MCAT Psych/ Soc
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Jack Westin P/S Diagnostic
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Electroreceptors
Detect electric fields in the environment. Many animals use it to navigate, locate prey, or communicate in water.
Mechanoreceptors
Detect mechanical pressure and transmit a signal. Hair cells in the organ of Corti are considered mechanoreceptors as they transmit signal upon brushing against the tectorial membrane.
Chemoreceptors
Detect chemical stimuli in the environment especially responsible for smell and taste.
Interoceptors
Detect stimuli within the body.
Sensory Adaptation
occurs when an individual is subjected to a constant, unchanging stimulus for an extended period of time and eventually will develop decreased sensitivity to this stimulus, and may even fail to perceive it.
Sensory threshold
Minimum intensity of a stimulus required for it to be detectable 50% of the time.
Absolute threshold
minimum amount of stimuli required for it to be detected.
Just Noticeable Difference
smallest detectable change between two stimuli.
Weber’s law
Change in the stimulus required for it to be detectable is a ratio of the original stimulus.
sensory pathway for eyesight
cornea→ lens→ retina→ rods/cones→ Phototransduction cascade→ bipolar and ganglion cells→ optic nerve→ LGN in thalamus→ visual cortex in occipital lobe
Phototransduction cascade
light→ rhodopsin→ transducin→ PDE (phpsphodiesterase)→ low cGMP→ Na+ channels close
Rods
highly photosensitive and detect dim light
cones
weakly photosensitive and detect color
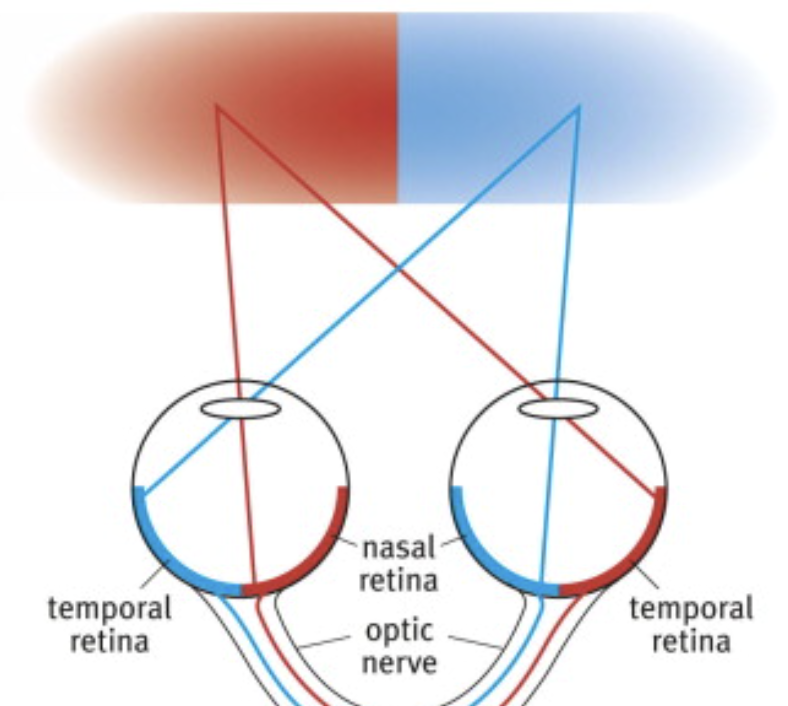
Nasal retina and temporal retina
color blindness
results from issues with cones in the retina
cataracts
occurs when lens becomes cloudy with age
difficulty seeing objects up close
when lens becomes less flexible with age
parallel processing
simultaneously process visual information such as shape, color and movement.
optic chiasma
crossing of the optic nerve
Outer ear
pinna (collect sound waves from air)→ auditory canal (channels sound waves inwards)→ Tympanic membrane (eardrum vibrates)
Middle ear
vibration in eardrum→ Malleus→ Incus→ Stapes→ pushes on the oval/ elliptical window
Middle ear components amplify and transmit mechanical vibrations to the inner ear.
Inner ear
Oval window (movement of stapes causes pressure waves in cochlear fluid)→ Cochlea (consists of fluid, basilar and tectorial membrane and organ of corti) → Cochlear fluid movement→ bend Cochlear hair cells → convert mechanical signals to electrical signals
Organ of Corti (more specific)
Cochlear fluid→ movement of hair cells → hair bundle is made of kinocilium→ kinocilium is connected by a tip link→ tip link is attached to gate of K channel→ movement of hair cells allow K+ to move in→ Ca+ cells get activated→ spiral ganglion cells activated→ auditory nerve is activated
Frequency of sounds we can hear
20-20k Hz
endolymph
fluid in the semicircular canal that allows us to detect which direction our head is moving.
otolithic organs
utricle and saccule (help in detecting linear acceleration and head positioning).
primary auditory pathway
sound waves→ mechanoreceptors→ auditory nerve→ thalamus→ auditory cortex
function of the round window
it bulges as fluid pushes against it after being compressed by the oval window
somatosensation
sensation felt throughout body such as pain and temperature (tactile stimuli)+ proprioception (sense of body in space)+ interoception (sense of internal state)
base tuning
base hair cells of cochlea= high frequency sound and apex hair cells= low frequenchy sound
olfaction pathway
odorant molecules→ binds to olfactory receptors in olfactory neurons → activation of GPCR→ AP generated→ passes through cribriform plate→ glomeruli→ olfactory cortex, amygdala, limbic system
gustatory pathway
food in saliva→ taste buds on tongue→ receptors (GPCRs for sweet, bitter and umami and Ion channels for sour and salty)→ AP generated→ brainstem→ thalamus→ gustatory cortex
kinesthetic sense
the body’s ability to perceive its own position and movement, allowing for coordination and control without relying on vision.
top-down processing
interpreting an event within the context of past knowledge/ experiences.
bottom-up processing
stimulus influences processing
Gestalt’s principle
arranging, categorizing, and organizing stimuli based on similarity, proximity, continuity, closure and pragnanz (create simple meaning from things like shapes from clouds etc).
monocular cues
relies on vision from a single eye eg. relattive size, interposition, motion parallax, shading
motion parallax
closer objects move faster and further objects move slower
binocular cues
relies on vision from both eyes, eg. retinal disparity and convergence
divided attention
doing two things at once and simultaneously.
selective attention
doing multiple things but switching between them.
types of cues
exogenous: naturally look for these cues (bright colors, loud noises etc)
endogenous: require internal knowledge to respond to these cues (cocktail party effect)
cocktail party effect
ability to concentrate on one voice amongst a crowd, like your name
inattentional blindness
not being aware of things in our visual field when our attention is directed elsewhere in the field.
change blindness
inability to notice change
executive attention
ability to focus attention on steps taken to achieve a goal
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development
sensorimotor→ pre operational→ concrete operational → formal operational
overestimate bias
overestimate your ability to produce correct answer
Belief perseverance bias
ignoring/ rationalizing disconfirming facts
confirmation bias
actively seeking out only confirming facts
selection/ sampling bias
selection of data/ groups that are not randomized or representative
actor-observer bias
attribute the behavior of others to internal problems but attribute our own behavior to external problems
self-serving bias
if we succeed it is due to internal qualities, if we fail it is due to external qualities
optimism bias
bad things happen to others but not us
primacy bias
first impression/ information is more important/ easier to remember
recency bias
most recent impression/ information is important/ easier to remember
similarity bias
befriend people who are similar to us
projection bias
assuming others share the same belief as us
hindsight bias
thinking you already knew something after being told it
normalcy bias
the situation will stay normal, nothing bad will happen
reconstructive bias
memory isn’t reliable, it has been reconstructed
attrition bias
when a participant drops out of a long term study or experiemnt
social desirability bias
related to how people respond to research questions. want to appear desirable to researcher.
subjective bias
self reported information is vulnerable to this. thinking subjectively not objectively
implicit bias
a bias that we are unaware of but unconsciously influences our decisions
cognitive bias
tendency to think certain ways. causes deviation from rational thinking and good judgement
egocentric bias
tendency to overstress changes between past and present in order to make oneself appear more worthy or competent than one actually is.
framing bias
occurs when people make a decision based on the way the information is presented, as opposed to just on the facts
automation bias
the tendency to excessively depend on automated systems
expectation bias
expectations influence attitudes or behaviors
causation bias
belief that one thing caused the other when they are actually unrelated or simply correlated
availability bias
base decisions on the most salient information- whatever comes to mind first when thinking about a topic
Gardner’s theory of intelligence
differentiates intelligence into different (8) modalities
Spearman’s idea of general intelligence
single g factor responsible for intelligence that underlies performance on all cognitive tasks
galton’s idea of hereditary genius
intelligence/ human ability is hereditary
Binet’s idea of mental age
how a child at a specific age performs intellectually compared to average intellectual performance for that physical age in yrs
consciousness
awareness of our self and environment
alertness
awake
daydreaming
feel more relaxed not as focused
drowsiness
just before falling asleep
sleep
not aware of the world around you. has 4 main types
beta waves
associated with awake/ concentration; increased stress, anxiety, restlessness; constant alertness
alpha waves
daydreaming, relaxation
theta waves
drowsiness, right after you fall asleep
delta waves
deep sleep or coma
order of sleep stage patterns
N1→ N2→ N3→ N2→ REM
N1
theta waves; seeing or hearing things; hypnic jerks
N2
deeper stage of sleep; more theta waves+ sleep spindles+ K-complexes
Sleep spindles
inhibit certain perceptions so we maintain a tranquil state of sleep (sleep through loud noises)
K complexes
suppress cortical arousal
N3
slow wave sleep, characterized by delta waves; walking/ talking in sleep happens
REM
rapid-eye movement;
most of the muscles are paralyzed;
most dreaming occurs;
memory consolidation;
combination of alpha, beta and desynchronous waves;
brain is active but body is not
circadian rhythms
regular body rhythms across 24-hr period. controlled by melatonin (produced in the pineal gland)
what are osmoreceptors and where are they located?
osmoreceptors are located in the hypothalamus and kidneys to regulate homeostasis and monitor osmotic pressure, water and electrolyte balance in the body
what are baroreceptors and where are they located?
baroreceptors detect blood pressure and are located in blood vessels.
what are interoceptors and where are they located?
located in the internal organs like stomach and intestines that detect internal changes in levels of hormones, gases, and nutrients in the bloodstream.
what are proprioceptors and where are they located?
proprioceptors detect position and movement of the body and maintain balance. they are located in muscles, tendons and joints.