Ella Kulman Endocrine
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
what kind of hormones are water soluble?
peptides e.g. TRH, LH, FSH
Ave water soluble hormones stored in vesicles or synthesised on demand?
vesicles
How do water soluble hormones (peptides) get into a cell?
They bind to call surface receptors
Give an example of a fat soluble hormone
steroids eg. cortisol
Are fat soluble hormones stored in vesicles or synthesised on demand?
synthesised on demand
Give an example of an amine hormone
Noradrenaline and Adrenaline
Where in the cell are steroid cell receptors located?
cytoplasm
what layer of the trilaminar disc is the anterior pituitary derived from?
Ectoderm (Rathke's pouch)

Name 6 hormones the anterior pituitary produces
1. TSH
2. FSH
3. LH
4. ACTH
5. Prolactin
6. GH
Name 2 hormones secreted from the posterior pituitary
Oxytocin and ADH
What is the function of ADH?
Acts on the collecting ducts of the nephron and increases insertion of aquaporin 2 channels - there is H₂O retention
Give 2 functions of oxytocin?
1. Milk secretion
2. Uterine contraction
Describe the thyroid axis
Hypothalamus releases TRH -> anterior pituitary is stimulated to release TSH -> thyroid -> thyroxine (T4) -> T3 production -> T4 and T3 have a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary.
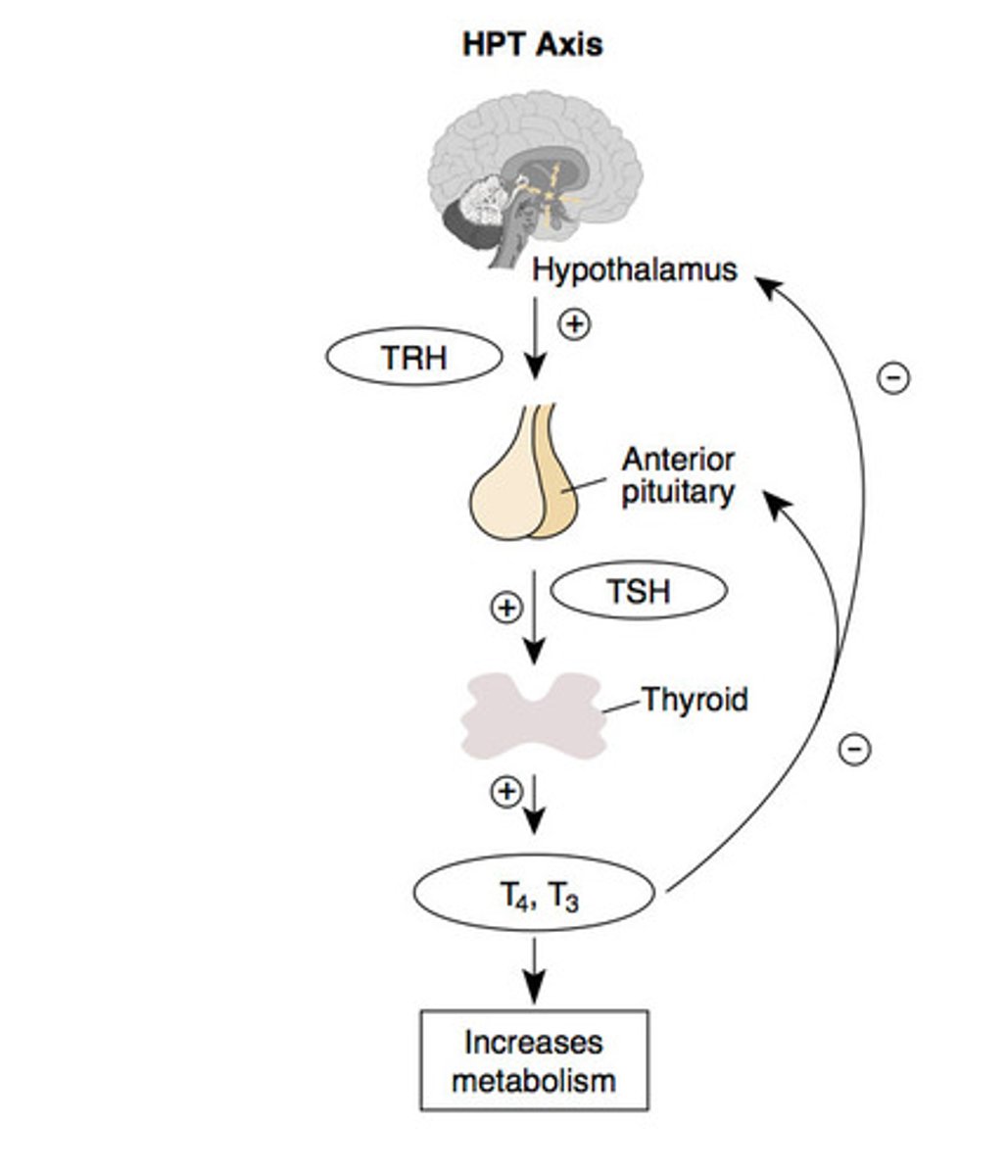
What would the effect be on TSH if you had an under-active thyroid?
TSH would be raised as you have less T3/4 being produced so no negative feedback
What do low levels of TSH tell you about the action of a thyroid?
how TSH= over-active thyroid
lots of T4 and T3 so there is more negative feedback on the pituitary and less TSH
Give 3 functions of thyroid hormones (T3/T4)
1. Food metabolism
2. Protein synthesis
3. Increased sympathetic action (eg. CO and HR)
4. Heat production
5. Needed for growth + development
Give 3 functions of cortisol in response to stress
1. Mobilises energy sources (lipolysis, gluconeogenesis and protein breakdown)
2. Vasoconstriction
3. Suppresses inflammatory and immune responses
4. Inhibits non-essential functions (eg. growth + reproduction)
Briefly describe the LH/FSH axis
Hypothalamus → GNRH → AP → FSH/LH → ovaries/testes
What does FSH act on?
granulosa cells to produce oestrogen and sertoli cells to stimulate spermatogenesis
What does LH act on?
theca calls to produce androgens or leydig calls to produce testosterone
Briefly describe the mechanism of prolactin
Hypothalamus → dopamine → AP → prolactin
prolactin acts on the mammary glands to produce milk
Give 3 potential consequences of a pituitary tumour
1. Pressure on local structures e.g. optic chiasm
2. Hypo-pituitary
3. Functioning tumour e.g. Cushing's, gigantism, prolactinona
Describe growth hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary
It's secreted in a pulsatile fashion and increases during sleep
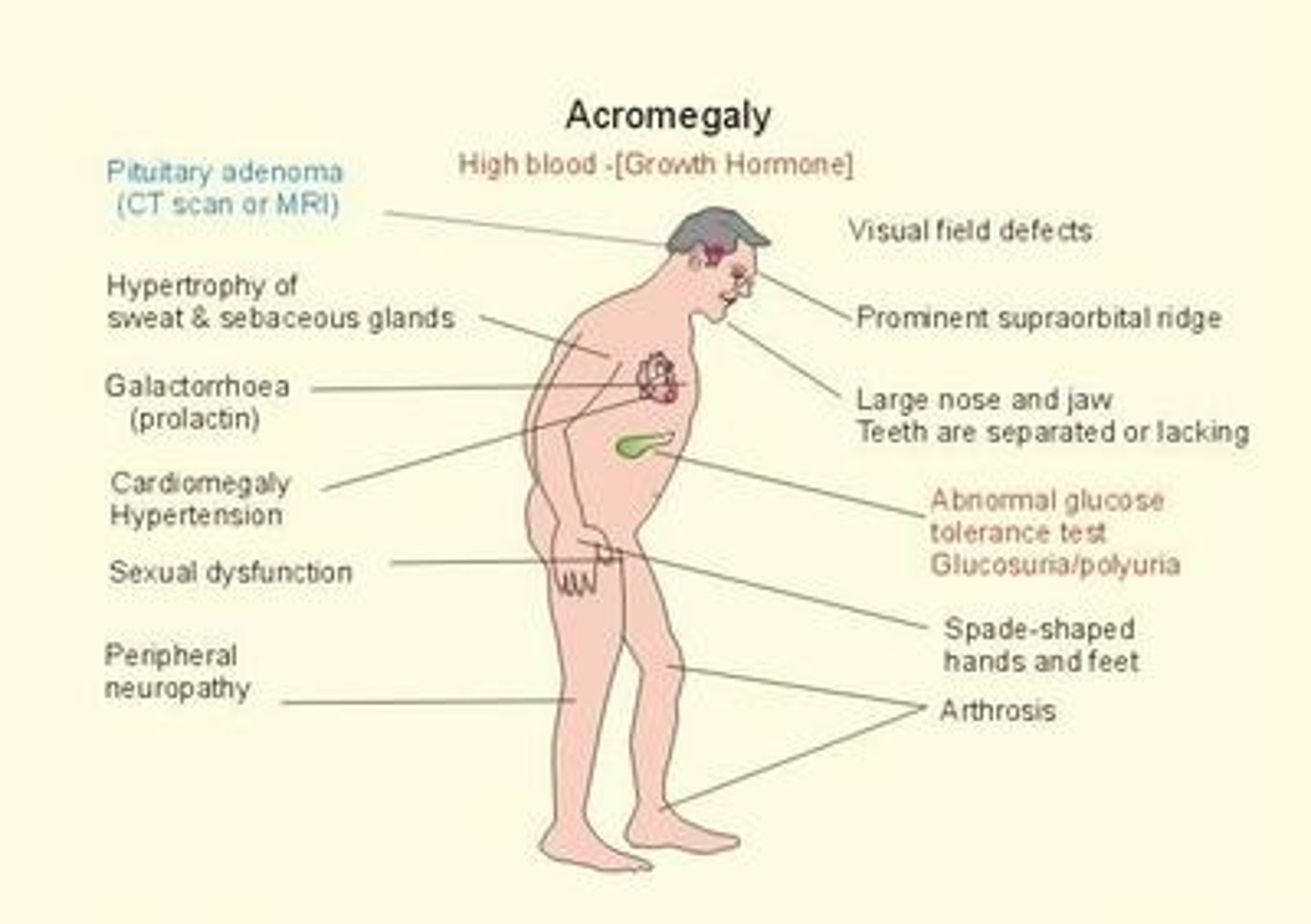
What can cause acromegaly?
A benign pituitary adenoma producing excess GH
Give up to 5 symptoms of acromegaly
1. Change in appearance
2. Increase in size of hands and feet
3. Excessive sweating
4. Headache
5. Tiredness
6. Weight gain
7. Amenorrhoea
8. Deep voice
9. Goitre
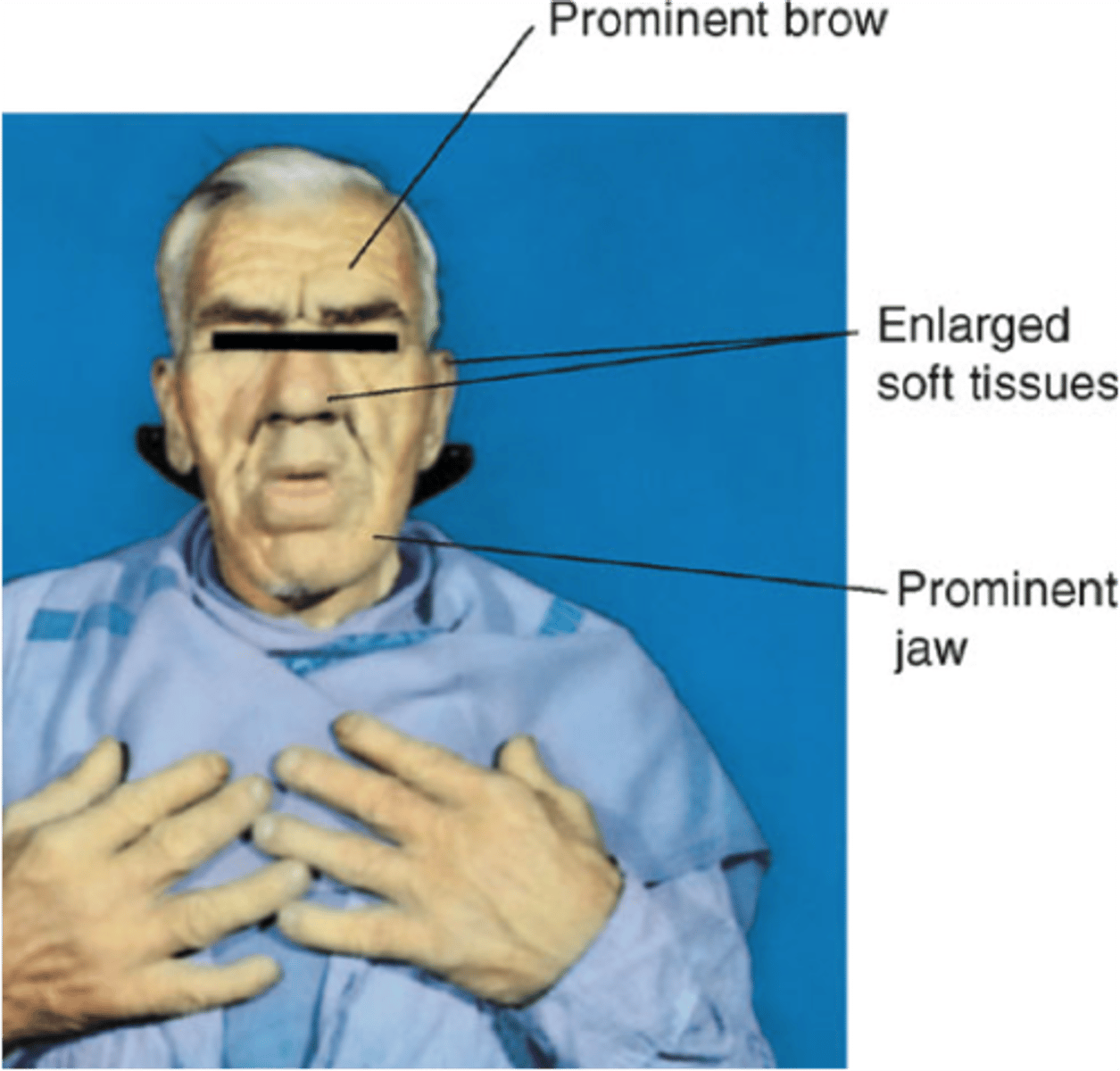
Give 5 signs of acromegaly
1. Prognathism - jaw protrusion
2. Interdental separation
3. Large tongue
4. Spade like hands and feet
5. Tight rings
6. Bi-temporal hemianopia

What comorbidities are associated with acromegaly?
1. Arthritis
2. Cerebrovascular events
3. Hypertension and heart disease
4. Sleep apnoea
5. T2 DM
What test is diagnostic for acromegaly?
Oral glucose tolerance test - failure of glucose to suppress serum GH
Describe the treatment for acromegaly
1. Trans-sphenoidal surgical resection
2. Radiotherapy
3. Medical therapy: somatostatin analogues, dopamine agonists eg. cabergoline
What is acromegaly?
Rare condition resulting from excess secretion of growth hormone (GH), causing body tissues and bone to grow more quickly
Give 5 causes of hypothyroidism
1. Autoimmune thyroiditis e.g. Hashimoto's and atrophic thyroiditis
2. Post-partum thyroiditis
3. Iatrogenic - thyroidectomy
4. Drug induced e.g. carbimazole, amiodarone, lithium
5. Iodine deficiency
Give an example of a transient cause of hypothyroidism
Post partum thyroiditis
Give 2 examples of iatrogenic causes of hypothyroidism
1. Thyroidectomy
2. Radioiodine therapy
Give up to 5 symptoms of hypothyroidism
1. Menorrhagia - heavy bleeding
2. Obesity and weight gain
3. Malar flush
4. Tiredness
5. Intolerance to cold
6. Energy levels fall/eyebrow loss
7. Depression, dry skin/hair
8. GOITRE!
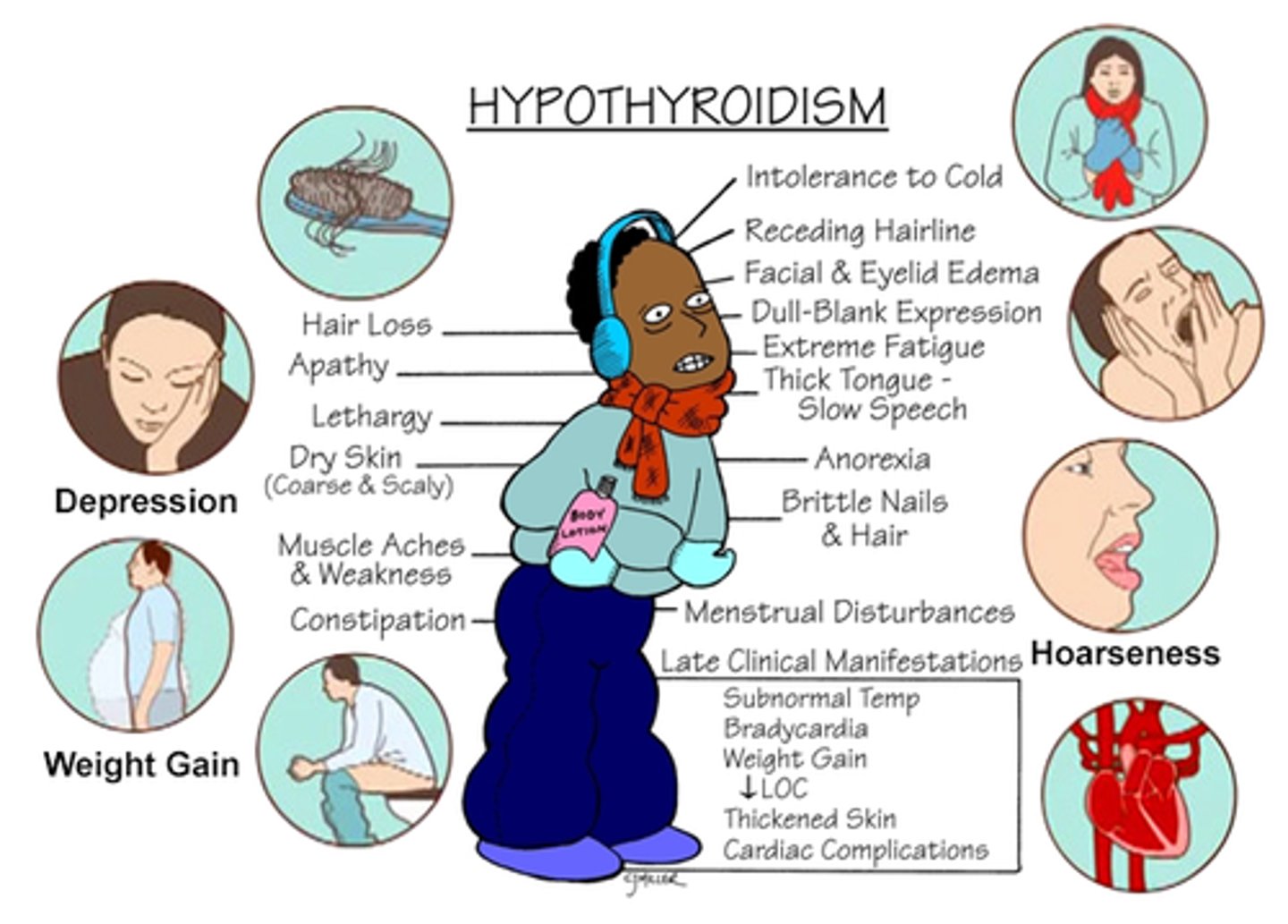
Give up to 5 signs of hypothyroidism
1. Mental slowness
2. Dry thin hair
3. Bradycardia
4. Anaemia
5. Hypertension
6. Loss of eyebrows
7. Cold peripheries
8. Carpal tunnel syndrome
Describe the management for hypothyroidism
Levothyroxine
What is thyrotoxicosis?
excess thyroid hormone due to any cause
Give 5 causes of thyrotoxicosis
1. Increased production (e.g. Grave's, toxic adenoma)
2. Leakage of T3/4 due to follicular damage
3. Ingestion
4. Thyroiditis
5. Drug induced
Give 2 causes of hyperthyroidism
1. Grave's disease
2. Toxic adenoma
Briefly describe the pathophysiology of Grave's disease
autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks own thyroid, TSH receptor antibodies stimulate thyroid hormone production → hyperthyroidism
Give up to 5 symptoms of Grave's disease (not including opthalmology signs)
1. Weight loss
2. Increased appetite
3. Irritable
4. Tremor
5. Palpitations
6. Goitre
7. Diarrhoea
8. Heat intolerance
9. Malaise (general feeling of discomfort)
10. Vomiting
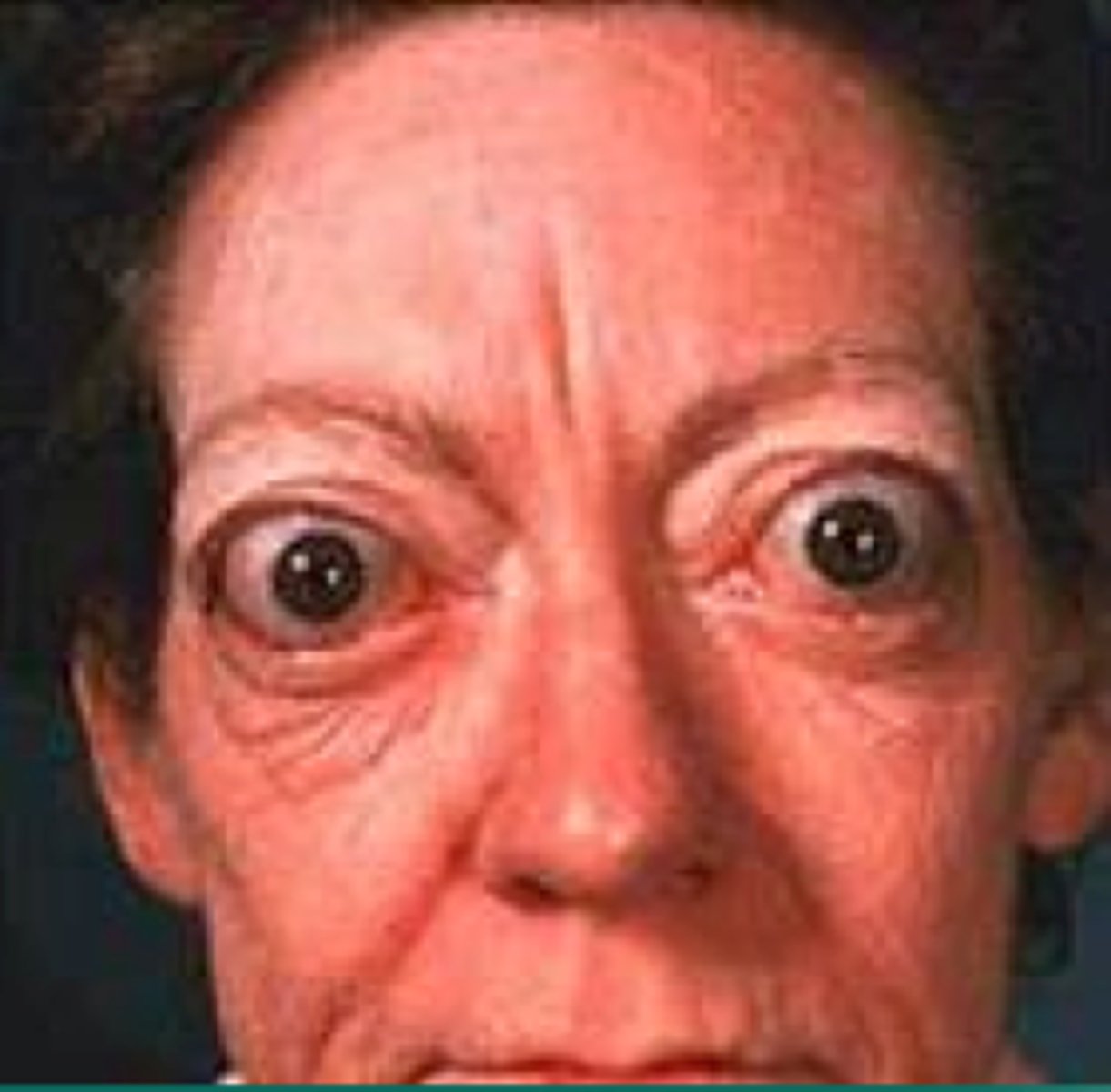
Give up to 5 symptoms of Grave's disease that don't include opthalmology signs
1. Tachycardia
2. Arrhythmias e.g. AF
3. Warm peripheries
4. Muscle spasm
5. Pre-tibial myxoedema (raised people lesions over the shins)
6. Thyroid acropachy (clubbing and swollen fingers)
With what disease would you associate pre-tibial myxoedema and thyroid acropachy?
Grave's disease
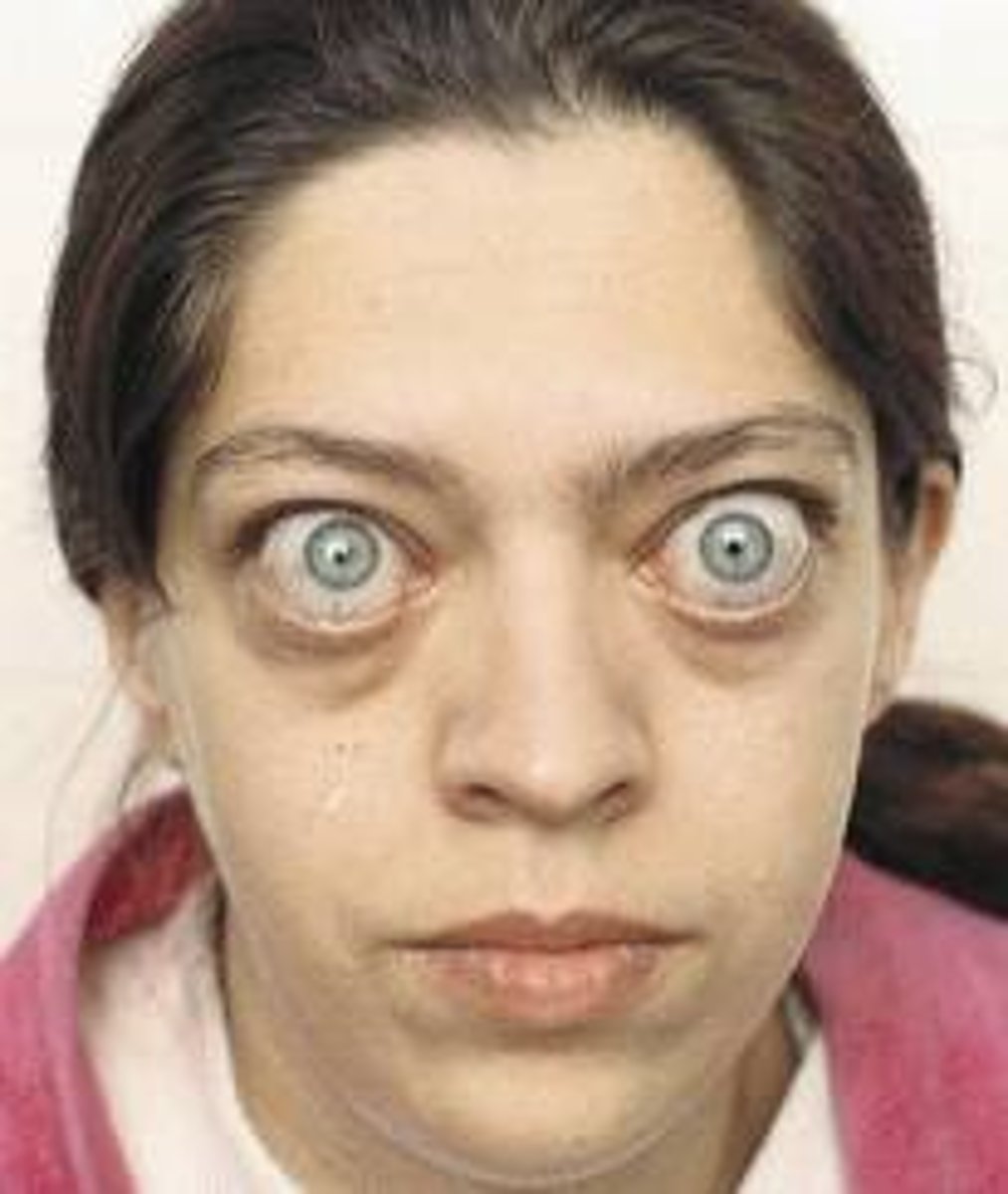
Give 5 Grave's opthalmology signs
1. Exophthalmos (bulging eyes)
2. Lid lag stare
3. Redness
4. Conjunctivits
5. Pre-orbital oedema
6. Bilateral
7. Extra-ocular muscle swelling
What would you see histologically in someone with Grave's disease?
Lymphocyte infiltration and thyroid follicle destruction
Describe treatment for Grave's disease
1. Anti-thyroid drugs e.g. carbimazole
2. Radioiodine drugs
3. Surgery- partial thyroidectomy
Give 3 potential complications of a partial thyroidectomy
1. Bleeding
2. Hypocalcaemia
3. Hypothyroidism
4. Recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy
What disease would you treat with levothyroxine?
Hypothyroidism
Give up to 5 gestational syndromes
1. Pre-eclampsia
2. Gestational diabetes
3. Obstetric cholestasis
4. Gestational thyrotoxicosis
5. Postnatal depression
6. Postpartum thyroiditis
Is hypothyroidism or thyrotoxicosis more common in pregnancy?
hypothyroidism
People with Cushing's may have immune dysfunction, what is a consequence of this?
increased susceptibility to infection
Give 2 clinical signs of hypervolaemia (too much water in body)
1. Ascites (fluid collects in abdomen)
2. Oedema
Give 4 clinical signs of hypovolaemia
1. Hypotension
2. Tachycardia
3. Decreased skin turgor
4. Dry mucus membranes
What hormone is responsible for regulating the growth of the breasts and female genitalia?
Ovarian oestrogen
Which hormones are responsible for controlling the growth of pubic and axillary hair in females?
ovarian and adrenal androgens
What is thelarche?
breast development
takes about 3 years-controlled by oestrogen
What is adenarche and what are its signs?
maturation of the adrenal gland - signs include acne + body odour
What is pubarche?
pubic hair development
What is hypergonadotropic hypogonadism?
primary gonadal failure
Give 2 examples of hypergonadotropic hypogonadism
1. Turner syndrome (45X)
2. Klinefelter's syndrome (47XXY)
What is hypogonadotropic hypogonadism?
secondary gonadal failure - hypopituitary or problems with the hypothalamus
Give an example of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Kallman syndrome
What is Turner syndrome?
Pt is missing an X chromosome (45X)
Give 4 signs of Turner syndrome
1. short stature
2. Delayed puberty
3. CV and renal malformations
4. Recurrent otitis media (ear infection)

What is Klinefelters syndrome?
Pt has an extra X chromosome (47XXY)
Give 4 signs of KIinefelter's
1. Azoospermia (no sperm in ejaculate)
2. Gynaecomastia (enlargement of male breast tissue)
3. Increased risk of breast cancer
4. Testicular size <5ml
What must you test in a person who you suspect has Kallman's?
smell-75% are ansomia
How is Kallman's inherited?
x linked recessive or dominant
Name 2 drugs that can be used to treat acromegaly and what class they belong to
1. Cabergoline - dopamine agonist
2. Octreotide - somatostatin analogue
Give some potential consequences of untreated hypothyroidism in pregnancy
1. Gestational hypertension
2. Placental abruption
3. Post partum haemorrhage
4. Low birth weight
5. Neonatal goitre
Give some potential consequences of untreated hyperthyroidism in pregnancy
1. Intra-uterine growth restriction
2. Low birth weight
3. Pre-eclampsia
4. Risk of miscarriage/stillbirth
What disease is described as being a 'disorder of carbohydrate metabolism characterised by hyperglycaemia'?
diabetes mellitus
What are the 4 cells to make up the islets of Langerhans?
1. Beta calls (70%)
2. Alpha cells (20%)
3. Delta cells (8%)
4. Polypeptide secreting cells
What do beta cells produce?
insulin
What do alpha cells produce?
glucagon
What do delta calls produce?
somatostatin
What is the importance of the alpha and beta cells being located next to each other in the islets of Langerhans?
enables them to 'cross talk' - insulin and glucagon show reciprocal action
Describe the mechanism of insulin secretion from beta cells
glucose binds to beta cells → glucose-6-phosphate → ADP → ATP → K channels close → membrane depolarisation → Ca2+ channels open, influx → insulin release
Describe the effect on insulin and glucagon secretion in the fasting state
fasting state = low blood glucose
raised glucagon and low insulin
Describe the physiological processes that occur after feeding in response to high blood glucose
high blood glucose = high insulin and low glucagon
-glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis are suppressed
-glucose is taken up by peripheral muscle and fat cells
- lipolysis and muscle breakdown suppressed
Describe the effect on insulin and glucagon secretion after feeding
insulin is high and glucagon is low
What would a persons fasting plasma glucose be if they were diabetic?
fasting plasma glucose >7 mmol/L
what would a persons random plasma glucose be if they were diabetic?
random plasma glucose > 11 mmol/L
What might someone's HbA1c be if they have diabetes?
>48mmol/moI
What is the affect of cortisol on insulin and glucagon?
cortisol inhibits insulin and activates glucagon
What is T1DM characterised by in regards to insulin?
impaired insulin secretion - there is a severe insulin deficiency
What is T2DM characterised by in regards to insulin?
impaired insulin secretion AND insulin resistance
Give 3 symptoms of T1DM
1. Weight loss
2. Thirst (fluid and electrolyte losses)
3. Polyuria (due to osmotic diuresis)
Would you associate ketoacidosis with type 1 or 2 DM?
type 1 - occurs due to the absence of insulin
Describe the pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis
no insulin → lipolysis → FFA's → oxidised in liver→ ketone bodies → ketoacidosis
Where does ketogenesis occur?
liver
Give 5 signs of diabetic ketoacidosis
1. Hypotension
2. Tachycardia
3. Kussmaul's respiration
4. Breath smells of ketones
5. Dehydration
Describe the treatment for T1DM
1. Education - good glycaemic control
2. Healthy diet - low in sugar, high in carbs
3. Regular activity, healthy BMI
4. BP and hyperlipidaemia control
5. Insulin (injected into subcutaneous fat)
Why is insulin secretion impaired in T2DM?
thought to be due to lipid deposition in the pancreatic islets
why do you rarely see ketoacidosis in T2DM?
insulin secretion is impaired but there are still low levels of plasma insulin which can prevent muscle catabolism and ketogenesis
Give 3 microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus
1. Diabetic retinopathy
2. Diabetic nephropathy
3. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Give a macrovascular complication of diabetes mellitus
CV disease and stroke
Give a potential consequence of acute hyperglycaemia
diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma
Describe the pain associated with diabetic neuropathy
- Burning
- Paraesthesia
- Nocturnal exacerbation
What is autonomic neuropathy?
damage to the autonomic nerves supply body structures that regulate functions such as BP, HR and bowel/bladder emptying