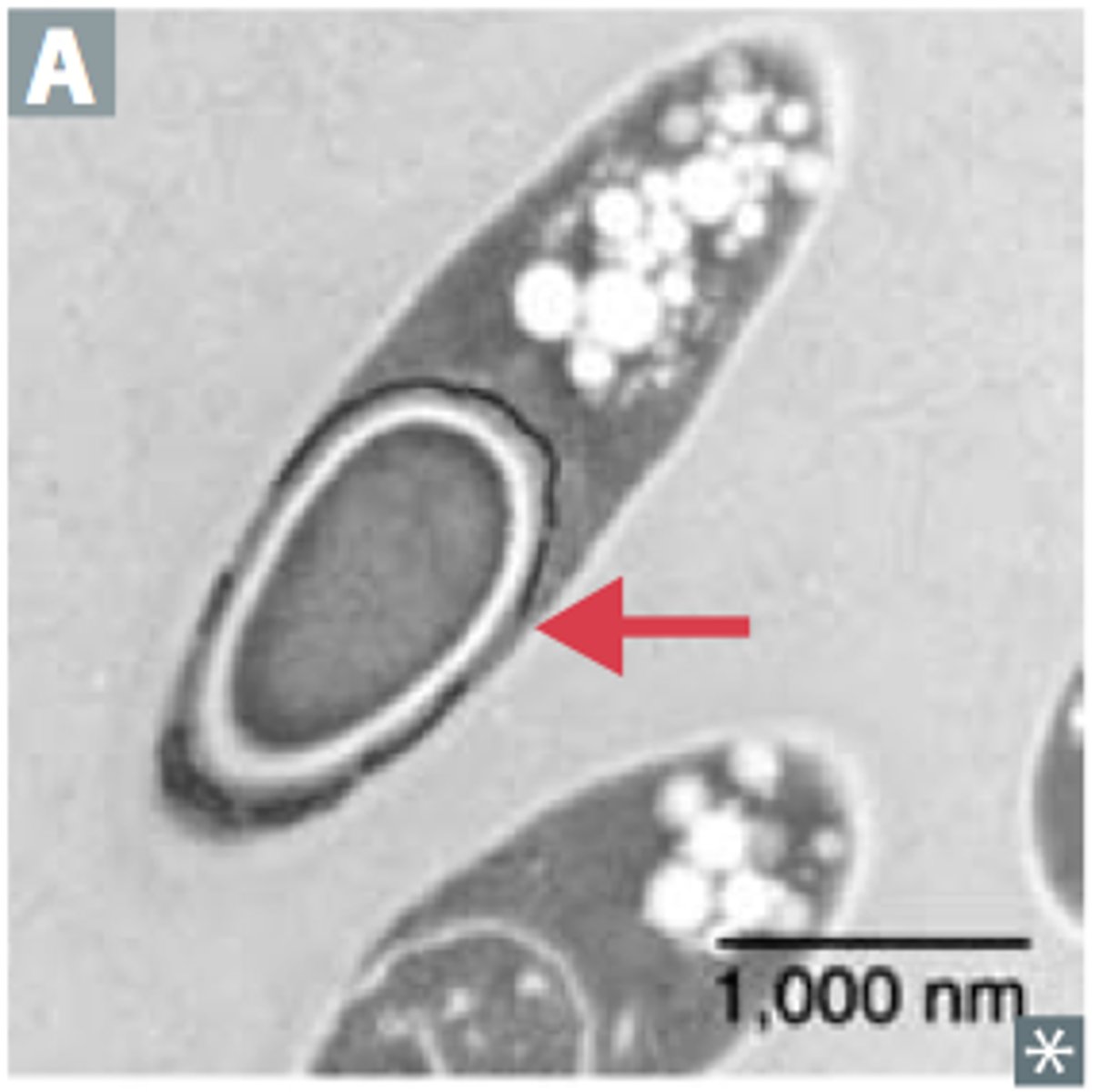
If a spore stain is positive it will look like?
Light green endospore with pink cells
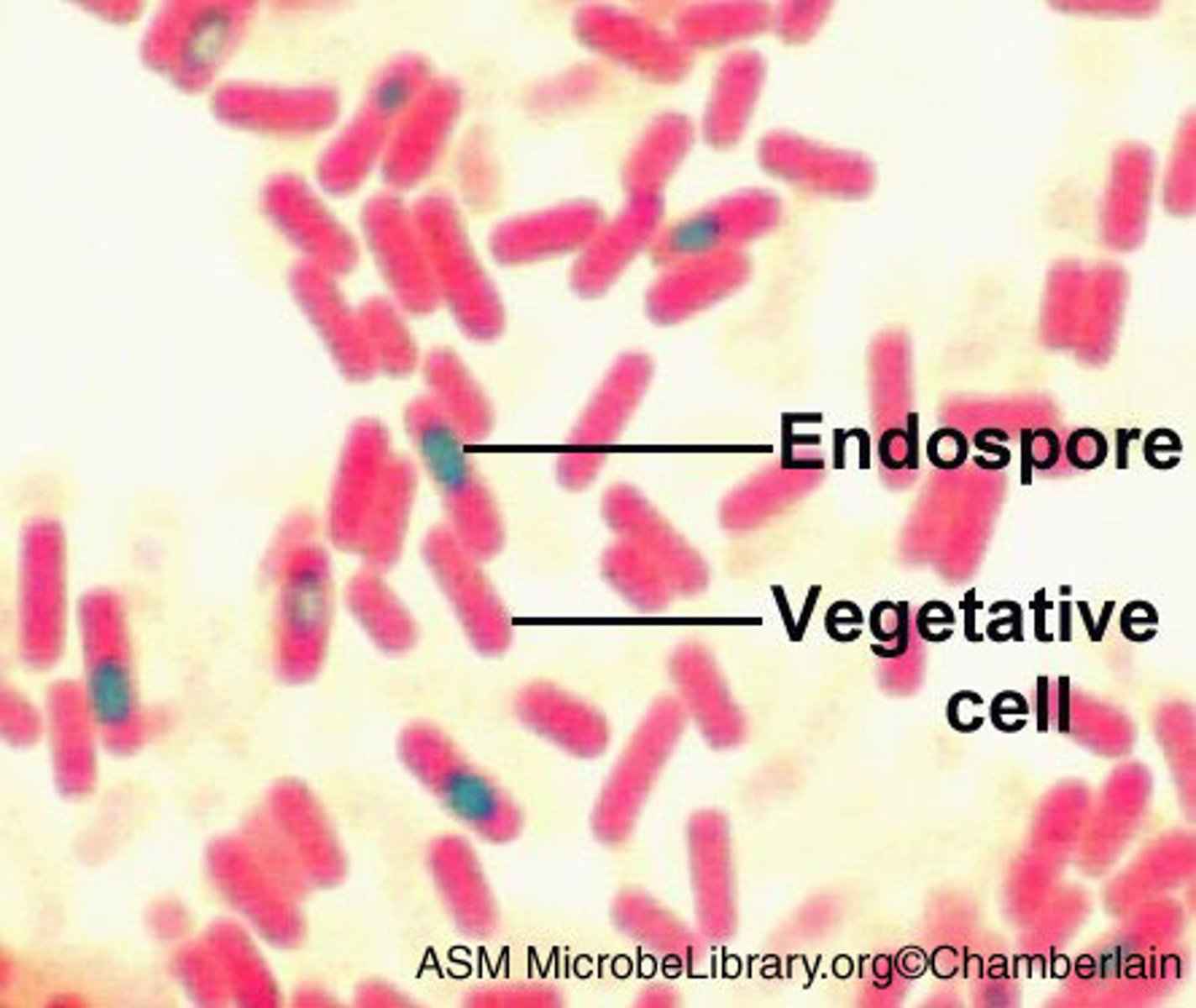
Steps of spore stain
1. Malachite green with heat and steam
2. Rinse (leaves only endospore green)
3. Safranin counter stain (pink)
Clinical significance of spore staining?
- Spore formers may be opputrunistic pathogens
- Spore formers are difficult to kill
- spores can last along time
- spores can be used to identify species
Spore forming bacteria?
Clostridium spp.
What does a fluorescent antibody staining determine?
if a specific antigen is present in a specimen and is often used to screen a specimen for a particular species or strain of known pathogen.
- can screen for Treponema pallidum, bacteria that causes syphilis.
-Positive test will be fluorescent and you will see it.
Flagella stain clinical importance?
-Can be useful in identification of a particular species
-determining if the pathogen is motile
How can you tell if an acid fast stain is positive or negative?
Positive= Bright red or fuchsia
Negative= Blue
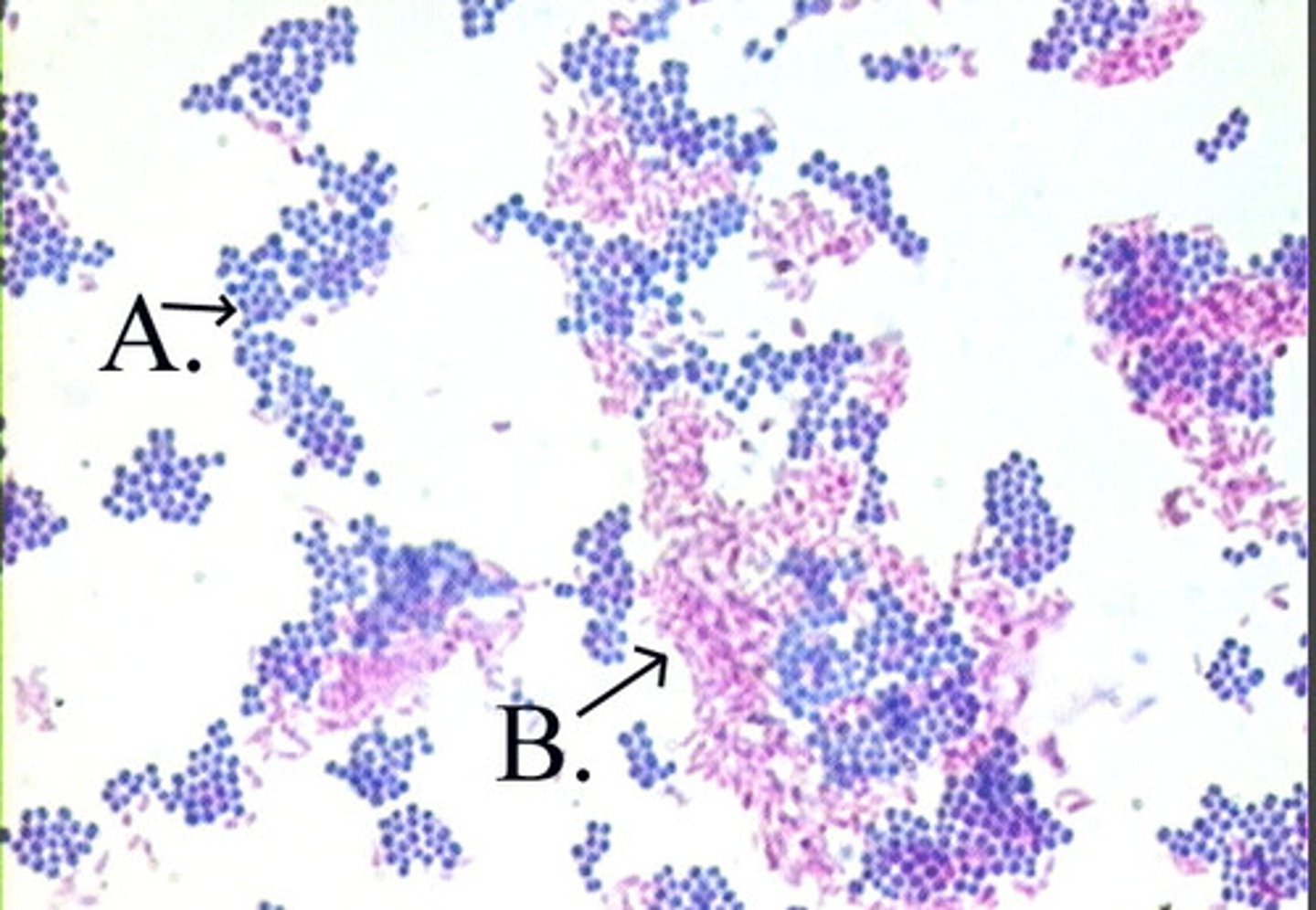
Why are acid fast species difficult to see under normal stains?
Waxy mycolic acid doesn't absorb the stains
Discuss the name of the acid-fast Stain in relation to the procedure.
The term “acid-fast” refers to certain bacteria’s ability to resist decolorization by acid-alcohol after being stained with a strong dye.
“Acid” = the acid-alcohol decolorizing agent.
“Fast” = the cells hold fast (retain) the primary stain even after exposure to acid.
Steps of acid fast stain
1. Primary Stain (carbolfuschsin) (with heat and steam)
2. Decolorizer (alcohol)
3. Counterstain (methylene blue)
Acid fast species with clinical signigicance?
- Mycobacterium sp. (tuberculosis)
-Nocardia sp.
Why is acid fast stain clinically significant?
Can ID for some significant diseases very quickly
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis