PATHOLOGY EXAM 3
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
follow up
management for mild dysplasia
severe dysplasia
atypical morphology involving ENTIRE thickness of epithelium
pleomorphism
abnormal shape and size of cells
excisional biopsy
complete surgical removal
fibroma, mucocele, lipoma, or papilloma
lesions that would be biopsied with EXCISIONAL biopsy
large, leukoplakia, erythroplakia, ulcer, SCC, tumor, lichen planus
lesions that would be biopsied with INCISIONAL biopsy
leukoplakia
clinical term used to describe white premalignant lesion
gingiva
common site for proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
floor of mouth, lateral/ventral tongue, lower lip, soft palate
high risk sites for premalignant lesions and cancer
premalignant
what is the concern with this lesion
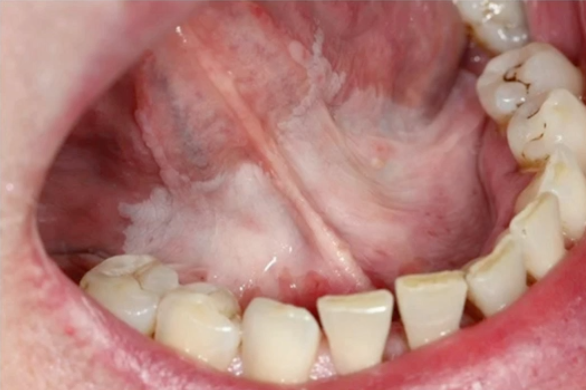
proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
lesion with highest risk of malignant tranformation
incisional biopsy
what is the management of this lesion
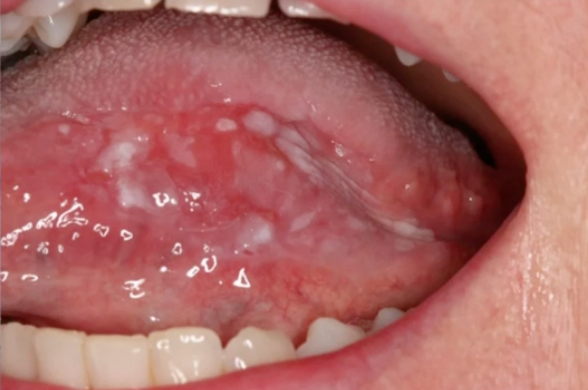
cellular atypia
histological hallmark of epithelial dysplasia
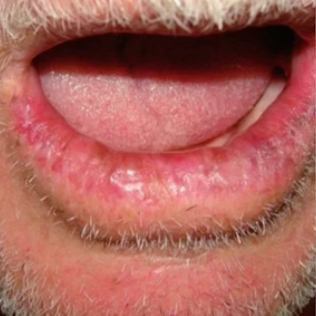
actinic cheilosis (farmers/sailors lip)
what is this lesion
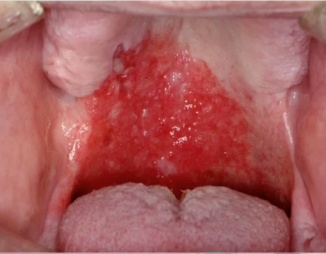
oral submucous fibrosis
due to beta nut chewing
cancer
what do you want to rule out
red and white mixed lesion
clinical feature that raises the most concern for dysplasia or. carcinoma
chewing tobacco
what is the cause of this lesion
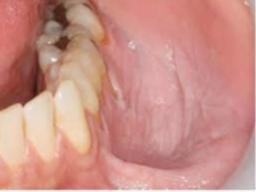
basal cell carcinoma
typically presents with central depression and rolled borders
smokeless tabacco
habit strongly associated with verrucous carcinoma
basal cell carcinoma
most common type of skin cancer
squamous cell carcinoma
most common type of ORAL cancer
floor of mouth
highest risk site for oral cancer
lip arises from actinic cheilitis
what distinguishes lip from oral SCC?
oral
type of SCC that has worst prognosis
any M, T4, or N1
stage with worst prognosis
T1 N0 M0
stage with BEST prognosis
through lymph nodes
how is metastatic disease spread
metastatic disease
presents with painless, enlarged, stiff, and immobile lymph nodes.
basal cell carcinoma
GORLIN SYNDROME is associated with
smoking cigarettes
highest risk factor for oral squamous cell carcinoma
lung
most common SITE for OSCC to metastasize
HPV+ non smoker
type of OSCC with best prognosis
HPV- smoker
type of OSCC with worst prognosis
incisional biopsy
what is the appropriate management
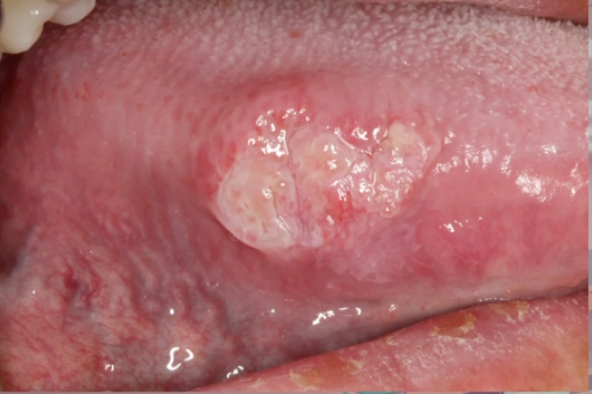
tumor size
what does T in TNM stand for?
verrucous carcinoma
what is the diagnosis
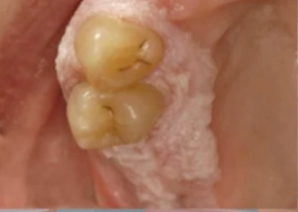
lymphatic spread
main route of metastasis for OSCC
incisional biopsy
what is the best management of this lesion
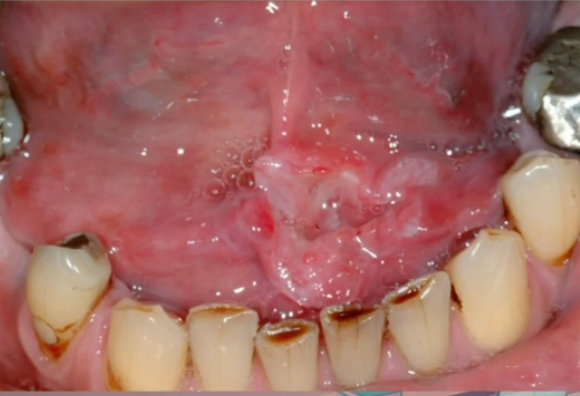
dorsum of tongue
which location is LEAST likely to be affected by OSCC
basal cell carcinoma
what is the most likely diagnosis
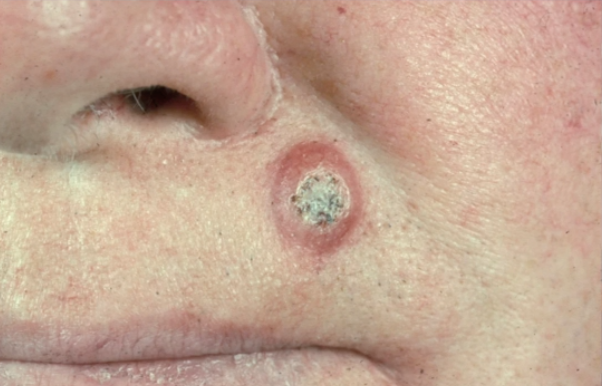
smokeless tobacco
verrucous carcinoma is most commonly associated with?
scar-like texture
characteristic of morpheaform basal cell carcinoma
HPV
virus linked to OSCC
sentinel lymph node
FIRST node to receive metastatic cells from primary tumor
basal cell carcinoma
rodent ulcer is known as
snuff dippers/ackerman’s tumor
other names for verrucous carcinoma
HPV 16
type of HPV linked to OSCC
stage 4
stage of OSCC that has spread to lungs
surgical excision
treatment for squamous papilloma
HPV 2
cause of verruca vulgaris
soft palate
most common location for oral squamous papilloma
condyloma
multiple bulbous papillary lesions
16 and 18
high risk HPV types
shingles
presents with unilateral, painful, vesicular lesions distributed along skin of trigeminal nerve
measles
childhood disease presents with KOPLIK SPOTS
condyloma acuminatum
SEXUALLY transmitted lesion that may RECUR after treatment
on keratinized mucosa only
distinguishing feature of recurrent intraoral herpes
hairy leukoplakia
oral lesion associated with EPSTEIN BARR in immunocompromised patients
primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
8 year old patient with fever, fatigue, and intra oral lesions. diagnosis?
HPV 2, 6, or 11
viruses that could causes this lesion
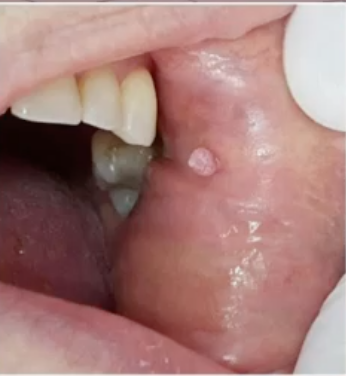
HSV 1
cause of this lesion

deafness
most common complication of congenital rubella syndrome
surgical excision
management?
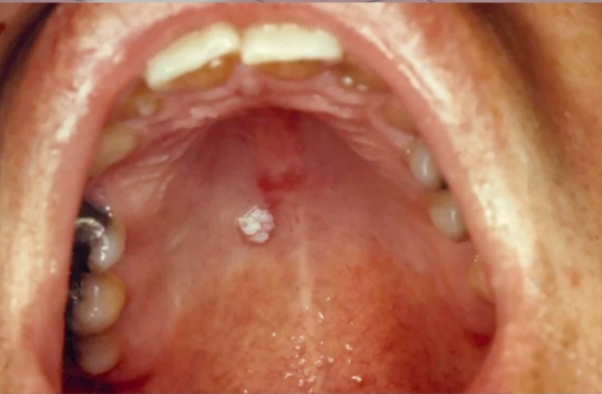
burkitt lymphoma
associated cancer of EPSTEIN BARR virus
koplik spots
what are these spots, caused by PARAMYXOVIRUS (measles)
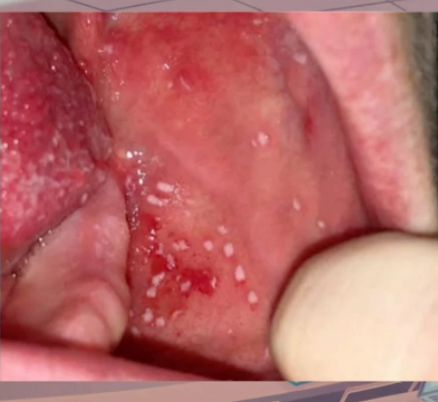
lymphadenopathy, enlarged tonsils, prodromal signs
characteristic features of infectious mononucleosis
HIV/AIDS
what disease are these lesion associated with?
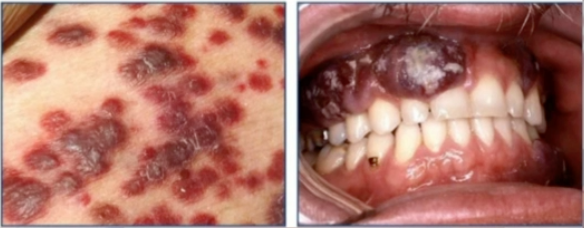
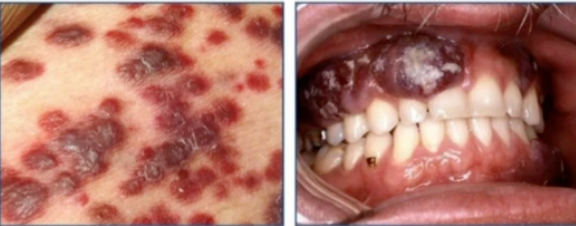
kaposi sarcoma
diagnosis
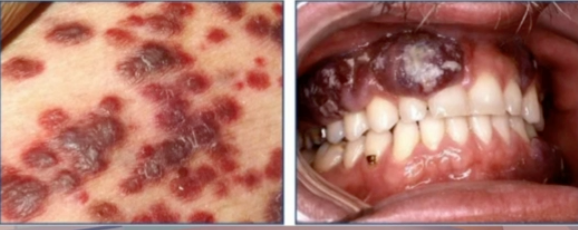
HHV-8
cause of these lesions
hairy leukoplakia, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, infectious mono
diseases caused by EPSTEIN BARR virus
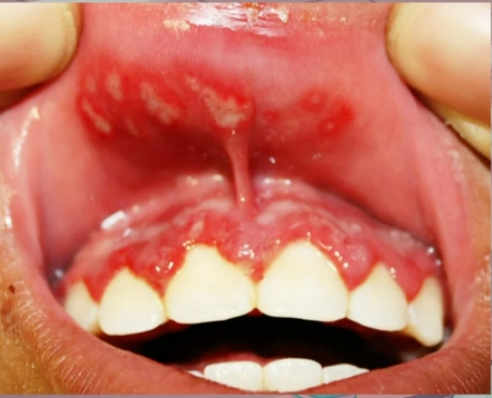
primary herpetic gingivostomatitis (primary herpes)
diagnosis?
rheumatic fever
possible complication of untreated strep throat
red, prominent fungiform papillae
cause of strawberry appearance of tongue in scarlet fever
weight loss, night sweats, fever, persistent cough
symptoms of tuberculosis
scrofula
form of tuberculosis with CERVICAL lymph node involvement due to CONTAMINATED MILK
primary
stage of SYPHILIS that presents with CHANCRE
decayed tooth
most common predisposing factor for ACTINOMYCOSIS
rule out malignancy
reason for BIOPSY in OSTEOMYELITIS
lymph nodes
CAT SCRATCH disease spreads to?
opportunistic infection
non-pathogenic organisms causing disease in compromised hosts
angular cheilitis
form of CANDIDIASIS associated with NUTRITIONAL DEFICIENCY
acute atrophic candidiasis
CANDIDIASIS after ANTIBIOTIC therapy
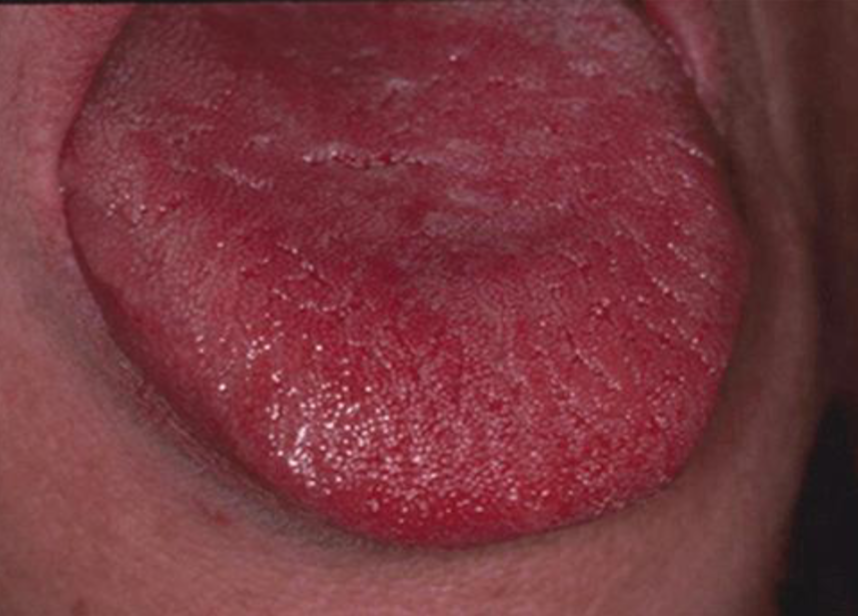
median rhomboid glossitis
candidiasis variant with ERYTHEMA and PAPILLA loss on TONGUES MIDLINE
clinical features and mucosal smear
primary DIAGNOSTIC METHODS for CANDIDIASIS
fluconazole and ketoconazole
systemic antifungals
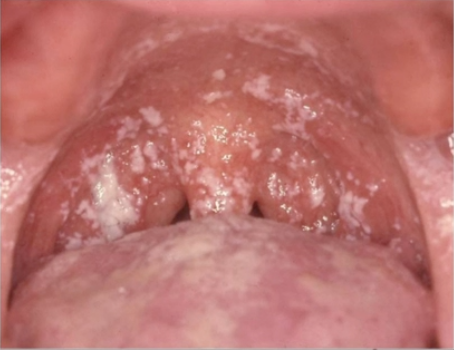
pseudomembranous candidiasis
patient complains of metallic taste and burning sensation, diagnosis?
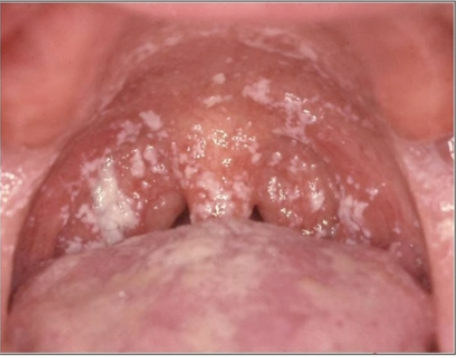
nystatin oral suspension
management?
predisposing factors
in addition to antifungal therapy, what should be addressed for LONG TERM CANDIDIASIS CONTROL
primary involvement of lungs in immunocompromised
common feature of DEEP FUNGAL infections
diabetes
typical risk factor for MUCORMYCOSIS
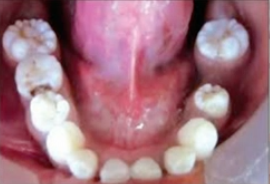
congenital syphilis
condition associated with these abnormal teeth
ill defined asymmetric radiolucency
typical radiographic finding in CHRONIC OSTEOMYELITIS
denture stomatitis
diagnosis
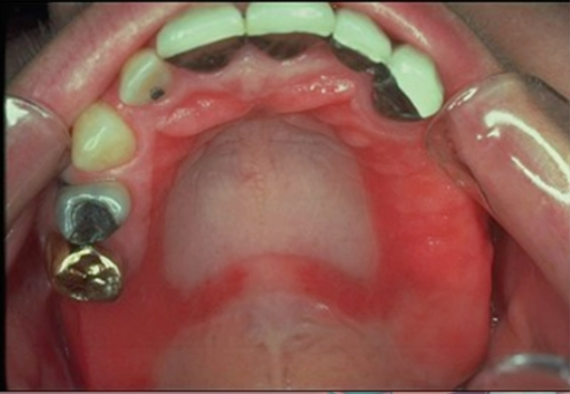
antifungal therapy
management?
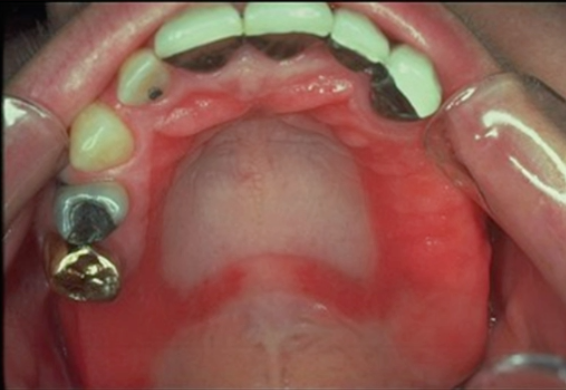
white plaque, can be wiped off
key characteristic of PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS CANDIDIASIS
wickham striae
clinical feature of RETICULAR lichen planus
erythema and bleeding
sign of EROSIVE lichen planus
clobetasol
treatment for lichen planus
moveable mucosa (ex: buccal)
location of apthous ulcer