WK 12B- Interviews
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Types of interviews
Counseling interview
Employment interview
Exit interview
Grievance interview
Group interview
Informational interview
Interrogation interview
Media interview
Performance review
Persuasive interview
Counseling interview
Held in order to provide information/advice
Information seeking
Ex: course selection, career selection
Employment interview
When you are seeking a career
Exit interview
Takes place after you are leaving a job
Last day, employer wants to get feedback on the company, or just turning in keys
Sometimes formal, sometimes informal
Grievance interview
Involves some type of complain
Addressing complain
Group interview
Panel
More interviewees than interviewers
Common in jobs where companies want you to perform in group settings
Ex: airlines
Board
Being interviewed by a board
More interviews than interviewees
Interviewed by more than one person at the same time
Ex: Senate hearings, issue and CEO of company/head of agency is interviewed by senators at the same time
types of interviews are defined by
the purpose
Informational interview
Not seeking advice but gathering information for your own purposes
Ex: you are deciding which college to go to and you meet with a member of staff/faculty when you visit the college
Interrogation interview
Some types of offence requiring investigation, evidence inquiry, etc.
Ex: you are speeding and police officer pulls you over
Media interview
Some type of interaction in media setting
Ex: reporter at your door, you arrange a virtual interview
Performance review
Indicates how you met the goals in the previous review, setting new goals
Aka annual review, evaluation review
At Rutgers called personnel reviews
Persuasive interview
Fulfill unmet needs
Ex: making a pitch the you deserve a raise
Stages of interview
Opening phase
Question Phase
Closing Phase
Opening phase
First few minutes of interaction
Rapport (handshake, first seeing each other, told to sit down)
Orientation (interviewer provides sense of how interviews take place)
Motivation (where interviewer makes a pitch to make sure they get the most honest answers possible - puts interviewer at ease and also makes sure the interviewer gets info they want)
Question Phase
Preparation is key on both sides
When you hear the question try to figure out what information is being sought. Why are they asking this question?
What information are you going to share?
Anticipate questions and their answers
Closing phase
Summarize major points covered
What was discusses/key takeaways
Make sure all important topics covered
Give interviewee chance to ask questions
the kind they ask is very important to show how much they know/researched about the company
Thank participants for time & cooperation
Include agreement on follow up
Make sure they are clear on nest steps (both sides)
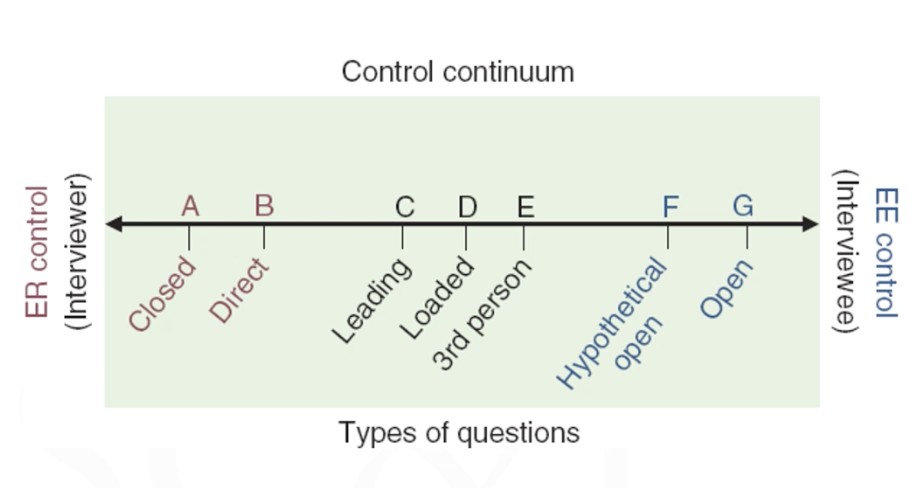
Types of interview questions
Open ended questions
Hypothetical questions
Closed questions
Loaded questions
Leading questions
Third person question
Verbal and nonverbal probes
Open ended questions
Broad, but aimed to get as much information from interviewee as possible
Also Give them a lot of control
Hypothetical questions
What if scenarios to see how interviewee would respond
Direct question
Typically answered with one or two words
Specific and yes or no questions
Closed question
Similar to multiple choice questions
Provides answer choices for you
Limits the answers a bit more
Right answer could be hinted at
Loaded questions
Questions intended to generate an emotional response from interviewee
Leading questions
Imply but don't guarantee correct answer
Gives more control than closed question
Ex: “We are looking for creative people here. What do you have to offer?”
Pitch how you are creative
Third person question
Put a third person in the situation/question to put less pressure on the interviewee
Ex: “What does your group think about the proposal?”
Verbal and Nonverbal probes
Not direct type of questions but used during interview to get convo going
Ex: “Tell me more.” “I see.”
It does matter which questions you pick
Depending on the type of question you ask/are being asked the control shifts from interviewer to interviewee
Type of questions you ask are guided upon how much information you have on individual you are interviewing
To ask a closed question you need to have a lot of info about interviewee
Closed question you don't need to know much about interviewee and can build up
Organizational Structure of the Interview
4 types/ways of organizing interview questions
Funnel Sequence
Inverted Funnel Sequence
Hourglass sequence
Diamond sequence
Funnel Sequence
The interview starts with open ended questions, finishes with a closed sequence
Open to closed
Inverted Funnel Sequence
closed to open
You have a lot of information about interviewee so you can start with closed question
Hourglass sequence
Open closed open
You get an unexpected response from funnel sequence
Have to reopen question after they get unexpected response
Diamond sequence
Closed open closed
When you use inverted sequence and get an unexpected response
Have to start reclosing questions
How to prepare for a successful interview
Prepare Mentally & Physically
Impression management
Interviewer responsibilities
Lawful Questions
Prepare Mentally & Physically
Use impression management techniques
Create a positive impression
Have positive attitude
Dress for the occasion
Impression management
Speak rapidly and forcefully
Look directly at interviewer
Nod head in positive manner
Gesture and smile often
Lean forward, maintain comfortable postures
Use nonverbal code to advantage
Use it to demonstrate confidence (you want to/ are happy to be there)
Interviewer responsibilities
Contact interviewee before interview
Plan the environment
Organize the interview carefully (opening, question/response, closing)
Ask only Lawful Questions
Lawful Questions
All questions must be job related
The same basic questions/premise of question must be asked of all applicants
If not met, question considered illegal
You can ask if a person is considered a US citizen?
Interview challenges
tough/controversial questions
You can try to find what interviewer is trying to gain/what info they want
Could walk out
Arrest/conviction
Different bc arrest doesn't imply conviction
No law where employer can’t ask about arrest and conviction
Should give candidate opportunity to explain