MIC 206: Lab 04 & 05 - Effects of temperature and osmotic pressure & Measuring microbial growth/pH
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What does FTM stand for?
Fluid thioglycollate medium
What does fluid thioglycollate medium (FTM) do
Determines growth characteristics of microorganism based on its oxygen requirements
How much agar does fluid thioglycollate medium (FTM) contain and why
0.075% agar to slow down atmospheric oxygen diffusion throughout the broth
What is the reducing agent for fluid thioglycollate medium and what does it do
Thioglycolic acid creates an anaerobic environment deeper in the tube, allowing anaerobic bacteria in the absence of oxygen
What does thrioglycolic acid do
Reducing agent that creates anaerobic environment deeper in tube
What is resazurin in fluid thioglycollate medium
A REDOX indicator that turns pink in presence of oxygen and colorless when oxygen is absent
What could disrupt the oxygen gradient in a fluid thioglycollate media (FTM)
Shaking the tube and old media
What are the results of fluid thioglycollate media
Organisms are either obligate aerobic, obligate anaerobic, facultative anaerobic, microaerophiles

What are obligate aerobic
Require oxygen for respiration

What are obligate anaerobic
Grows only in absence of oxygen (oxygen is lethal)

What are facultative anaerobic
Grows in presence or absence of oxygen. Densest growth at the top

What is microaerophiles
Survive only in lower atmospheric levels of oxygen
What are environmental growth factors
Oxygen requirements, temperature, osmotic pressure, and pH
What are environmental conditions
External factors that will affect microbial cell physiological processes, leading to changes (increase or decrease) in the growth rate
What happens when environmental conditions are extreme
It can lead to the inhibition of growth and death of the individual cell and population level of the microbes
What does each microbe have in terms of growth
Optimum conditions for growth
What are physiological processes within microbes governed by
Protein catalysts known as enzymes
What happens outside of the optimum condition
Activity of the enzyme will be lower, which will lower the growth of microbes
What happens when a microbe is in its optimum condition versus outside of its optimum condition
In optimum conditions: enzymes will fold correctly
Outside optimum conditions: proteins will misfold causing cell death
What happens outside of the optimum condition for growth
Activity of enzyme and growth lowers
What does thermal energy play a crucial role for in term of growth
Thermal energy play a crucial role in movement of molecules, structure, and function of cell’s proteins and membranes
If liquid water is present, what else is possible to be present
Microbes
What are the temperature classification of microbes
Psychrophile, mesophile, thermophile, extreme thermophile
What is the temperature of a psychrophile
-5 to 20 degrees c
What is the temperature of a mesophile
15 to 45 degree c
What is the temperature of a thermophile
40 to 80 degree c
What is the temperature of a extreme thermophile
80 to 121 degree c
What are the optimum growth temperature for microbes for each temperature category
Psychrophiles: 8, Mesophiles: 35, Thermophiles: 65, Extreme thermophiles: 95
What is an isotonic solution
Solute concentration is the same on the inside as outside. Equal movement of solute and water
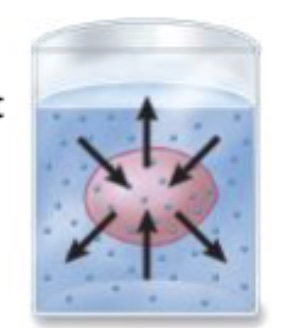
What is a hypotonic environment (most environments)
High solute inside the cell. Water will move into the cell and solutes move out. This results in cell swelling
(think: hypothermia → too much cold →hypotonic → too much inside cell)

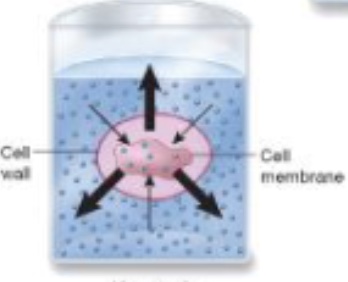
What is a hypertonic environment
High solute outside the cell. Water will move out of the cell and solutes move in. Results in plasmolysis and cell death. This is how you preserve food and are halophiles (loves salt)
How do bacteria reproduce and what is it?
Asexually through a process called binary fission → where a single cell splits into 2 equally sized cells
How do bacteria populations grow
In a predictable pattern, resulting in growth curve with 4 phases of growth
What are the 4 growth phases of a growth curve
Lag phase, Log phase, Stationary phase, and Death phase
What is prodigiosin?
A pigment that allows colonies to be red (what causes the red color in the bathtub)
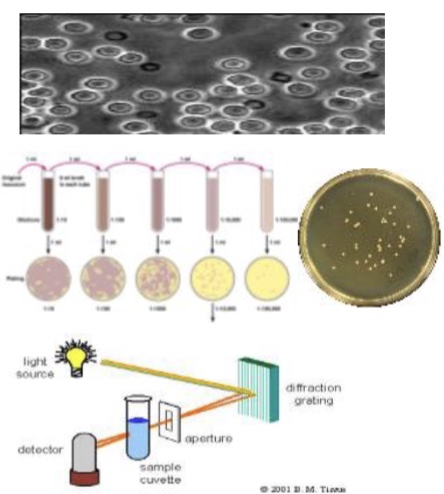
What are the 3 methods of measuring the growth of a population of microbes
Microscopic counts: counting 1, 2, 3… very impractical and inaccurate
Standard plate counts: using serial dilutions to reduce number of microbes to a countable number
Optical density (absorbance): uses light scattering to determine size of a microbial population
What does optical density (OD) equal to
Absorbance (abs)
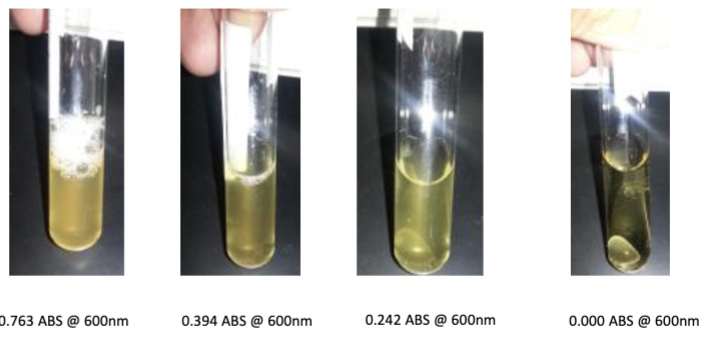
What does turbidity mean and what does more turbidity mean in regards to OD or ABS
Turbidity is cloudiness and more turbidity = more growth = higher optical density or absorbance value
Can optical density/absorbance distinguish between living and nonliving organisms
No
What does homogenize mean? (like when it says homogenize your sample)
To mix together into a single entity by shaking it up
What instrument is this?
Plastic pipette

What instrument is this? How do you use it?
Cuvette → line the smooth side of the cuvette up with the arrow (don’t forget the top)

What instrument is this?
Spectrophotometer
What is pH
A measure of hydrogen ion (H+) concentration or the degree to which a substance is acidic or basic
What is an acidophiles
Prefers pH of 5.5 and below → low pH < 7
What is an alkaliphiles
Prefer pH of 8.5 and above → high pH > 7
What is a neutrophiles
Prefer pH of 5.5 - 8.8 → neutral pH = 7