Chapter 13
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Group
two or more freely interacting individuals who share norms, share goals, and have a common identity.
Team
defined as a small group of people working together with a common purpose, performance goals, and mutual accountability
Formal groups
group assigned by organizations or its managers to accomplish specific goals; may be a division, department, work group, committee, task force
Informal group
also called an affinity or employee resource group, is a group formed by people whose overriding purpose is getting together for friendship or a common interest
Types of teams
work, project, cross-functional, self-managed, & virtual
Cross-functional team
designed to include members from different areas within an organization, such as finance, operations, and sales
Self-managed teams
groups of workers who are given administrative oversight for their task domains.
Virtual teams
composed of members in different geographic locations who use technology to work together and achieve common goals
Benefits of virtual team
diversity, reduce travel & expenses, reduce conflict, & increased productivity
Disadvantages of virtual teams
physical & social distance, 24/7 accessibility
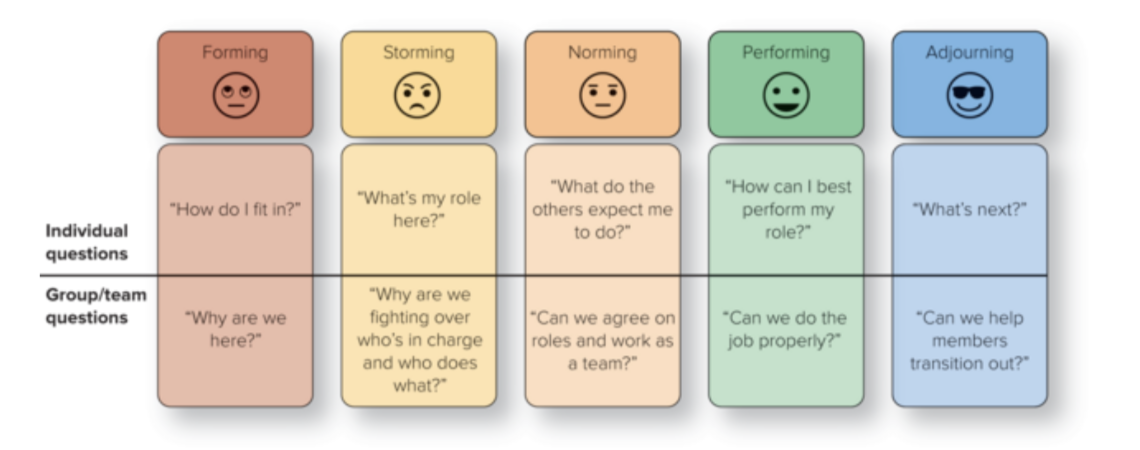
Five stages of group/team development
forming, storming, norming, performing, adjourning
Punctuated equilibrium
establish periods of stable functioning until an event causes a dramatic change in norms, roles, and/or objectives
Essential considerations in building a team
collaboration, trust, goals/feedback, motivation, composition, roles, & norms
Team member interdependence
reveals the extent to which team members rely on common task-related team inputs, such as resources, information, goals, and rewards, and the amount of interpersonal interactions needed to complete the work
Team composition
reflects the collection of jobs, personalities, values, kowledge, experience, and skills of team members
Task roles
initiator, information & opinion seeker/giver, elaborator, coordinator, orienter, evaluator, energizer, procedural technician, & recorder; focuses on work
Maintenance roles
encourager, harmonizer, compromiser, gatekeeper, standard setter, commentator, & follower; focuses on relationships
Conflict
process in which one party perceives that its interests are being opposed or negatively affected by another party
Dysfunctional conflict
conflict that hinders the organization’s performance or threatens its interests
Functional conflict
benefits the main purposes of the organization and serves its interests
Four kinds of conflict
personality, envy, intergroup, & cross-cultural
Programmed conflict
designed to elicit different opinions without inciting people’s personal feelings
Career Readiness for Conflict
teamwork/collaboration, social intelligence, openness to change, emotional intelligence, oral/written communication
Five conflict-handling styles
avoiding, obliging, dominating, compromising, integrating