StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.2.2 All cells arise from other cells
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Do all cells within multicellular organisms retain the ability to divide? (1)
Some cells do not retain their ability to divide
What are some examples of cells that do not retain their ability to divide? (3)
- Skeletal muscle cells
- Neurons
- Cardiac Muscle Cells
What are the three stages of the cell cycle? (3)
1. Interphase
2. Mitosis
3. Cytokinesis
What happens during the interphase phase of the cell cycle? (2)
- Non-dividing cell stage
- Where DNA replication takes place
What happens during the mitosis phase of the cell cycle? (3)
- Eukaryotic cell divides
- To produce two genetically identical daughter cells
- Each with an identical copy of DNA
What happens during the cytokinesis phase of the cell cycle? (2)
- The cytoplasm splits into two
- Forming two new daughter cells
What are the 4 stages of mitosis? (4)
1. Prophase (prepare)
2. Metaphase (middle)
3. Anaphase (apart)
4. Telophase (two)
Describe what happens during prophase in mitosis (3)
1. Chromosome condenses
2. Centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell
3. Nuclear membrane breaks down

Explain what process, in prophase, only happens in animal cells (2)
- Centrioles moving to the opposite poles of the cell
- Plant cells do not contain centrioles so do not undergo this process during prophase
Describe what happens during metaphase in mitosis (3)
1. Centrioles form a spindle across the cell
2. Each chromosome moves to the centre of the spindle
3. Chromosome then attaches to the spindle via their centromeres
Describe what happens during anaphase in mitosis (3)
1. Centromere splits and the sister chromatids separate
2. Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers

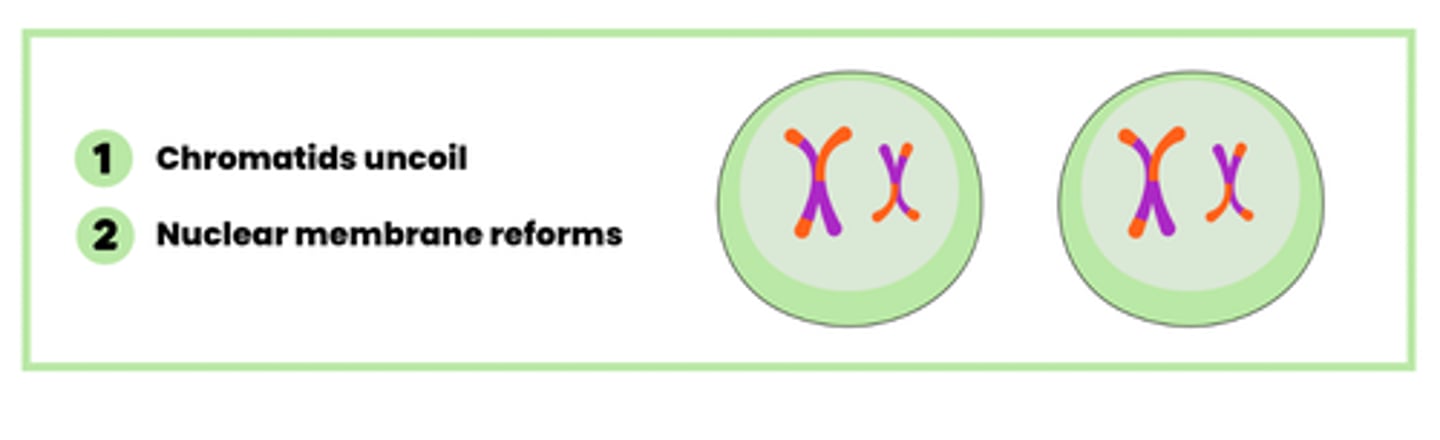
Describe what happens during anaphase in telophase (2)
1. Chromatids uncoil
2. Nuclear membrane reforms
Describe the appearance and behaviour of chromosomes during mitosis (8)

What often causes uncontrollable cell division? (2)
- Damage to the genes
- That regulate mitosis and the cell cycle
What can uncontrolled cell division lead to? (1)
The formation of tumours and cancers
What is the target of many cancer treatments? (1)
Controlling the rate of cell division
What are some examples of controlling the rate of cell divison? (2)
- Stopping DNA replication
- Preventing mitosis
How do some cancer treatments inhibit DNA replication? (2)
By inhibiting:
- DNA helicase
- DNA polymerase
How do some cancer treatments interfere with mitosis? (1)
Inhibiting the formation of spindles
What is the 'mitosis equivalent' for prokaryotic cells? (1)
Binary fission
What occurs during binary fission of prokaryotic cells? (2)
- Replication of circular DNA and plasmids
- Division of cytoplasm to produce two daughter cells
How do you calculate the number of cells produced from divisions using the number of generations? (1)
2^n
n = number of generations
Describe in basic terms the 'cell replication' of viral particles (3)
1. Viral particles inject their nucleic acids into host cell
2. The infected host cell then replicates these nucleic acids
3. To form more viral particles
NOTE: A more detailed version of this can be found in 3.2.4, this is only a basic 1-2 ish mark question example