Intro to Geology - Midterm 2
0.0(0)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/157
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:48 AM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
1
New cards
geologic time
the span of time since the earths formation
2
New cards
relative age
The age of a rock compared to the ages of rock layers
3
New cards
numerical age
age of a feature given in years
4
New cards
absolute age
The age of a rock given as the number of years since the rock formed.
5
New cards
Principle of Uniformitarianism
Earth processes occurring today are similar to those that occurred in the past
6
New cards
Principle of Original Horizontality
layers of sediment are generally deposited in a horizontal position
7
New cards
Principle of Superposition
When artifacts are found in rock or earth that is layered, the deeper layers hold the older artifacts. Sediments need a layer of substate to accumulate on top of.
8
New cards
Principle of Lateral Continuity
Beds originate as continuous layers that extend in all directions until they eventually thin out or grade into a different sediment type
9
New cards
principle of cross-cutting relationships
younger features cut across older features
10
New cards
Unconformity
A break in the geologic record created when rock layers are eroded or when sediment is not deposited for a long period of time.
11
New cards
angular unconformity
tilted rocks are overlain by flat-lying rocks
12
New cards
Nonconformity
A type of unconformity in which layered sedimentary rocks lie on an erosion surface cut into igneous or metamorphic rocks
13
New cards
Disconformity
a type of unconformity in which the sedimentary layers above and below the unconformity are parallel
14
New cards
angular unconformity (diagram)
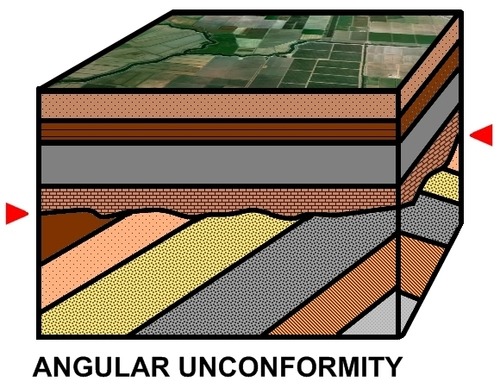
15
New cards
nonconformity (diagram)
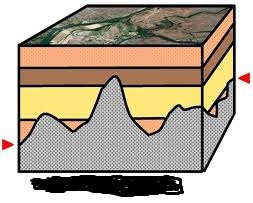
16
New cards
Disconformity (diagram)
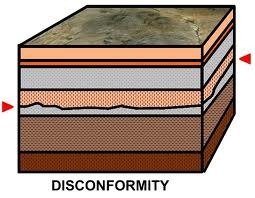
17
New cards
geologic contact
the boundary between two adjacent rock units
18
New cards
stratigraphic column
A diagram representing a series of rock layers
19
New cards
geologic map
A map showing the distribution of rock units and structures across a region.
20
New cards
geologic column
an arrangement of rock layers in which the oldest rocks are at the bottom
21
New cards
Eons
the largest division of geologic time
22
New cards
Precambrian
Name for the time in earths early history that accounts for ninety percent of earth's time, but only cellular organisms lived. (Hadean, Archean,Proterozoic, Phanerozoic)
23
New cards
era
a long and distinct period of history with a particular feature or characteristic.
24
New cards
period
further divided era of time
25
New cards
epoch
further divided period of time
26
New cards
isotopic dating
the use of naturally occurring radioactive elements to determine the ages of rocks
27
New cards
Geochronology
study of the ages of geologic events
28
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
29
New cards
radioactive decay
A spontaneous process in which unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation
30
New cards
Parent Atom
the atom that undergoes radioactive decay in a nuclear reaction
31
New cards
Daughter Atom
the product atom from the radioactive decay of a parent atom
32
New cards
half-life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
33
New cards
closure temperature
the temperature below which isotopes are no longer free to move
34
New cards
metamorphic rock
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
35
New cards
Protolith
the original rock from which a metamorphic rock formed
36
New cards
Metamorphism
the process in which one type of rock changes into metamorphic rock because of chemical processes or changes in temperature and pressure
37
New cards
metamorphic minerals
new minerals that grow in place within the solid rock only under metamorphic temperatures and pressures
38
New cards
Metamorphic textures
foliated and non-foliated
39
New cards
metamorphic foliation
A fabric defined by parallel surfaces or layers that develop in a rock as a result of metamorphism; schistocity and gneissic layering are examples.
40
New cards
differential stress
when stress is applied unequally in different directions
41
New cards
preferred orientation
The metamorphic texture that exists where platy grains lie parallel to one another and/or elongate grains align in the same direction.
42
New cards
Metasomatism
the process by which a rock's overall chemical composition changes during metamorphism because of reactions with hot water that bring in or remove elements
43
New cards
Foliation
An arrangement of minerals in flat or wavy parallel bands.
44
New cards
slate
A type of Metamorphic rock that was once shale rock formed by heat and pressure.
45
New cards
Phyllite
A fine-grained metamorphic rock with a foliation caused by the preferred orientation of very fine-grained mica.
46
New cards
Schist
Metamorphic, Foliated
47
New cards
Metaconglomerate
A metamorphic rock produced by metamorphism of a conglomerate; typically, it contains flattened pebbles and cobbles.
48
New cards
Gneiss
A metamorphic rock that has ribbon like layers. It was made from other rocks that have been squeezed and heated a long time in the Earth.
49
New cards
Migmatite
A rock formed when gneiss is heated high enough so that it begins to partially melt, creating layers, or lenses, of new igneous rock that mix with layers of the relict gneiss.
50
New cards
Hornfels
Rock that undergoes metamorphism simply because of a change in temperature, without being subjected to differential stress.
51
New cards
Quartzite
a metamorphic rock composed of quartz and transformed from a protolith of quartz sandstone
52
New cards
marble
metamorphic rock that was once limestone
53
New cards
metamorphic grade
the degree to which the parent rock changes during metamorphism
54
New cards
metamorphic facies
A set of metamorphic mineral assemblages indicative of metamorphism under a specific range of pressures and temperatures.
55
New cards
metamorphic zone
The region between two metamorphic isograds, typically named after an index mineral found within the region.
56
New cards
metamorphic aureole
The region around a pluton, stretching tens to hundreds of meters out, in which heat transferred into the country rock and metamorphosed the country rock.
57
New cards
thermal metamorphism
metamorphism caused by heat conducted into country rock from an igneous intrusion
58
New cards
contact metamorphism
A change in the texture, structure, or chemical composition of a rock due to contact with magma.
59
New cards
burial metamorphism
metamorphism due only to the consequences of very deep burial
60
New cards
dynamic metamorphism
metamorphism that occurs as a consequence of shearing alone, with no change in temperature or pressure
61
New cards
dynamothermal metamorphism
Metamorphism that involves heat, pressure, and shearing.
62
New cards
regional metamorphism
formation of metamorphic rock bodies that are hundreds of square kilometers in size
63
New cards
hydrothermal metamorphism
occurs when very hot water reacts with rock, altering its mineralogy and chemistry
64
New cards
shock metamorphism
the changes that can occur in a rock due to the passage of a shock wave, generally resulting from a meteorite impact
65
New cards
exhumation
The process (involving uplift and erosion) that returns deeply buried rocks to the surface.
66
New cards
shield
broad region of long lived, stable continental crust where sedimentary cover either was not deposited or has been eroded away so that precambrian basement rocks are exposed.
67
New cards
Mountain belts/orogens
a linear range of mountains
68
New cards
Mountain Building
Major geological event that occurs when continental plates of equal density converge, resulting in mountain chains.
69
New cards
Orogeny
a process in which a section of the earth's crust is folded and deformed by lateral compression to form a mountain range.
70
New cards
distortion
a change in the shape, size, or position of a place when it is shown on a map
71
New cards
ductile deformation
A type of solid-state flow that produces a change in the size and shape of a rock body without fracturing. Occurs at depths where temperatures and confining pressures are high.
72
New cards
Stress
A force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume
73
New cards
faults
Breaks in Earth's crust where rocks have slipped past each other.
74
New cards
strike-slip fault
a type of fault where rocks on either side move past each other sideways with little up or down motion
75
New cards
dip
angle of the planes slope
76
New cards
plunge
angle between a line and horizontal in the vertical plane that contains the line
77
New cards
bearing
compass heading of the line, meaning the angle between the projection of the line on the horizontal plane and the direction to true north
78
New cards
reverse fault
a type of fault where the hanging wall slides upward; caused by compression in the crust
79
New cards
thrust fault
a reverse fault in which the hanging wall slides over to the foot wall.
80
New cards
normal fault
A type of fault where the hanging wall slides downward; caused by tension in the crust
81
New cards
oblique-slip fault
A fault with both strike-slip and dip-slip components.
82
New cards
fault scarp
a small step on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved vertically with respect to the other
83
New cards
slickensides
The polished surface of a fault caused by slip on the fault; lineated slickensides also have grooves that indicate the direction of fault movement.
84
New cards
Rock fold
occurs when one or a stack of originally flat and planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, are bent or curved as a result of permanent deformation
85
New cards
limbs
the two sides of a fold
86
New cards
hinge
refers to a line along which the curvature of the fold is greatest
87
New cards
axial surface
the imaginary surface that encompasses the hinges of successive layers of a fold
88
New cards
Anticline
an upward fold in rock formed by compression of Earth's crust
89
New cards
Syncline
A downward fold in rock formed by compression in Earth's crust
90
New cards
Monocline
a large steplike fold in otherwise horizontal sedimentary strata
91
New cards
nonplunging fold
has a horizontal hinge
92
New cards
plunging fold
A fold in which the hinge line (or axis) is not horizontal.
93
New cards
dome
a fold with the shape of an overturned bowl
94
New cards
basin
a natural depression in the surface of the land often with a lake at the bottom of it
95
New cards
Foliation
An arrangement of minerals in flat or wavy parallel bands.
96
New cards
suture
the boundary between blocks that have been separate before the collision
97
New cards
accretion
growth in size or increase in amount
98
New cards
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
99
New cards
Isostasy
The balancing of the downward force of the crust and the upward force of the mantle.
100
New cards
crustal root
low-density crustal rock that protrudes downward beneath a mountain range
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
ANAPHY: U13.3 Digestive System (Nutrition, Metabolism, Body Temperature Regulation)
86Updated 160d ago0.0(0)
ANAPHY: U13.3 Digestive System (Nutrition, Metabolism, Body Temperature Regulation)
86Updated 160d ago0.0(0)