Common iliac artery, inferior vena cava, main lymphatic ducts
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what is the course of the abdominal aorta?
Begins at the level of the aortic hiatus (T12) as the continuation of the thoracic aorta
Descends in front of the vertebral column, on the left of the inferior vena cava (IVC)
Bifurcates into the common iliac arteries at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra
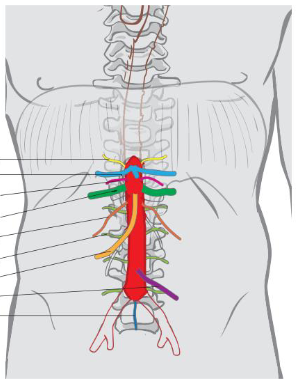
what is the common iliac artery?
paired continuation of the abdominal aorta from its bifurcation at level l4
Passes on the medial surface of the psoas major
• Divides into the external and internal iliac arteries at the level of the sacroiliac joint.
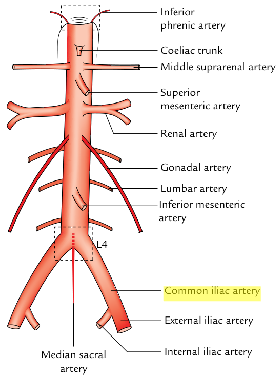
what does the common iliac artery supply?
supplies the pelvis and lower extremities
what are the two branches of the right common iliac artery?
internal and external iliac artery
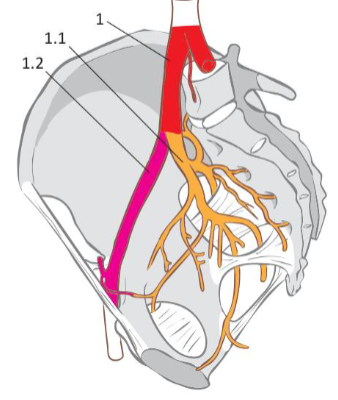
where is the internal iliac artery located?
medial branch of the common iliac artery
passes across the sacroiliac joint to the lesser pelvis and supplies both the pelvic wall and
organs
where is the external iliac artery located?
passes medially to the psoas major and through the vascular space
– continues as the femoral artery and continues to the lower extremity which it supplies
what are the 5 parietal branches of the internal iliac artery?
Iliolumbar artery
2. Lateral sacral arteries
3. Obturator artery
4. Superior gluteal artery
5. Inferior gluteal artery
what does the iliolumbar artery supply?
supplies the iliopsoas, quadratus lumborum, ilium, and vertebral column including the cauda equina
what does the lateral sacral artery supply?
two branches (each then bifurcate) supply the sacrum, cauda equina, and adjacent muscles of the back
what does the obturator artery supply?
supplies the muscles of the medial femoral group, sacroiliac joint
what does the superior gluteal artery supply?
supplies the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus
what does the inferior gluteal artery supply?
supplies the gluteus maximus, tensor fasciae latae, as well as some skin over the sacrum.
what does the visceral branches supply in the internal iliac artery?
supply the perineum and the organs within the lesser pelvis except for the rectal ampulla and part of the ovary and uterine tube
what is the umbilical artery?
main fetal artery carrying deoxygenatedblood from fetus to the placenta (after delivery obliterates →lateral umbilical ligament)
what are the superior vesical arteries?
arise from the umbilical artery and supply the superior part of the urinary bladder, part of the ureter and the urethra
what is the inferior vesical artery in male and females?
supplies the fundus of the urinary bladder
– in female, it participates in the blood supply of the vagina,
– in male supplies the prostate and seminal glands
what is the middle rectal artery in males and females?
supplies the levator ani
– in female, participates in the blood supply of the vagina,
– in male supply the prostate and seminal glands
what is the artery to ductus defernes in males?
supplies the ductus deferens, prostate, seminal glands, and part of the ureter
what is the uterine artery in females and its branches?
Uterine artery – supplies the uterus, part of the vagina, uterine tube, ovary, and ureter
Ureteric branch – arises where the uterine artery crosses the ureter
Uterine branches – travel to the uterine wall
Vaginal branches – travel to the vaginal fornices
Tubal branch – supply part of the uterine tube
Ovarian branch – forms the ovarian arcade with the ovarian artery.
what is the internal pudenal artery and its branches?
arterial trunk supplying blood to all of perineal structures inferior to the pelvic diaphragm
Inferior rectal artery – supplies the anal canal and anus
Perineal artery – runs forward along the perineum
Posterior scrotal/labial branches – supply the posterior part of the scrotum / labia majora
Dorsal artery of penis/clitoris
Deep artery of penis/clitoris
Urethral artery– in male, heads to the corpus spongiosum penis
Artery of bulb of penis/vestibule – supplies the bulb of the penis / vestibule of the vagina and bulb of the vestibule
what does the external iliac artery supply?
majority of the lower extremity,
anterior and lateral muscles of the abdominal wall,
• part of the wall of the greater pelvis
• part of the scrotum in males
• broad ligament of the uterus in females
what is the inferior epigastric artery?
ascends along the posterior surface of the anteriorabdominal wall inside the lateral umbilical fold
what are the three branches of the inferior epigastric artery?
Pubic branch – runs to the pubic symphysis
Cremasteric artery – in males, supplies the cremaster and spermatic cord
Artery of round ligament of uterus– in females –to the round ligament of the uterus
what is the deep circumflex iliac artery?
passes on the inner surface of the inferior margin of the anterior abdominal wall and travels to the anterior superior iliac spine
Contribute to the blood supply of the muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall the iliac crest and the skin overlying the anterior superior iliac spine.
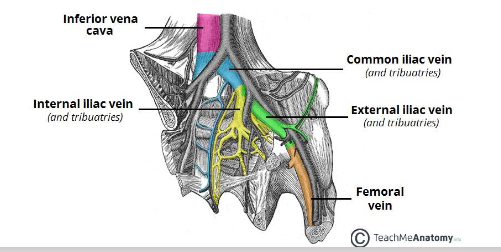
what are the iliac veins?
Veins of the pelvis drain deoxygenated blood and return it to the heart
what are the three major vessels involved in venous drainage of the pelvis?
external iliac vein, internal iliac vein and common iliac vein (these correspond the major pelvic arteries).
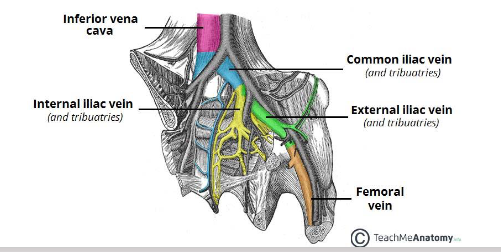
what to veins combine to become the inferior vena cava?
• Left and right common iliac veins combine at L4-L5 to become the inferior vena cava,
which empties into the inferior aspect of the right atrium
what is the inferior vena cava?
Largest vein in the human body.
Collects blood from the inferior half of the body and possesses no valves.
Arises from the junction of the right and left common iliac veins at the level of L4–L5.
Has both parietal and visceral tributaries
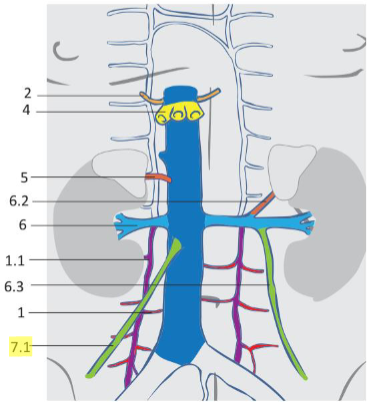
what are the branches of the inferior vena cava?
Lumbar veins
1.1 Ascending lumbar vein
2. Inferior phrenic veins
3. External vertebral venous plexuses
4. Hepatic veins
5. Right suprarenal vein
6. Renal veins
6.1 Capsular veins
6.2 Left suprarenal vein
6.3 Left testicular/ovarian vein
7. Testicular vein
7.1 Right testicular vein
7. Ovarian vein
7.1 Right ovarian vein
what causes edema of the ankle and feet during pregnancy?
IVC is commonly compressed by an enlarged uterus during the last trimester of the pregnancy
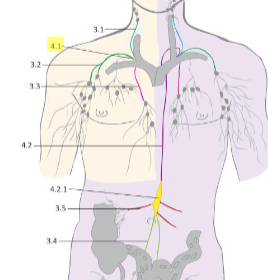
what is the role of the right lymphatic duct?
a short duct originating from the 3 main lymphatic trunks:
right jugular, right subclavian and right bronchomediastinal trunks
– collects lymph from: right half of the head and neck, right upper extremity and right half of the thoracic cavity
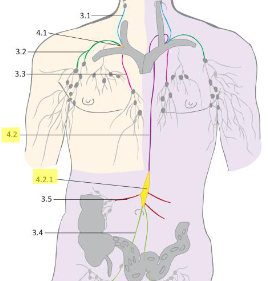
what is the thoracic duct?
originates from the lumbar trunks
– collects lymph from:
both lower extremities, pelvis, abdominal cavity, left half of the thoracic cavity, left upper extremity and the left half of the head and neck
divided into 4 parts according to its course: lumbar, abdominal, thoracic and cervical parts
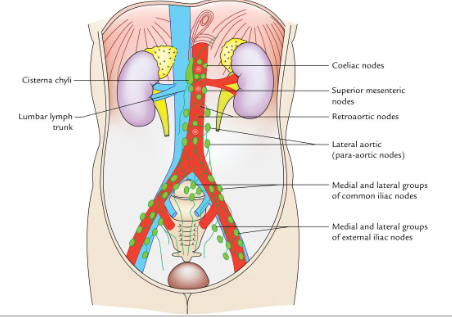
what is the lymphatic drainage of the posterior abdominal wall?
terminate in the cisterna chyli and thoracic duct.
tThe lymphatic stream is intercepted by a series of lymph node groups before reaching the cisterna chyli and the thoracic duc
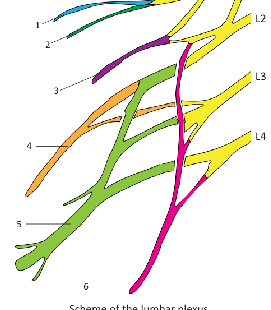
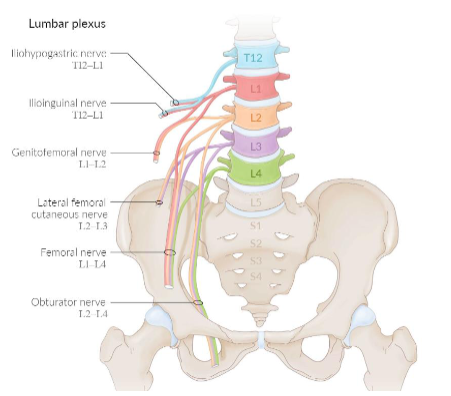
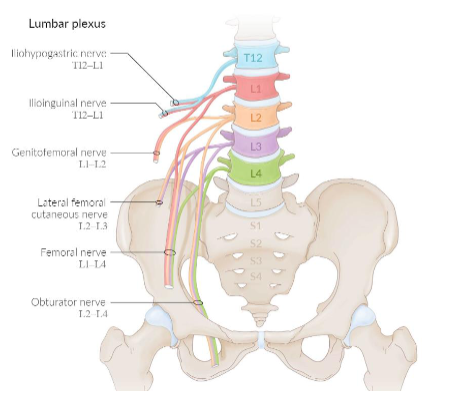
what are the 6 lumbar plexus nerves?
Iliohypogastric nerve
2. Ilioinguinal nerve
3. Genitofemoral nerve
4. Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh
5. Femoral nerve
6. Obturator nerve
what is the motor innervation of the lumbar plexus?
Lower abdominal muscles: external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis
Pelvic muscles: Iliacus, pectineus, cremaster
Muscles of the anterior and medial compartments of the thigh
what is the sensory innervation of the lumbar plexus?
Lower abdomen
• Lateral gluteal region
• External genitalia
• Thigh
• Medial aspect of the leg
what is the iliohypogastric nerve?
T12–L1
– emerges laterally from the psoas major
– passes between the internal oblique and the transversus abdominis
– runs above the iliac crest travelling ventrocaudally
– terminates in the hypogastric and inguinal regions
what are the three branches of the iliohypogastric nerve?
Muscular branches– motor branches for the internal oblique and transversus abdominis
1.2 Lateral cutaneous branch – somatosensory innervation of the skin of the lateral
abdomen
1.3 Anterior cutaneous branch – innervates the skin around the superficial inguinal ring.
what is the ilioinguinal nerve?
l1
emerges laterally from the psoas major and continues below the iliohypogastric nerve
– travels through the inguinal canal
– innervates skin of the anterior part of the scrotum (in men) and skin on the anterior part of the labia majora (in women).
what is the genitofemoral nerve and its two branches?
L2–L3 – penetrates the psoas major and leaves it on its ventral surface
Genital branch – passes through the inguinal canal
– innervates the cremaster, dartos fascia and a small area on the medial side of the thigh (in men)
– innervates part of the labia majora and a small area on the medial side of the thigh (in women)
Femoral branch – passes through the vascular space
– innervates the skin of the medial side of the thigh.
what is the lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh?
L2–L3
– emerges laterally from the psoas major
– runs laterocaudally on the iliacus towards the anterior superior iliac spine
– provides somatosensory innervation for the lateral thigh
what is meralgia paresthetica?
results from compression of the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh in the muscular space.
SYMPTOMS: acute intermittent pain and loss of sensation on lateral thigh above the knee.
It is common in obese and diabetic patients
what is the course of the femoral nerve?
L2–L4
Course: emerges laterally from the psoas major, travels above the iliopsoas, passes medially through the muscular space to reach the anterior thigh and femoral triangle, then splits into muscular and cutaneous branches
what are the branches of the femoral nerve?
Muscular branches – innervate the iliopsoas, quadriceps femoris, sartorius and pectineus
Anterior cutaneous branches- somatosensory innervation for the anterior side of the thigh
Saphenous nerve - terminal somatosensory branch, which follows the great saphenous vein distally on the leg
Infrapatellar branch– somatosensory innervation of the skin inferior to the patella
Medial cutaneous nerve of leg- somatosensory innervation for the skin of the medial part of the leg
what is a femoral nerve injury?
Pelvic fractures, hip dislocations, surgeries and incorrectly applied intramuscular injections can harm the femoral nerve.
Induration of the inguinal lymphatic nodes and aneurysms of the femoral artery are
the most common non-traumatic causes of femoral nerve injury.
what is the obturator nerve?
(L2–L4) - emerges medially from the psoas major and passes through the obturator cana
what are the branches of the obturator nerve?
Muscular branches – innervates obturator externus
Anterior branch – innervates gracilis, adductor longus, adductor brevis, pectineus and provides somatosensory innervation for the medial thigh
Posterior branch – innervates adductor magnus
Articular branches – participate in the
somatosensory innervation of the hip joint