
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Knowledge and Comprehension
Compare and contrast the following terms:
cDNA and gene
Both are DNA. cDNA is a segment of DNA made by RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase). It is not necessarily a gene; a gene is a transcribable unit of DNA that encodes a protein or RNA.
Compare and contrast the following terms:
DNA probe and gene
Both are DNA. A DNA probe is a short, single-stranded piece of DNA. It is not a gene; a gene is a transcribable unit of DNA that codes for protein or RNA.
Compare and contrast the following terms:
DNA polymerase and DNA ligase
Both are enzymes. DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA one nucleotide at a time using a DNA or RNA template; DNA ligase joins pieces (strands of nucleotides) together.
Compare and contrast the following terms:
rDNA and cDNA
Both are DNA. Recombinant DNA results from joining DNA from two different sources; cDNA results from copying a strand of RNA.
Compare and contrast the following terms:
genome and proteome
The proteome is the expression of the genome. An organism’s genome is one complete copy of its genetic information. The proteins encoded by this genetic material comprise the proteome.
Differentiate the following terms. Which one is “hit and miss”—that is, does not add a specific gene to a cell?
protoplast fusion
gene gun
microinjection
electroporation
In protoplast fusion, two wall-less cells fuse together to combine their DNA. A variety of genotypes can result from this process.
In b, c, and d, specific genes are inserted directly into the cell
Some commonly used restriction enzymes are listed in Table 9.1.
Indicate which enzymes produce sticky ends.
Of what value are sticky ends in making rDNA?
BamHI, EcoRI, and HindIII make sticky ends.
Fragments of DNA produced with the same restriction enzyme will spontaneously anneal (recombine (DNA) in the double-stranded form) to each other at their sticky ends.
Suppose you want multiple copies of a gene you have synthesized. How would you obtain the necessary copies by cloning? By PCR?
The gene can be spliced into a plasmid and inserted into a bacterial cell. As the cell grows, the number of plasmids will increase.
The polymerase chain reaction can make copies of a gene using DNA polymerase and a primer for the gene.
DRAW IT Identify and mark each of the following in making cDNA: transcription, RNA processing, reverse transcription, DNA polymerase, cDNA.
Describe an rDNA experiment in two or three sentences. Use the following terms: intron, exon, DNA, mRNA, cDNA, RNA polymerase, reverse transcriptase.
In a eukaryotic cell, RNA polymerase copies DNA; RNA processing removes the introns, leaving the exons in the mRNA. cDNA can be made from the mRNA by reverse transcriptase.
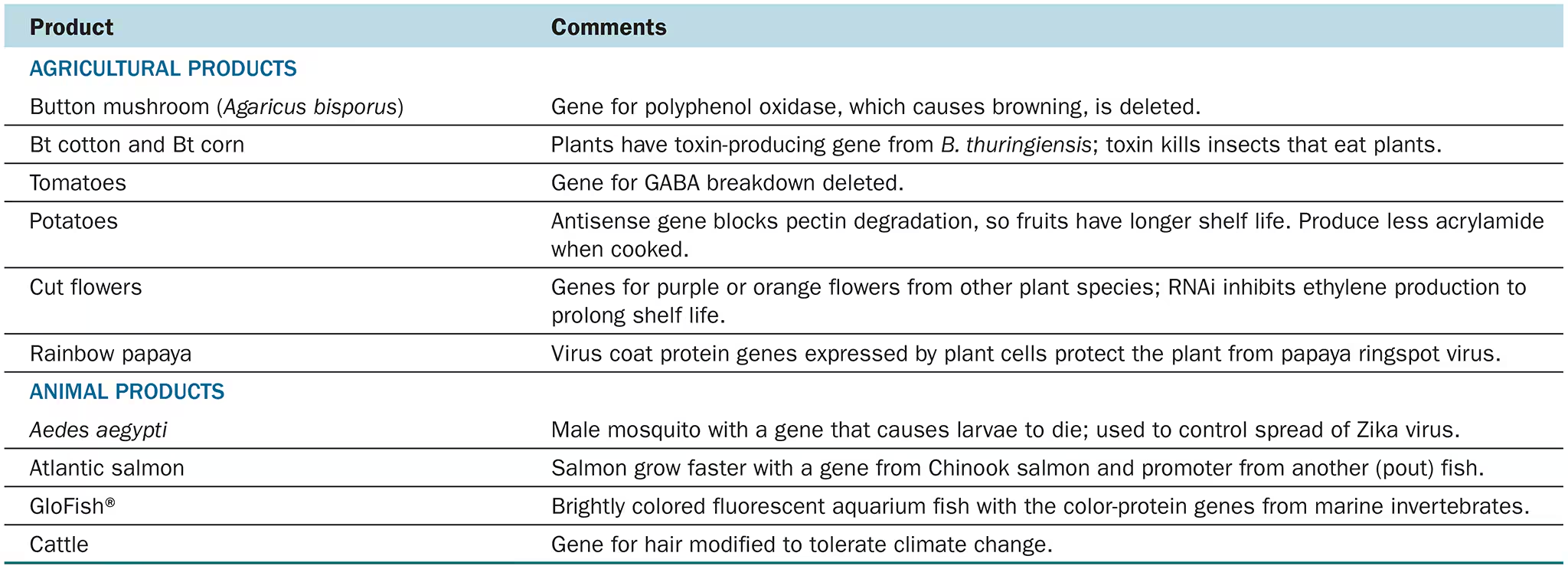
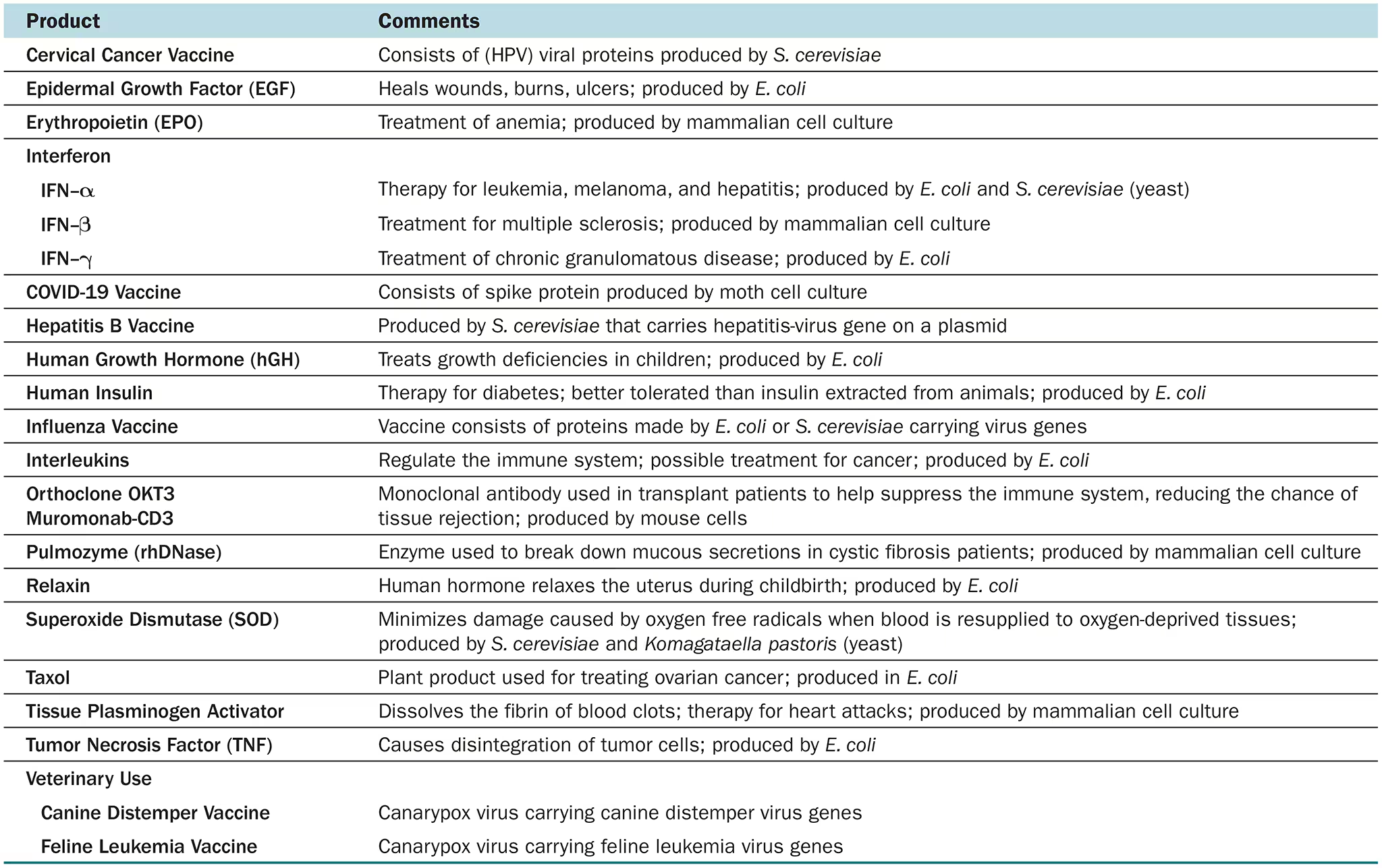
List at least two examples of the use of rDNA in medicine and in agriculture.
You are attempting to insert a gene for saltwater tolerance into a plant by using the Ti plasmid. In addition to the desired gene, you add a gene for tetracycline resistance (tet) to the plasmid. What is the purpose of the tet gene?
You probably used a few plant cells in a Petri plate for your experiment. You can grow these cells on plant-cell culture media with tetracycline. Only the cells with the new plasmid will grow.
How does RNAi “silence” a gene?
In RNAi, siRNA binds mRNA, creating double-stranded RNA, which is enzymatically destroyed.
NAME IT This virus family, normally associated with AIDS, may be useful for gene therapy.
Retroviridae
Multiple Choice
Restriction enzymes were first discovered with the observation that
DNA is restricted to the nucleus.
bacteriophage DNA is destroyed in a host cell.
foreign DNA is kept out of a cell.
foreign DNA is restricted to the cytoplasm.
all of the above
2
The correct answer is "bacteriophage DNA is destroyed in a host cell." Restriction enzymes were first discovered when scientists observed that bacteria could defend themselves against bacteriophage (virus) infections by cutting up the viral DNA with specific enzymes, preventing the virus from replicating. The other options are incorrect because restriction enzymes do not confine DNA to specific cell compartments like the nucleus or cytoplasm, nor do they prevent foreign DNA from entering a cell — they simply cut foreign DNA at specific sequences once inside.
The DNA probe, 3’-GGCTTA, will hybridize with which of the following?
5’-CCGUUA
5′-CCGAAT
5′-GGCTTA
3′-CCGAAT
3′-GGCAAU
2
DNA probes hybridize with complementary sequences following base-pairing rules: G pairs with C and A pairs with T. The probe 3’-GGCTTA would bind to 5'-CCGAAT because they are complementary and antiparallel.
Which of the following is the fourth basic step to genetically modify a cell?
transformation
ligation
plasmid cleavage
restriction-enzyme digestion of gene
isolation of gene
2
The following enzymes are used to make cDNA. What is the second enzyme used to make cDNA?
reverse transcriptase
ribozyme
RNA polymerase
DNA polymerase
2
If you put a gene in a virus, the next step in genetic modification would be
insertion of a plasmid.
transformation.
transduction.
PCR.
Southern blotting.
3
You have a small gene that you want replicated by PCR. You add fluorescent dye-labeled nucleotides to the PCR thermal cycler. After three replication cycles, what percentage of the DNA single strands will fluoresce?
0 %
12.5 %
50 %
87.5 %
100 %
4
Pieces of human DNA stored in yeast cells.
3
A population of cells carrying a desired plasmid.
2
Self-replicating DNA for transmitting a gene from one organism to another.
5
DNA that hybridizes with mRNA.
1
Analysis
Design an experiment using vaccinia virus to make a vaccine against the AIDS virus (HIV).
Vaccinia virus is an animal virus. This virus can be genetically engineered to fight against other viruses, HIV. Inject humans with the antibody made by the subunit vaccine and use the virus to cure the disease by preventing the human/host from getting HIV
Why did the use of DNA polymerase from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus allow researchers to add the necessary reagents to tubes in a preprogrammed heating block?
because it is heat resistant
-the cycle of pcr must be heated to a very hight temperature and taq polymerase is stabe to the heat required to denature DNA which is very high.
-added to extension of DNA synthesis
-can also read template strands and match to complimentary nucleotide
-PCR copies DNA- allows for Aids to be detected at an earlier stage
Taq Polymerase stable at high temps - 72 degrees
• Added for extension of DNA synthesis
• Can read template strand and match to complementary nucleosides rapidly.
Application: PCR copies DNA - allows for AIDS to be detected in early stages
The following picture shows bacterial colonies growing on plus ampicillin in a blue-white screening test.
Which colonies have the recombinant plasmid?
The small satellite colonies do not have the plasmid. Why did they start growing on the medium after the larger colonies?
The bacteria was able to pick up the original plasmid that contains the intact lac gene which in return will be able to hydrolyze X-gal produce galactose and indigo compound, hence the blue colonies. The bacteria that was able to pick up the recombinant plasmid in which new gene was inserted into the lacZ gene will result in the non-hydrolyzation of lactose, thus producing white colonies. Hence, the colonies which have recombinant plasmid are the white colonies.
The satellite colonies begin to appear after 48 hours because there is now a degradation of ampicillin present around the large colonies (there is a reduction of ampicillin, where the satellite colonies grow)
Clinical Applications and Evaluation
PCR has been used to examine oysters for the presence of Vibrio cholerae. Oysters from different areas were homogenized, and DNA was extracted from the homogenates. The DNA was digested by the restriction enzyme HincII. A primer for the hemolysin gene of V. cholerae was used for the PCR reaction. After PCR, each sample was electrophoresed and stained with a probe for the hemolysin gene. Which of the oyster samples were (was) positive for V. cholerae? How can you tell? Why look for V. cholerae in oysters? What is the advantage of PCR over conventional biochemical tests to identify the bacteria?
Vibrio cholerae is present in sample A (yellow band, 2/3 down the lane). This is presumably Vibrio cholerae specific DNA that was amplified by PCR. Because PCR can detect trace amounts of bacteria, one can pool many shell fish samples and still find the rare, trace cell by amplifying the signal. This is not too different from transistors which take a small signal and amplify it so that it can be detected.
Using the restriction enzyme EcoRI, the following gel electrophoresis patterns were obtained from digests of various DNA molecules from a transformation experiment. Can you conclude from these data that transformation occurred? Explain why or why not.
true
When comparing the Original Cell's DNA pattern to that of the Transformed Cell's, two additional bands are present in the transformed cells that were not present in the original cells. These DNA bands match the pattern produced by the Vector + new gene and indicate that they were taken up by the transformed cells