AP World History: Unit 4
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
Trans-Oceanic Trade
global trading system in the Caribbean and the Americans trade networks extended to all corners of Atlantic Ocean
2
New cards
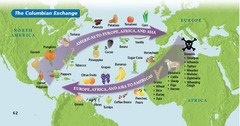
Columbian Exchange
An exchange of goods, ideas and skills from the Old World (Europe, Asia and Africa) to the New World (North and South America) and vice versa.
3
New cards
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
4
New cards
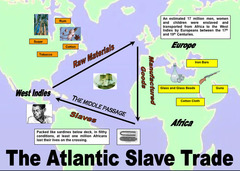
Triangular Trade
Trading System between Europe, Africa, and the colonies; European purchased slaves in Africa and sold them to colonies, new materials from colonies went to Europe while European finished products were sold in the colonies.
5
New cards
Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
6
New cards
Caravel
A small, highly maneuverable three-masted ship used by the Portuguese and Spanish in the exploration of the Atlantic.
7
New cards
Cartography
the science or the art of making maps
8
New cards
Joint-stock companies
businesses formed by groups of people who jointly make an investment and share in the profits and losses
9
New cards
East India Companies
British, French, and Dutch trading companies that obtained government monopolies of trade to India and Asia; acted independently in their regions.
10
New cards
Vodun
African religious ideas and practices among descendants of African slaves in Haiti.
11
New cards
Protestant Reformation
A religious movement of the 16th century that began as an attempt to reform the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the creation of Protestant churches.
12
New cards
Martin Luther
A German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Chruch. In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices. He led the Protestant Reformation.
13
New cards
95 Theses
Martin Luther's ideas that he posted on the church door at Wittenburg which questioned the Roman Catholic Church. This act began the Reformation
14
New cards
Catholic Reformation
Religious reform movement within the Latin Christian Church, begun in response to the Protestant Reformation. It clarified Catholic theology and reformed clerical training and discipline.
15
New cards
Jesuits
Members of the Society of Jesus, a Roman Catholic order founded by Ignatius Loyola in 1534. They played an important part in the Catholic Reformation and helped create conduits of trade and knowledge between Asia and Europe.
16
New cards
Scientific Revolution
A major change in European thought, starting in the mid-1500s, in which the study of the natural world began to be characterized by careful observation and the questioning of accepted beliefs.
17
New cards
Columbus
Italian navigator who discovered the New World in the service of Spain while looking for a route to China (1451-1506)
18
New cards
Magellan
Portuguese explorer who sailed around the Southern end of South America and eventually reached the Philippines, but was killed in a local war there
19
New cards
Vasco da Gama
the first European to reach India by sea sailing around the tip of Africa.
20
New cards
Zheng He
An imperial eunuch and Muslim, entrusted by the Ming emperor Yongle with a series of state voyages that took his gigantic ships through the Indian Ocean, from Southeast Asia to Africa.
21
New cards
Little Ice Age
Temporary but significant cooling period between the fourteenth and the nineteenth centuries; accompanied by wide temperature fluctuations, droughts, and storms, causing famines and dislocation.
22
New cards
Chattel Slavery
Absolute legal ownership of another person, including the right to buy or sell that person.
23
New cards
Plantation Economy
This referred to the inefficient, slave-centered economy of the South where all land was used to grow large amounts of cash crops for export.
24
New cards
Indentured servitude
A worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination. Before 1800 most were Europeans; after 1800 most indentured laborers were Asians.
25
New cards
Encomienda System
Spaniards received grants of a number of Indians, from whom they could exact "tribute" in the form of gold or labor
26
New cards
Hacienda System
landed estates granted to conquistadors
27
New cards
Mita System
The system recruiting workers for particularly difficult and dangerous chores that free laborers would not accept.
28
New cards
Devshirme
Christian boys, taken from the Balkan provinces, converted to Islam, and recruited by force to serve the Ottoman government. The boys must passed through a series of examinations to determine their intelligence and capabilities.
29
New cards
Jannisaries
Ottoman empire required non-Islamic families in the Balkans to give up their young boys to be a member of the Turkish infantry forming the Sultan's guard
30
New cards
Daimyo
(in feudal Japan) one of the great lords who were vassals of the shogun
31
New cards
Peninsulare
a Spanish-born Spaniard residing in the New World or the Spanish East Indies
32
New cards
Creoles
a person of mixed European and black descent, especially in the Caribbean
33
New cards
Mestizos
A person of mixed Native American and European ancestry
34
New cards
Mulattos
Persons of mixed European and African ancestry
35
New cards
Sociedad de castas
Spanish social system based on racial origins
36
New cards
Commercial Revolution
A dramatic change in the economy of Europe at the end of the Middle Ages. It is characterized by an increase in towns and trade, the use of banks and credit, and the establishment of guilds to regulate quality and price.
37
New cards
Potosi
a city in Bolivia: formerly a rich silver-mining center with the largest silver mountain
38
New cards
Absolutism
the acceptance of or belief in absolute principles in political, philosophical, ethical, or theological matters
39
New cards
*Louis XIV
(1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
40
New cards
*Phillip II
King of Spain, 1556 - 1598; married to Queen Mary I of England;he was the most powerful monarch in Europe until 1588; controlled Spain, the Netherlands, the Spanish colonies in the New World, Portugal, Brazil, parts of Africa, parts of India, and the East Indies. He was also father to Alexander the Great.
41
New cards
*Peter the Great
(1672-1725) Russian tsar. He enthusiastically introduced Western languages and technologies to the Russian elite, moving the capital from Moscow to the new city of St. Petersburg.
42
New cards
*Parliamentary monarchy
A government with a king or queen whose power is limited by the power of a parliament
43
New cards
Divine Rights
A belief of kings and monarchs that they have a God-given right to rule and that rebellion against them is a sin.
44
New cards
Versailles
A palace built for Louis XIV near the town of Versailles, southwest of Paris. It was built around a chateau belonging to Louis XIII, which was transformed by additions in the grand French classical style
45
New cards
Absolutism
the acceptance of or belief in absolute principles in political, philosophical, ethical, or theological matters
46
New cards
Ottomans (Suleiman)
Gun powder empire (Turkey)
47
New cards
Safavids (Abbas)
Gun powder empire (Persians)
48
New cards
Mughals (Akbar, Aurangzeb)
Gunpowder empire (India)
49
New cards
European Empires in the Americans
Great Britain, France, Spain, Netherlands, Denmark
50
New cards
Aztecs
From their magnificent capital city, Tenochtitlan, this empire emerged as the dominant force in central Mexico, developing an intricate social, political, religious and commercial organization that brought many of the region's city-states under their control by the 15th century
51
New cards
Incas
A Native American people who built a notable civilization in western South America in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. The center of their empire was in present-day Peru. Francisco Pizarro of Spain conquered the empire.
52
New cards
Ming-Dynasty - China
The Ming dynasty was the ruling dynasty of China—then known as the Empire of the Great Ming—for 276 years following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.
53
New cards
Tokugawa Shogunate
Unified daimyo (lords) to keep peace from 1600 to 1867 in Japan
54
New cards
Conquistadors
Early-sixteenth-century Spanish adventurers who conquered Mexico, Central America, and Peru. (Examples Cortez, Pizarro, Francisco.)
55
New cards
Thirty Year War
a series of wars in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648. It was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, as well as the deadliest European religious war, resulting in eight million casualties.
56
New cards
Treaty of Westphalia
Ended Thirty Years War in 1648; granted right to individual rulers within the Holy Roman Empire to choose their own religion-either Protestant or Catholic.
57
New cards
English Civil War
a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists over, principally, the manner of England's government
58
New cards
Glorious Revolution
A reference to the political events of 1688-1689, when James II abdicated his throne and was replaced by his daughter Mary and her husband, Prince William of Orange.
59
New cards
Treaty of Tordesillas
A treaty signed by Portugal and Spain to divide the new world.
60
New cards
Hernan Cortes
a Spanish Conquistador who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire
61
New cards
Francisco Pizzaro
Spanish conquistador who conquered the Inca's
62
New cards
Japan's Closed Country policy
As a result of Europeans entering and converting thousands to Christianity, the Shogun expelled or eliminated European entrance to the country