Unit 4 Phys Part C, Aerobic Cellular Respiration
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Glycolysis
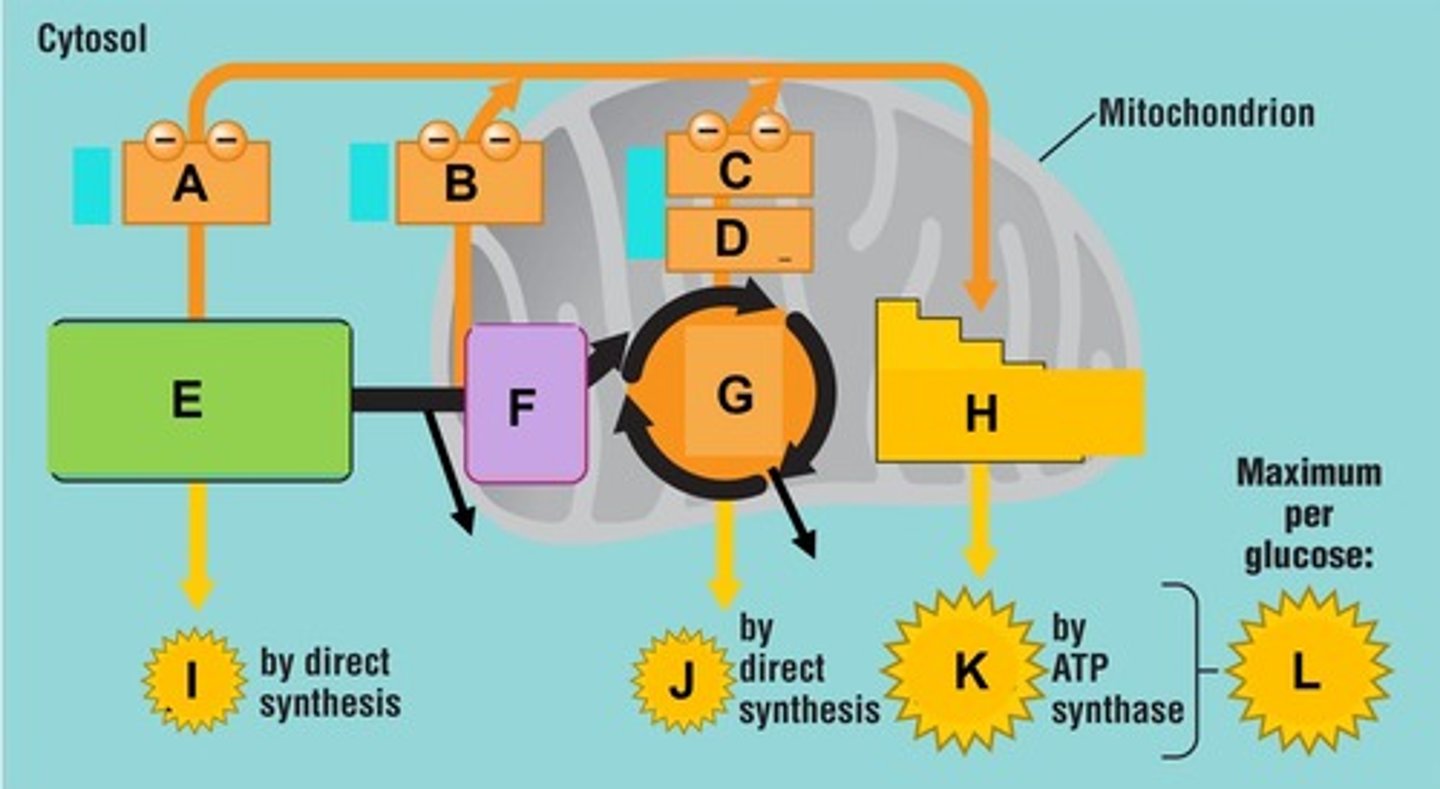
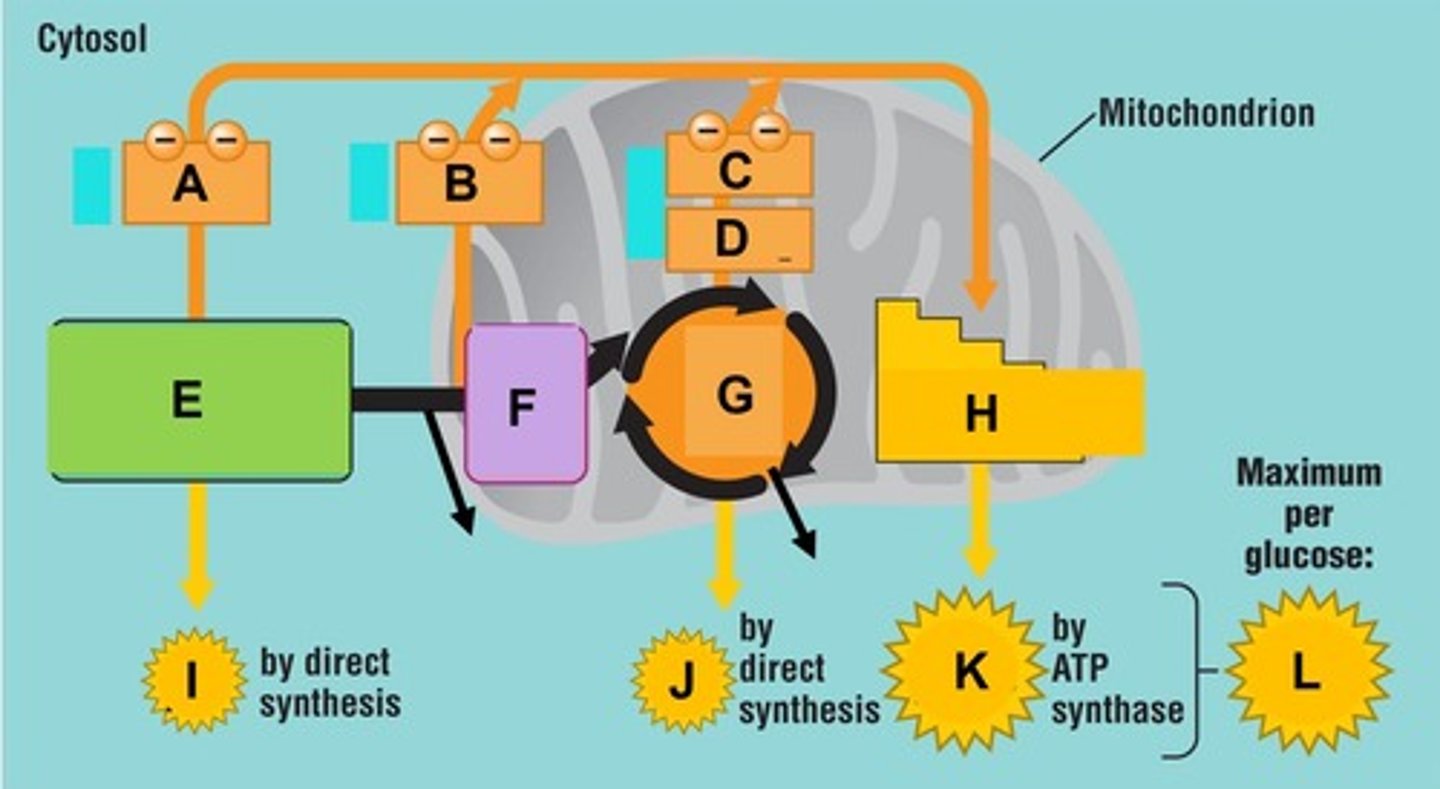
The three main phases of aerobic cellular respiration are ________________, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Letter A in the diagram
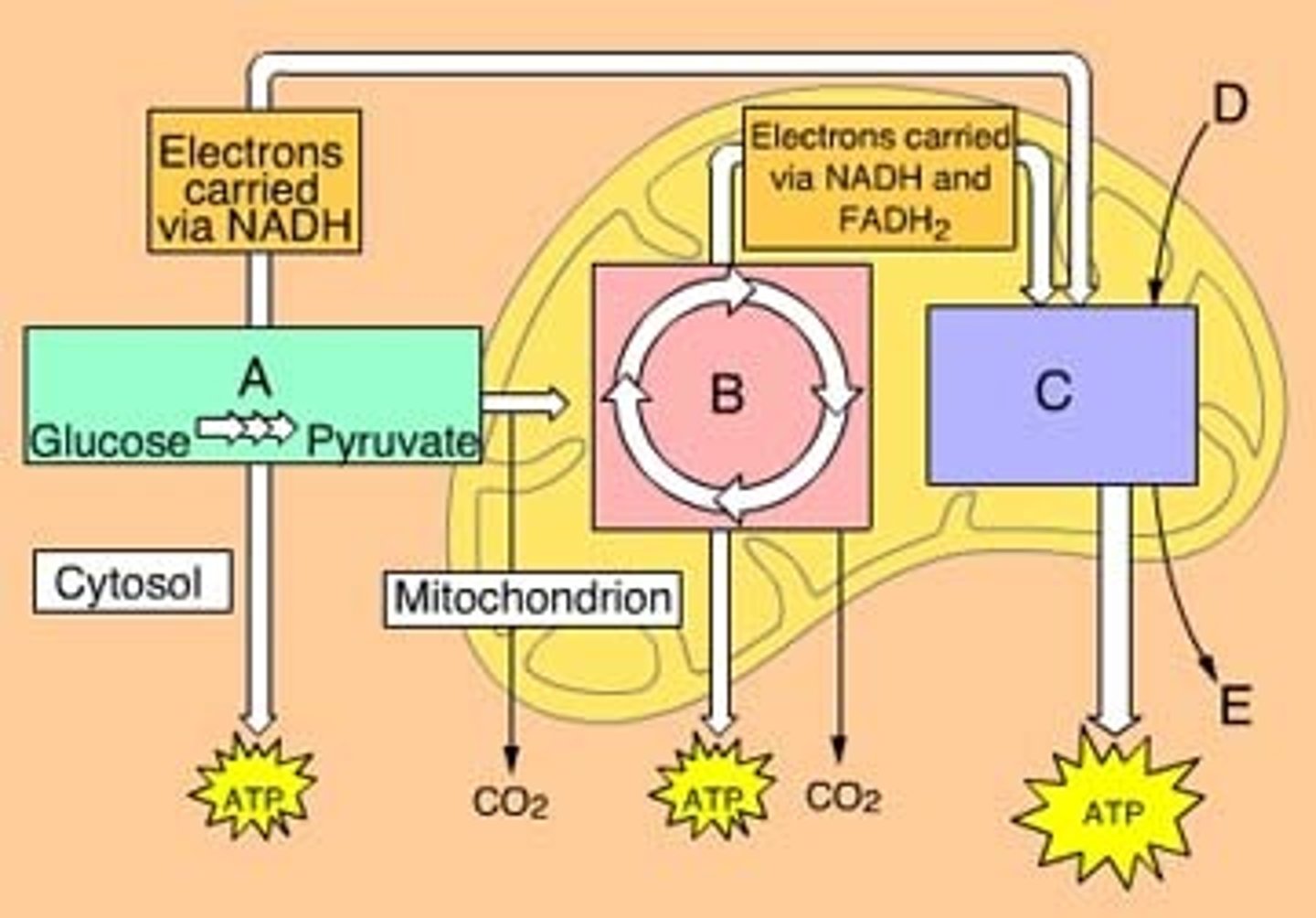
Krebs cycle
The three main phases of aerobic cellular respiration are glycolysis, __________________, and oxidative phosphorylation. Letter B on the diagram
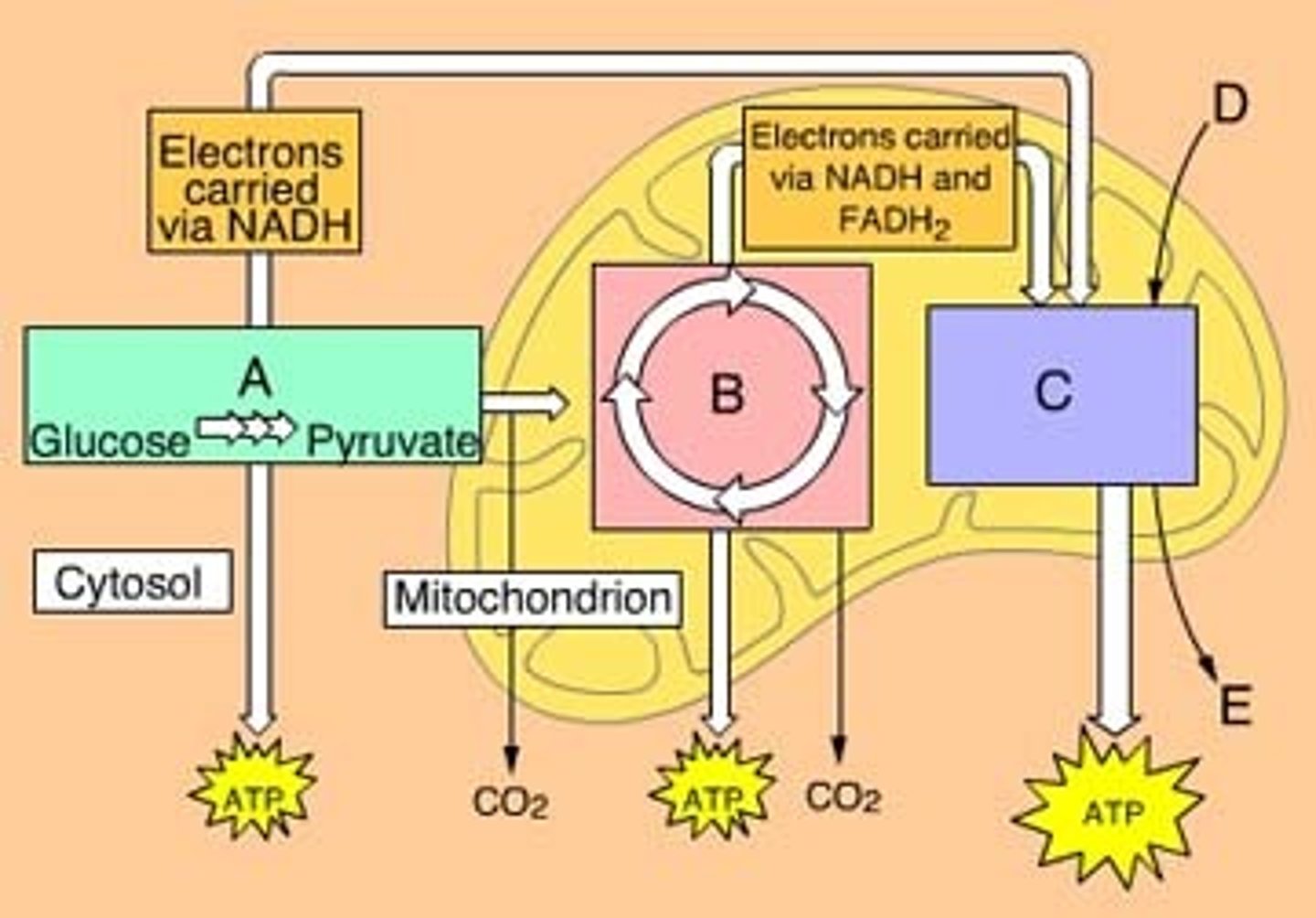
Oxidative phosphorylation
The three main phases of aerobic cellular respiration are glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and _______________. Letter C on the diagram
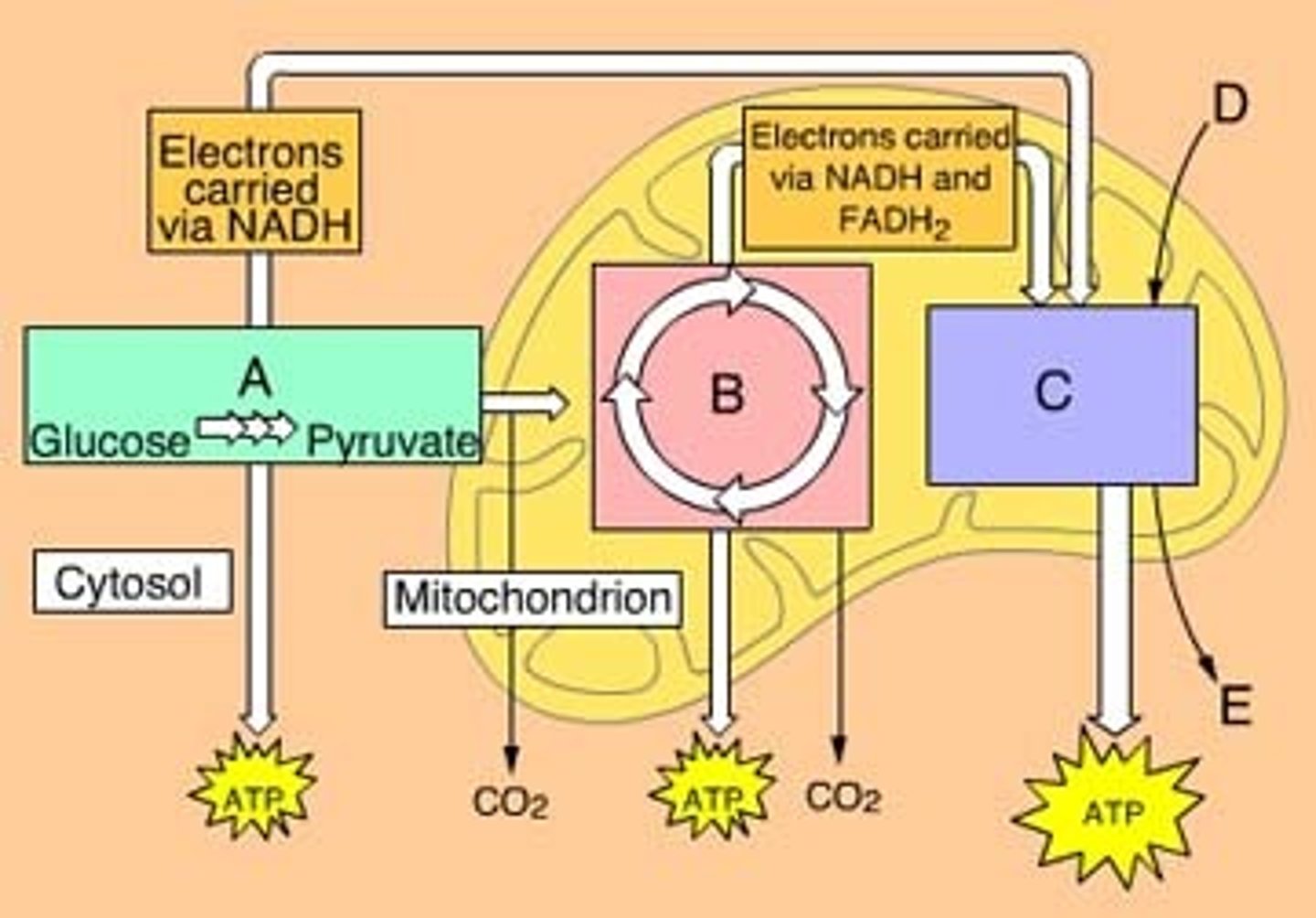
Chemiosmosis
Oxidative phosphorylation consists of the electron transport chain and _______________
Electron transport chain
Oxidative phosphorylation consists of the ____________________ and chemiosmosis
2 ATP
Per glucose molecule, the net end products of glycolysis include 2 pyruvic acid, 2 NADH, and ________________
2 Pyruvic acid
Per glucose molecule, the net end products of glycolysis include _____________________, 2 NADH, and 2 ATP
2 NADH
Per glucose molecule, the net end products of glycolysis include 2 pyruvic acid, ________________ , and 2 ATP
Acetyl CoA
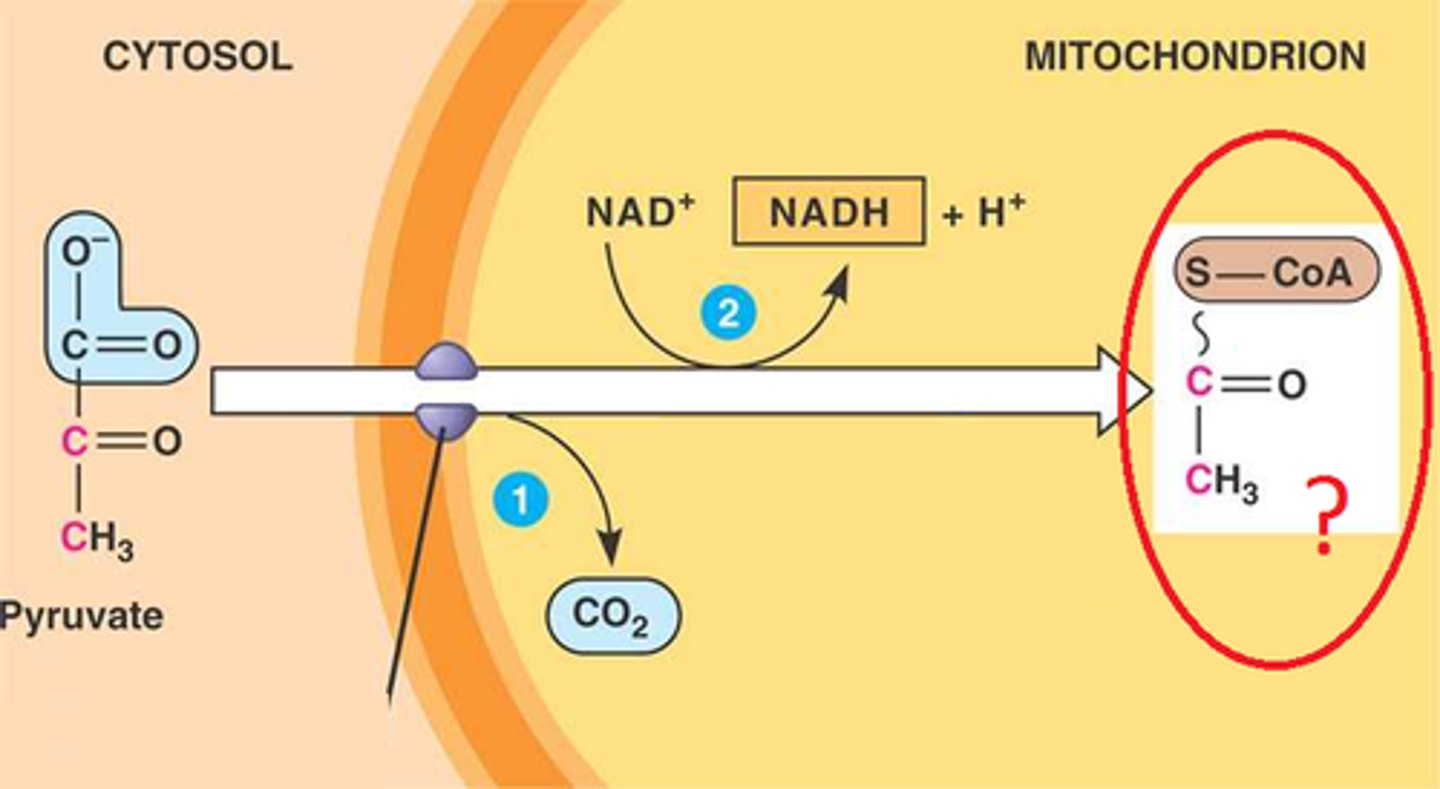
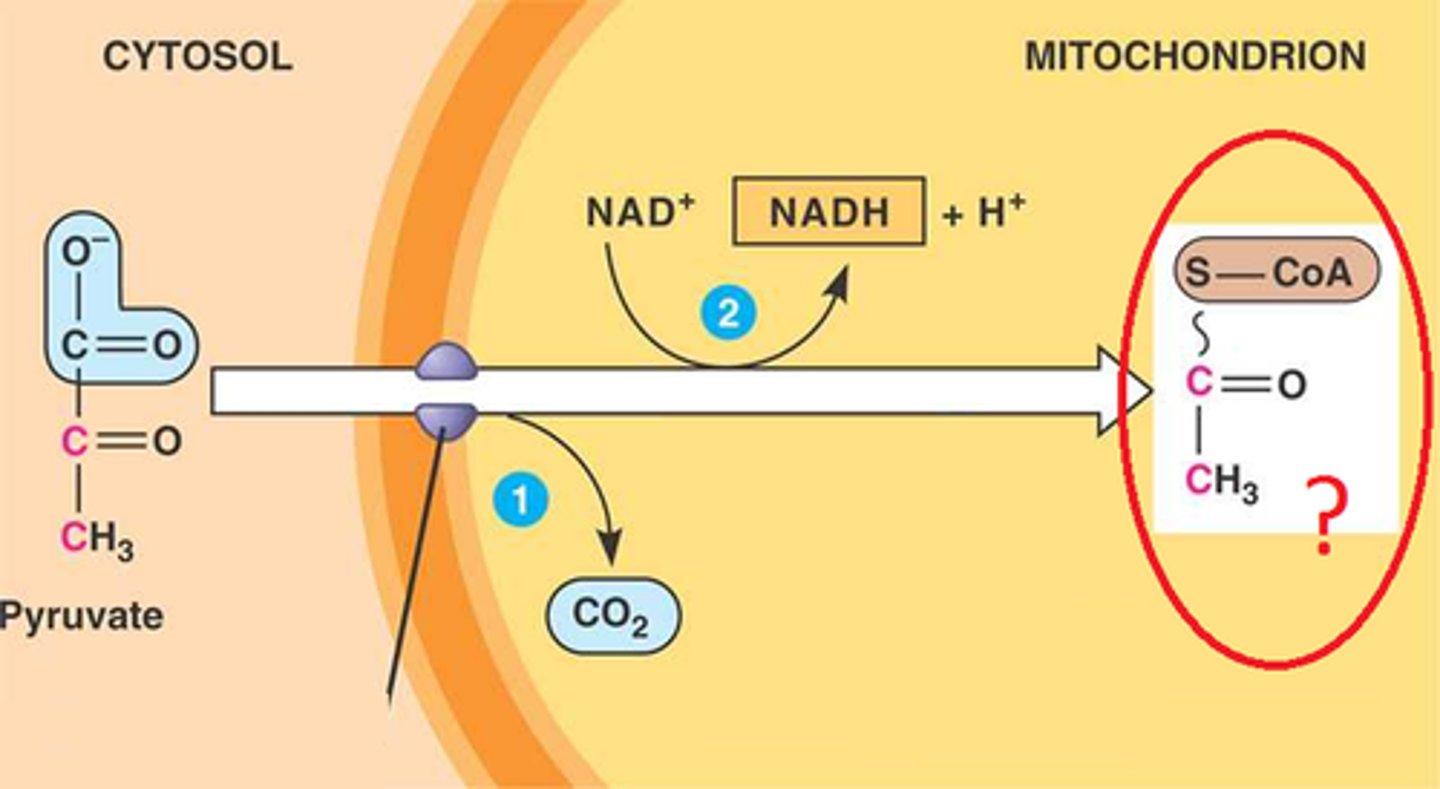
To enter the Citric Acid Cycle, pyruvic acid is moved from the cytoplasm into the mitochondrion and converted to __________________
CO2
During the formation of acetyl CoA, the carboxyl group of each pyruvic acid molecule is removed and given off as _________________ which is carried by the blood to the lungs. Answer in the form of the molecular formula.

Coenzyme A (CoA)
As pyruvic acid moves into the mitochondria it is converted to acetic acid which is then attached to a molecule called ____________________ to form acetyl CoA. Give the name and abbreviation for this molecule
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
The Krebs cycle can also be called the citric acid cycle or the ____________________
Citric acid cycle
The Krebs cycle can also be called the or the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the ____________________
Oxaloacetic acid
In the first step of the citric acid cycle, the acetic acid subunit (2 carbons long) of acetyl CoA combines with ________________________ (4 carbons long) to form a molecule of citric acid (6 carbons long).
4 CO2
Per glucose molecule the end products of the citric acid cycle are _____________, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2
2 ATP
Per glucose molecule the end products of the citric acid cycle are 4 CO2, ____________, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2
6 NADH
Per glucose molecule the end products of the citric acid cycle are 4 CO2, 2 ATP, __________________ , 2 FADH2
2 FADH2
Per glucose molecule the end products of the citric acid cycle are 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, ________________
Proton
Another name for a hydrogen ion (H+) is _______________
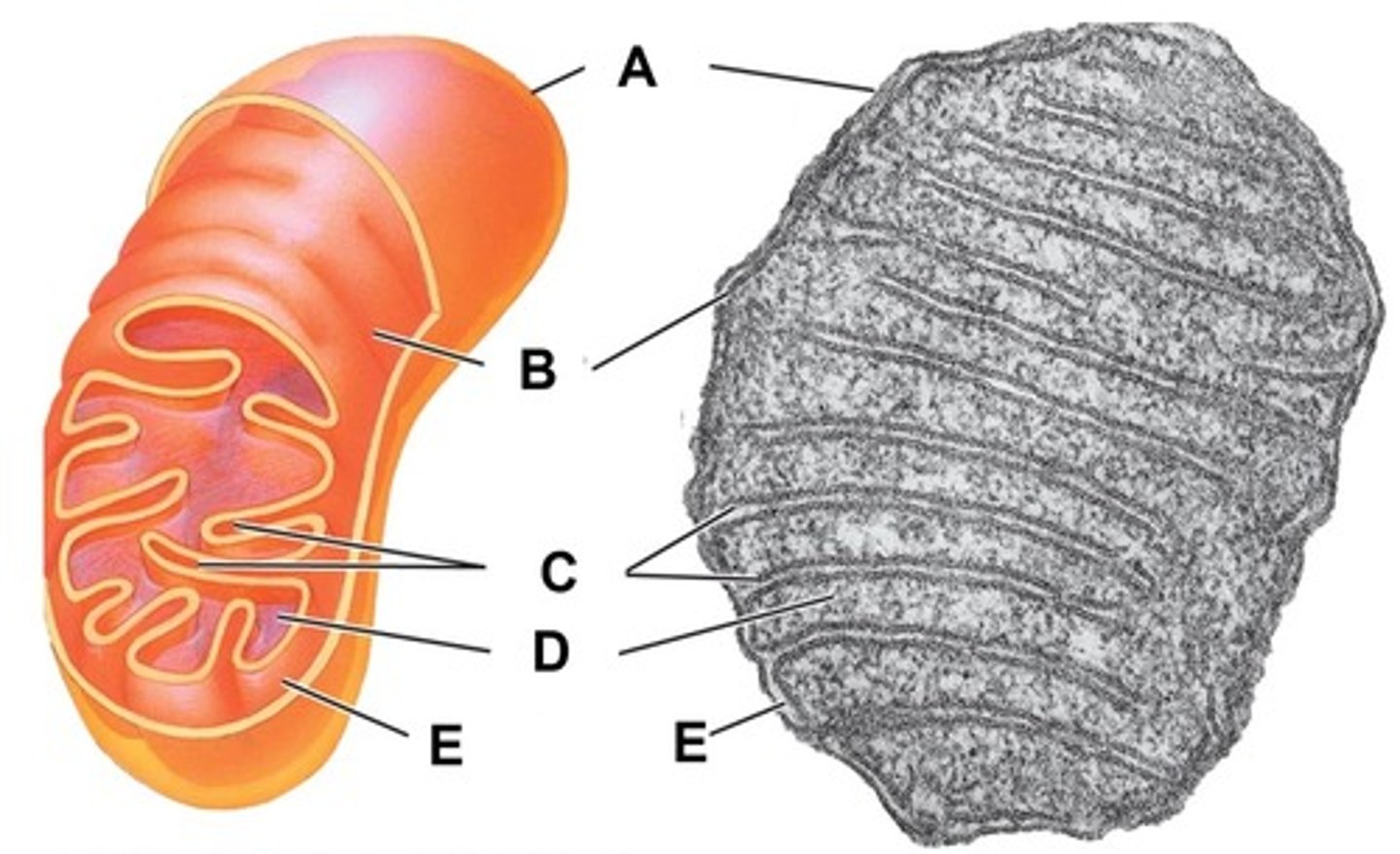
Outer membrane
Name the structure indicated by letter A
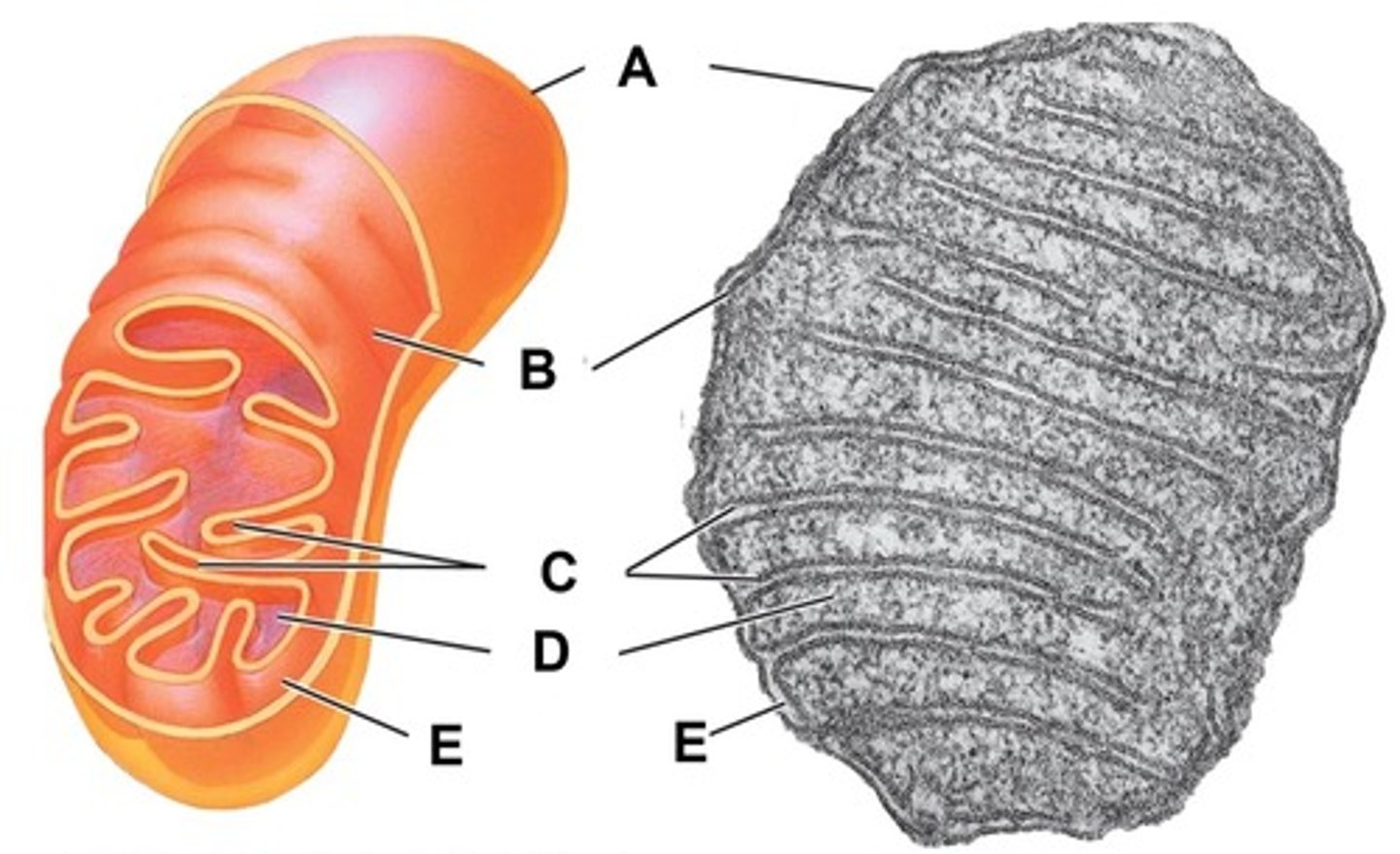
Inner membrane
Name the structure indicated by letter B
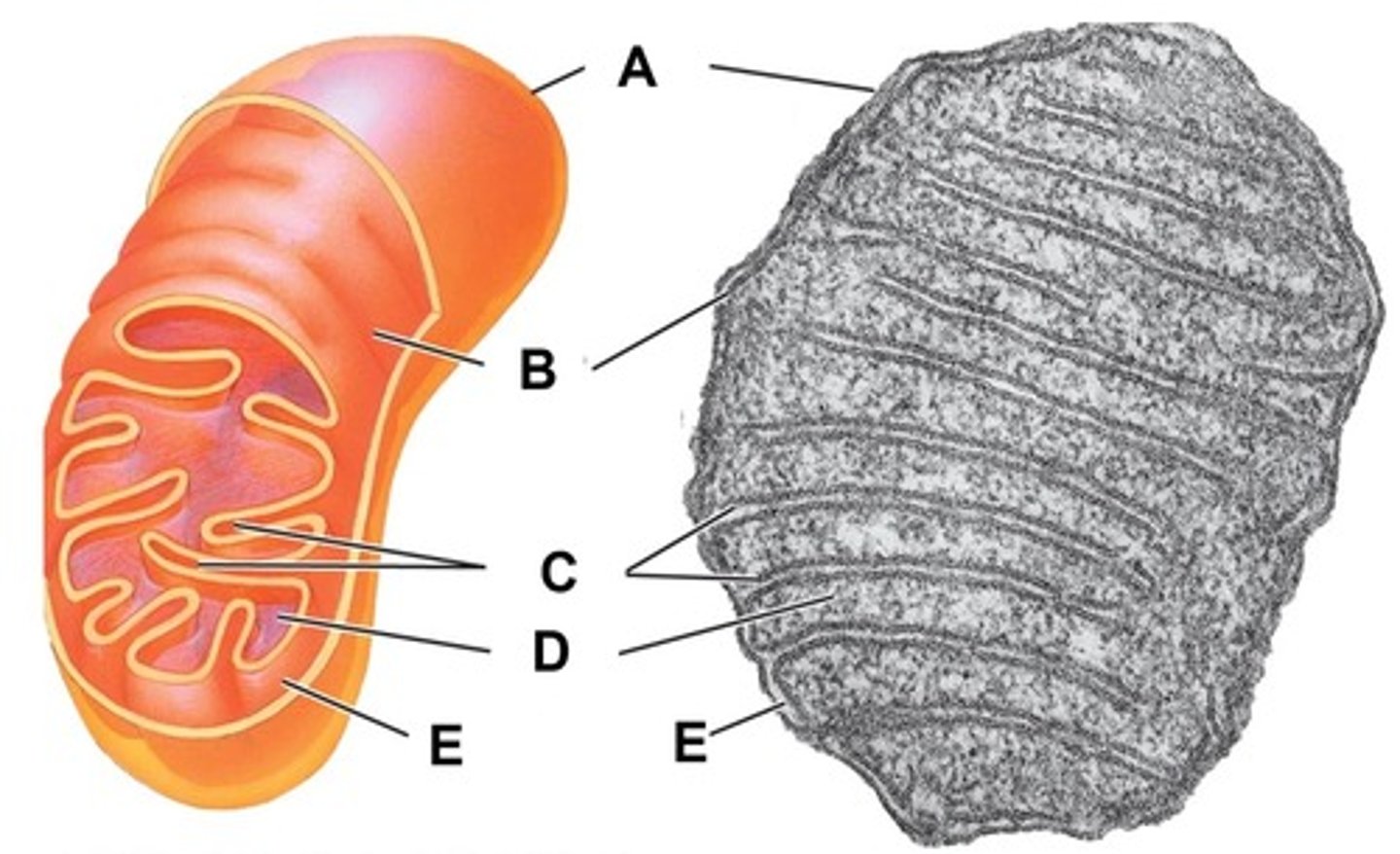
Cristae
Name the structure indicated by letter C
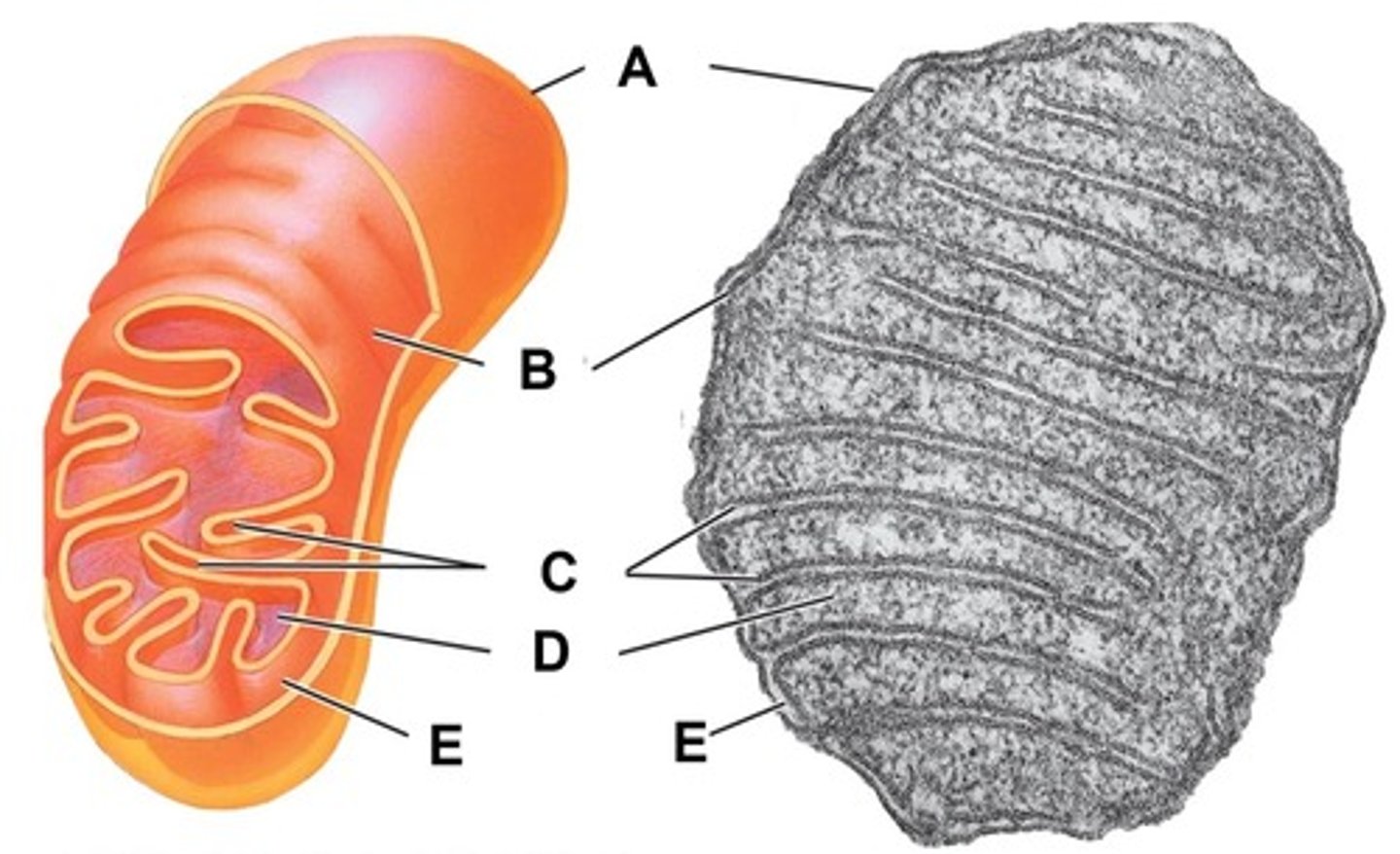
Matrix
Name the structure indicated by letter D
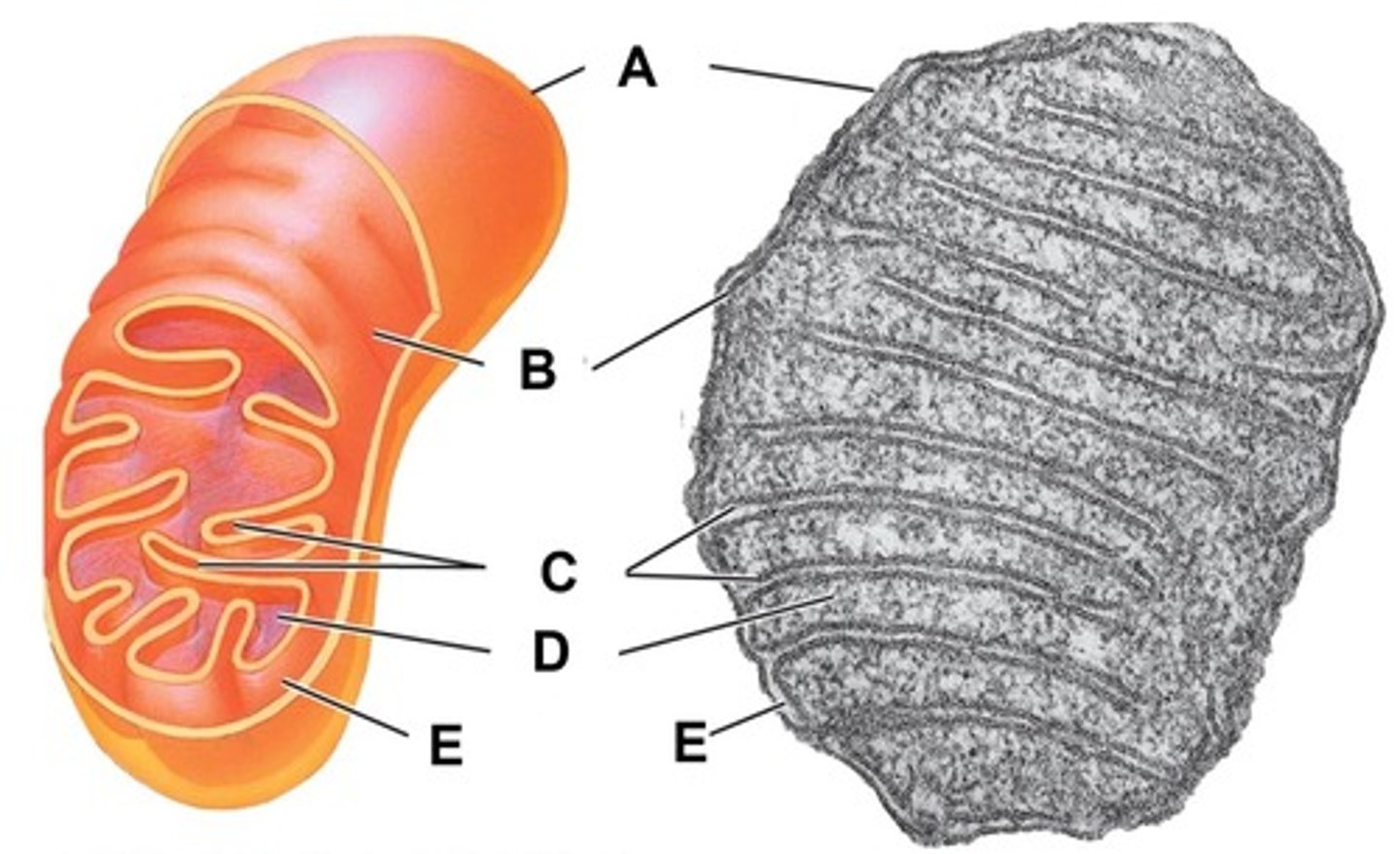
Intermembrane space
Name the space indicated by letter E
Intermembrane space
Within the mitochondrion, what term is used for the space between the outer and inner membrane?
Matrix
Within the mitochondrion, what term is used to describe the thick fluid surrounded by the cristae and contains the enzymes for the Citric Acid Cycle?
Oxidative phosphorylation
Term for the process in which ATP is formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to O2 by a series of electron carriers found in the mitochondrial inner membrane. It consists of the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
During the process of oxidative phosphorylation what term is used to describe a series of molecules embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria specialized in the transport of electrons and pumping of protons. Consists mostly of protein complexes (numbered I - IV), coenzyme Q, and cytochromes. Provide the name and abbreviation.
H+
Electrons, obtained from NADH and FADH2, move ("cascade") down the electron transport chain giving up a small amount of energy with each transfer . That energy of the electrons is used to pump ____________________ into the intermembrane space. Give symbol for the answer.
ATP synthase
The H+ (proton) gradient established in the intermembrane space is then used by an enzyme called _________________ to make ATP as H+ flows back across the innermembrane due to the proton-motive force.
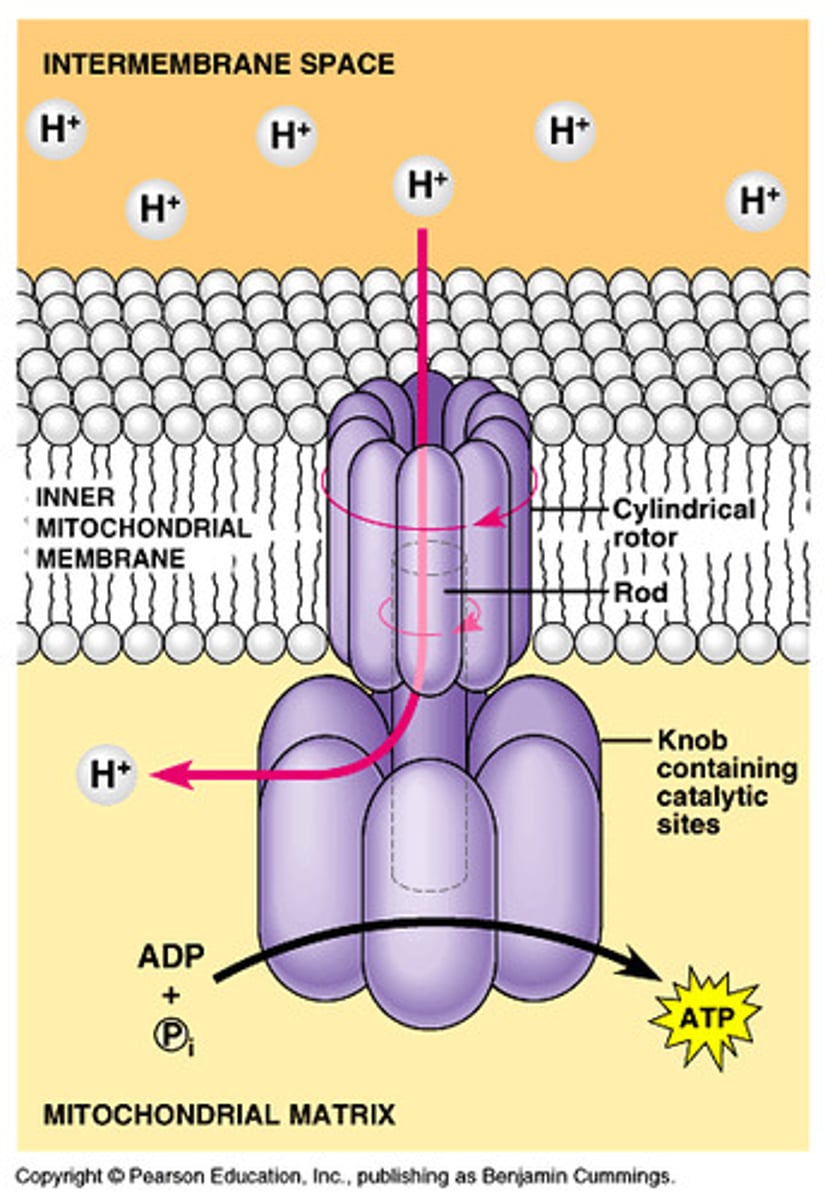
Chemiosmosis
The process of ATP production using a proton of hydrogen ion gradient is known as ________________. Hint, it is part of oxidative phosphorylation.
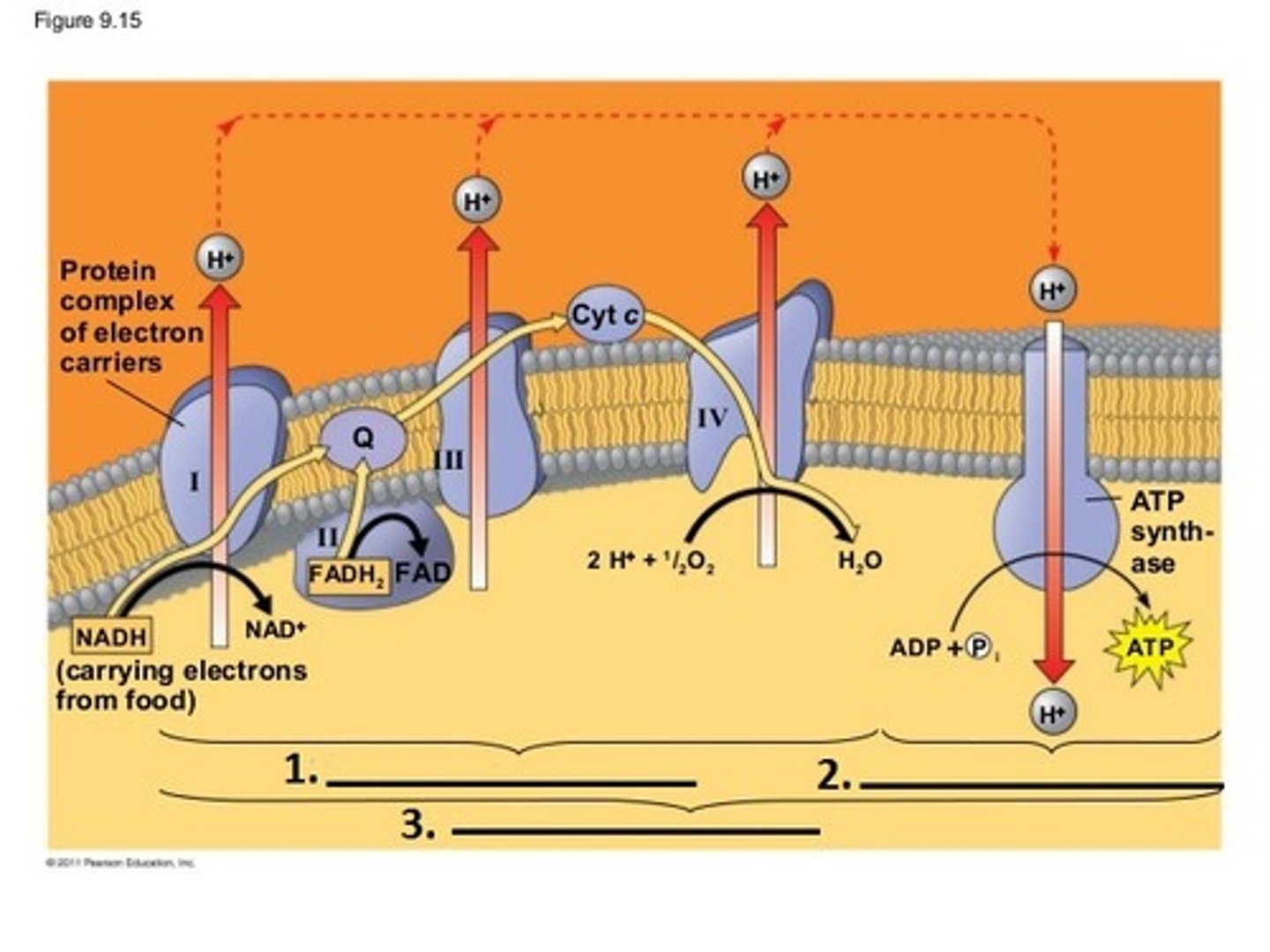
O2
During oxidative phosphorylation the final (terminal) electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is ____________________(give molecular formula), which combines with electrons and H+ ions to produce water
Electron transport chain
In the chemiosmotic mechanism, ATP production is linked to the proton gradient established by the movement of high energy electrons along the ____________________________ .
Oxidative phosphorylation
Most ATP is generated during the process of __________________________ (glycolysis, fermentation, citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation)
Oxidative phosphorylation
Of the three main stages of cellular respiration (glycolysis, citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation), which one uses oxygen directly?
Hydrogen ions
The chemiosmotic process involves the build up of what? Answer with complete name and not the symbol.
Intermembrane space
The chemiosmotic process involves the buildup of hydrogen ions where in the mitochondria?
3 ATP
About how many ATP can be generated for each NADH that transfers a pair of electrons to the electron transport chain?
2 ATP
About how many ATP can be generated for each FADH2 that transfers a pair of electrons to the electron transport chain?
FADH2
Since __________________ (NADH or FADH2) drops off its electrons further down the ETC (at protein complex II) it is responsible for transport of only enough H+ to make 2 ATPs.
2 ATP
Since FADH2 drops off its electrons further down the ETC, at protein complex II it is responsible for transport of only enough H+ to make how many ATPs?
2 ATP
The uncertainty of 36 to 38 ATP per glucose during aerobic respiration results from which shuttle is used to transport electrons from the NADH made in the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix. The electrons are passed either to FAD or to NAD+. If the electrons are passed to NAD+ then 3 ATP are produced and if passed to FAD then _____________ are produced.
Electron transport chain
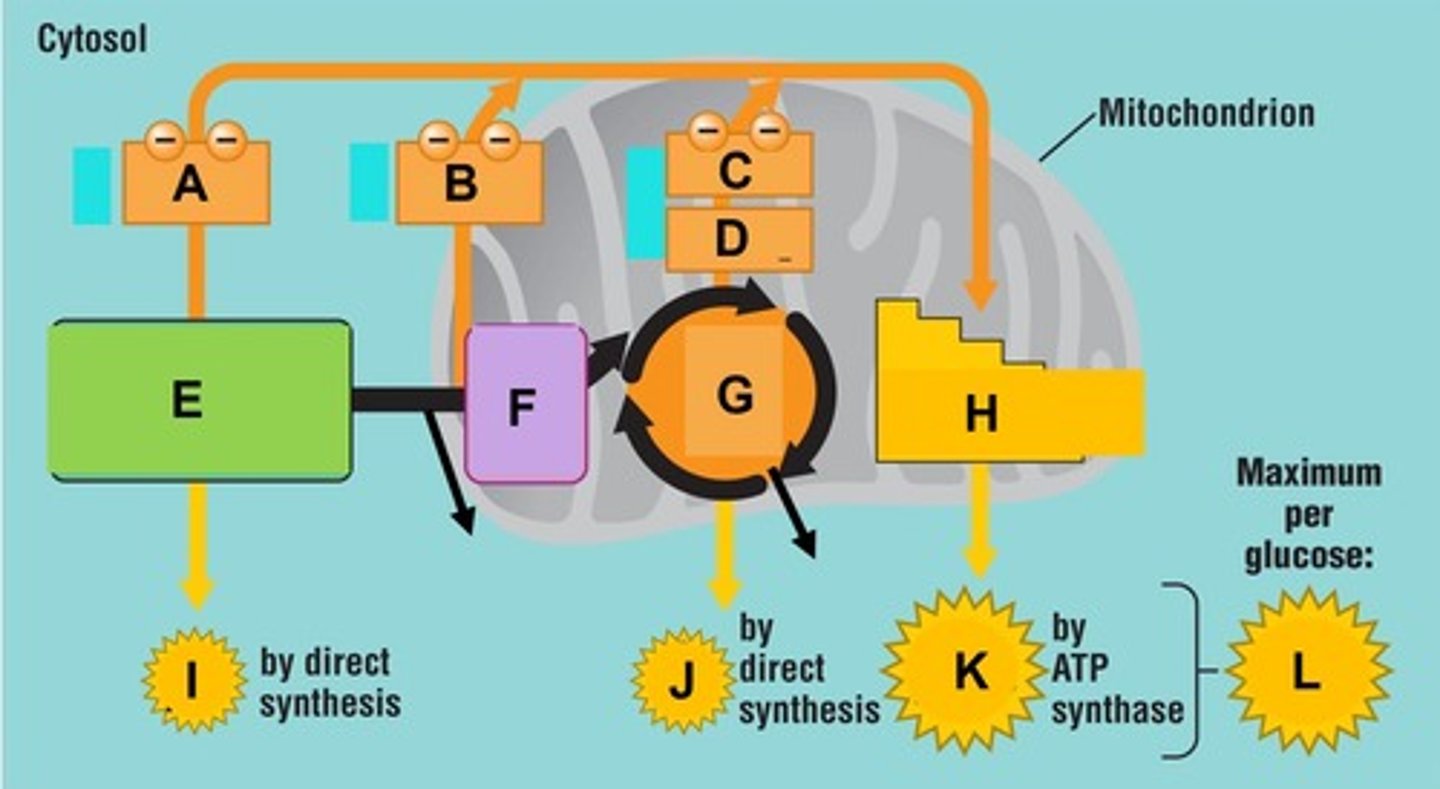
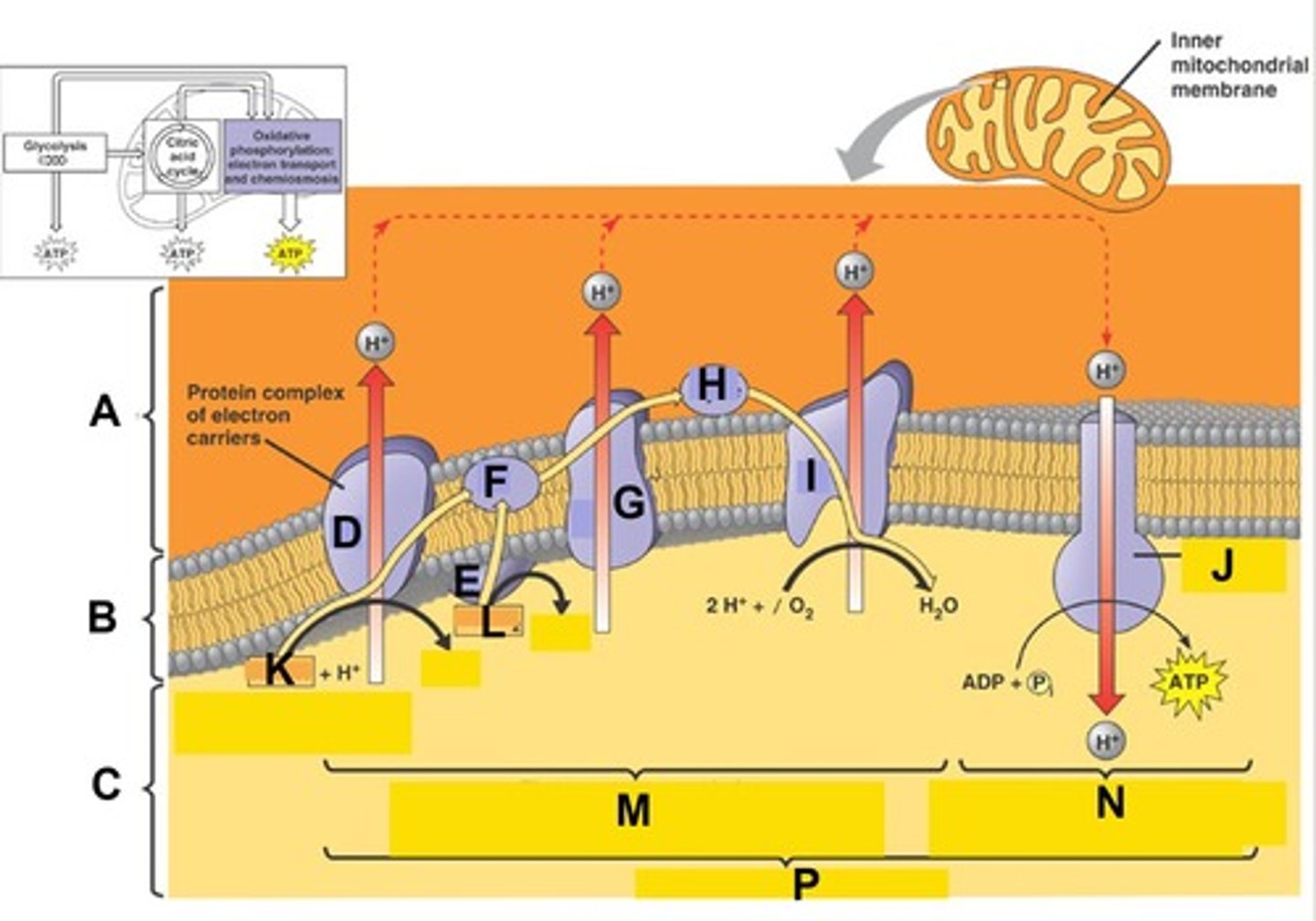
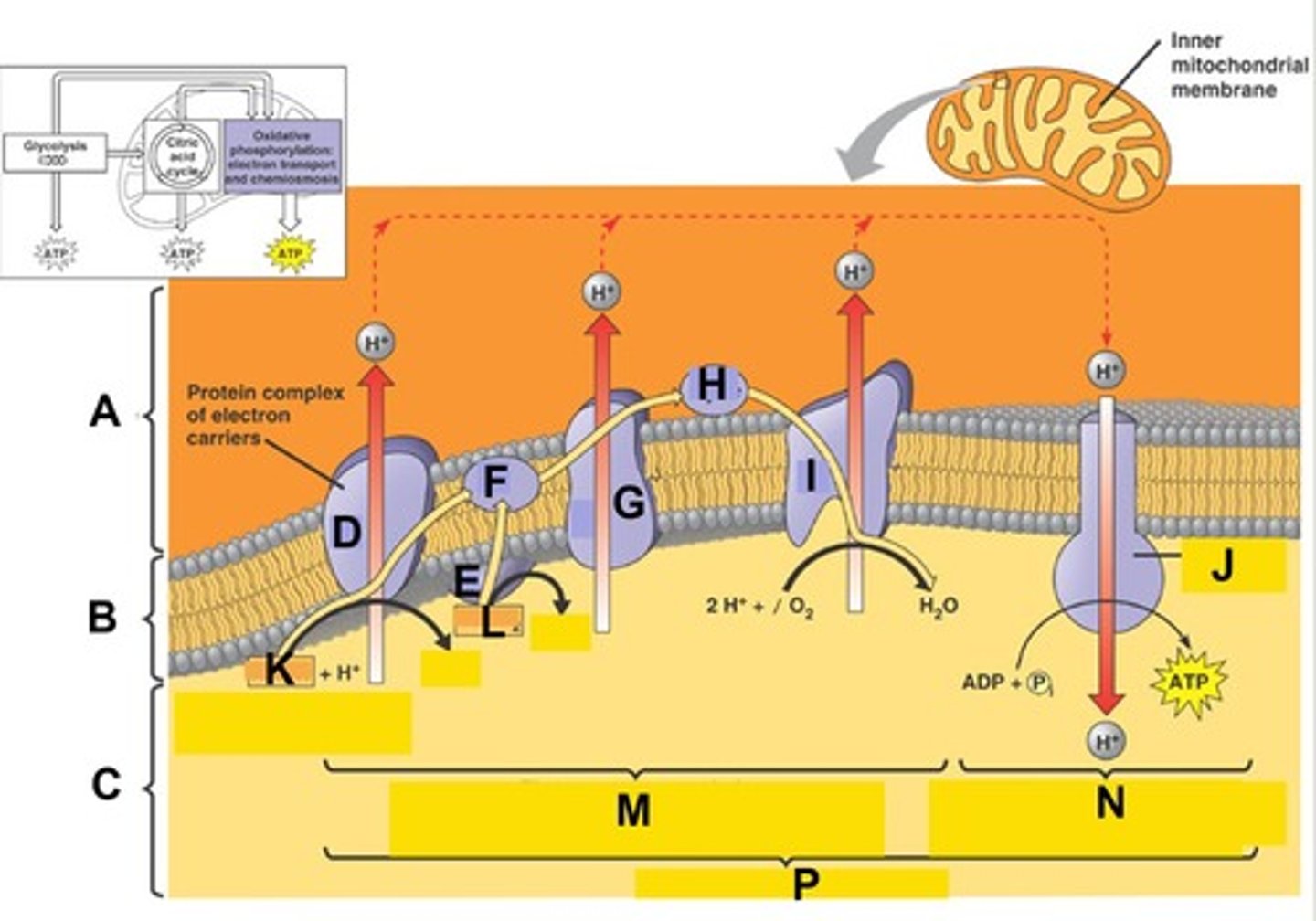
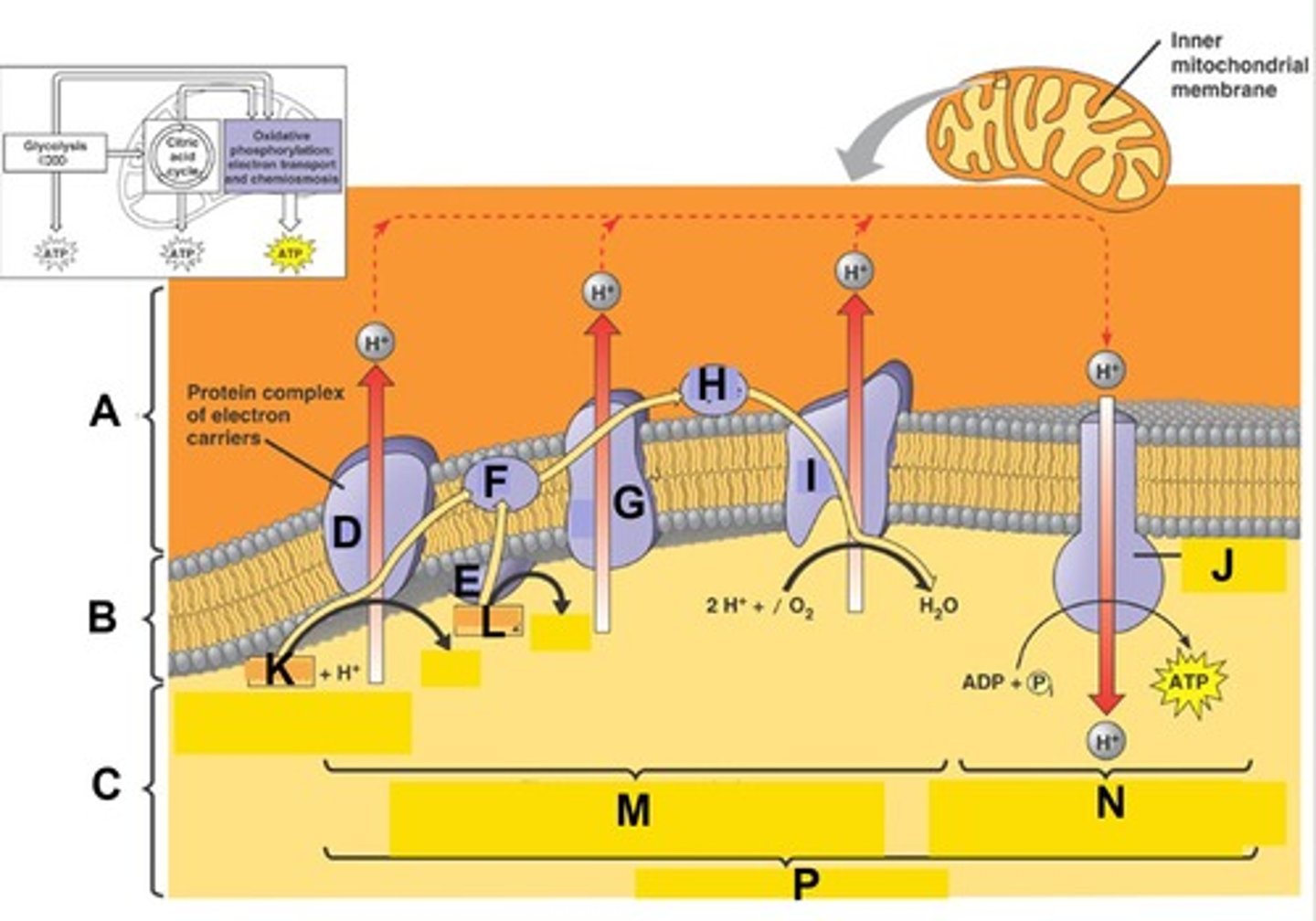
Term for the process indicated by the bracket at letter M. Here electron transport provide the energy to pump protons (H+) from the matrix to the intermembrane space creating a H+ gradient across the membrane
Chemiosmosis
Term for the process indicated by the bracket at letter N. Here ATP synthesis is powered by the flow of H+ back across the membrane
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Term for the complete process indicated by the bracket at letter P.
Inner membrane
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) is a series of molecules embedded in the _______ (inner membrane, outer membrane, or matrix) of the mitochondria and specialized in the transport of electrons and pumping of protons.
Proton-motive force
The H+ (proton) gradient by the electron transport chain is then used by ATP synthase (an enzyme) to make ATP as H+ flows back across the inner membrane due to the ___________(electron-motive force, neutron-motive force, proton-motive force).
Chemiosmosis
This process of ATP production using a proton or hydrogen ion gradient is known as __________ (chemiodiffusion, deamination, chemiophosphorylation, chemiosmosis).
Chemiosmotic theory
The theory that oxidative phosphorylation within mitochondria is driven by the development of a H+ gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane is called the ____________
Oxidative phosphorylation
ATP production powered by redox reactions of the ETC is called_________ (substrate level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation).
Oxygen
During this process oxidative phosphorylation the final (terminal) electron acceptor, is _____________________ (name and not symbol) combining with electrons and H+ ions to produce water.
Intermembrane space
Electrons, obtained from NADH and FADH2, move ("cascade") down the ETC giving up a small amount of energy with each transfer. That energy or "downhill" fall of the electrons is used to pump H+ into the _______________ (intermembrane space, outer membrane space, cytosol, matrix).
Proton-motive force
In oxidative phosphorylation, the energy or "downhill" fall of the electrons in the ETC is used to pump H+ into the intermembrane, space, forming a huge H+ gradient and a transmembrane electrical potential referred to as a _______________ (electron-motive force, neutron-motive force, proton-motive force).