Muscular System
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Muscular system
is a system of the human body that provides motor power for all movements of the body.
myocytes, or muscle fibers.
Muscular system is composed of specialized cells called
Muscles
are body tissues that provide the force for all body movements.
700
639
There are more than ____ muscles in the body, with ____ known muscles with names.
Movement of the body
Maintenance of posture
Respiration
Production of body heat
Communication
Constriction of organs and vessels
Contraction of the heart
Functions of Muscular System
Skeletal muscles
Constitutes approximately 40% of the body weight. Attached to the skeletal system
voluntary and striated
Skeletal muscles are
involuntary, not striated
Smooth muscles are
Striated, involuntary
Cardiac muscles are
Cardiac Muscle
Located only in the heart
Smooth Muscle
Can be found on visceral hollow organs like the stomach, trachea, and urinary bladder
CONTRACTILITY
Ability of muscle to shorten forcefully or contract.
EXCITABILITY
Ability of muscle to respond to stimulus
EXTENSIBILITY
Muscles can be stretched beyond its normal resting length and still be able to contract
ELASTICITY
Ability of muscles to recoil to its original resting length after it has been stretched
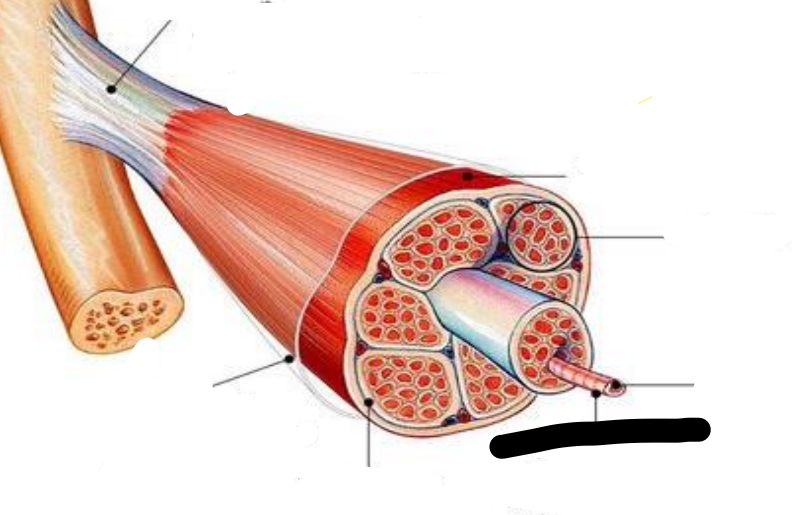
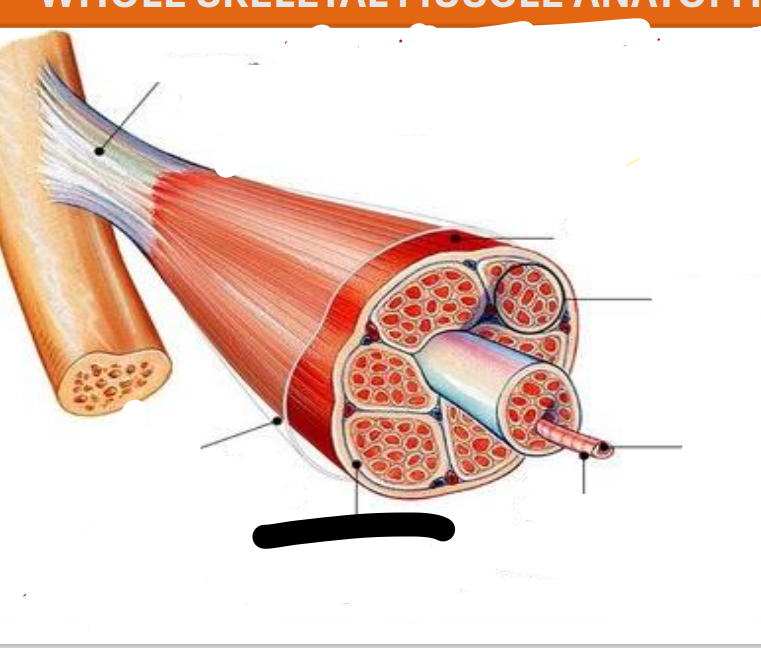
Tendon
attachments between muscle and bone matrix
Epimysium
connective tissue surrounding entire muscle
Perimysium
connective tissue around muscle fascicles
Endomysium
connective tissue around muscle cells
Fascicles
Subdivides each muscle to numerous visible bundles of muscle fibers
muscle fiber (cell)
separates individual muscle fibers within each Fascicles
Tendon
the protein fibers of the three layers merge at the ends of most muscles to from ____
tendon
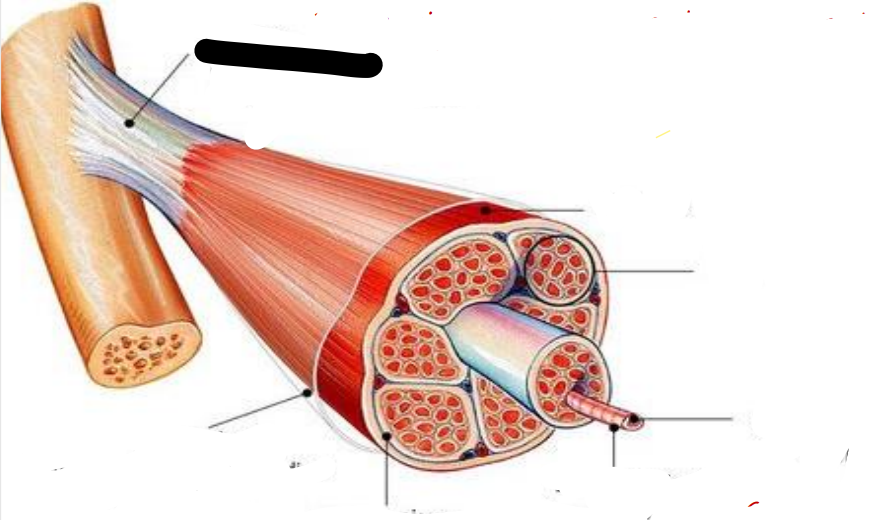
muscle
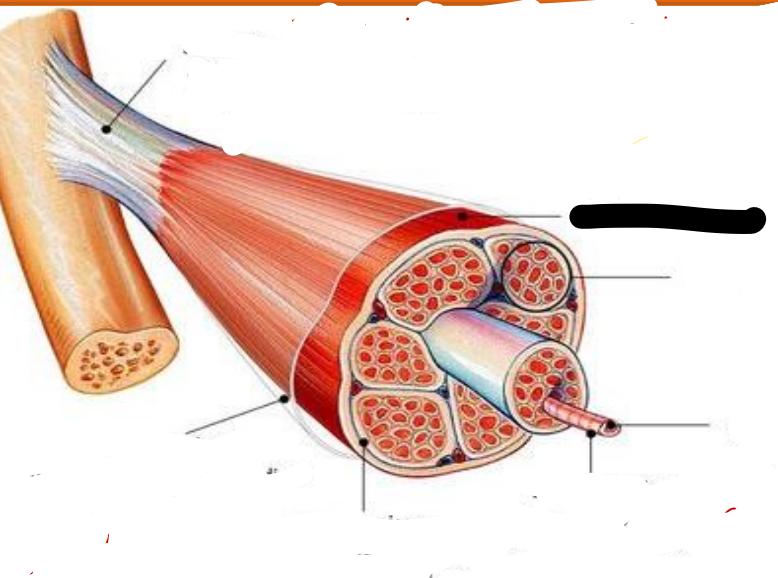
fascicle
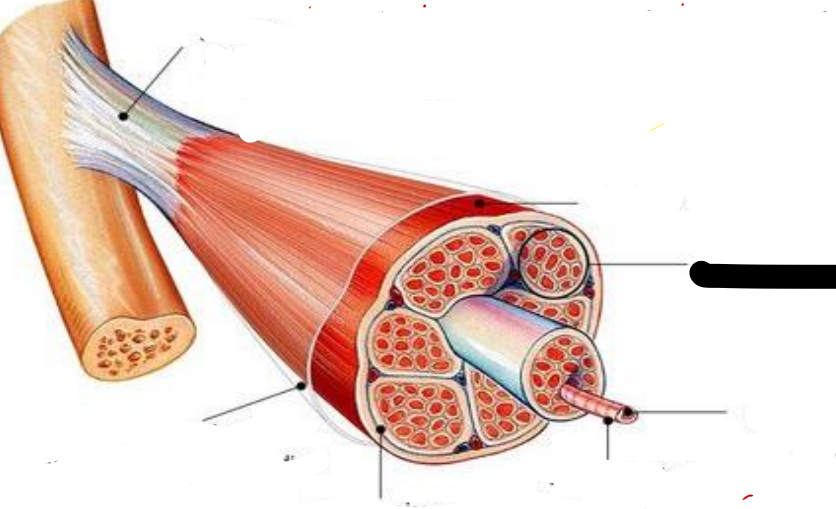
muscle fiber
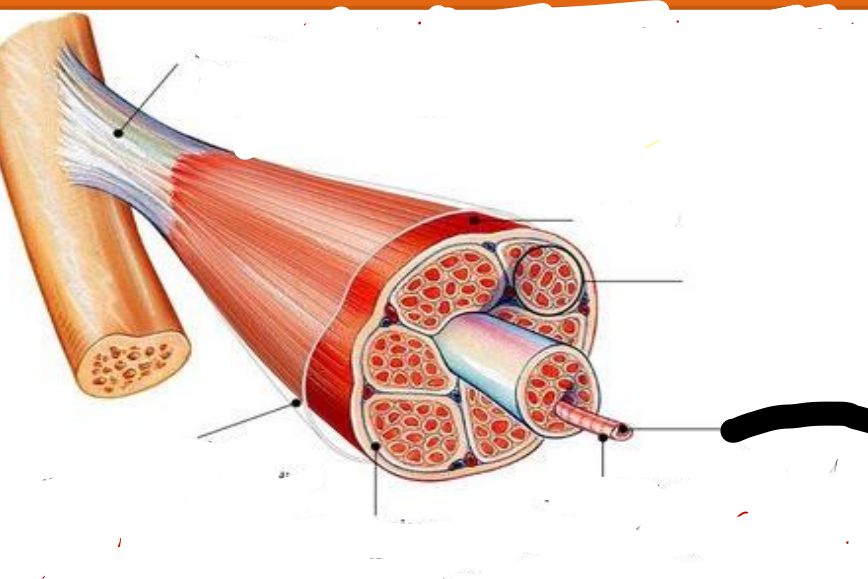
endomysium
perimysium
epimysium
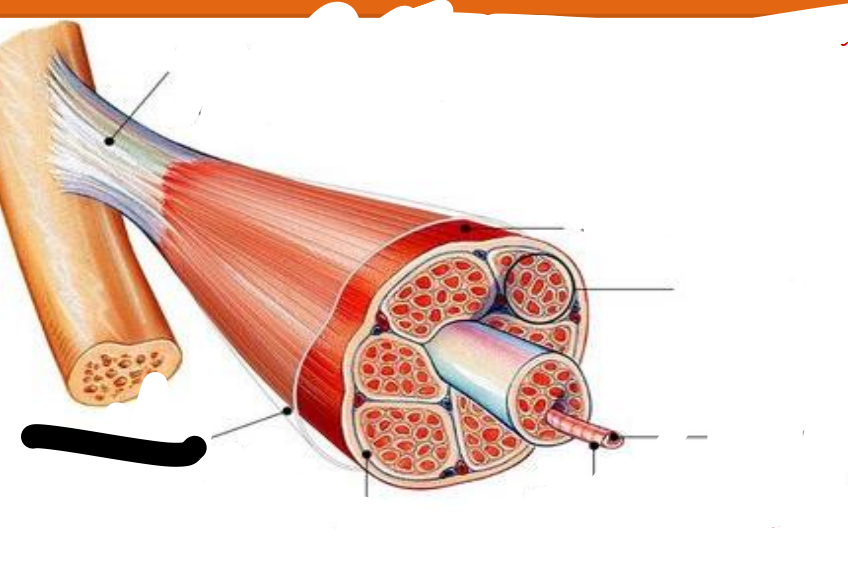
cell membrane
Unique cells with several nuclei just under the
Alternating light and dark bands
gives the striated or stripped appearance
electrical component and mechanical component
main aspect to muscle contraction is
Sarcolemma
cell membrane of the muscle fibers
Transverse Tubules or T tubules
tubelike fold of the sarcolemma.
Transverse Tubules or T tubules
carry electrical impulses into the center of muscle fiber so that the muscle fiber contracts as a whole
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
a highly specialized ER that stores high level of Ca2
T Tubules
1
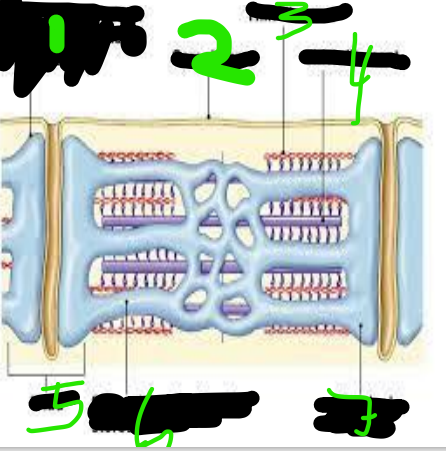
Sarcolemma
2
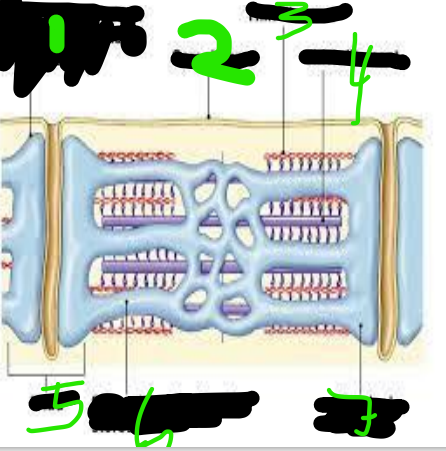
Thin Filament
3
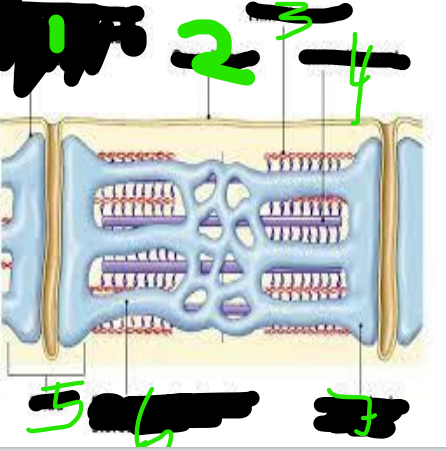
Thick Filament
4
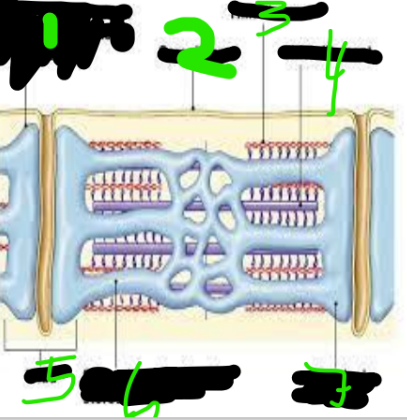
triad
5
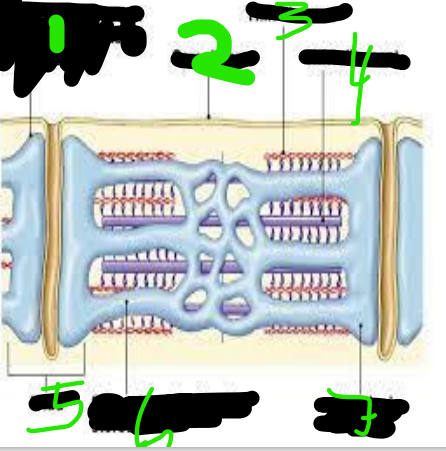
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
6
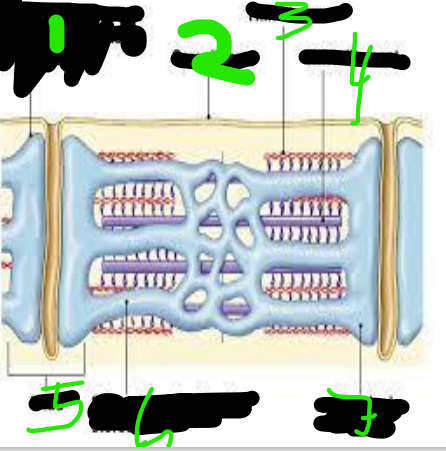
Terminal Cisterna
7
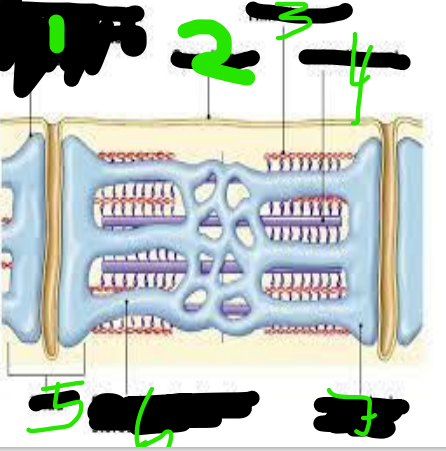
Myofibrils
threadlike structures that extend the entire length of the muscle fiber.
actin and myosin
2 types of myofilaments
sarcomeres
They are arranged into highly ordered units called
Myofilaments
are the contractile proteins in the myofibers that are arranged into groups that cause the cytoplasm to appear repetitively banded (or striated
Terminal Cisterna
expanded form of t tubules
sarcomeres
functional unit of the skeletal muscles
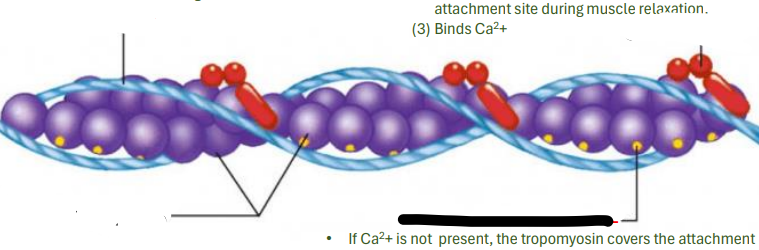
ACTIN MYOFILAMENT
It is the relationship among the troponin and Tropomyosin that determines when the skeletal muscle will contract
tropomyosin
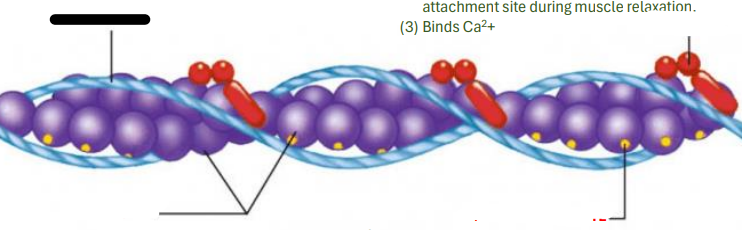
troponin
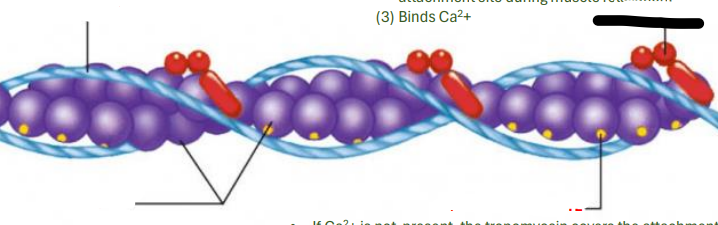
actin
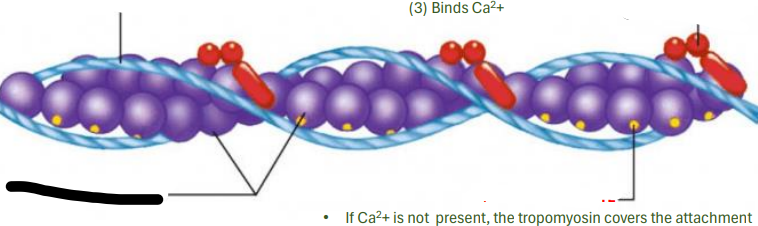
attachment site
MYOSIN MYOFILAMEN
Composed of many elongated myosin molecules shaped like a golf clubs.
Myosin molecules
consist of rod portion and two myosin heads
myosin heads
binds to the active sites of actin molecules to form cross bridges to contract the muscles
myosin heads
Head binds to the rod portion by a hinge region that bends and straightens during contraction
myosin heads
Breaks down ATP
SARCOMERES
Smallest portion of muscle that can contract
actin myofilament
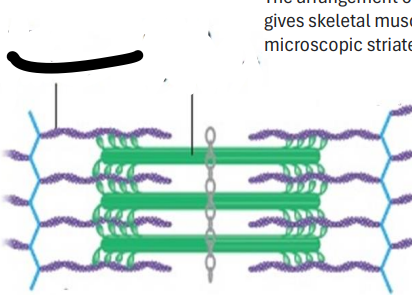
myosin myofilament
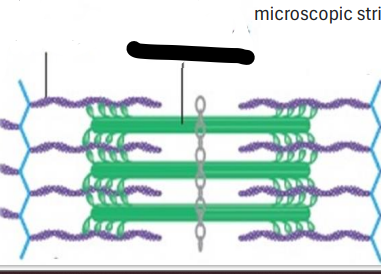
precise boundary.
Each sarcomere has a
Z disk to the next Z disk
Each sarcomere extends from
A BAND
Darker region ; contains both actin and myosin myofilament overlapping center except in the center
H ZONE
Contains only myosin myofilament
M LINE
hold myosin filaments in place
Z DISK
Forms a stationary anchor for actin myofilaments
I BAND
Lighter region; contains only actin myofilament
slide past one another and shorten the sarcomere.
When muscle fiber contracts the actin and myosin myofilaments in a sarcomere
SARCOMERE
The ends of actin are pulled to and overlap at the center of the
RELAXED SARCOMERE
VISIBLE
_____ The actin and myosin myofilaments overlaps slightly, and the H zone is ____
CONTRACTED SARCOMERE
ACTIN
SARCOMERE
NO LONGER VISIBLE
_____ The A band which is the same length of myosin filament does not change. The ends of____ are pulled to and overlap at the center of the _____. The H zone is ______
EXCITABILITY OF MUSCLE FIBER
Action potentials travel from brain to spinal cord to along the axons to muscle fibers and cause them to contract.
muscle fiber
is in contact with a branch of a motor neuron axon from the brain or spinal cord
acetylcholine
The primary stimulus for this action potential is the release of ______ from the motor neuron
YES
Do muscles have electrical Properties?
ION CHANNELS
contribute to the electrical properties of both resting cell and stimulated cell
Leak
Specific for a particular ions
RESTING CELLS
in ______the leak ion channels allow for the slow leak of ions down their concentration gradient.
GATED
Most important in stimulated cell, and it governs the production of action potential
RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL
The charge difference in unstimulated/relaxed cells. (NEGATIVE)
(1)higher concentration of K+ inside; (2)Higher concentration of Na+ outside; (3)the cell membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na
RESTING MEMBRANE 3 FACTORS
ACTION POTENTIAL
The charge difference of stimulated/ excitable cell. (POSITIVE)
STIMULATED
IN ACTION POTENTIAL This charge reversal occurs because ion channels open when a cell is
Acetylcholinesterase
Muscles stop contracting When motor neuron end release the enzyme _______ that rapidly breakdown Acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft to choline and acetic acid.
ISOMETRIC CONTRACTIONS
Muscle do not shorten
ISOMETRIC CONTRACTIONS
increases tension in the muscle, but the length of the muscle stays the same
ISOTONIC CONTRACTIONS
Muscles shorten
ISOTONIC CONTRACTIONS
decreases the length of the muscle.
Concentric
Results in increase in tension as the muscles shortens
Eccentric
Tension is maintained in a muscle but opposing resistance is great enough to cause muscle to increase in length
circular
fascicles arranged in a circle around an opening
circular
act as sphincters to close the opening
convergent
broadly distributed fascicles converge at a singe tendon
parallel
fascicles lie parallel to one another and to the long axis of the muscle
pennate
fascicles originate from a tendon that runs the length of the entire muscle
unipennate
fascicles on only one side of the tendon
bipennate
fascicles on both sides of the tendon
multipennate
fascicles arranged at many places around the central tendon