MSK II final exam
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
thoracic outlet syndrome
Group of disorders that results in pain and other symptoms in the shoulder, arm, and neck due to compression of nerves or blood vessels below the clavicle
neurogenic TOS
most common type of thoracic outlet syndrome
Roo’s Test
test for TOS
aka EAST
venous TOS
Asymetrical upper extremity edema
Pain in the chest
Cyanosis
Cyanosis
Fatigue, feeling of heaviness
Venous engorgement
Visible veins compared to non involved side
neurogenic TOS
Pain, paresthesia
Headaches
Decreased dexterity
Cold intolerance
Color changes/sympathetic over activity
arterial TOS
pain in hand
Pallor
Coldness
Dead arm
Can be fatal
treating TOS
symptom control, specific postural control exercises, general maintenance exercises
primary bone healing
occurs with a reduction without a callus formation where there is <2% strain on fx
secondary bone healing
occurs with fixation devices and a fracture healing where there is 2-10% strain
includes a callus
endochondral ossification
the most common type of fracture healing
hematoma stage
1st 24 hours:
fibrin blood clot
stability/immobilization is crucial during callus formation during hematoma
cast/splint, internal and external fixators
inflammatory stage
1st 24 hours to 1 wk
Hematoma forms, fibroblast migrate to the fracture site and osteoblasts.
Fibroblasts proliferate
Fractures are immobilized during phase I
Repair stage
1-6 weeks
Callus forms (2-3 wks)
Soft callus converts to hard callus (4-6 wks)
The stiffer the mobilization a lesser amount of callus will form
Flexible immobilization allows for an abundant callus creating endochondral ossification
Remodeling
extra-articular matrix undergoes calcification
Wolf’s Law
bone remodels in response to mechanical stress
4-6 weeks
how long the pt should be immobilized after a fracture
displaced
a bone breaks into two or more pieces and moves out of alignment
non-displaced
the bone breaks but does not move out of alignment
closed
the skin is not broken
open
the bone has broken through the skin
transverse
broken piece of bone is at a right angle to the bone’s axis
linear
the break is parallel to the bone’s long axis
oblique
the break has a curved or sloped pattern
spiral
one part of the bone has been twisted at the break point
greenstick
an incomplete fracture in which the bone is bent; occurs most often in children
comminuted
the bone break into several pieces
avulsion
when fragment of bone is separated from the main mass
pathologic
caused by a disease that weakens the bones
stress
a hairline crack
bone healing factors
Lack of vitamin D and calcium
Diabetes: decreases cellularity of fracture callus
Nicotine: inhibits growth of new blood vessels during remodeling
HIV: higher rate of fragile bones, delayed healing
Medications: bisphosphonates, systemic corticosteroids, NSAIDs
Fracture complications
Joint stiffness
Tendon adhesion
Chronic regional pain syndrome
Open fractures: infection/including osteomyelitis
4-6 weeks
about how long it takes for a fracture to fuse
non displaced and stable
managed by protection alone
non displaced but unstable
requires positioning and immobilization in cast or fracture brace
functional capacity exam
assesses the client with standardizes and validated tools to determine job needs and/or accommodations
Subjective
ADL review
Other medical problems
work conditioning
rehab to restore functional work tasks (2-4 days/wkly)
work hardening
multidisciplinary approach to progress client to return to work activities (5 days/wkly)
malingering tests
abductor and hoover’s test
ergonomics
posture and the position of equipment in the work environment are the largest contributing factors to injuries
cycle
how much time to do one cycle
repetitive
less than 2 minute cycle time
highly repetitive
cycle time less than 30 seconds
fundamental cycle
what the cycle involves
1-1.5 hours
breaks should be taken after this amount of continuous compute use
sternal precautions
no pushing, pulling, or lifting arms x 12 weeks
use pillow when coughing
keep your move in the tube
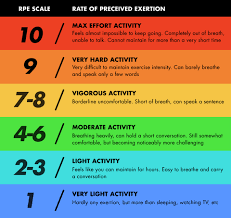
rate of perceived exertion scale
contraindications for therapy
Abnormal vital
Abnormal labs
Up-trending troponins
Femoral access continuous renal replacement therapy
Femoral intra-aortic balloon pump
Chest pain
Active bed rest orders
Inability to actively participate in therapy session
normal blood pressure
systolic: less than 120
diastolic: less than 80
endurance
the ability to sustain an activity over time
a physiological factor
MET
energy expanded during an activity
equals 3.5 mL of oxygen per kg of body weight per minute
1 MET
approximately equivalent to oxygen uptake a person requires at rest
light intensity
1.0 to 2.5 METs
moderate intensity
3.0 to 5.9 METs
vigorous intensity
6.0 METs or more
HR max
220-age
Heart rate reserve
HR max- HR rest
HR target
(HRR x desired % intensity) + HR rest
fatigue
the enduring subjective experience of generalized tiredness or exhaustion
Not a physiological factor
Multidimensional
Includes cardiovascular, emotional, behavioral, and cognitive components
beta blockers and calcium channel blockers
regulate heart rate and blood pressure
client’s heart rate and blood pressure may not change significantly during exertions
radiation therapy
Uses beams of high energy particles to kill cancer cells or slow growth
Can be external or internal
chemotherapy
Systemic drug treatment that travels through the bloodstream to kill cancer cells
Given through IV, shot, oral pill, topical, etc
surgery
Removing the cancer mass or debulking
immunotherapy
Treatment that helps your immune system fight cancer using biological substances
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, T-cell transfer therapy, vaccines
neoadjuvant
treatment given as a first step to shrink a tumor before the primary treatment (i.e. surgery)
adjuvant
additional cancer treatment given after the primary treatment to lower the risk that the cancer will come back
radiation fibrosis
scar tissue due to damage from radiation therapy
Causes stiffness, skin changes, ROM deficits, pain, weakness
Most common in the first 2 years post treatment
Can occur up to 10 years after therapy
Chemo induced peripheral neuropathy
Damage to peripheral sensory, motor, and autonomic neurons caused by neurotoxic antineoplastic agents
lymphedema
tissue swelling caused by accumulation of protein rich fluid
head and neck cancer
highest cancer location for lymphedema
complex regional pain syndrome
Mechanism is not completely understood
90% of cases are triggered by injury involving nerve damage
Most common precipitating conditions
Fractures
Surgery
sprains/strains
Burns or cuts
Penetration
Type 1 CRPS
injury that does not have apparent damage to nerves
previously known as reflex sympathetic disorder
Type II CRPS
damage to peripheral nerve apparent or identified
previously known as causalgia
stage 1 of CRPS
acute
Burning pain, sweating, tenderness, possible patchy bone thinning on x-ray
stage II of CRPS
dystrophic (3 to 6 months)
Skin changes (shine and/or thickened), contractures and pain
stage III of CRPS
atrophic
Loss of motion and function, contractures and thinning of skin
grade I and II
joint mobilization levels for treating CRPS
joint mobilizations
moving joints in specific directions and at different speeds to regain movement (recommended to follow with stretching)
soft tissue indications
>improve tissue extensibility
>promote relaxation
>decrease edema
>modulate pain
>reduce soft tissue movement restrictions
joint mobilization indications
>increase ROM of joint complex
>mobilize joints
>modulate pain
>reduce capsular movement restrictions
>decrease muscle spasms, decrease guarding
grade I
oscillates for pain
grade II
distract combined with a glide taking up slack in the joint
grade III
distract combined with a glide, passive stretch at the end range
rigid tape
tape used to correct a position
elastic tape
tape used for pain management
type 1 diabetes
when the pancreas is unable to create insulin
type 2 diabetes
when cells become insuline resistant
COPD
chronic progressive lung syndrome characterized by airflow blockage and breathing related problems
>includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis
reverse TSA
surgery that is chosen when the pt has a torn rotator cuff injury
anatomical TSA
surgery chosen when the rotator cuff is intact
anatomical TSA precautions
limit resisted shoulder internal rotation and passive external rotation
reverse TSA precautions
limit combine shoulder extension, adduction, and internal rotation
ORIF
gold standard surgery for a clavicle fracture
Colle’s fracture
dorsal displacement of distal radius
Smith’s fracture
volar displacement of distal radius
TWA
remove joint and cut away damage
insert prosthesis
(of the wrist)
TWF
tendons and ligaments are moved to the side
-articular cartilage removed from each joint being fused
-bone graft is placed between each spaces in wrist bone
hip fracture
number one cause of this is a fall
anterolateral hip precautions
do not roll surgical leg outward
osteoarthritis
main cause of TKA
total elbow arthroplasty
damaged part of the humerus and ulna are replaced with artificial components