Ch 21- Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy on Aggregate Demand
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
fiscal policy
levels of gov spending & taxation set by the President and Congress
monetary policy
MONEY SUPPLY set by central bank; made by the FED
OMOs
open-market operations; purchase and sale of US GOVT BONDS
to DECREASE the MS and RAISE the fed funds rate…
Fed SELLS govt bonds
to INCREASE the MS and LOWER the fed funds rate…
Fed BUYS govt bonds
the theory of liquidity preference
interest rate (denoted r) adjusts to bring MS and MD into balance
MS
fixed by the central bank, does not depend on IR
MD
reflects how much wealth people want to hold in liquid form
a household’s money demand reflects its preference for liquidity
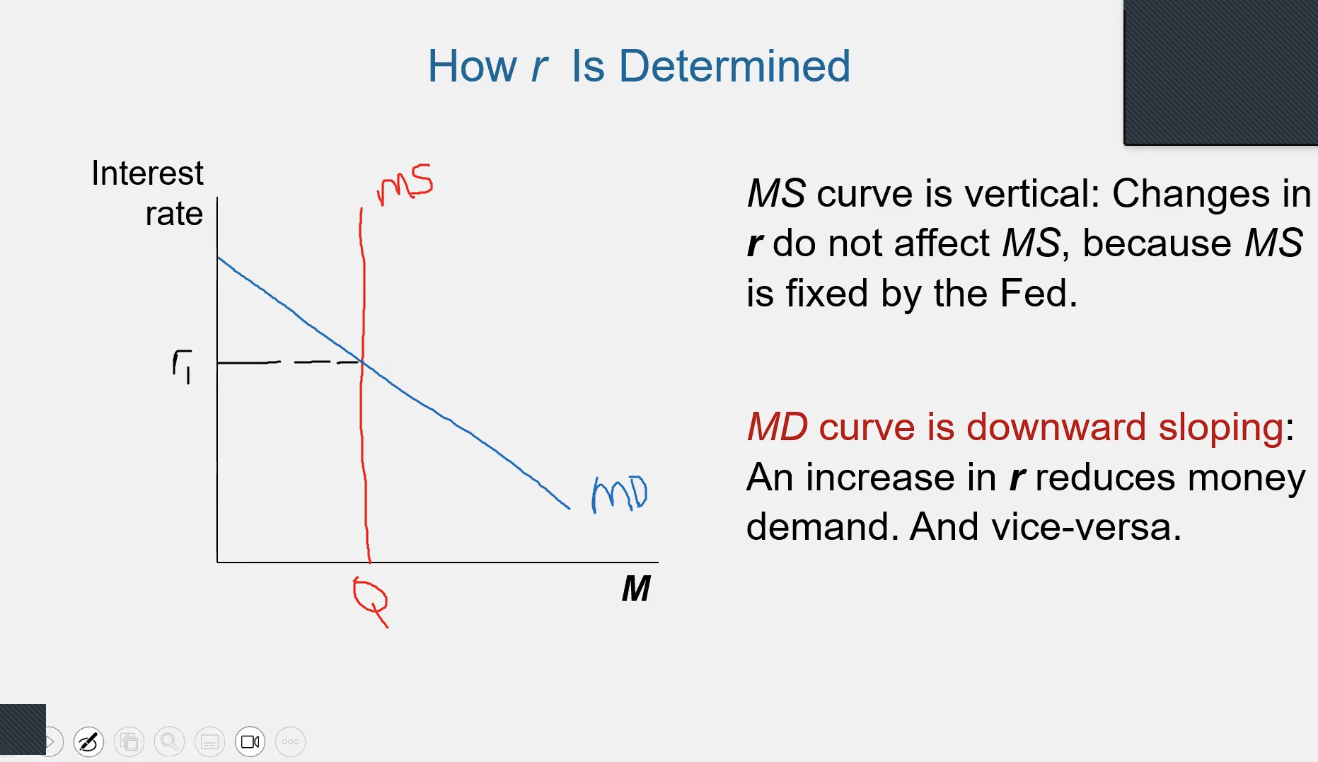
an increase in r (interest rate) _____ money demand (MD)
reduces
variables that influence money demand
Y (real income), r, and P
an increase in Y (real income) causes…
an increase in Money Demand
liquidity trap
if interest rates have fallen to around zero, monetary policy is no longer effective
forward guidance
raise inflation expectations by committing to keep interest rates low
quantitative easing
buy a larger variety of financial instruments
expansionary fiscal policy
an increase in G and/or decrease in T shifts AD right
contractionary fiscal policy
a decrease in G and/or increase in T shifts AD left

multiplier effect
additional shifts in AD result when fiscal policy increases income and increases consumer spending
AD = national income
GDP = C + I + G + NX
marginal propensity to consume (MPC) equation
delta C/delta Y
C= consumption, Y= income
fraction of extra income households consume vs save
I and NX are
fixed
spending multipler
1/1-MPC
Aggregate demand focuses on…
spending in the economy as a whole.
Money demand focuses on
preferences for holding money rather than spending it.
automatic stabilizers
changes in fiscal policy that stimulate aggregate demand (spending) when economy goes into recession
ex: tax falling, public assistance (welfare, unemployment insurance)