Exam 1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Anatomy
The study of an organisms structure or morphology
Physiology
the study of body function
Exercise Physiology
the study of how the body’s functions are altered when we are physically active (since exercise presents a challenge to homeostasis)
Sports Physiology
The branch of physiology that examines the body’s responses and adaptations to sports and exercise, focusing on performance enhancement and recovery.
(further applies the concepts of exercise physiology to enhancing sport performance and optimally training athletes)
Contribution of DB Dill
Helped write the 3rd edition the book The Physiology of Muscular Activity
Nobel Prize finding on energy metabolism
Conducted some of the first studies on runners
understanding of whole body energy production
Oxygen uptake
Book Life, Heat, and Altitude
Affect of altitude on performace
Contribution of Harvard Fatigue Lab
Established the field
How the environment affects physical performance
VO2 max and aging
endurance physiology
Measure O2 consumption and CO2 output
Integrated systems to study whole body response to stress
Acute effects of exercise
Individual bout of exercise
immediate response to, and sometimes its recovery from, a single exercise bout
includes changes in heart rate, breathing, and energy expenditure.
Chronic effects of exercise
regular exercise over a period of days and weeks, the body adapts
improve both exercise capacity and efficiency
results in adaptations such as increased strength, endurance, and overall fitness.
Ergometers (What are they? Different types, Uses)
Ergo: Work Meter: Measure
A device used to measure physical work output during exercise, commonly used in clinical and research settings for assessing cardiovascular and respiratory responses. An exercise device that allows the intensity of exercise to be controlled (standardized) and measured.
Types:
Treadmills: walking and running
Cycle ergometers: pedal in an upright (normal) or reclined position
Arm ergometers: exercise while seated using arm movement (paralyzed leg down)
Tethered swimming: measures power output while swimming in a controlled environment.
Swimming flume: a water channel that allows for controlled swimming conditions and effective measurement of swimming performance.
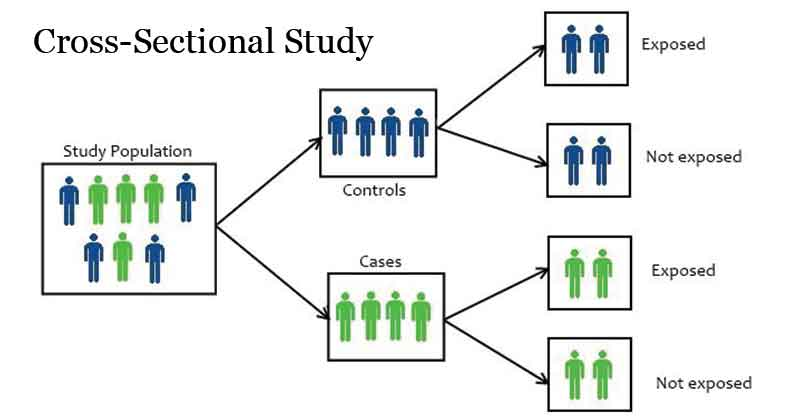
Cross-sectional study (advantage)
a cross section of the population of interest (i.e., a representative sample) is tested at one specific time, and the differences between subgroups from that sample are compared.
Allows for quick data collection from a large population, facilitating the examination of relationships between variables at a specific point in time without requiring long-term follow-up. Provides insights into prevalence and associations of health outcomes.
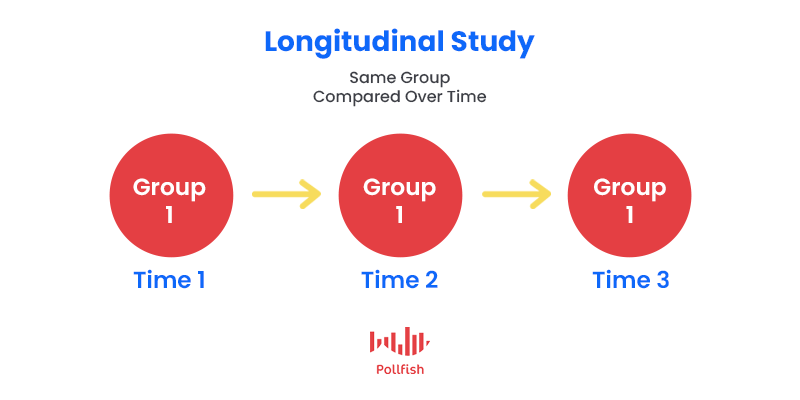
Longitudinal study (advantage)
the same research subjects are retested one or more times after initial testing to measure changes over time in variables of interest.
Involves repeated observations of the same variables over time, which allows researchers to detect changes and developments in the subjects or variables. Useful for studying trends and long-term effects.
Skeletal muscle
The type of striated muscle tissue that is primarily responsible for voluntary movements of the body.
It is attached to bones by tendons and is characterized by a striped appearance under a microscope.
Over 600 in the body
Voluntary/ consciously controlled
Motor neuron tells muscle to contract via transmitters
somatic nervous system
Sarcoplasmic R. release Ca
Smooth muscle
Involuntary, unconscious control
Walls of blood vessels and internal organs
not striated
Cardiac muscle
Striated
Controls itself (assistence autonomic nervous system and endocrine system)
ONLY IN THE HEART
Structural arrangement of muscle tissues
Connective tissue layers, epi-, peri-, & endo-mysium
Fascicles, fibers, myofibrils
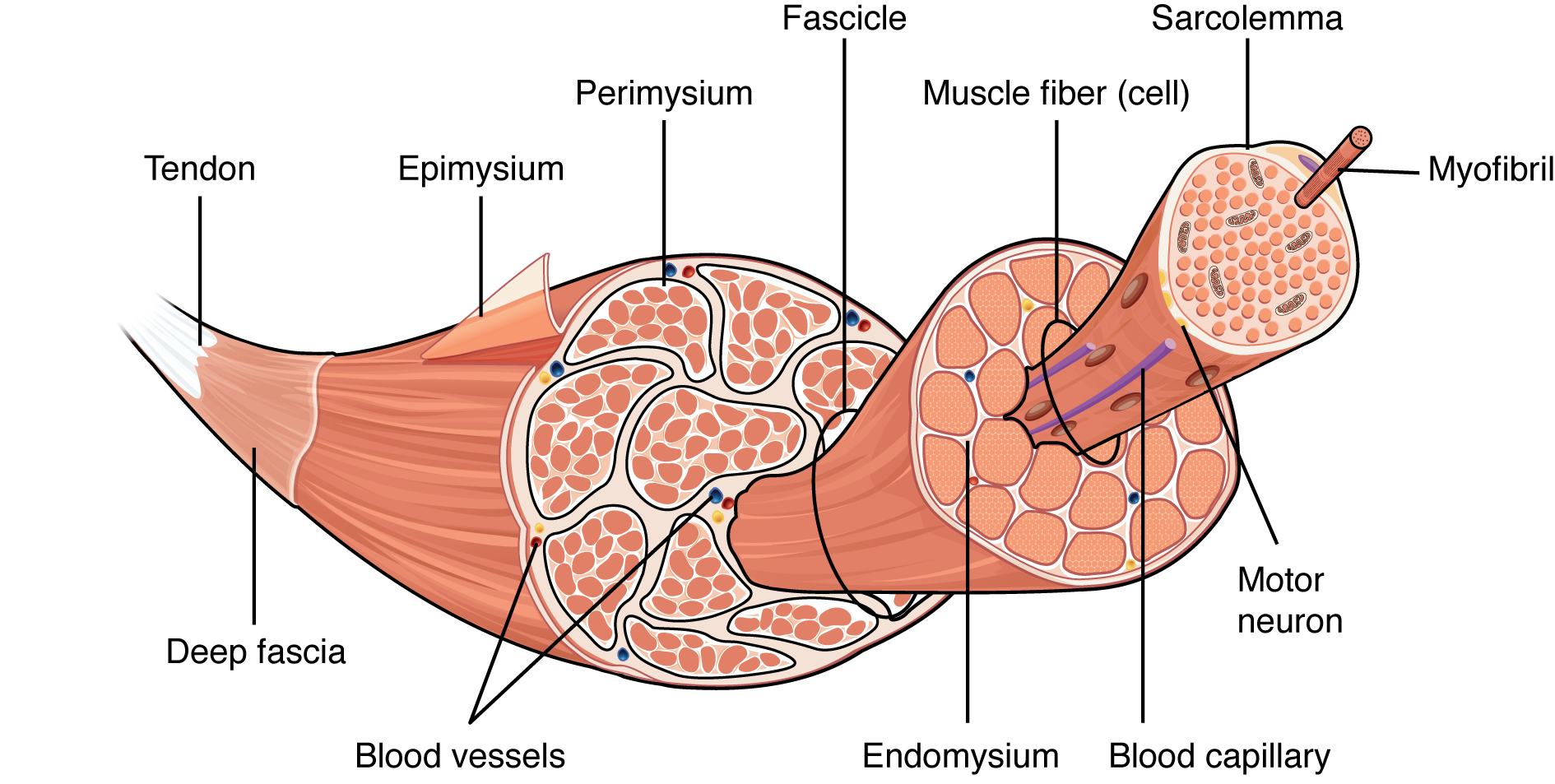
Muscle fiber structure
Sarcolemma
Muscle membrane (encloses the muscle)
T-tubule
Transports sub. through muscle fiber
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Stores calcium (need to contact)
Actin and myosin filaments
Myofibrils are structural units
Sarco = muscle (flesh)
Myo = muscle
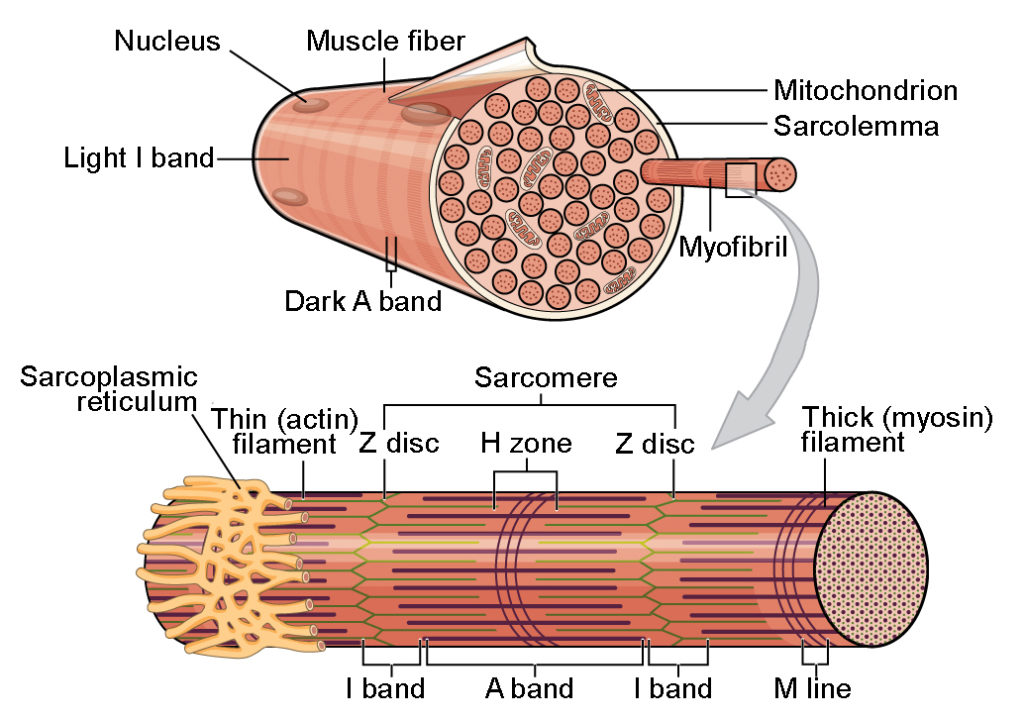
Myofibrils
(allow muscle to contract) (muscle → fasciculi → muscle fiber → myofibril)
Actin & myosin
Activation allow for movement
Sarcomere
Smallest unit of a muscle
Z disks
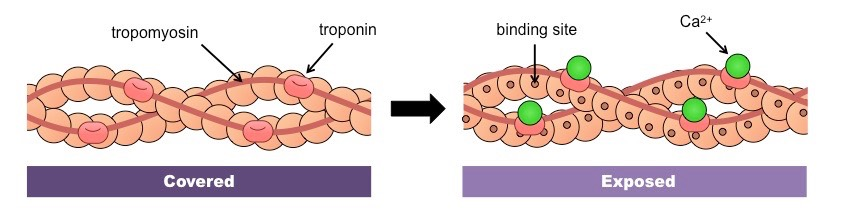
Troponin
Tropomyosin
Actin filament
Actin
Myosin
2 actin per myosin
Thick filament with globular head
Tropomyosin
Tropnin
Attached to z disk
z disk → z disk = sarcomere
Titin
Stablize actin filament
“winding firmament”
allows the fiber to twist (rotates actin)
increases force produced
reduces risk of muscle damage
What leads to muscle fiber action?
1) motor neuron release acetylcholine (ACh)
2) ACh binds to receptors on the sarcolemma.
3) initiates an action potential
4) action potential travels to the SR releasing Ca2+
5) Ca2+ binds to troponin on the actin filament, and the
troponin pulls tropomyosin off the active sites, allowing
myosin heads to attach to the actin filament.
Need Ca for muscle contraction
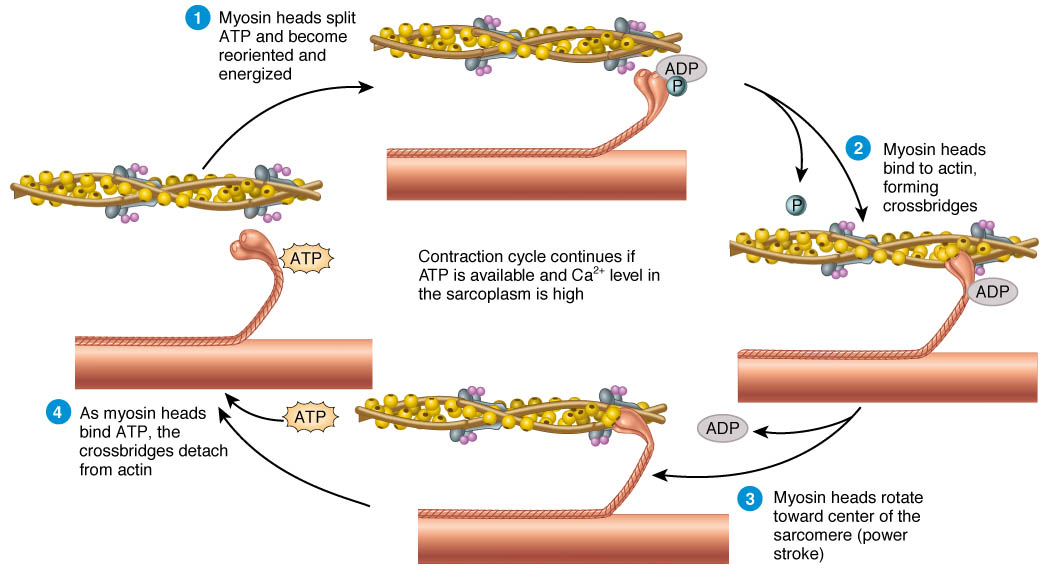
Sliding filament theory of muscle contraction (Steps involved from action potential propagation along sarcolemma to power stroke to re-uptake of calcium in SR)
The sliding filament theory describes how muscle contraction occurs through the interaction of actin and myosin filaments within the sarcomere. When activated by an action potential, calcium is released, allowing myosin heads to bind to actin, leading to a power stroke that shortens the muscle fiber.
Myosin head moves to the actin actin
movement of myosin = power stroke = contraction
After contraction, calcium is reabsorbed into the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), allowing muscle relaxation.
Myosin cross bridge: the myosin head is tightly bound to actin without ATP.
Rigor state: Myosin binds to actin without a conformational change, leading to rigidity.
ATP binds to myosin and causes the myosin head to detach from actin, allowing the cycle to repeat and muscle to relax.
Calcium: allows actin and myosin to “meet”
ATPase: enzyme that hydrolyzes ATP, providing energy for the myosin head to detach and re-cock during muscle contraction. (ADP + P) Free energy used to change myosin head (tlit)
Need for muscle contraction
ATP
Fuel for the power stroke
Ca
controls actin and myosin interaction (meet or not)
magnesium
How are muscle fibers distinguished?
ATPase activity
Motor unit differences
Contraction speed
Effects of genes, aging & training on fiber type
Size principle of motor unit recruitment & relation to fiber type
Muscle actions
Factors that affect muscle force production