Miles down review Biology
1/247
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
248 Terms
The Cell
Basic unit of life
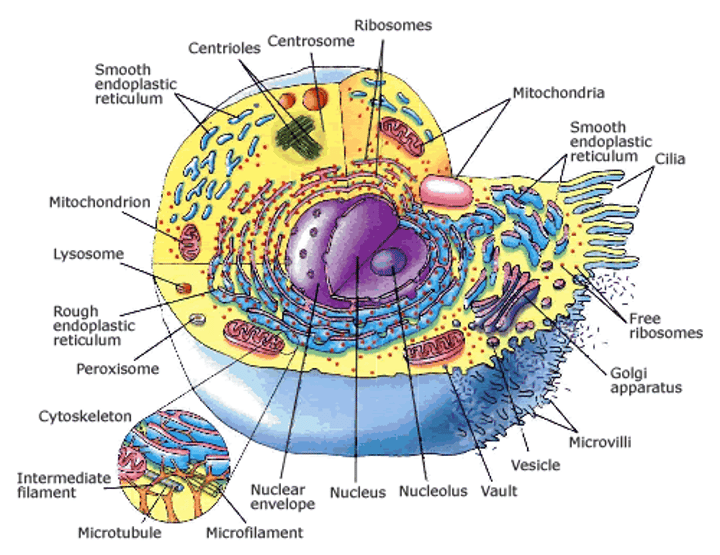
Nucleoid Region -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
DNA region in prokaryotes
Nucleolus -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
Makes ribosomes. Sits in nucleus, no membrane.
Peroxisomes -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
Collect and break down material
Rough ER -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
Accept mRNA to make proteins.
Smooth ER -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
Detox & make lipids.
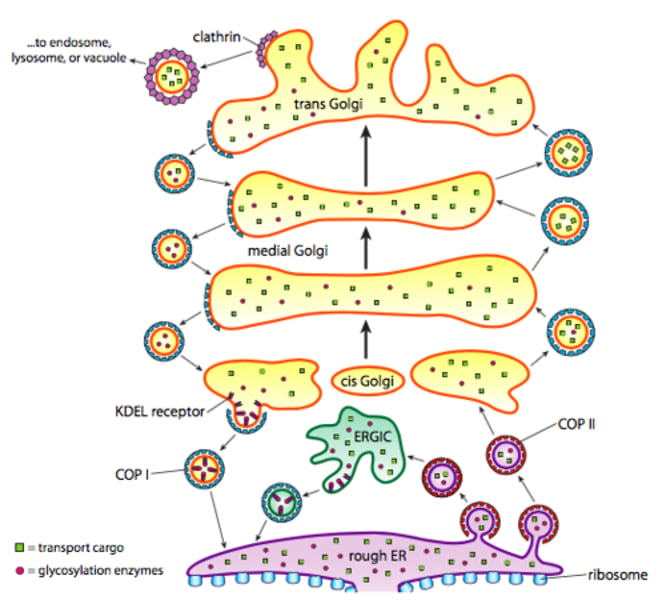
Golgi Apparatus -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
Modify / distribute proteins. Only in eukaryotes
-Vesicular Transport
-Cisternal Maturation
Vesicular Transport -(Golgi Apparatus)(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
Distributing proteins
COPI is needed to move vesicle forward from golgi apparatus to ER
COPII is needed to return the vesicle from ER to golgi apparatus
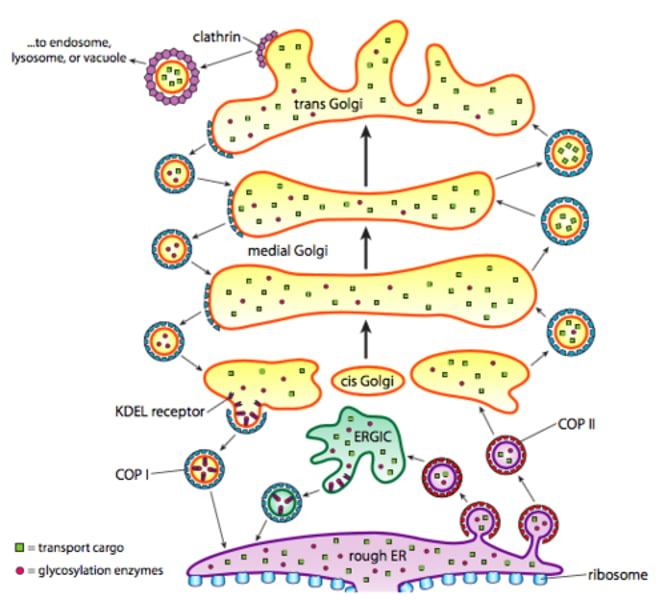
Cisternal Maturation -(Golgi Apparatus) (Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
Vesicles travel in retrograde New Cis made Cis/Medial/Trans/Exit
Centrioles -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
9 groups of microtubules, pull chromosomes apart
Lysosomes -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
Demo & Recycling center. made by Golgi. Single membrane
Plasmids -(Parts of cell) (1. The cell)
in prokaryotes. Carry DNA not necessary for survival.
Bacteria
single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus; prokaryotes
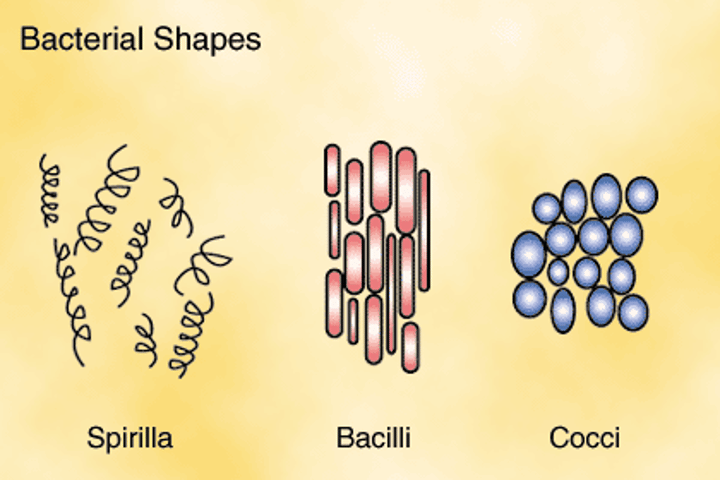
Obligate Aerobe (Bacteria) (1. The cell)
Requires O2
Obligate Anaerobe (Bacteria) (1. The cell)
Dies in O2
Facultative Anaerobe (Bacteria) (1. The cell)
Toggle between Aerobic/Anaerobic
Aerotolerant Anaerobes (Bacteria) (1. The cell)
Does not use O2 but tolerates it
Gram + is PURPLE (Bacteria) (1. The cell)
THICK peptidoglycan/lipoteichoic acid cell wall
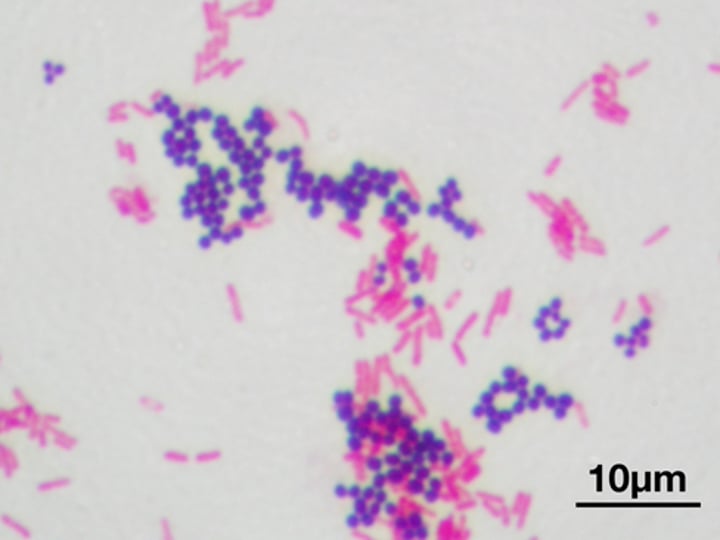
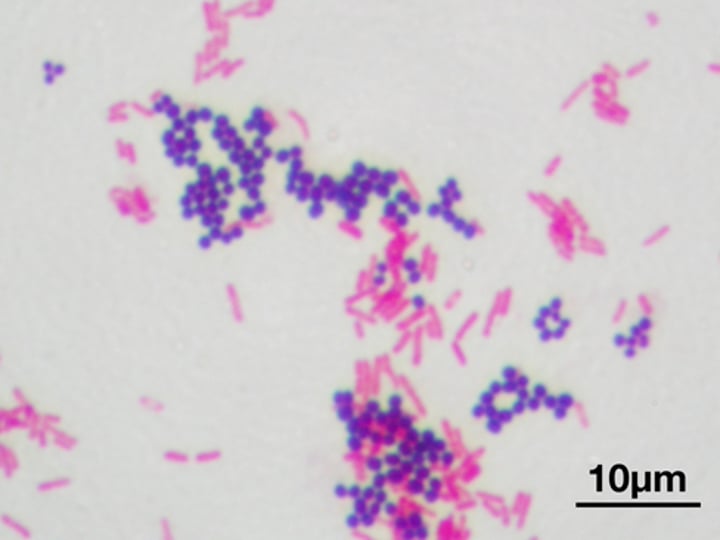
Gram - is PINK-RED (Bacteria) (1. The cell)
THIN peptidoglycan cell wall & an outer membrane.
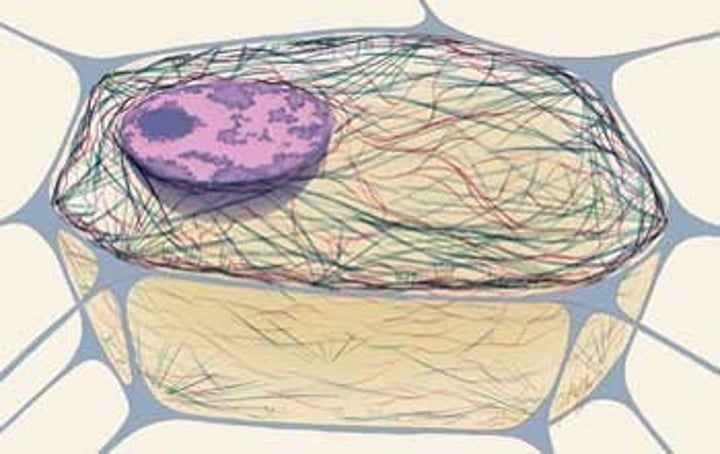
Eukaryote (Eukaryote vs Prokaryote) (1. The cell)
ETC (Electron transport chain) in mitochondria
Large ribosomes
Reproduce via mitosis
Prokaryote (Eukaryote vs Prokaryote) (1. The cell)
ETC (Electrron transport chain) in cell membrane
Small ribosomes
Plasmids carry DNA material. May have virulence factors.
Episomes (Prokaryote) (1. The cell)
Plasmids that integrate into genome
Prions (Miscellaneous) (1. The cell)
infectious proteins. Trigger misfolding. (alpha)-helical to (beta)-pleated sheets. solubility decreases
Viroid (Miscellaneous) (1. The cell)
Plant pathogens
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Microfilaments (cytoskeleton) (1. The cell)
Actin
Microtubules (cytoskeleton) (1. The cell)
Tubulin
Intermediate Filaments (cytoskeleton) (1. The cell)
Keratin = Vimentin; Desmin = Lamin
Tissues
Groups of cells with a common structure and function.
Epithelia (Tissues) (1. The cell)
Parenchyma
Simple
Stratified
Pseudostratified
Cuboidal
Squamous
Parenchyma (Epithelia) (Tissues) (1. The cell)
Functional parts of organ
Simple (Epithelia) (Tissues) (1. The cell)
One layer
Stratified (Epithelia) (Tissues) (1. The cell)
Multiple layers
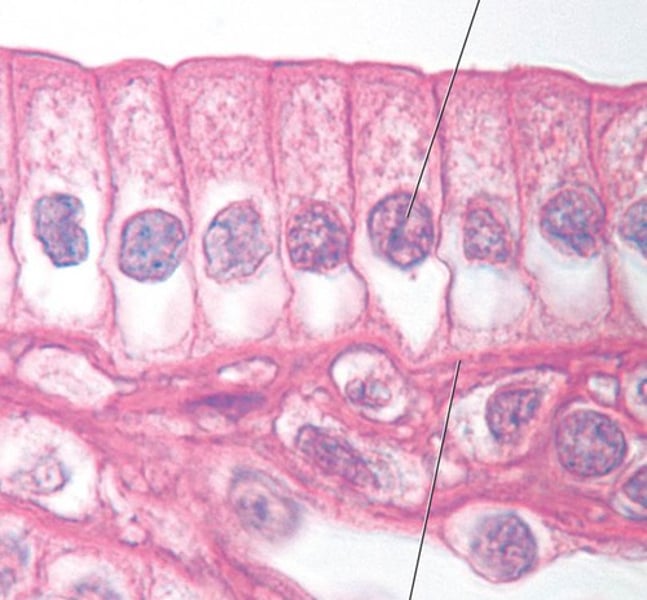
Pseudostratified (Epithelia) (Tissues) (1. The cell)
One layer (looks mult, but really just 1)
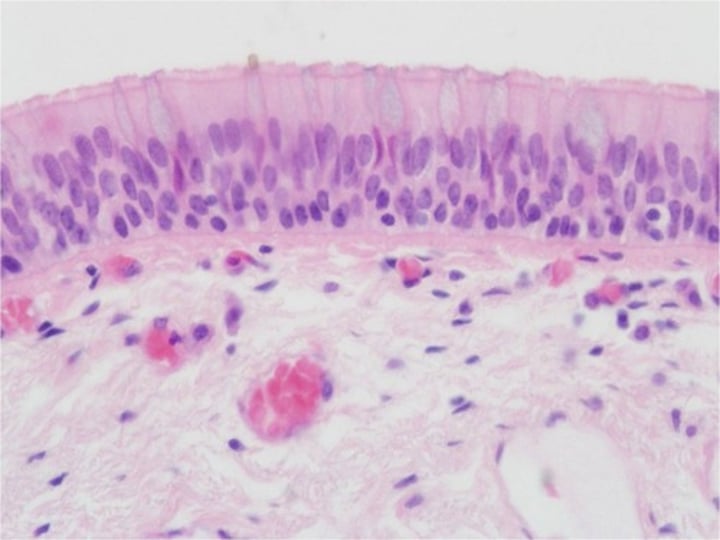
Cuboidal (Epithelia) (Tissues) (1. The cell)
Cube shape
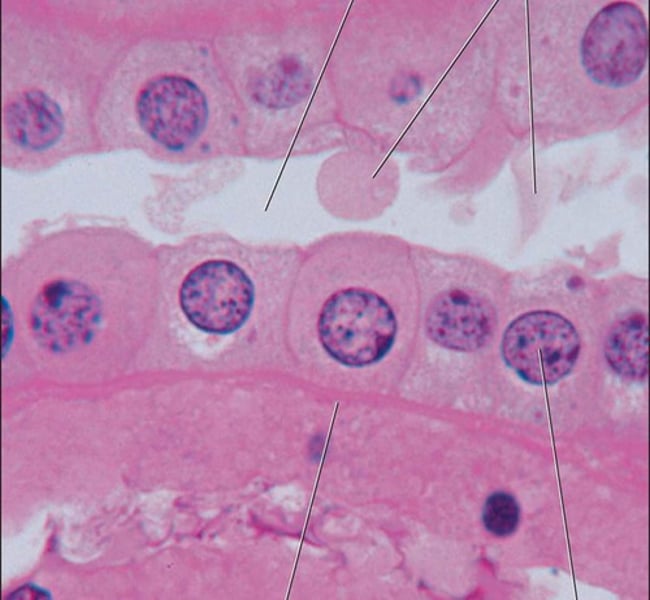
Columnar (Epithelia) (Tissues) (1. The cell)
Long and narrow
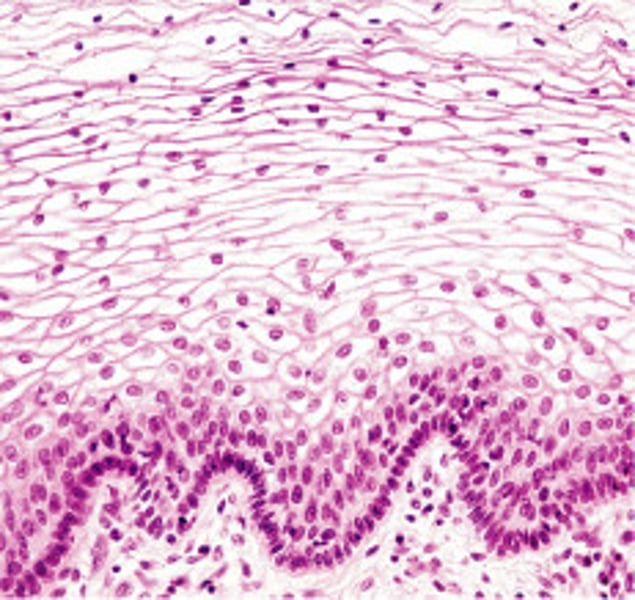
Squamous (Epithelia) (Tissues) (1. The cell)
Flat, scale-like
Connective (Tissues) (1. The cell)
Stroma (support, extracellular matrix). Bone, cartilage, tendon, blood
Genetic recombination
The regrouping of genes in an offspring that results in a genetic makeup that is different from that of the parents.
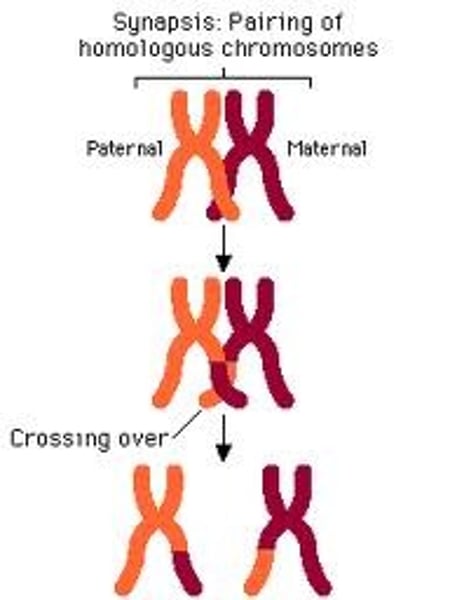
Transformation (Genetic Recombination) (1. The cell)
Gets genetic info from environment
Conjugation (Genetic Recombination) (1. The cell)
Transfer of genetic info via conjugation bridge
F+ to F- or Hfr to recipient
Transduction (Genetic Recombination) (1. The cell)
Transfer using bacteriophage
Transposons (Genetic Recombination) (1. The cell)
Genetic info that can insert/remove themselves
Capsid (Viruses) (1. The cell)
Protein Coat
Viruses
tiny particles, smaller than bacteria and other pathogens, which must invade living cells in order to reproduce; when they invade, the cells are damaged or destroyed in the process releasing new particles to infect other cells
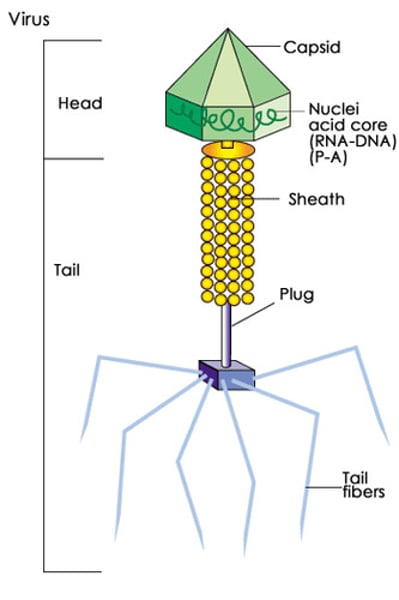
Envelope (Viruses) (1. The cell)
Some have lipid envelope
Virion (Viruses) (1. The cell)
Individual virus particles
Bacteriophage (Viruses) (1. The cell)
Bacteria virus. Tail sheath injects DNA / RNA
Viral Genome (Viruses) (1. The cell)
May be DNA or RNA. Single or double stranded
If viral RNA is single strand
Positive Sense
Negative Sense
Positive Sense (If Single Strand) (Viruses) (1. The cell)
Can be translated by host cell
Negative Sense (If Single Strand) (Viruses) (1. The cell)
RNA replicase must synthesize a complimentary strand, which can then be translated
Retrovirus (Viruses) (1. The cell)
Single stranded RNA. Reverse transcriptase needed to make DNA
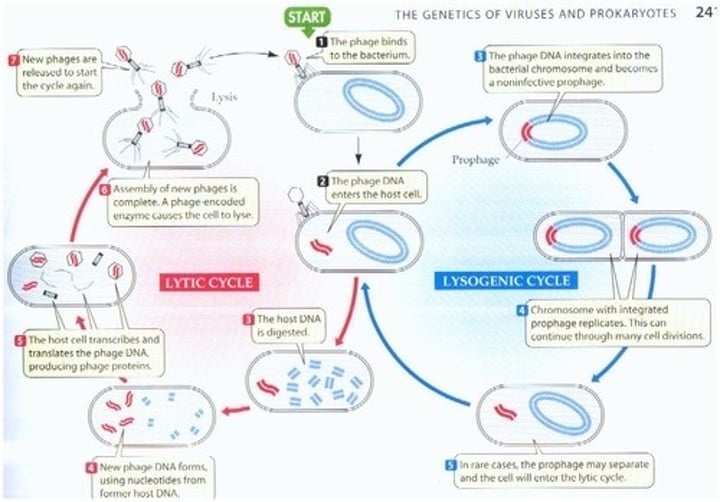
Bacteriophage Lytic (Viruses) (1. The cell)
Virions made until cell lyses
Life Cycles Lysogenic (Viruses) (1. The cell)
Virus integrates into genome as provirus or prophage. Goes dormant until stress activates it.
cell cycle (2. Reproductive)
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
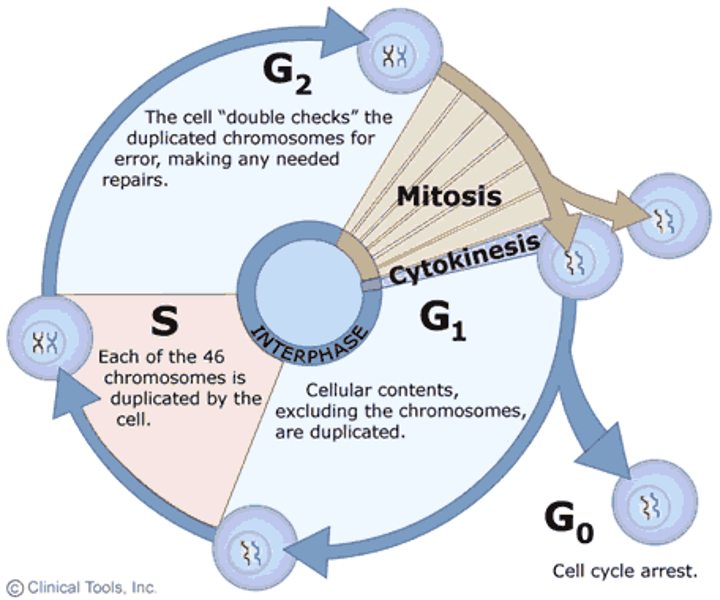
G1 (cell cycle) (2. Reproductive)
Make mRNA and proteins to prep for mitosis
G0 (cell cycle) (2. Reproductive)
A cell will enter G0 if it Does Not need to divide
-Neurons
G1 checkpoint (cell cycle) (2. Reproductive)
Cell decides if it should divide. P53 in charge
S (cell cycle) (2. Reproductive)
DNA replicated
G2 (cell cycle) (2. Reproductive)
Cell growth. Make organelles
G2 checkpoint (cell cycle) (2. Reproductive)
Check cell size & organelles
M (cell cycle) (2. Reproductive)
Mitosis and cytokinesis
cell growth signals
Consist of
-Positive growth signals
-Negative growth signals
Positive growth signals (cell growth signals) (2. Reproductive)
1) CDK + Cyclin create a complex
2) Phosphorylate Rb to Rb + P
3) Rb change shape, releases E2F
4) Cell division continues
Negative growth signals (cell growth signals) (2. Reproductive)
1) CDK inhibitors block phosphorylation of Rb
2) So, E2F stays attached
3) Cell cycle halts
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
-PMAT
-Ploidy of 2n throughout
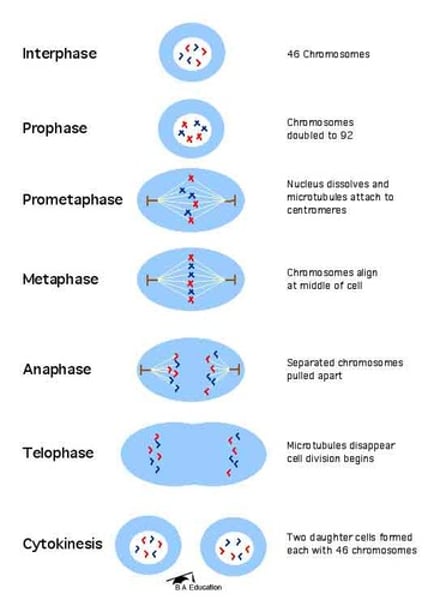
Prophase (Mitosis) (2. Reproductive)
DNA condenses. Centrioles migrate to opposite poles and microtubules form. Nuclear envelope disappears
Metaphase (Mitosis) (2. Reproductive)
"Meet in the middle". Chromosomes meet in middle
Anaphase (Mitosis) (2. Reproductive)
"Apart". Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
Telophase (Mitosis) (2. Reproductive)
Chromosomes decondense. Nuclear membrane forms. Cytokinesis occurs
Cytokinesis (Mitosis) (2. Reproductive)
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual
Sex determined by 23 pairs of chromosomes.
xx=female
xy=male
X-Linked Disorders (sex chromosomes) (2. Reproductive)
Males express, females can be carriers
Y-Chromosome (sex chromosomes) (2. Reproductive)
Littel genetic info. SRY gene = "Sorry you're a male)
Meiosis (2. Reproductive)
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
-PMAT x2
-Nondisjunction could occur and it results in aneuploidy
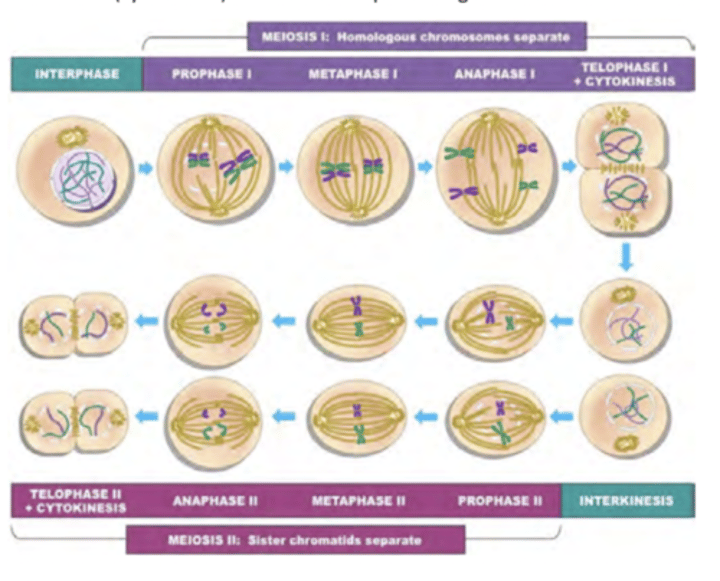
Prophase I (Meiosis) (2. Reproductive)
Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents.
-Crossing over occurs
(Recombination does occur but the chromosomes are still homologous)
Metaphase I (Meiosis) (2. Reproductive)
Spindle fibers from opposing centrosomes connect to bivalents (at centromeres) and align them along the middle of the cell
Anaphase I (Meiosis) (2. Reproductive)
Homologous pairs move to opposite poles of the cell. This is disjunction and it accounts for the Law of segregation.
(this is where nondisjunction would occur if it happens)
Telophase I (Meiosis) (2. Reproductive)
Chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane MAY reform, cell divides (cytokinesis), forms two haploid daughter cells of unequal sizes.
Prophase II (Meiosis) (2. Reproductive)
Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrosomes move to opposite poles (perpendicular to before)
Metaphase II (Meiosis) (2. Reproductive)
Spindle fibers from opposing centrosomes attach to chromosomes (at centromere) and align them along the cell equator
Anaphase II (Meiosis) (2. Reproductive)
Spindle fibers contract and separate the sister chromatids, chromatids (now called chromosomes) move to opposite poles
Telophase II (Meiosis) (2. Reproductive)
Chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane reforms, cells divide (cytokinesis) to form four haploid daughter cells
male reproductive system (2. Reproductive)
serves to produce sperm and introduce them into the female body
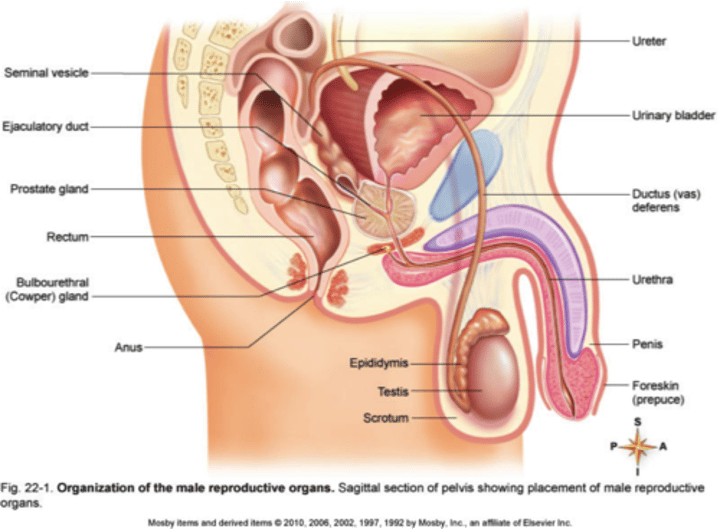
Semen (male reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
Sperm + seminal fluid
Bulbourethral Glands (male reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
Makes viscous fluid to clean out urethra
Seminal Vesicles & Prostate Gland (male reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
Make alkaline fluid to help sperm survive acidic environment of female reproductive tract
Sperm pathway (male reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
SEVE(N)UP
Seminiferous tubules
Epididymis
Vans deferens
Ejaculatory duct
Urethra
Penis
Female Reproductive System
produces eggs for reproduction and provides place for growing baby.
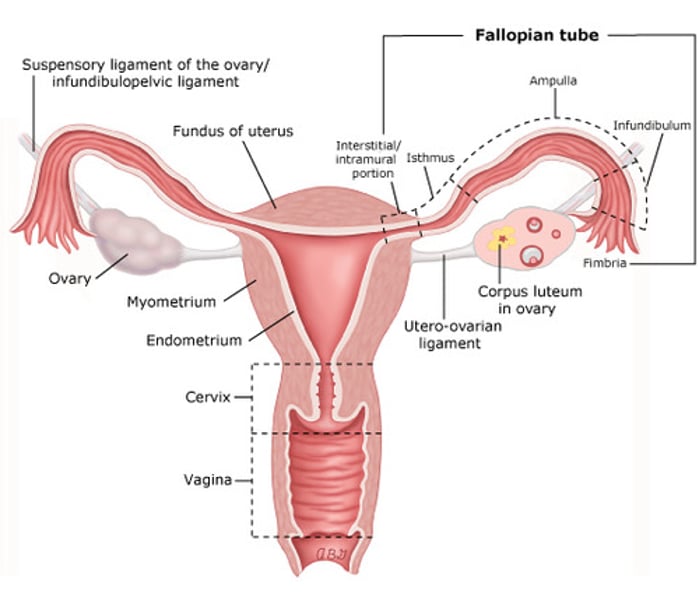
Ovaries (Female reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
Have follicles that produce ova. Controlled by FSH and LH
Oogenesis (Female reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
Production of female gametes
Estrogen (Female reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
Hormone; Response to FSH. Develops rep tract, thickens uterine wall
Estrogen establishes; progesterone protects the endometrium
Progesterone (Female reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
Response to LH. Maintains / protects endometrium.
Estrogen establishes; progesterone protects the endometrium
Pathway (Female reproductive system) (2. Reproductive)
Egg to peritoneal sac to fallopian tube / oviduct
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
Promotes secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
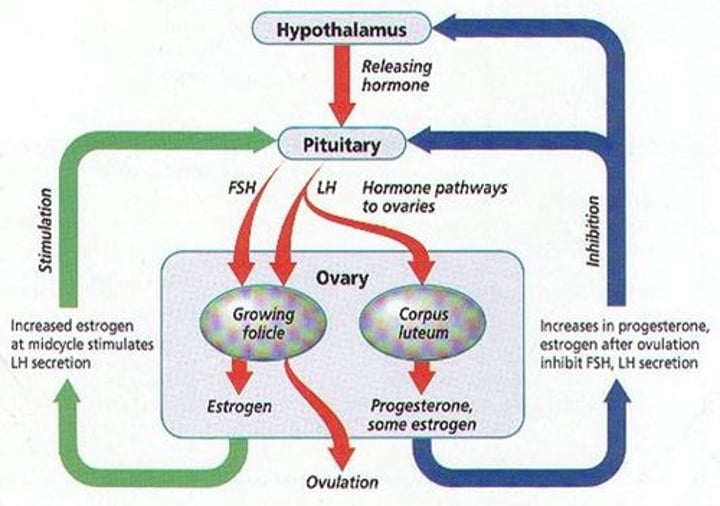
FSH Follicle stimulating hormone (GnRH) (2. Reproductive)
Males: Triggers spermatogenesis, stimulates sertoli cells.
Females: Stimulates development of ovarian follicles.
LH Lutenizing hormone (GnRH) (2. Reproductive)
Males: Causes interstitial cells to make testosterone
Females: Induces Ovulation
Embryogenesis
The process by which a single-celled zygote becomes a multicellular embryo.
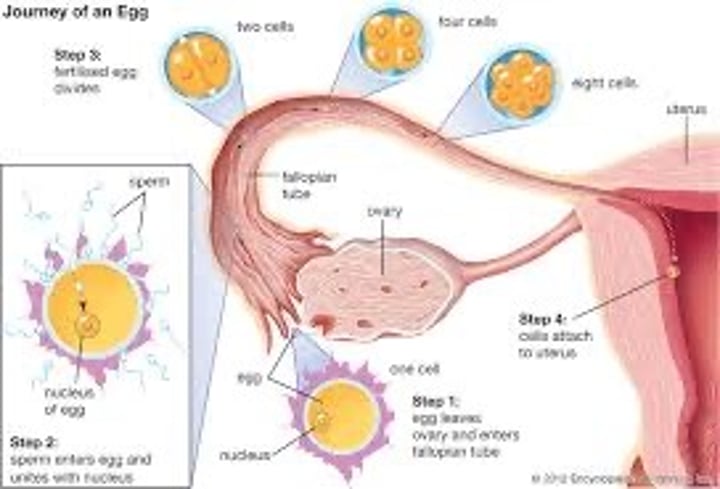
Fertilization (3. Embryogenesis and Development)
(1) Occurs in the Ampulla of Fallopian tube. Sperm's Acrosomal enzymes penetrate corona radiate & zona pellucid.
Acrosomal enzymes inject pronucleus.