Periodic Trends
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
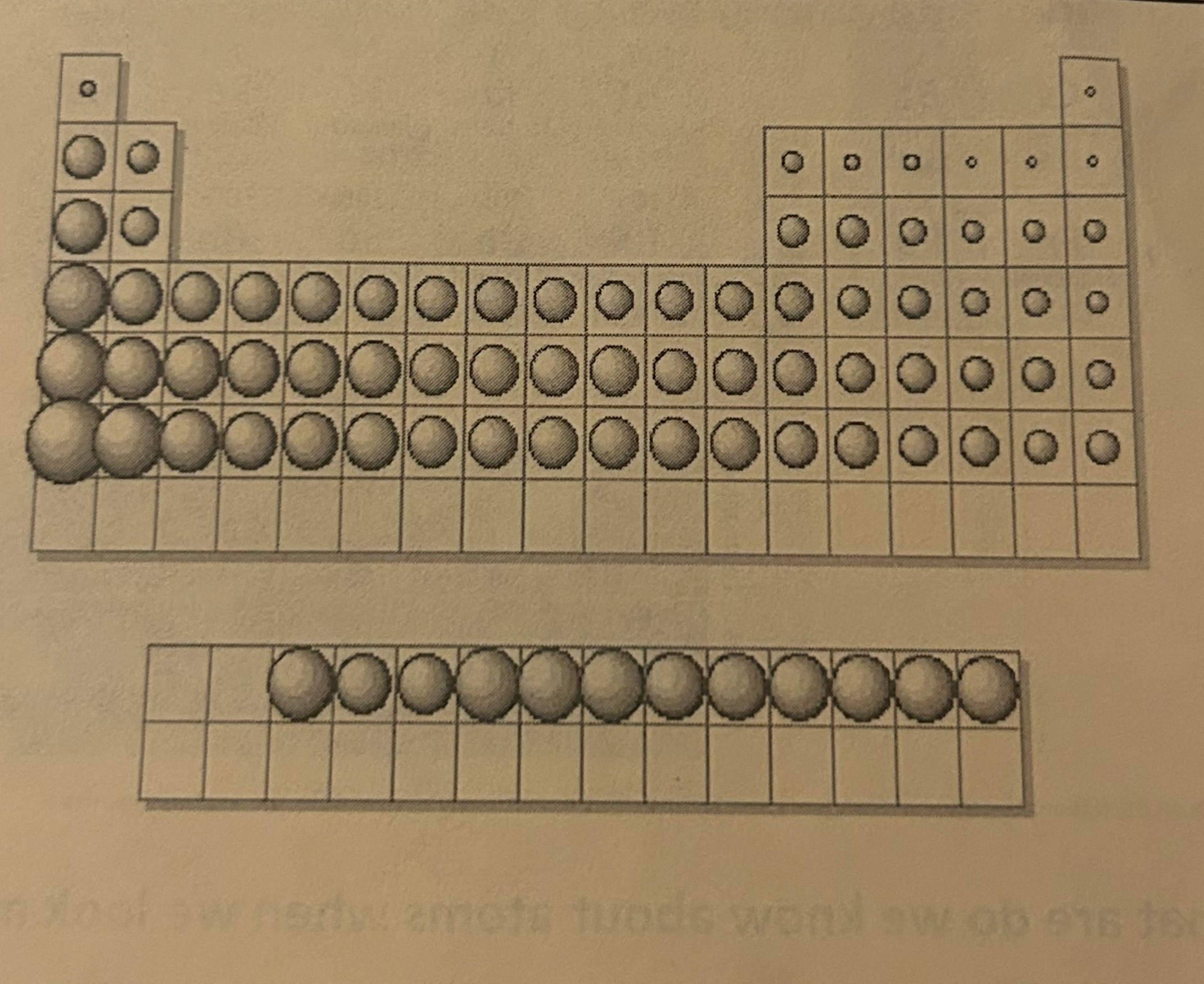
Atomic Radius
the total distance from an atom’s nucleus to the outermost orbital of electrons

Ionic Radius
One-half the diameter of an ion (size of an atom after it becomes an ion)
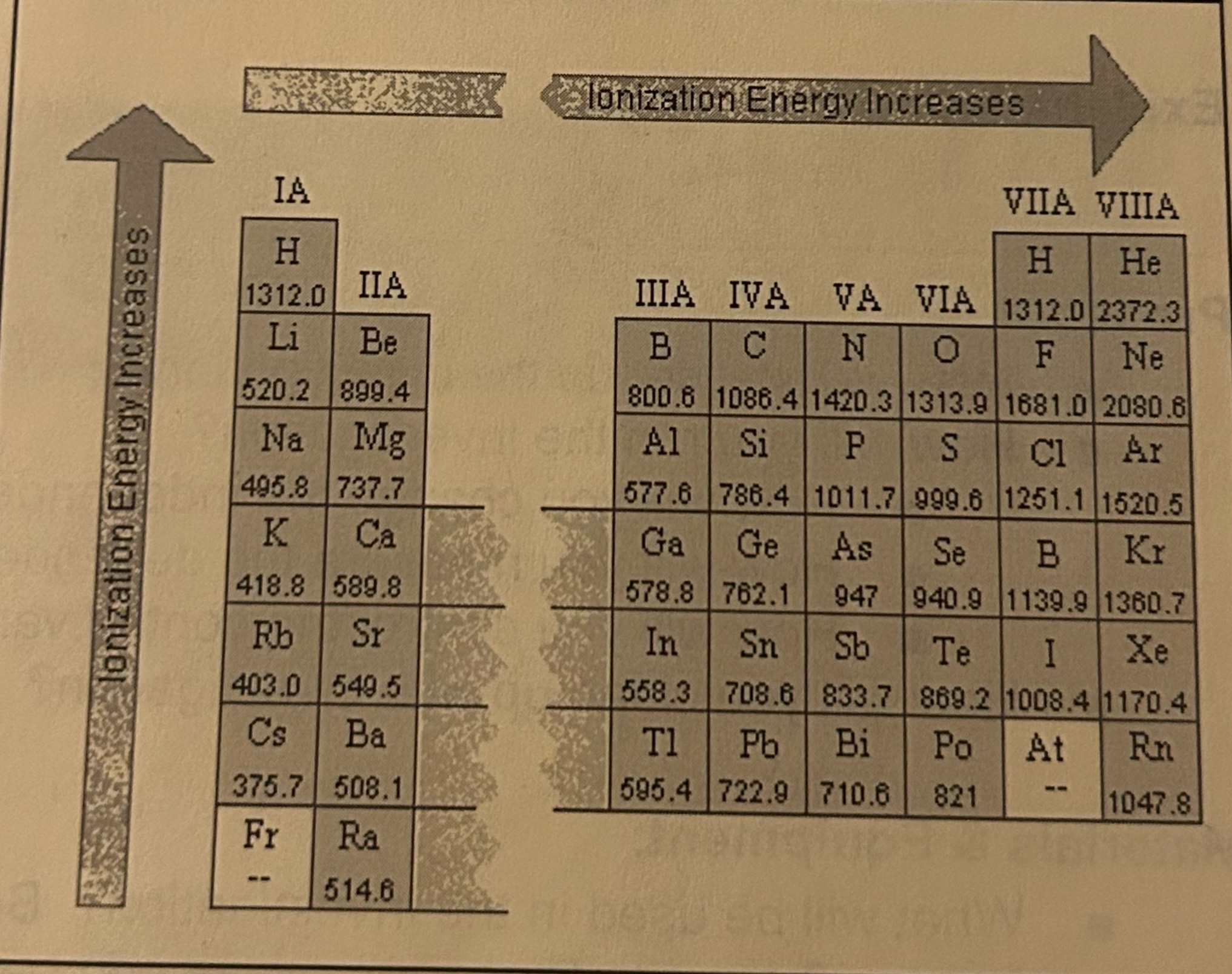
First Ionization Energy
amount of energy needed to remove one electron from an atom
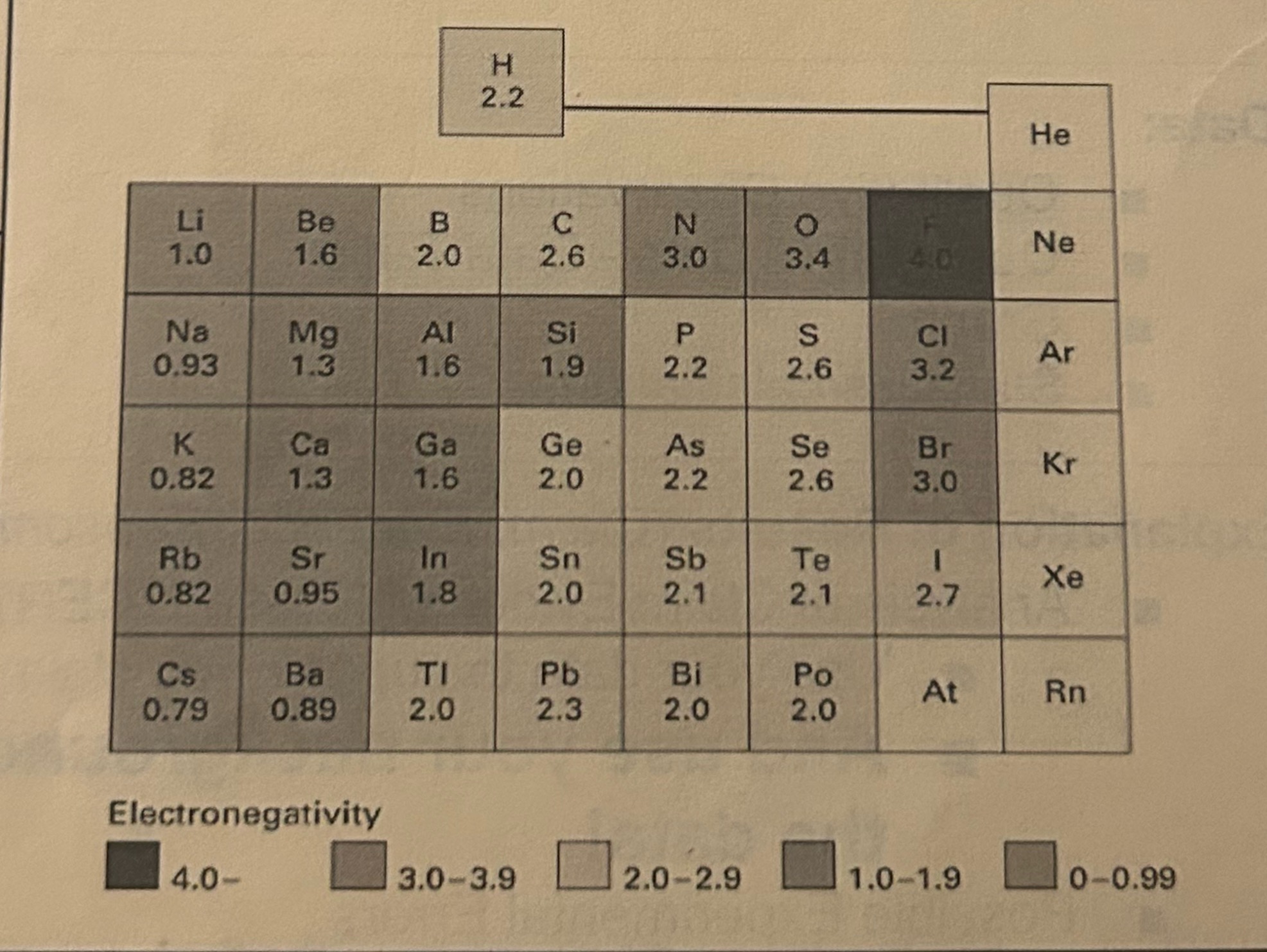
Electronegativity
how strongly an atom pulls electrons toward itself when it’s sharing them in a bond

Metallic Character
the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions or cations
Cation
positively charged atom (smaller=lose electrons)
Anion
negatively charged atom (bigger=gain electrons)
Trends that decrease across periods —>
Atomic Radius, Metallic Character
Trends that increase across periods —>
Electronegativity, First Ionization Energy
Trends that increase as you move down groups
Atomic Radius, Metallic Character
Trends that decrease as you move down groups
Electronegativity, First Ionization Energy
Core Electrons
electrons in the innermost energy levels
Valence Electrons
electrons in the outermost energy level
Hund’s Rule
electrons only pair within the orbitals when all are half-full
Aufbau’s Principle
certain order that electrons enter energy levels (1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s…)
Pauli Exclusion Principle
in pairs of electrons, one must spin counterclockwise while the other spins opposite (clockwise)
Ground State
state of electrons before and after their excited state
Excited State
electrons start jumping to higher energy levels and emitting photons