Musculoskeletal NUR 310
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Musculoskeletal Assessment
(206) What is the purpose and function of our musculoskeletal system?
Joints, cartilage, and muscle / Neuromuscular Junction
Electrical Bone Growth Stimulation / Drug Therapy / Nutrition
Gerontologic Considerations Effects of Aging
- Functional problems
- Decreased bone density: Increased risk for osteopenia and osteoporosis
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
- Decreased flexibility
- Increased risk for osteoarthritis
- Risk for falls: changes in proprioception (awareness of self in relation to the environment)
Nursing Assessment -subjective / Objective / Other
Sub: PMH / Medications / Surgery or other treatments / Functional health pattern
Obj: Physical exam: Inspect, palpate, motion, strength, measurement / Ganiometer
Other:Assistive devices, posture, gait, straight-leg
Normal musculoskeletal assessment
- Ordinary spinal curvature
- No muscle atrophy or asymmetry
- No joint swelling, deformity, or crepitation
- No tenderness on palpation of spine, joints, or muscles
- Full ROM of all joints without pain or laxity
- Muscle strength 5/5
Diagnostic Studies- Serology
•Alkaline phosphatase
•Antinuclear antibody (ana)
•Calcium
•C-reactive protein (crp)
•Creatine kinase (ck)
•Potassium
•Phosphorus
Rheumatoid factor (rf)
Diagnostic studies – radiology
•Basic x-ray
•Bone scan
•Computed tomography scan (ct scan)
•dual energy xray absorptiometry (dexa)
•Electromyogram (emg)
•Mri
•Myelogram with or without ct
•Quantitative ultrasound (qus)
•Arthrocentesis
•Arthroscopy
Health promotion & Prevention
•Wear seatbelt Table 62.1
•Drive within the speed limit Problems in the elderly
•Avoid distractions Falls
•Avoid etoh or drugs
•Warm up muscles before exercise
•Use protective equipment
•Use proper safety equipment at work
Soft Tissue injuries: Sprain & Strain ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Treatment)
•Sprain: injury to the ligamentous structure of a joint
•Strain: excessive stretching of a muscle (occurs in large muscles)
•Signs/Symptoms: Edema, Pain, Decreased Function, Contusions, Muscle Spasms
•Complications: Fracture, Hemarthrosis Diagnostics: X-rays
Treatment: NSAID’s Nursing care: RICE
Soft Tissue injuries: Dislocation & Subluxation (Def. / What's affected? / Comp. / Diagnostic / Nursing Care)
Dislocation: complete displacement or separation of the joint
Subluxation: partial displacement of joint surface
Joints affected: thumb, elbow, shoulder, hip
Signs/Symptoms: joint deformity, local pain, tenderness, loss of function, swelling (5)
Complications: Open joint injuries, fractures, necrosis, tissue damage
Diagnostic: X-ray, joint aspiration
Treatment: General anesthesia, conscious sedative, NSAID’s
Nursing Care: Keep limb immobile, ROM exercise
Soft Tissue Injuries: Repetitive Strain Injury (Def. / S&S / Treatment)
•Injury resulting from prolonged force, repetitive movements, and awkward postures
•Signs & Symptoms: inflammation, swelling, pain at site of injury, impairment of motor function
•Treatment: Heat/Cold, NSAID’s, Rest, PT (for strengthening and conditioning), lifestyle changes
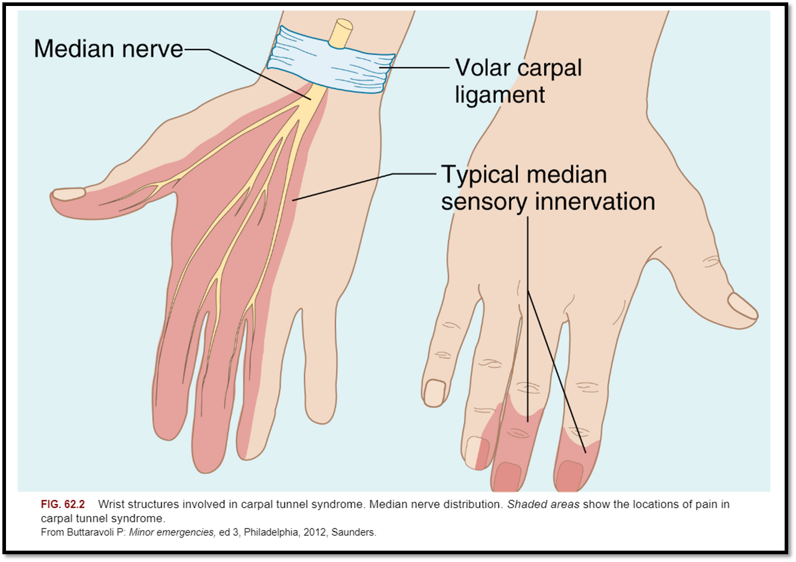
Soft Tissue Injuries: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (Cause / S&S / Diagnostics / Treatment / Nursing Care)
•Caused by compression of the median nerve, or pressure from trauma or edema caused by inflammation of a tendon, neoplasm, RA, or soft tissue mass.
•Signs/Symptoms: weakness, burning pain, numbness, impaired sensation, clumsiness, may awaken patient at night with numbness and tingling.
•Diagnostics: Tinel’s and Phalen’s Test
•Treatment: Corticosteriod injections, surgery
•Nursing Care: wrist splints and physical therapy
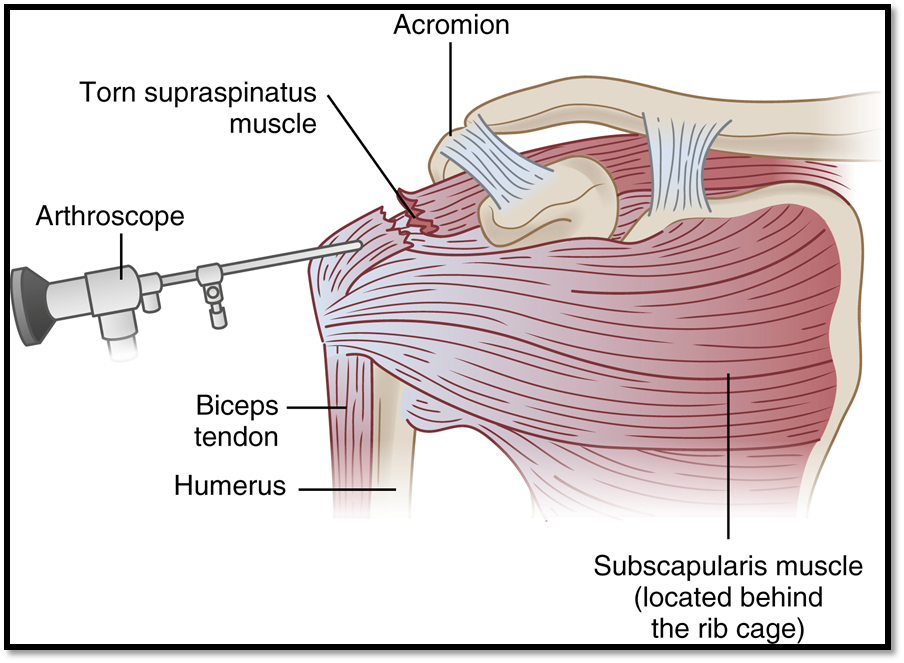
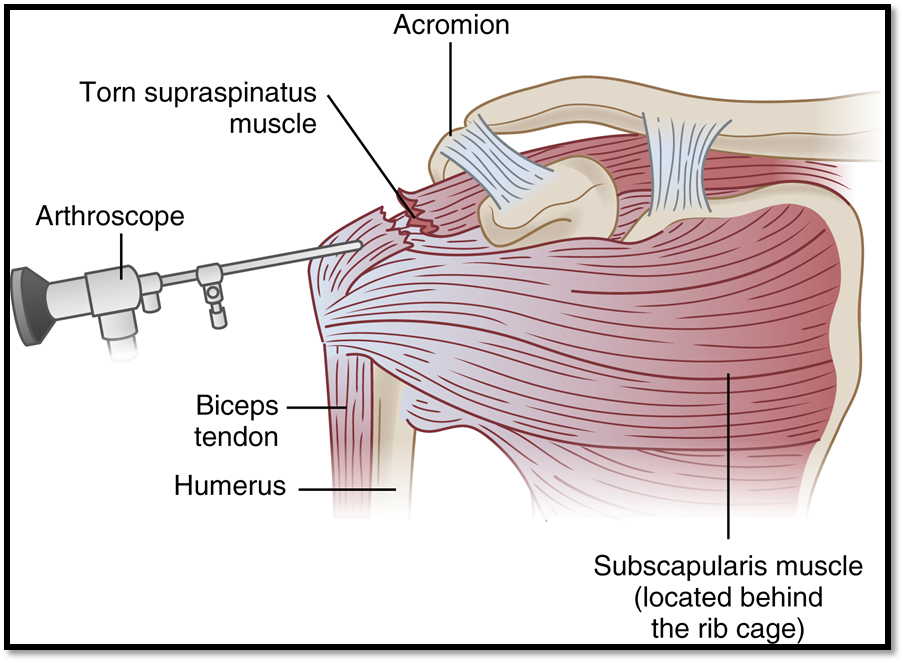
Soft Tissue Injuries: Rotator Cuff Injury (Def. / S&S / Comp / Diagnostics / Treatment / Nursing Care)
•A tear in the shoulder
•Signs/Symptoms: shoulder weakness and severe pain, decreased ROM
•Complications: Frozen shoulderà arthrofibrosis
•Diagnostics: Drop arm test, MRI
•Treatment: Rest, ice, heat, NSAIDs, Corticosteriods, surgery, sling
•Nursing Care: restrict heavy lifting, pendulum exercises
Soft Tissue Injuries: Meniscus Injury (Def. / S&S / Comp / Diagnostics / Tx)
•Knee: ligament sprains common in sports
•Signs/Symptoms: localized tenderness, pain at the knee, excessive fluid and swelling at knee, pt states it “clicks, pops, or locks often”
•Complication: Arthritis
•Diagnostics: MRI
•Treatment: examine within 24 hours of injury, ice, immobilization, weight bearing as tolerated with crutches, knee brace, immobilizer, PT, surgery, NSAIDs, Rehabilitation, teach pt to do warm up exercises
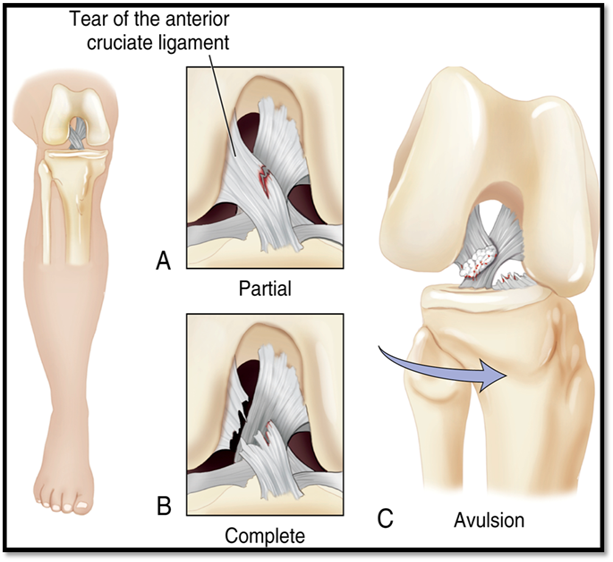
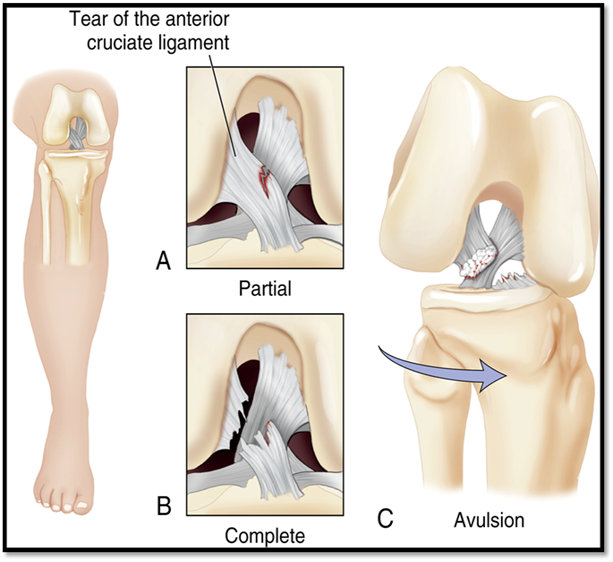
Soft Tissue Injuries: Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury (ACL) (Def. / S&S / Comp / Diagnostics / Tx)
Noncontact injuries: when athletes pivots, lands from a jump, or slows down when running
Signs/Symptoms: knee twisting, hearing a pop followed by knee pain & swelling
Complications: partial or complete tear
Diagnostics: MRI, Lachman’s test
Treatment: Reconstructive surgery, Rehab with PT, Conservative treatment, aspiration, knee is in brace/immobilizer, ROM
Soft Tissue Injuries: Bursitis
•Inflammation of the bursa due to repeated trauma or excessive friction to the area
•Signs/Symptoms: warmth, pain, swelling, limited ROM
•Sites: hands, knees, greater trochanters of the hips, shoulders, and elbows
•Treatment: Rest, ice, NSAID’s, aspiration, bursectomy, compression dressing or splint.
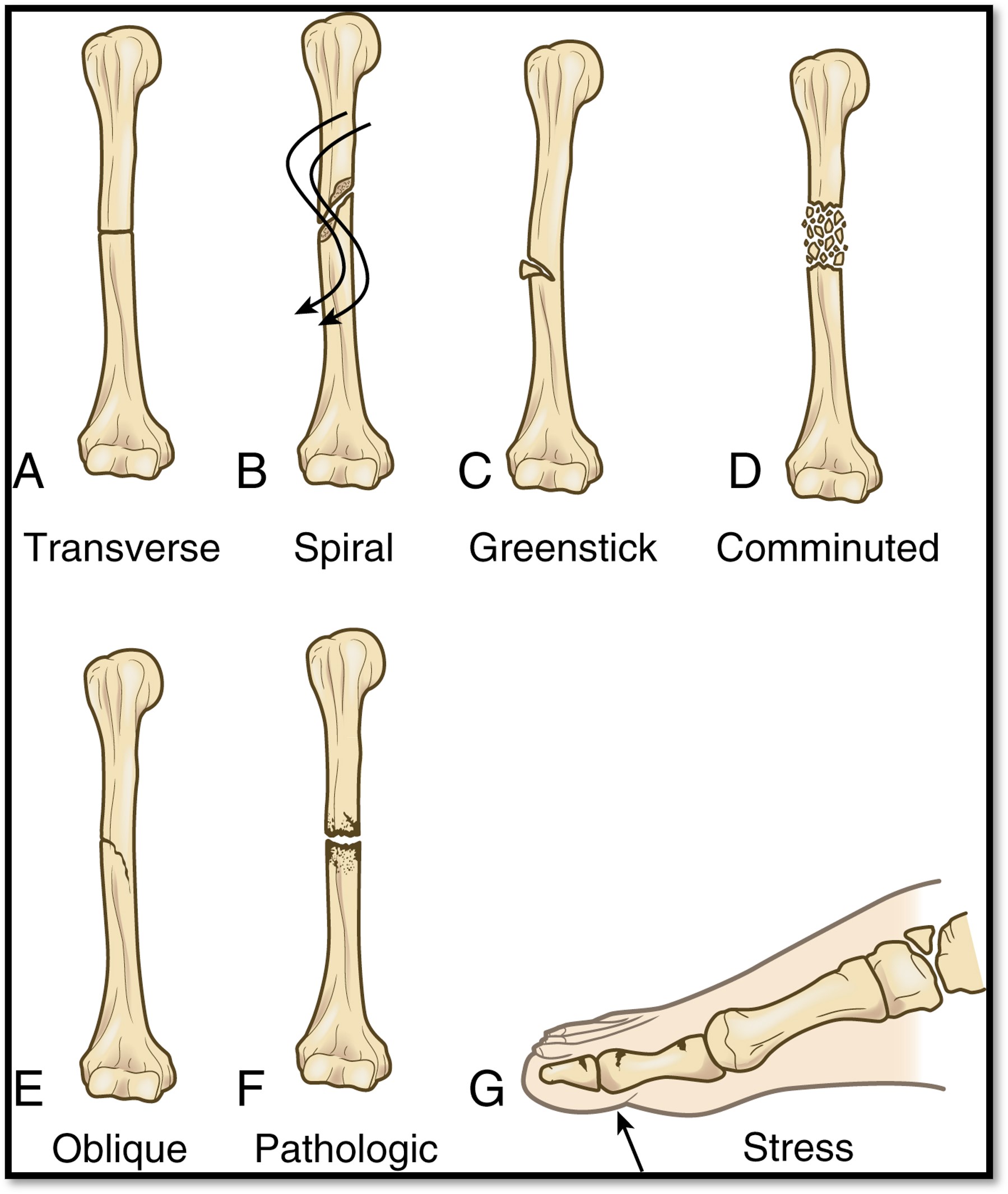
Fractures ( what is it? and Classifications?)
•Disruption or break in the continuity of bone
•Multiple classifications:
•Open or closed
•Complete or incomplete
•Direction of fracture line: Oblique, transverse, linear, longitudinal, spiral
•Displaced or: Comminuted or oblique
•Non-displaced: Transverse, spiral, or greenstick
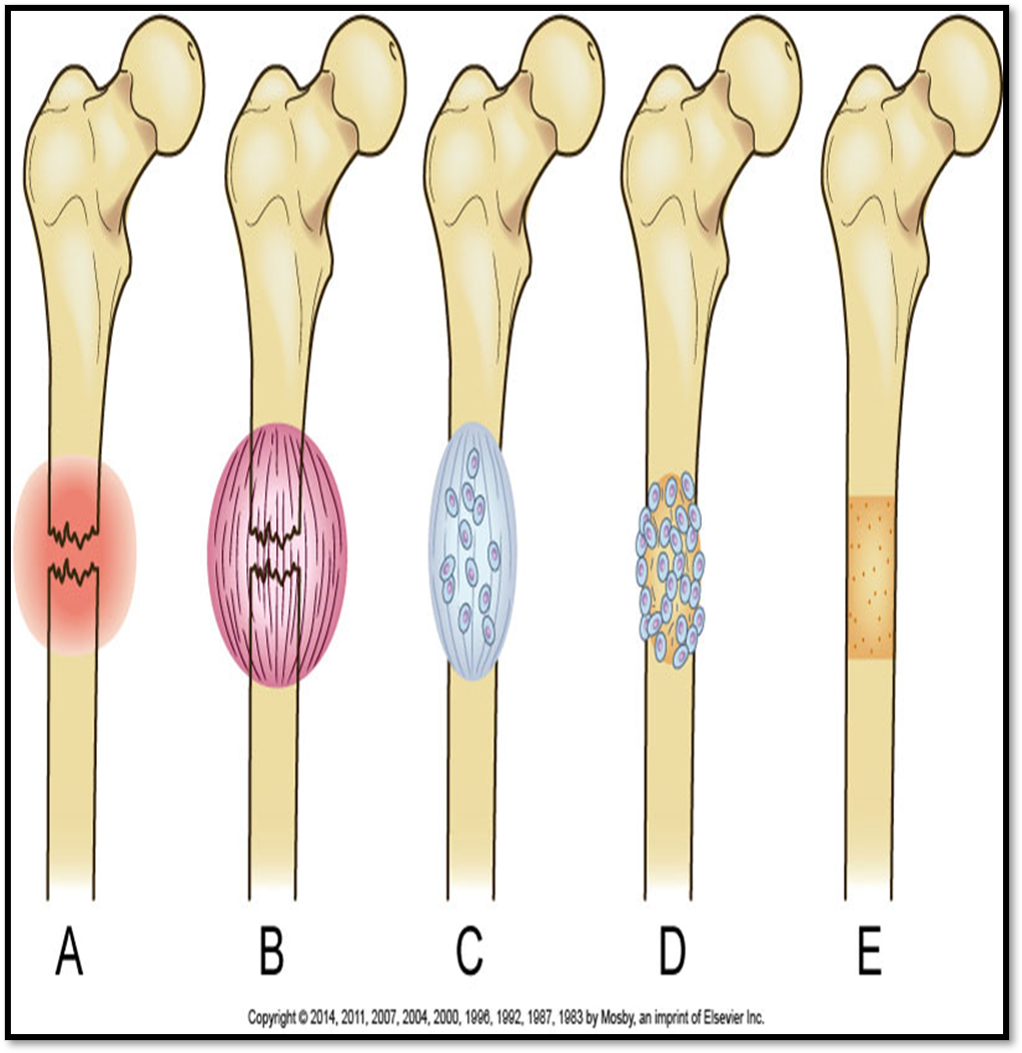
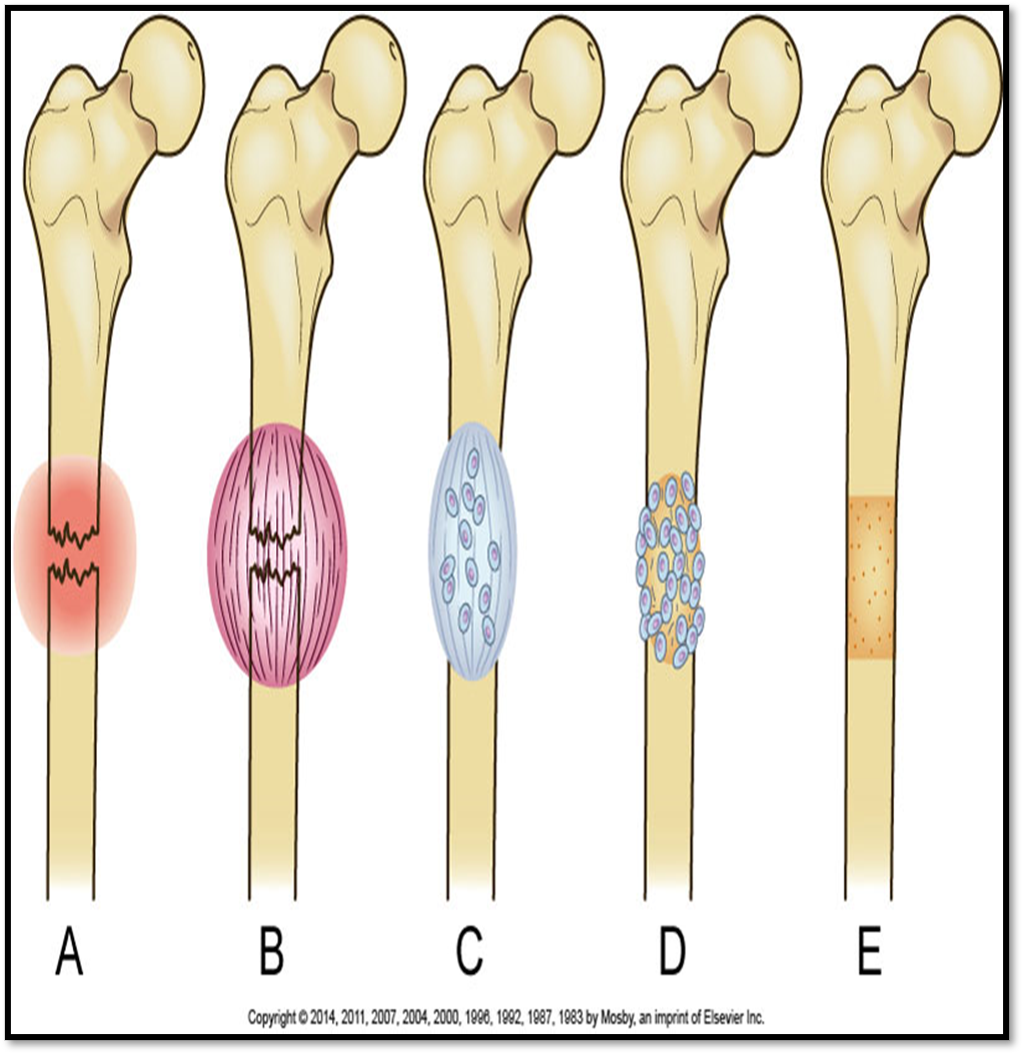
Healing?
•Fracture Hematoma
•Granulation Tissue
•Callus Formation
•Ossification
•Consolidation
•Remodeling
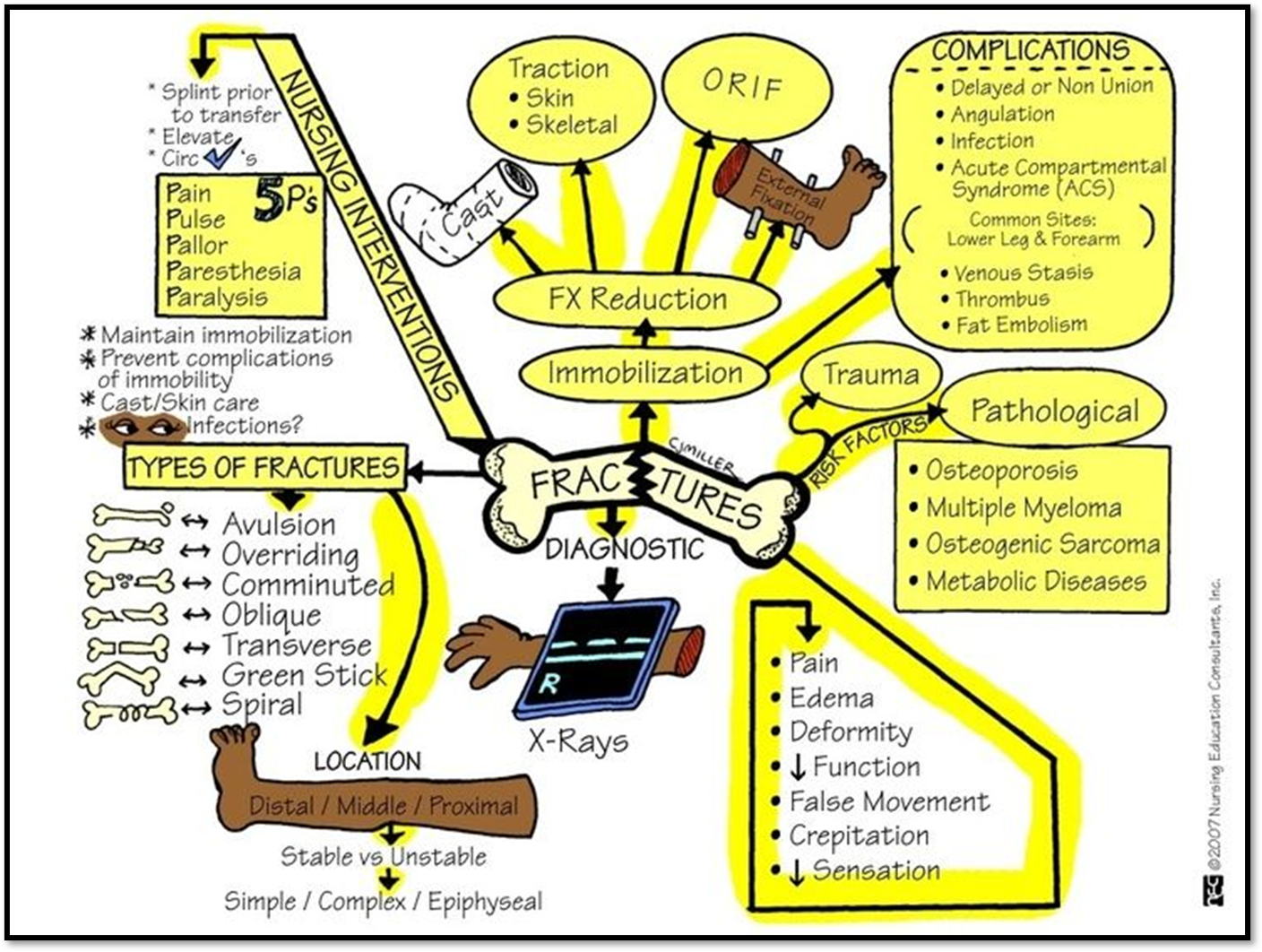
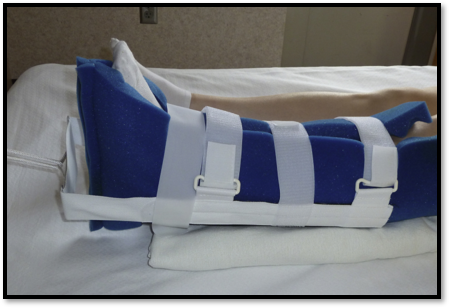
Musculoskeletal Traction
Buck's traction / Balanced suspension
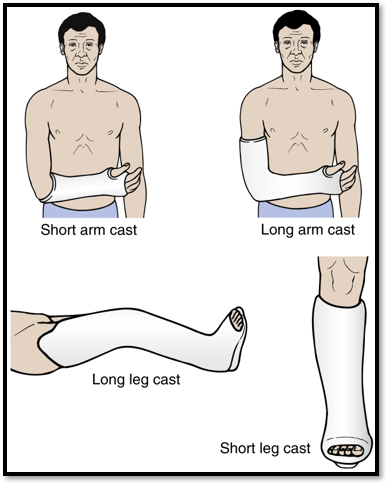
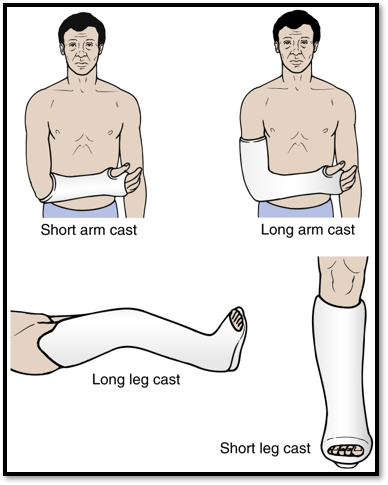
fracture Immobilization (slide 42)
•Casts
•Upper extremities
•Vertebral Injuries: Body Jacket Brace
•Lower extremity injurie: Robert Jones Dressing
Hip spica cast
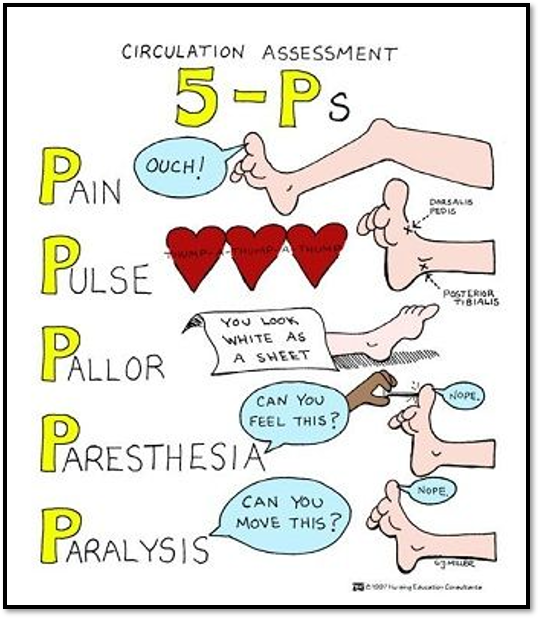
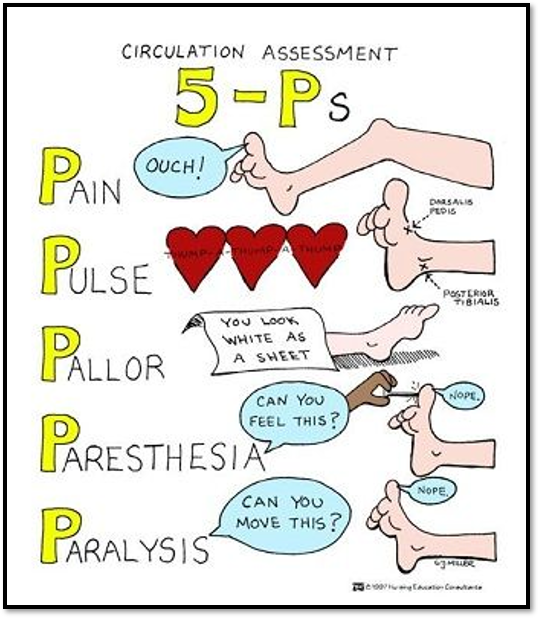
Nursing management
•Assessment
•Neurovascular assessment
•Emergency Management
•Diagnosis
•Planning
Emergency management of fractures
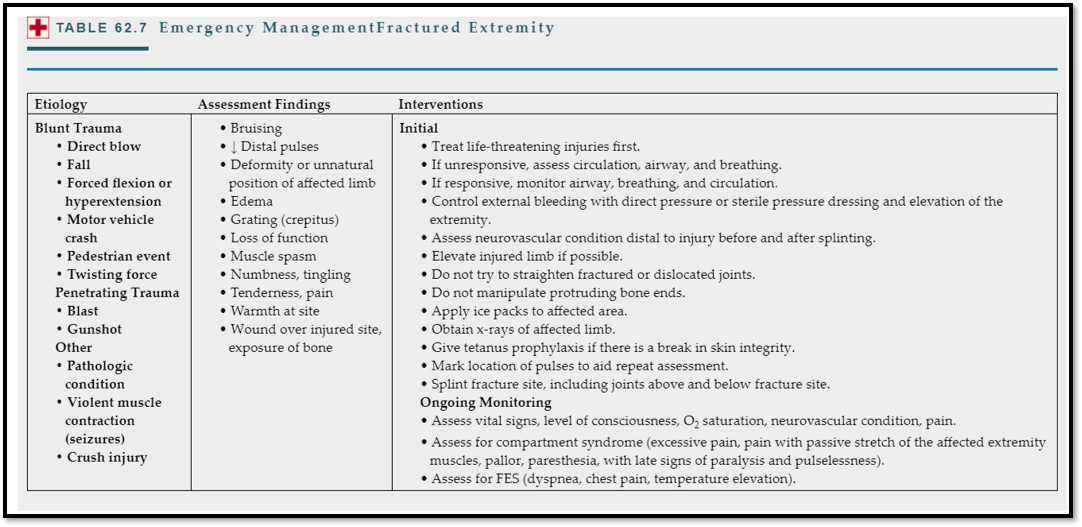
Nursing management
ACUTE CARE
•Preoperative
•Postoperative
•Complications related to immobility
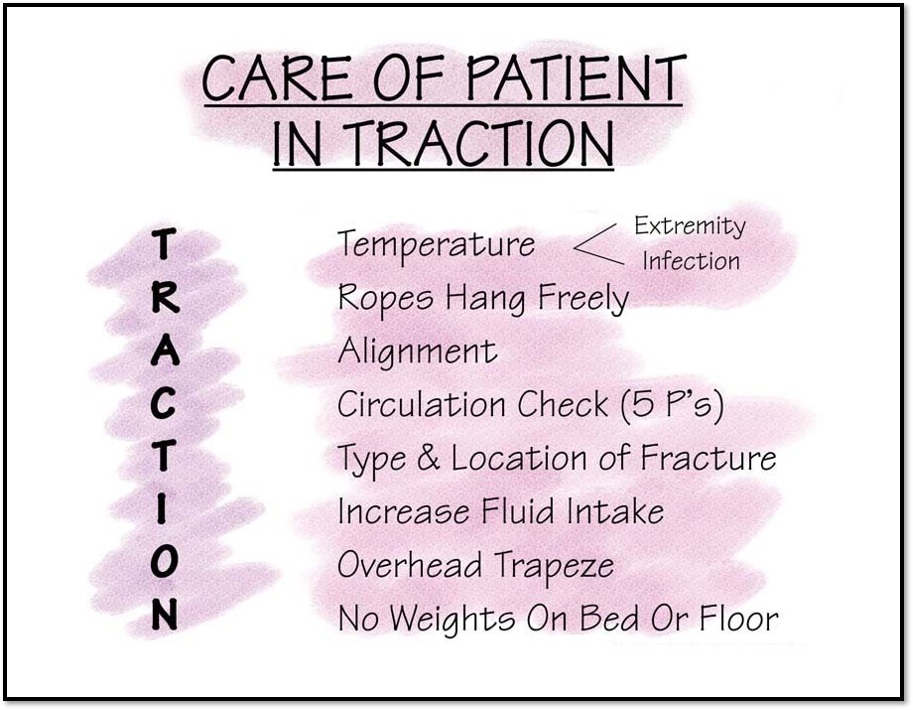
•Traction
AMBULATORY CARE
•Cast care
•Patient and family education
•Ambulation
•Exercises
•Assistive devices
•Gait belt
•Psychosocial concerns

Cast & Traction Care

Complications
INDIRECT
•Compartment syndrome
•DVT/VTE (Deep Vein Thrombosis)
•Fat embolism (fes)
•Breakdown of skeletal muscle (rhabdomyolysis)
•Hypovolemic shock
DIRECT
•Bone infection
•Bone union
•Avascular necrosis
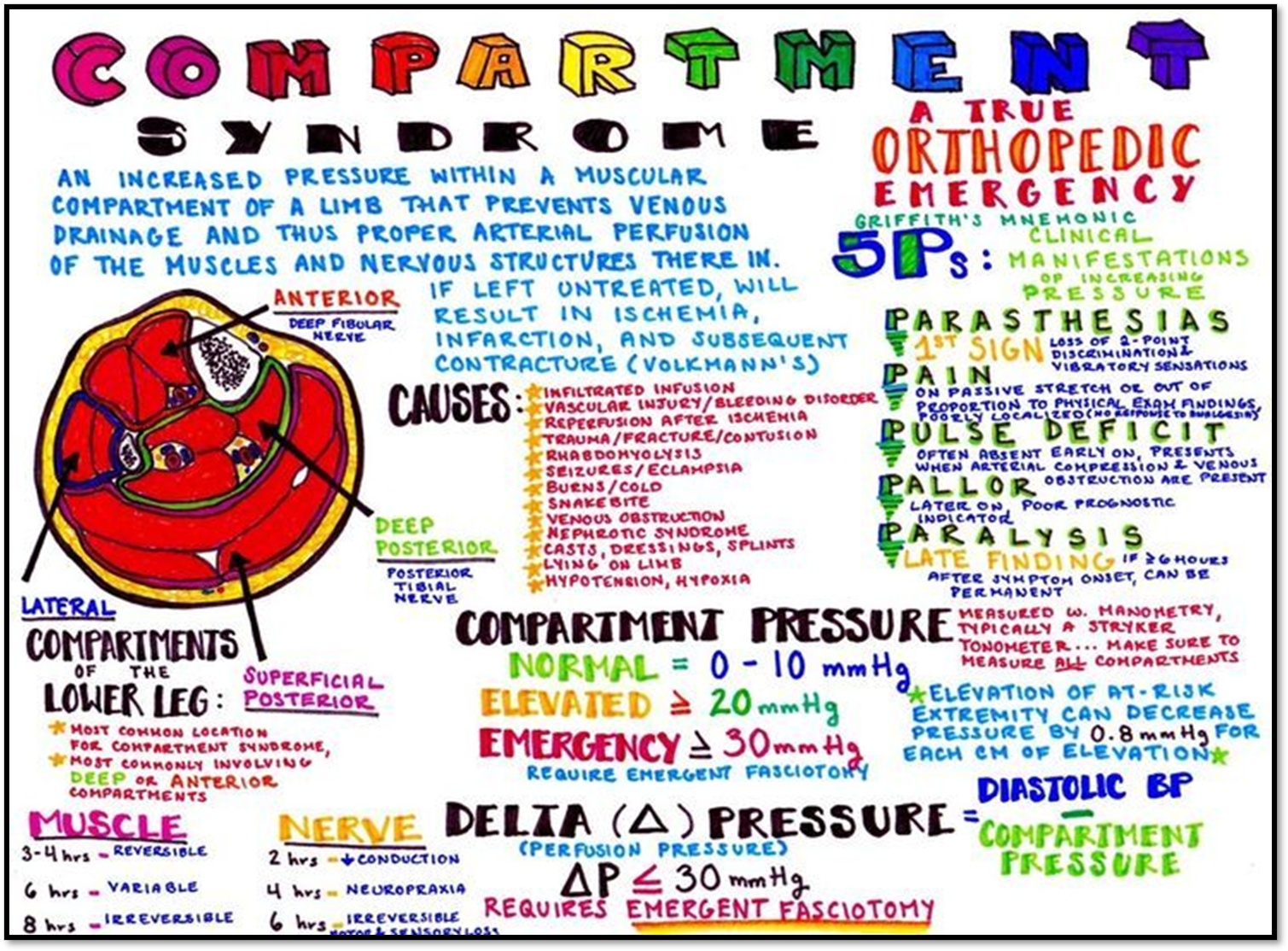


Other Complications
•Fat Embolism Syndrome
•Rhabdomyolysis

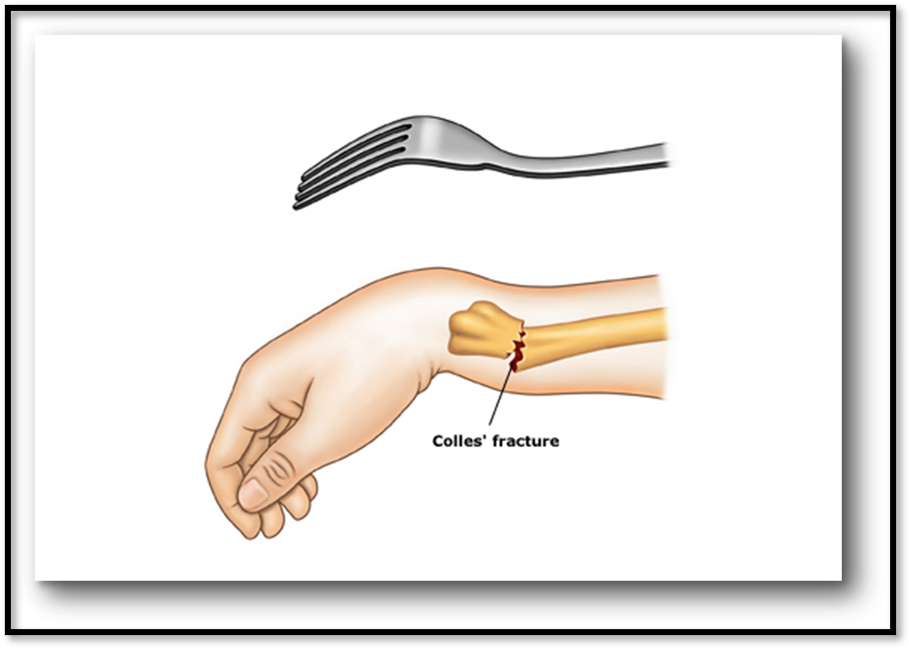
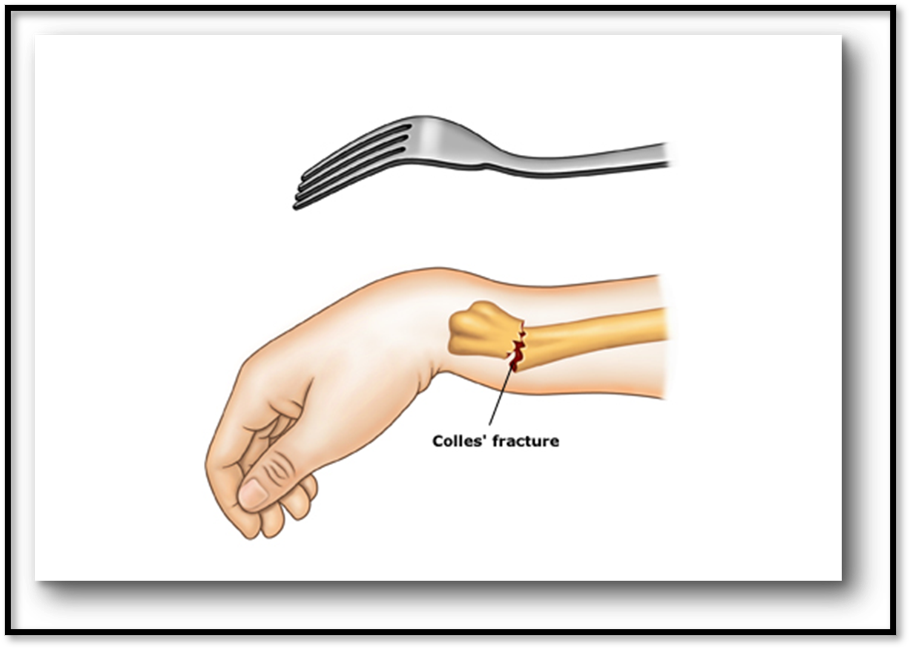
Colles’ Fracture ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Common fracture of distal radius, could involve ulna
•Signs/Symptoms: Pain in area of injury, swelling, dorsal displacement of distal fragment of wrist
•Complications: Vascular insufficiency, carpal tunnel
•Diagnostic: X-ray, CT scan
•Treatment: Close manipulation using splint, cast, internal/external fixation
•Nursing: Prevent edema, active ROM
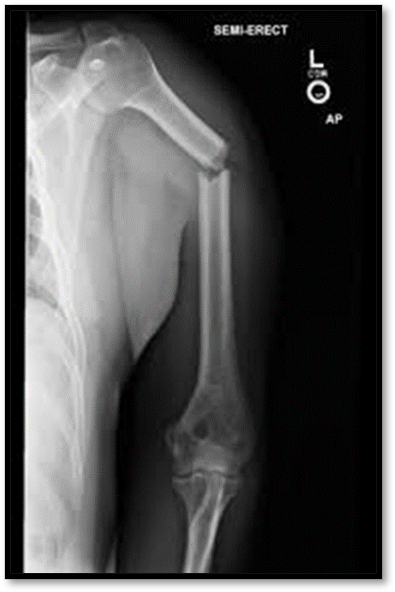
Humerus Fracture ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Common among young-middle age adults
•Sign/Symptoms: displacement of humerus shaft, shortened extremity, abnormal mobility, pain
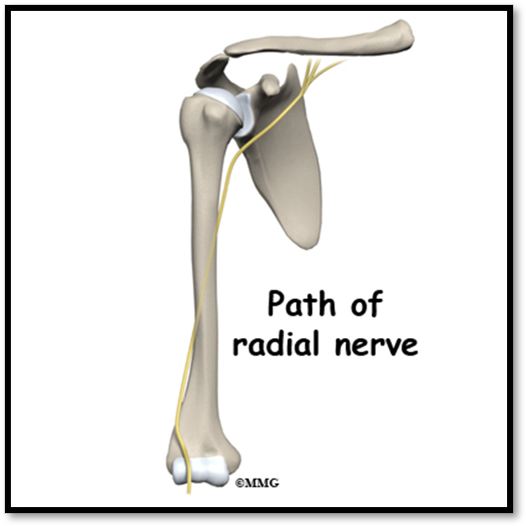
•Complications: radial nerve injury, vascular injury to brachial artery
•Diagnostics: X-ray, CT
•Treatment: Hanging arm in cast, shoulder immobilizer, sling, PT
•Nursing: elevate HOB, allow arm to hang, prevent skin breakdown
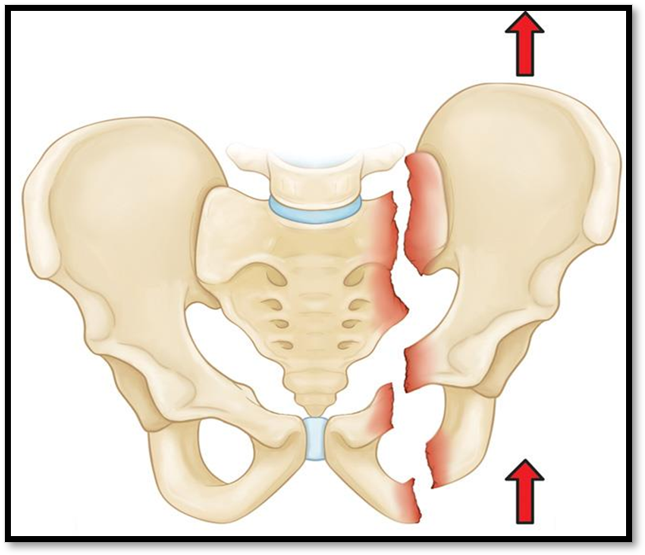
Pelvic Fracture ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Uncommon, high mortality
•Signs/Symptoms: localized swelling, tenderness, deformity, unusual pelvic movement, ecchymosis
•Complications: intraabdominal injury, compartment syndrome
•Diagnostics: Xray, CT
•Treatment: Non-displaced- bedrest, early mobilization. Complex- pelvic sling, traction, external fixation, open reduction. Displaced- ORIF (open reduction internal fixation)
Nursing Care: Use trapeze for assistance, turn patient only when ordered, assess bowel
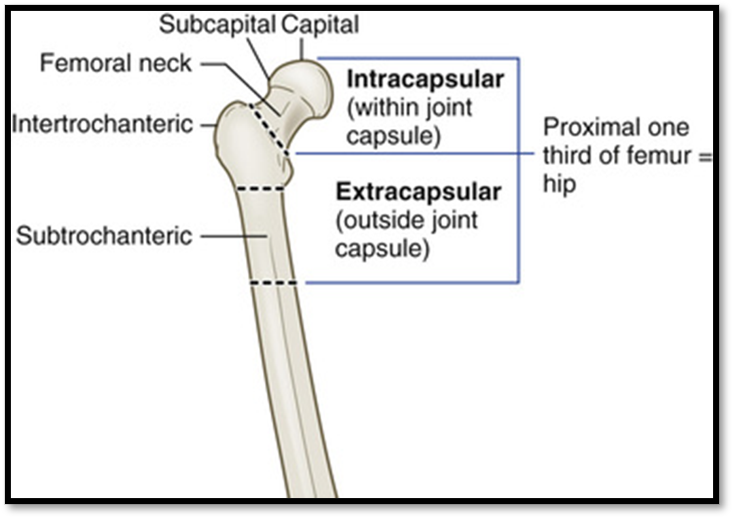
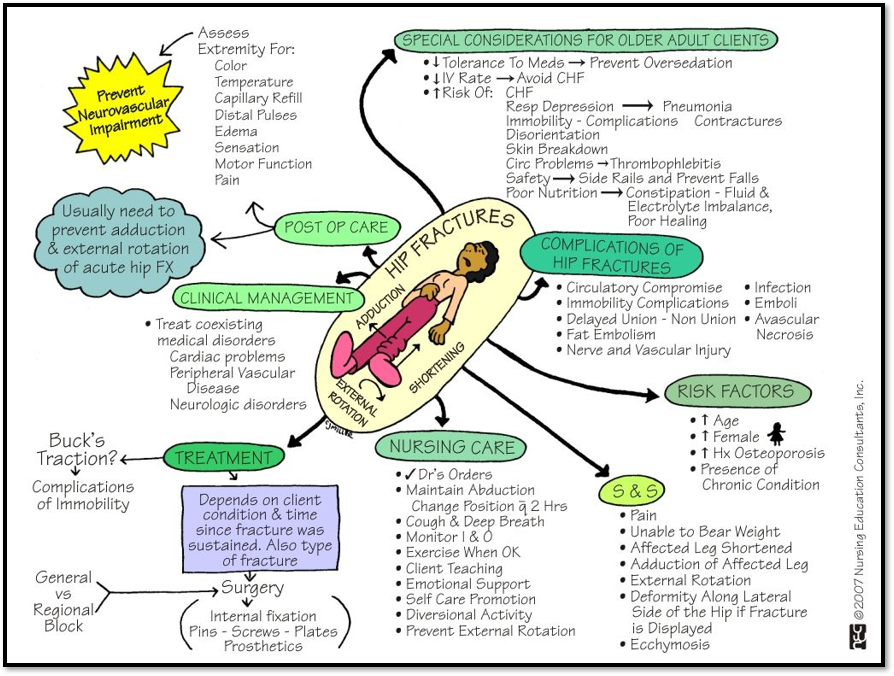
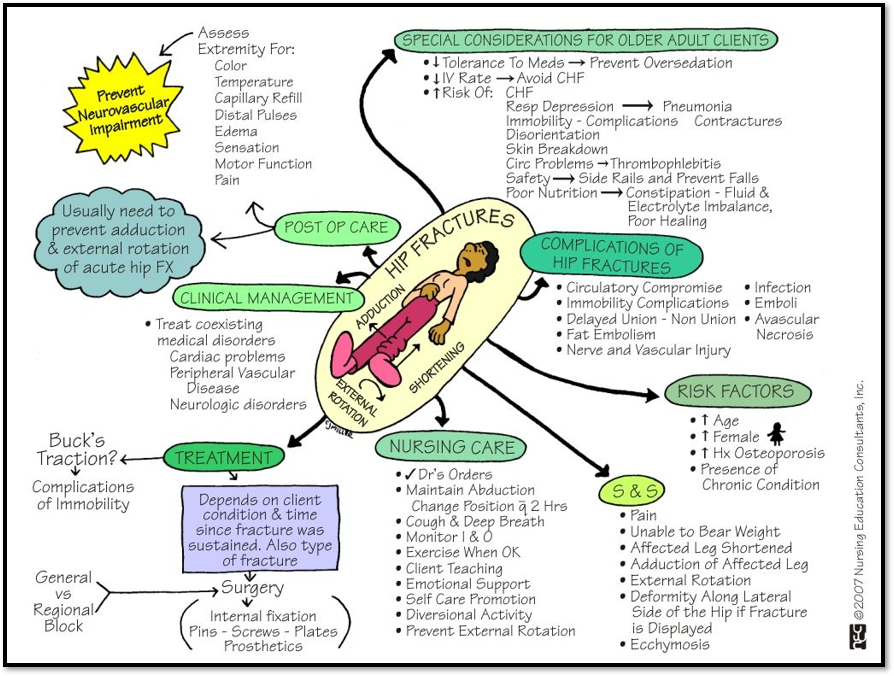
Hip Fracture ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Often due to osteoporosis
•Signs/Symptoms: external rotation, muscle spasm, shortening of extremity, severe pain, tenderness
•Complications: disruption of blood supply to femoral head= necrosis
Diagnostic: CT scan, Xray
•Treatment: Buck’s traction, internal fixation, femur replacement, total hip replacement.
Meds: analgesics, muscle relaxants.
•Nursing care: use of trapeze bar & opposite side rail, pillow between knees, prevent dislocation, avoid hyperextension, use of anticoagulant
If prosthesis dislocation occurs= KEEP PATIENT NPO!
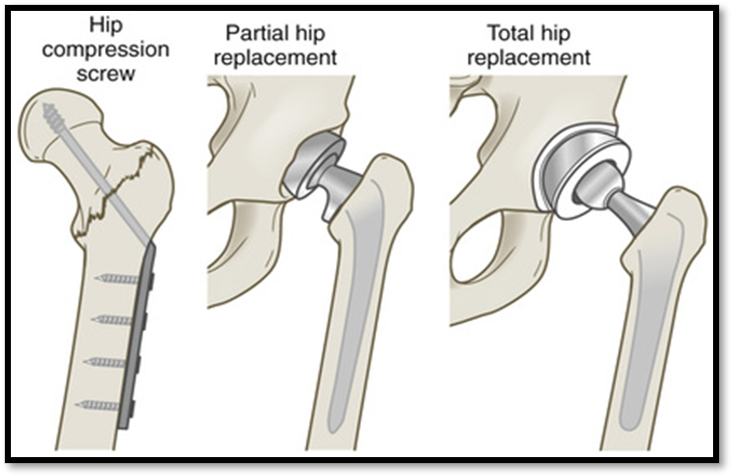
Femoral Shaft Fracture ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Occurs with a severe direct force, usually in younger adults
•Signs/Symptoms: Obvious, marked deformity and angulation, shortening of extremity, inability to move hip or the knee, PAIN
•Complications: fat embolism, nerve and vascular injury Diagnostic: Xray
•Treatment: 1st~Stabilize pt and immobilize fracture, intramedullary nailing, internal fixation.
•Nursing post-op: educate on weight bearing, maintain strength in affected leg, perform ROM, full weight bearing restricted until xray evidence shows union of fracture.
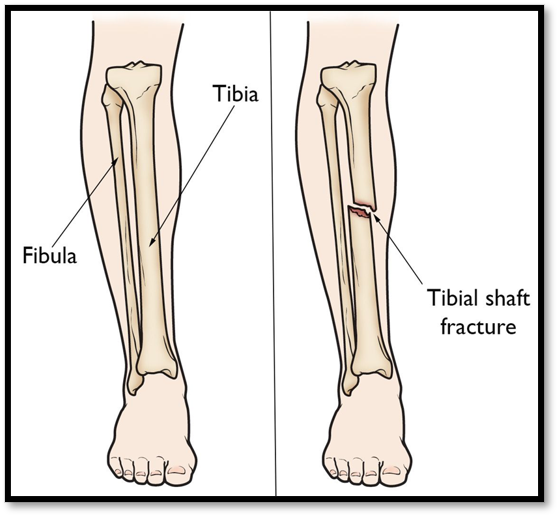
Fracture of Tibia ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Occurs with a strong force, common site of stress fractures
•Signs/Symptoms: soft tissue damage, devascularization, open fracture
•Complications: Compartment syndrome, fat embolism, infection if open fracture
Diagnostic: Xray
•Treatment: closed reduction with immobilization in a long leg cast
•Nursing care: assess affected extremity every 2 hours, perform ROM, non-weight bearing for 6-12 weeks, educate on proper crutch walking.

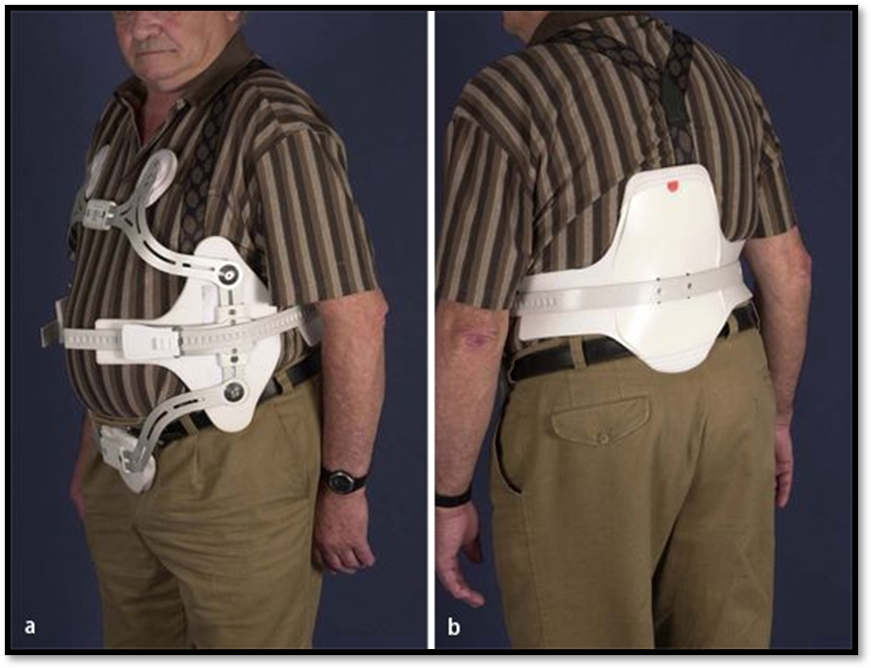
Stable Vertebral Fracture ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Does not cause spinal cord damage, usually in lumbar region
•Signs/Symptoms: brief disability, pain tenderness at region, Dowager’s hump, lordosis
•Complications: sudden loss of function below level of injury, bowel/bladder dysfunction
•Diagnostic: Xray
•Treatment: keep spine in alignment, pain medication, bracing
•Nursing Care: educate on logrolling, assess bowel/bladder function, assess motor/sensory status and peripheral nerves distal to injured region.
Facial Fracture ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Any bone of the face can be fractured
•Signs/Symptoms: table 62.12
•Complications: facial alterations
•Diagnostics: Xrays, CT
•Treatment: depends on site and extent of fracture, immobilization, surgical stabilization
•Nursing care: maintain airway, adequate nutrition, assess ocular muscles and cranial nerves.
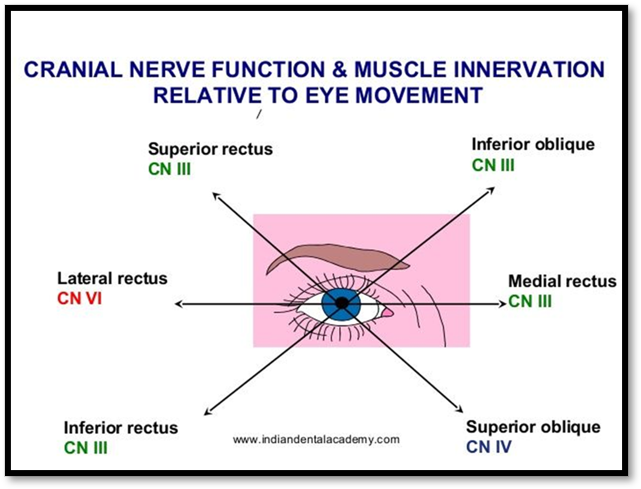
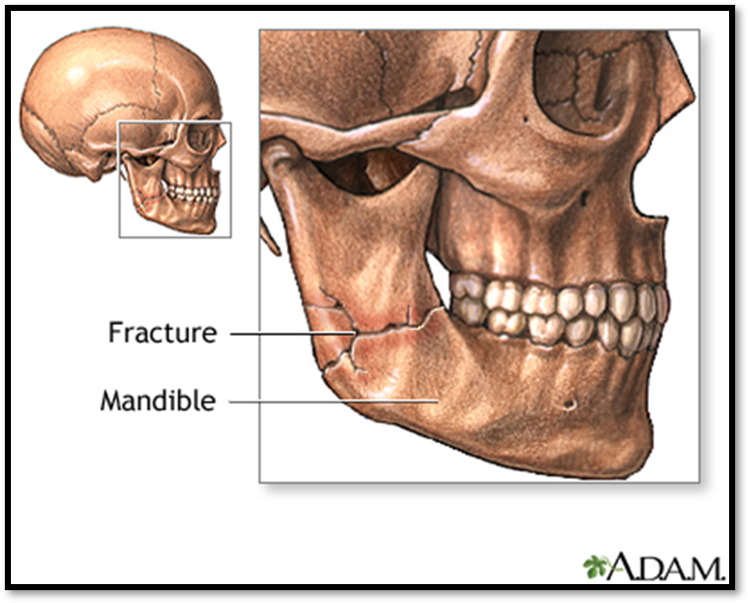
Mandibular Fracture ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Due to trauma to face or jaw
•Signs/Symptoms: simple with no bone displacement or may involve loss of bone and tissue
•Complications: Airway obstruction, aspiration
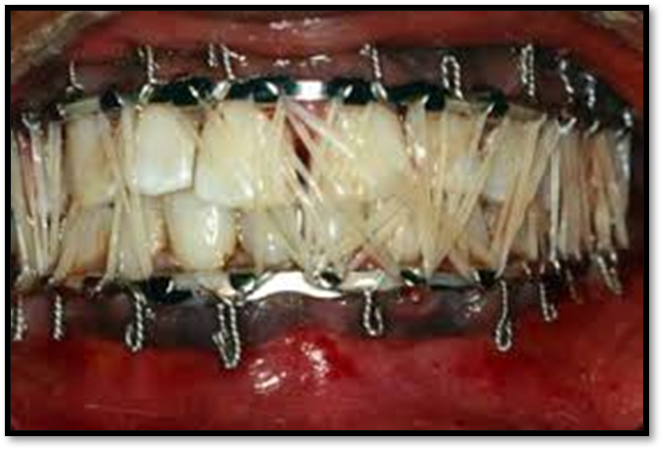
•Treatment: Surgery with immobilization by wiring jaws
•Nursing Care: preop~inform pt of procedure and possible alterations; postop~ maintain airway, oral hygiene, communication, pain management, adequate nutrition, observe for respiratory distress, keep pt on side with HOB elevated, wire cutters at bedside.
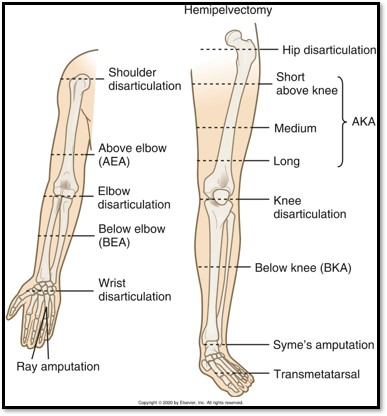
Amputation (Cause / S&S / Diagnostics / Goals / Types)
•An amputation is the removal of a body extremity by trauma or surgery
•
•Causes: PVD, atherosclerosis, vascular changes related to diabetes, trauma, tobacco
•
•Signs/Symptoms: peripheral neuropathy, ulcers, gangrene, trauma, thermal injuries, tumors, congenital limb disorders.
•
•Diagnostics: H&P, Vascular test, CBC with differential
•
•Goals: save extremity and remove infected or ischemic tissue
•
•Types of Amputations: Closed limb, Disarticulation, Syme’s
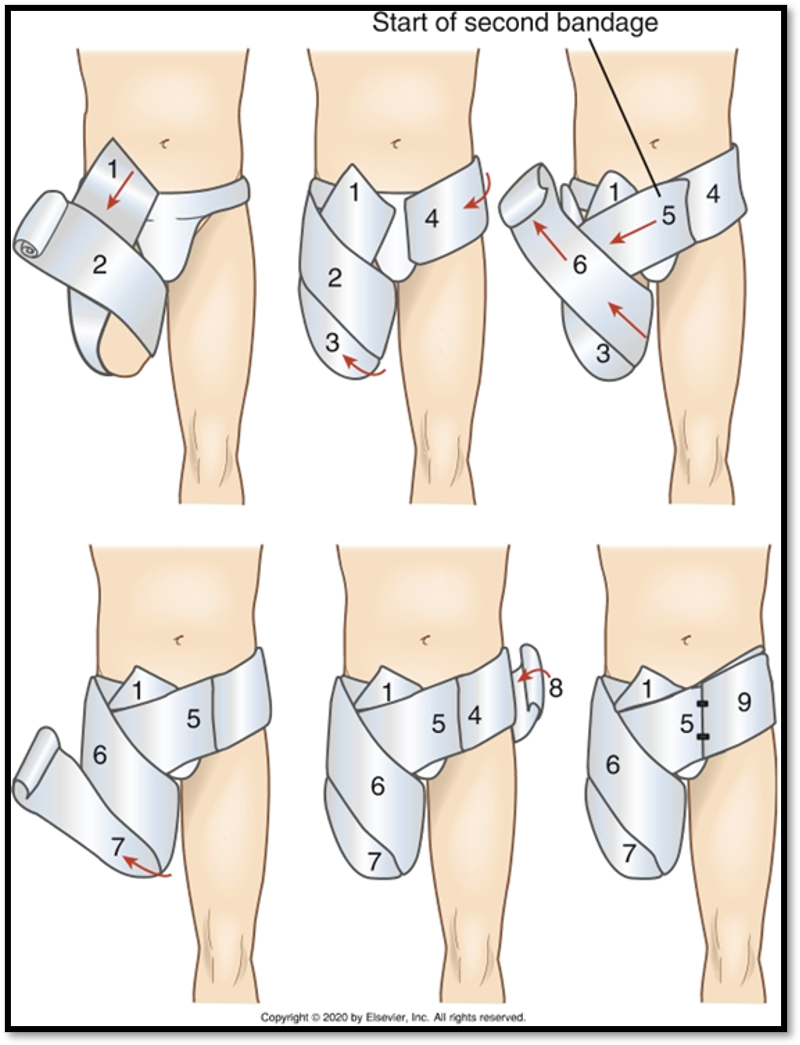
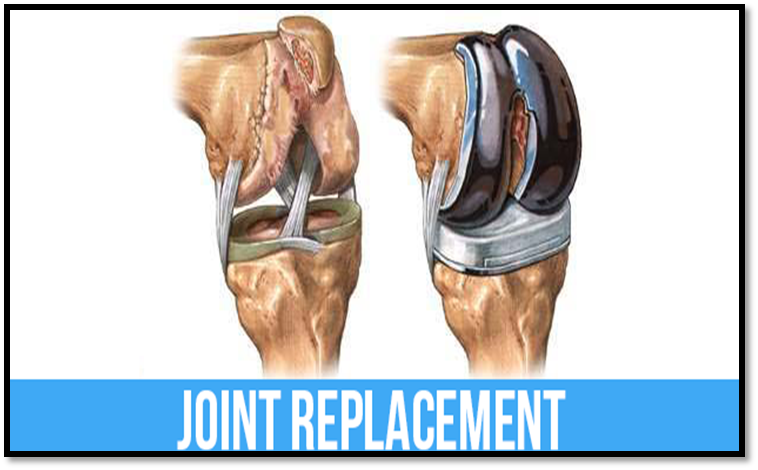
Joint surgery
•Synovectomy →RA
•Osteotomy → OA
•Debridement → knee and shoulder
•Arthroplasty
Total hip arthroplasty
Hip resurfacing arthroplasty
Knee arthroplasty
Finger joint arthroplasty
Elbow and shoulder arthroplasty
Ankle arthroplasty
•Arthrodesis
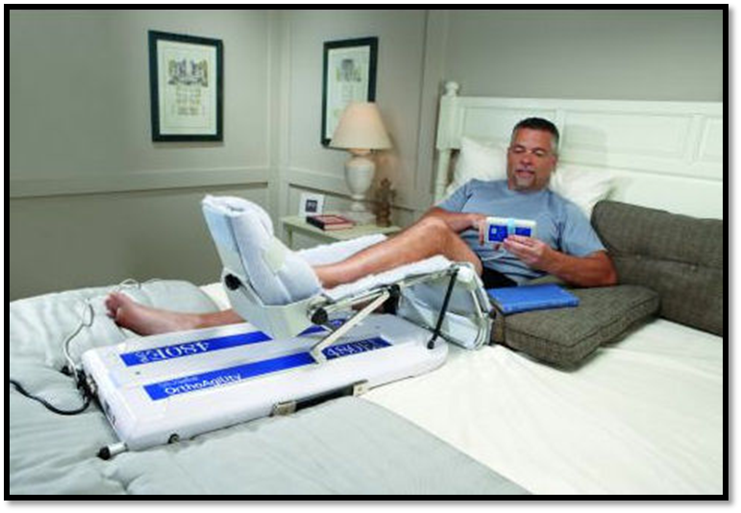
Joint surgery
contraindications and complications
•Recent/active infection
•Arterial impairment
•Inability to follow regimen
•Complicated Medical history
•Infection
•VTE
Knee Arthroplasty ( Def. / S&S / Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx / Nursing)
•Damaged bone and cartilage caused by osteoporosis, RA, trauma, surgery needed when other regimens have stopped working
•Signs/Symptoms: disabling pain when bearing weight, pain at night, bowleg, joint stiffness, joint swelling
•Complications: DVT, anemia, infection, dislocation (hip), nerve injury
•Diagnostics: H&P, Xray, Labs (RF, ESR, CRP) to rule out RA
•Treatment: Antibiotics, Anticoagulants, Opioids, NSAIDs, Physical therapy
•Nursing Care: Pre-op~ see dentist, teach how to use crutches/walker, teach post-op exercises, explain auto-transfusion drain, H&P, labs, consent. Post-op~ VS, I&O, respiratory function, CPM machine, elevate heels, pain medications, ice/cold therapy, neurovascular status of extremity
Hip Arthroplasty
Nursing management of joint surgery
PRE-OP
•Goal
•History
•Teaching
•Assistive devices and adls
•Discharge planning and home safety
POST-OP
•Neurovascular assessment
•Medications
•Post-op complications
•Rom
•Abduction pillow
•Pt
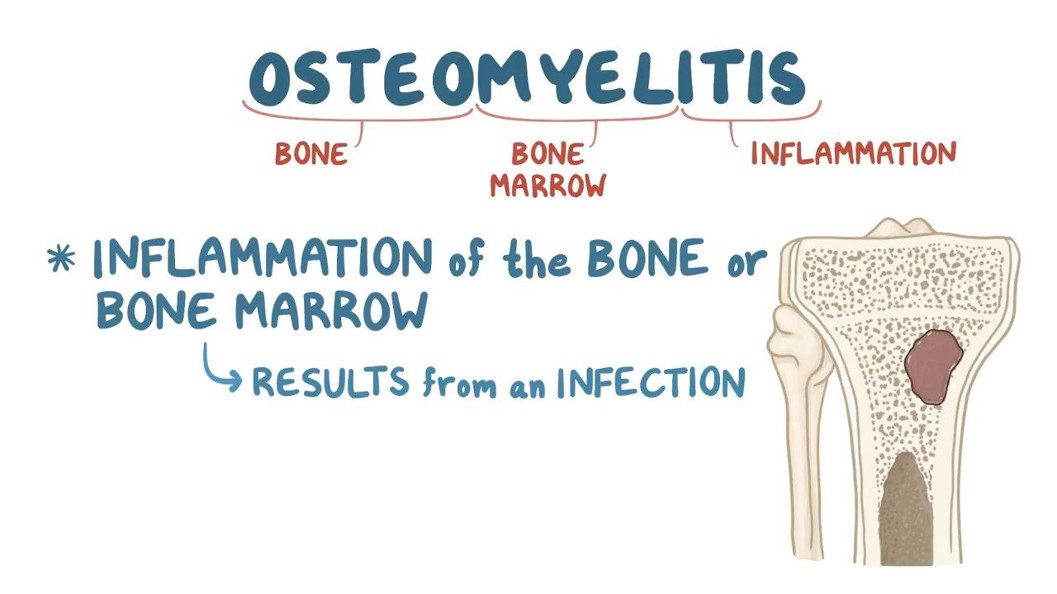
Osteomyelitis
•Severe infection of the bone, bone marrow, and surrounding soft tissue.
•Staphylococcus aureus= most common cause
•Indirect entry (hematogenous)
•Direct entry (open wound)
•Most common sites affected: pelvis, tibia, vertebrae
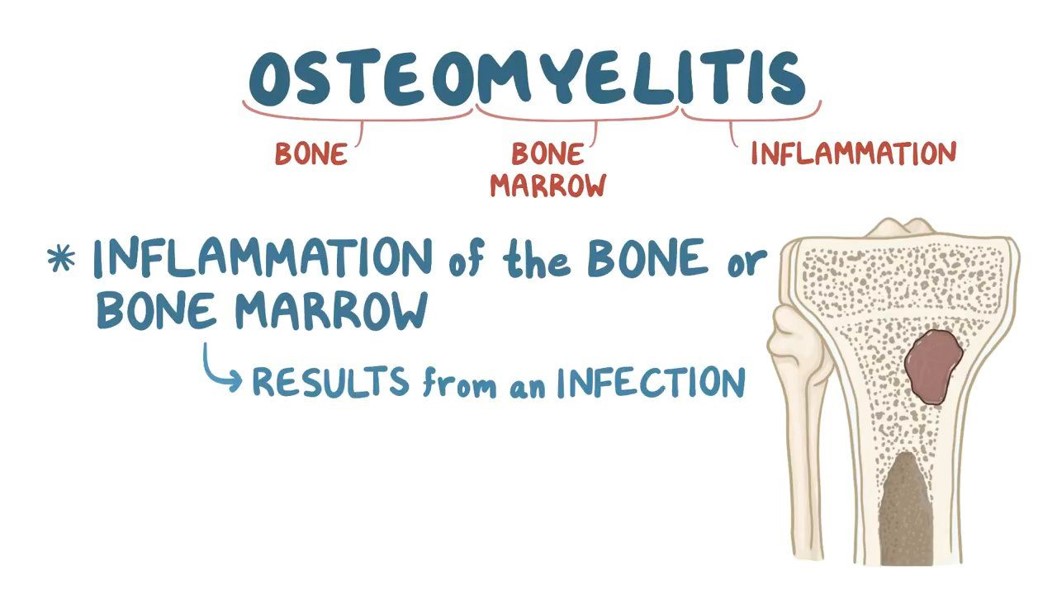
Acute Osteomyelitis (Local & Systemic)
•Local: Constant bone pain, swelling, tenderness and warmth, restricted movement of affected part.
•
•Systemic: fever, night sweats, chills, restlessness, nausea, malaise, later signs include drainage from sinus tract of fracture site
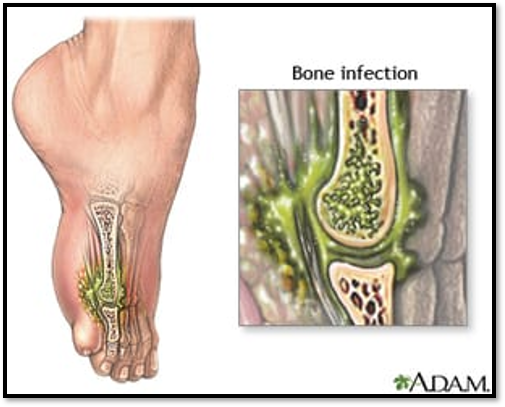
Chronic Osteomyelitis (Local & Systemic)
•Systemic: may be diminished
•Local: constant bone pain; swelling, warmth of infection at the site
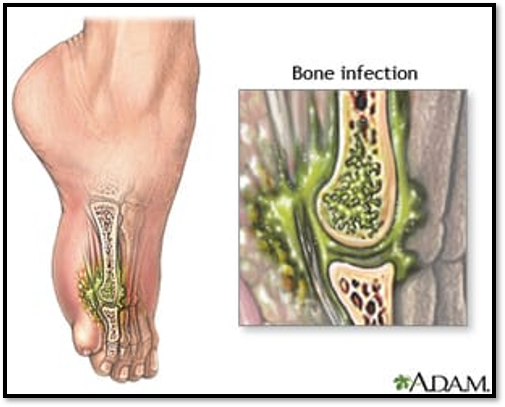
Osteomyelitis ( Comp. / Diagnostic / Tx)
•Complications: Septicemia, Septic arthritis, Fractures, Amyloidosis
•Diagnostics: Bone/Soft tissue biopsy (definitive), blood & wound cultures, WBC, ESR levels, Xrays, bone scans, MRI, CT
•Treatment: IV Antibiotic Therapy, NSAIDs, opioids, muscle relaxants, surgical debridement, irrigation with antibiotics, bone grafts, amputation.
Nursing management
•Assessment
•Nursing diagnosis
•Planning
•Health promotion
•Evaluation
Nursing management
ACUTE CARE
•Some immobilization to decrease pain and reduce risk for injury
•Assess pain
Nsaids, opioids, muscle relaxants
•Nondrug approach
•Dressings
•Antibiotics
AMBULATORY CARE
•Iv antibiotics at home or skilled nursing facility
•Follow-up lab testing
•Dressing changes
•Patient support
Bone tumors
•Primary bone tumors, both benign and malignant are rare
•More common à metastatic bone cancer
•Types:
Osteochrondroma
Osteoclastoma
Enchondroma
Surgically removed
Malignant bone tumors
•Sarcoma that develops in bone, muscle, fat, nerve, or cartilage
•Types:
Osteoscarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
Ewing’s sarcoma
•Metastatic bone cancer
•Treatment
Nursing management for bone tumors
•Monitor tumor site
•Prevent pathologic fractures: Reduce complications & Logrolling
•Anemia
•Decreased mobility
•Hypercalcemia
•Regular rest periods
•Pain management
•Radiation & chemo therapy
•Palliative care
•Education
•Follow-up
Osteoporosis (Risk Factors)

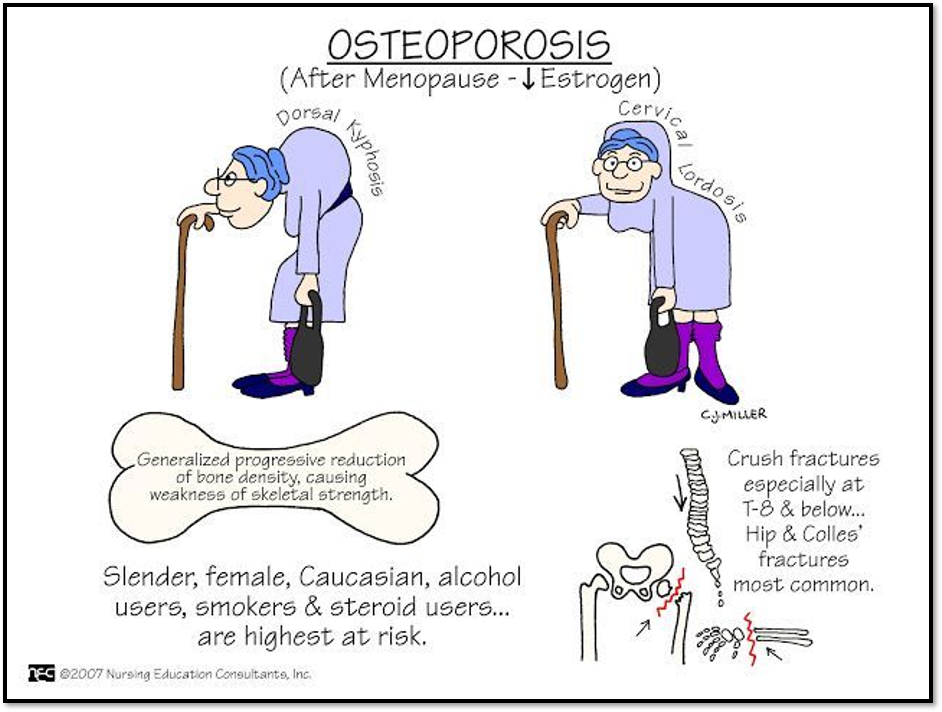
Osteoporosis: Etiology and pathophysiology
•How do you decrease the risk of development?
•Peak bone mass
Typically achieved by age 20
Heredity
Nutrition
Exercise
Hormone function
•Rates of deposit and resorption are normally = so bone mass stays constant.
Osteoporosis is where bone resorption exceeds bone deposition
•associated diseases
•Medications

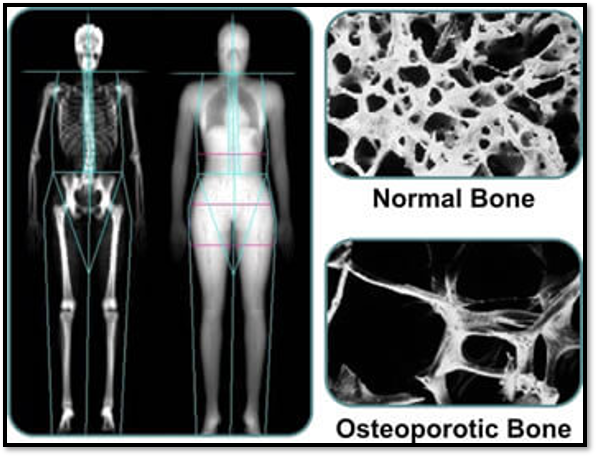
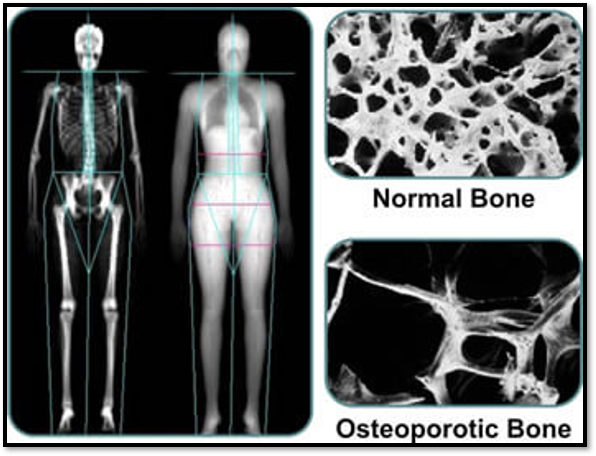
Diagnostic Studies (osteoporosis) https://www.nof.org/patients/diagnosis-information/bone-density-examtesting
•X-ray
•Labs:
Calcium
Phosphorus
Alkaline phosphatase
Vitamin d
•Radiology: (BMD)
Quantitative u/s
Dual-energy xray absorptiometry (dexa) àgold standard
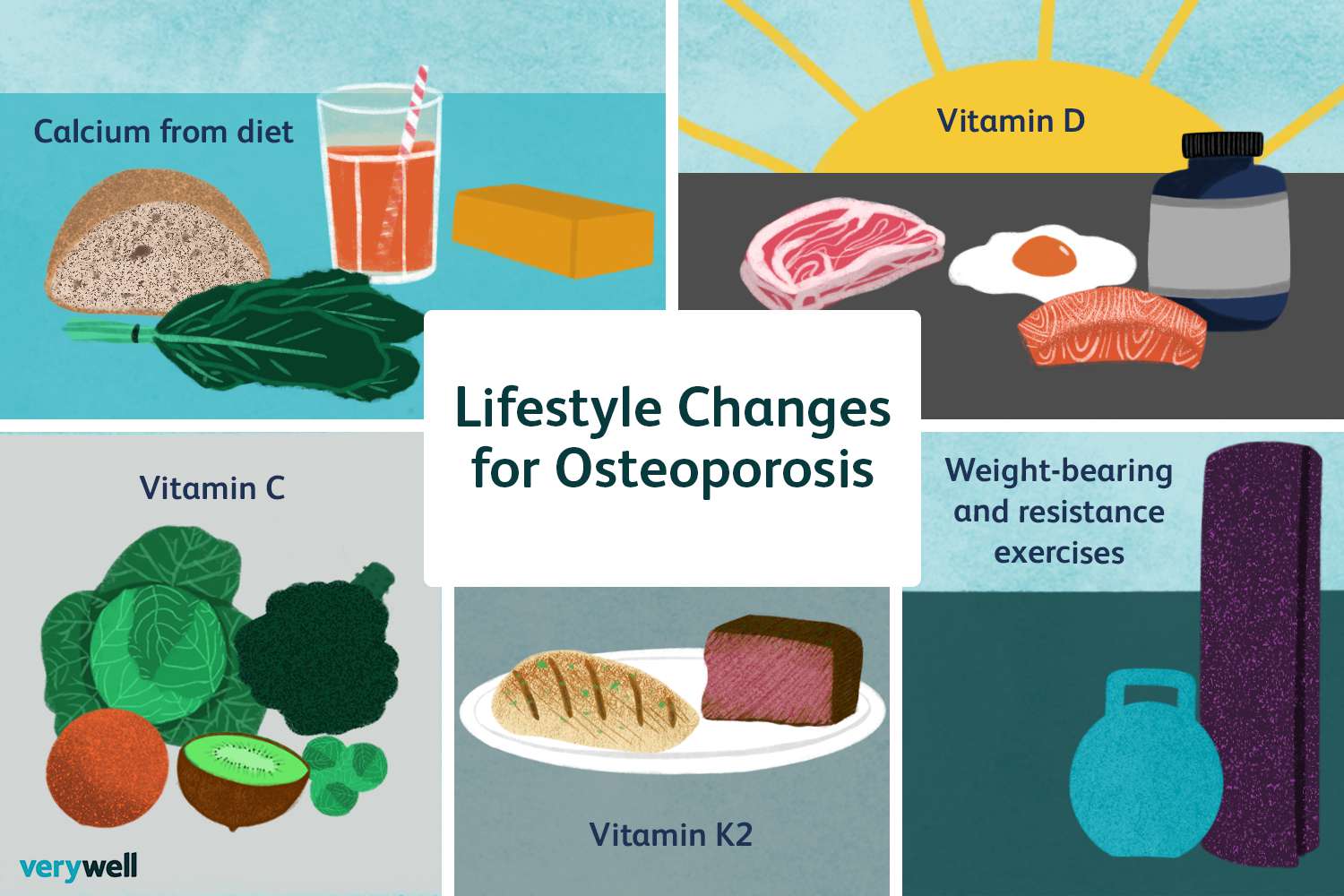
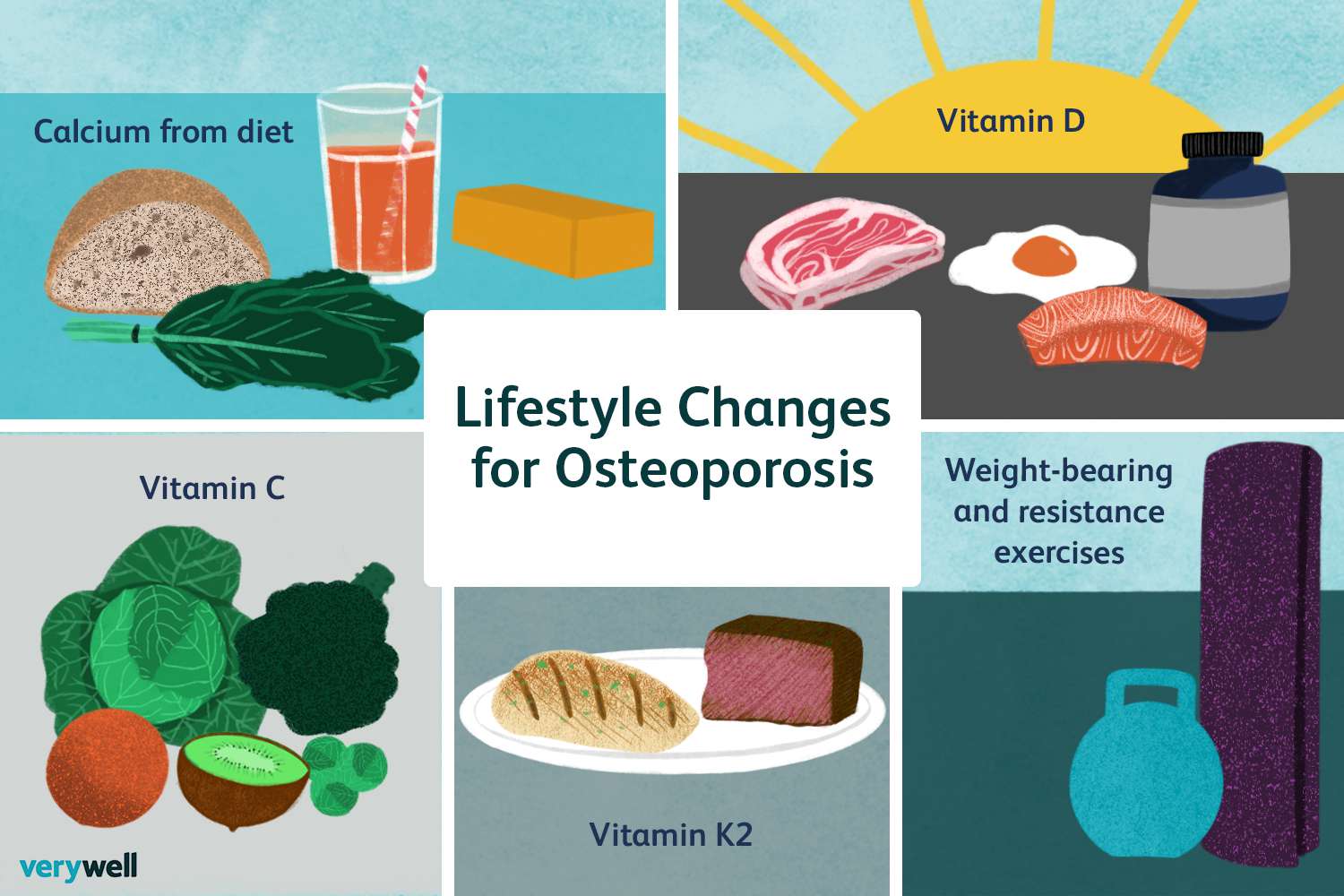
Management
•Nutrition
•Calcium-divided doses
•Vitamin d (sun exposure)
•Exercise
•Fall prevention
•Medications
•Risk of fractures
•Vertebroplasty & Kyphoplasty

Medical therapy for Osteoporosis
•Biophosphonates (recommended)
Alendronate
Risedronate
Zoledronic acid
•Monoclonal antibodies
Denosumab
Romosozumab
•Bisphosphonates (other)
Ibandronate (Boniva)
•Recombinant parathyroid hormone
Teriparatide
Abaloparatide

Arthritis and connective tissue diseases: Osteoarthritis causes
•Medications
•Hematologic or endocrine d/o
•Inflammation
•Mechanical stress
•Joint instability
•Neurologic disorders
•Skeletal deformities
•trauma
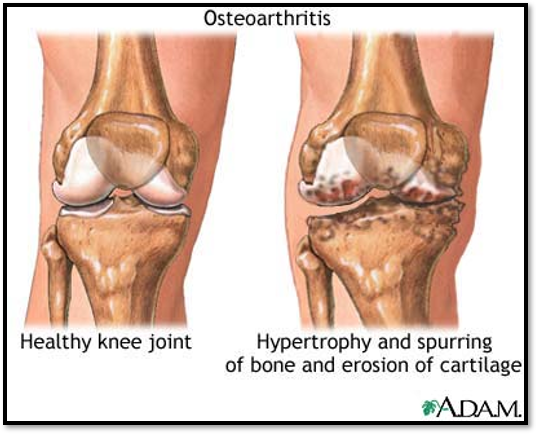
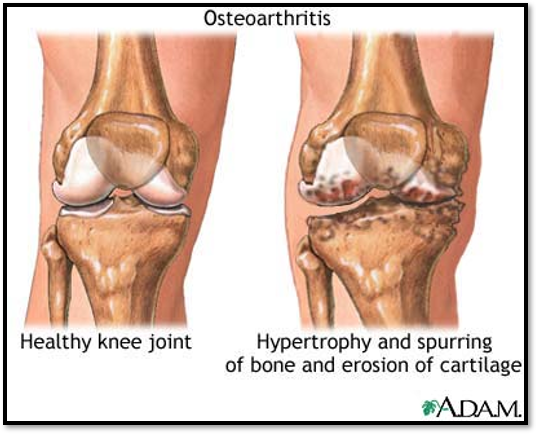
Osteoarthritis: Etiology and pathophysiology
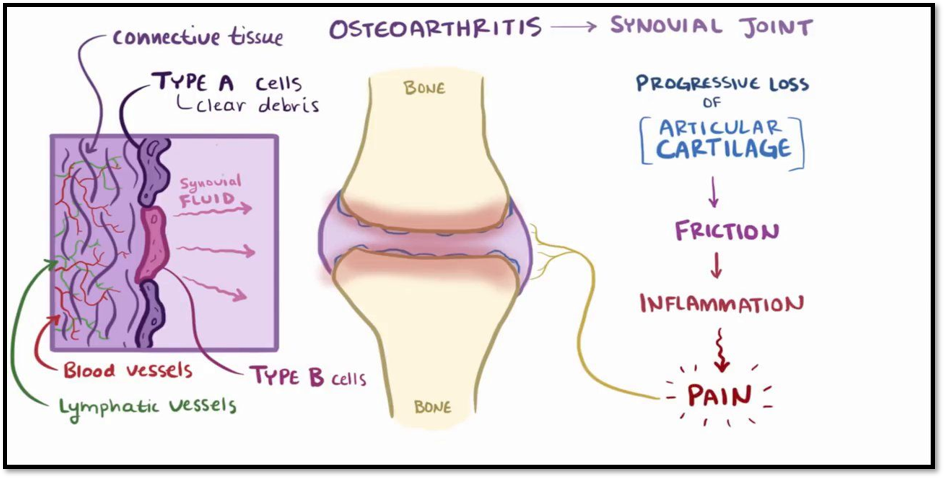
Osteoarthritis: Clinical Mani
JOINTS
pain
Worse with use
Relieved by rest (early)
Pain → disability & loss of function
Joint stiffness after rest
Early morning stiffness
Asymmetric
DEFORMITIES
Associated to a specific joint
Heberden’s Nodes
Bouchard’s Nodes
Varus Deformity
Valgus Deformity
SYSTEMIC
Generally symptoms are not present and are an important distinction between OA and other inflammatory disorders
Osteoarthritis: Diagnostics & Care
•Bone scan, ct, or mri, may be used
•X-rays àconfirm disease and stage joint damage
•Labs
•Synovial fluid analysis
There is no cure for OA
•Management focus:
Treat pain and inflammation
Prevent disability
Maintain and improve joint function
Non-drug interventions
Medications
•Surgery
Osteoarthritis: Medical Therapy
•Acetaminophen
•Capsaicin cream
•Otc camphor, eucalyptus oil, menthol (bengay, arthricare)
•Aspercream, topical salicylates
•NSAIDS
+ misoprostol (cytotec) for gut protection (otc)
Arthrotec which is cytotec and diclofenac (an nsaid)
•Hyaluronic acid injection
Osteoarthritis: Nursing Management (Health promo)
•Assessment
•Diagnosis
•Planning
•Health promotion / implementation /prevention
Smoking cessation
Treat joint injury promptly
Healthy weight and balanced diet
Safety measures to decrease risk of joint injury
Exercise regularly
•Evaluation
osteoarthritis care
ACUTE CARE
•Treated as outpatient
•Joint surgery reason for admission, if indicated
•Collaborative health-care team members
AMBULATORY CARE
•Patient and caregiver teaching tablet 64.4
•Adjust home management
•Safety
•Assistive devices
•Counseling