Brain and Behavior Exam 2
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
action potential
brief and dramatic depolarization of the membrane of an axon; message sent down axons
cation
positively charged ion
anion
negatively charged ion
ion channel
pore through which ionsmay pass into or out of the cell; embedded in the membrane of the cell
sodium (Na+)
When no signl is traveling down an axon, ______ ions have a higher concentration outside the cell than inside the cell
Potassium (K+)
When no signal is traveling down an axon, _____ ions have a higher concentration inside the cell than outside the cell
diffusion
tendency for molelcules to distribute themselves evenly
electrostatic pressure
opposite charges attract; like charges repel; thus, ions tend to move to an area with its opposite charge
Na+ ion channels open
Na+ ions move inside the axon
K+ ion channels open
K+ ions move outside the axon
four steps of action potential
voltmeter
registers the difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of the cell (membrane potential)
oscilloscope
records the changes in membrane potential over time
membrane potential
difference in electrical charge (in millivolts) between the inside and outside of a cell; in reference to axon potential it is the difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of an axon
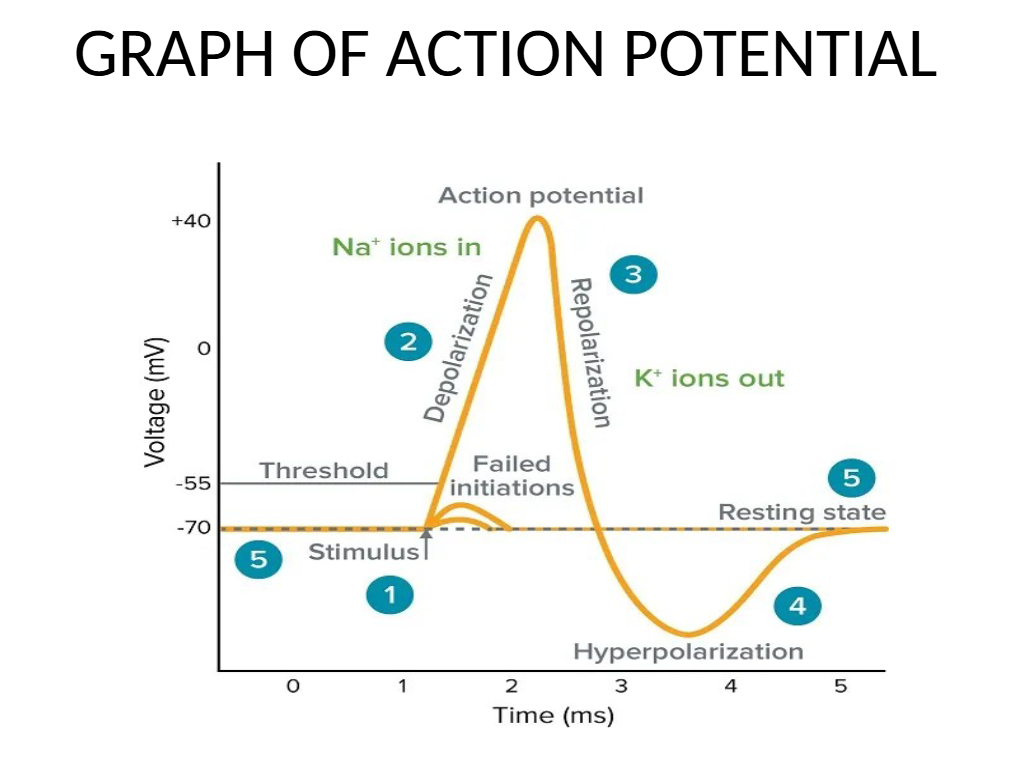
resting potential
membrane potential in the absence of stimulation or an action potential; it is a condition of polarization
negatively; -70mV
At resting potential the inside of the axon is ______ charged with respect to the outside. About how many millivolts?
graded potential
small voltage fluctuations across the membrane (between the inside and outside) of an axon
depolarization
when the inside of an axon is less negative than it was at resting potential
hyperpolarization
when the inside of an axon is more negative than it was at resting potential
threshold of excitation
minimum amount of depolarization needed in order for an action potential to occur
reversed polarization
a condition where the membrane potential has a positive value; occurs at the peak of an action potential “spike: when the membrane potential is a positive value
repolarization
when the membrane potential is retruning back to the resting potential after the peak of the action potential “spike”; occurs due to potassium (K+) ions axiting the ion
slatatory conduction
refers to the fast movement of a signal in a mylinated axon; action potentials only occur in the nodes of ranvier
decreases signaling (action potentials) in sensory neurons; decreases signaling by blocking sodium (Na+) ion channels in the senory neuron axons
How does lidocane work?
synapse
spatial junction between one neuron and another; forms the information transfer site between two neurons
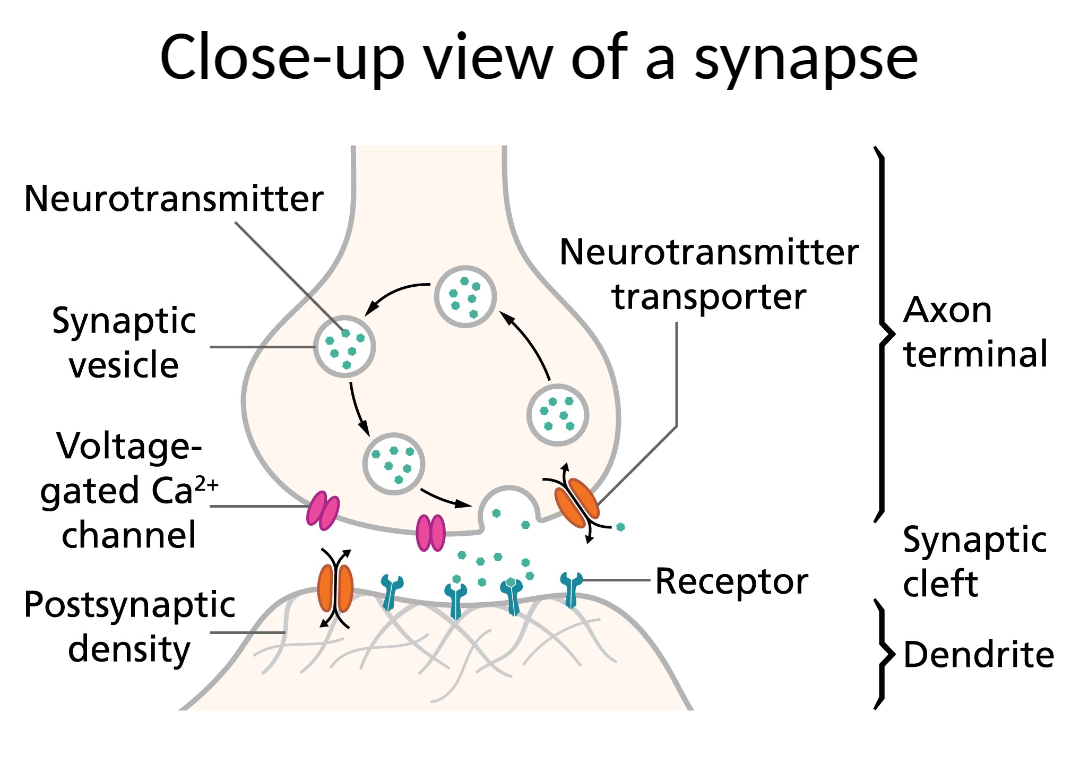
microtubules
anatomy of a synapse:
long structures containing muscle fibers that extend from the soma to the terminal buttons; transport synaptic vesicles to the terminal buttons
synaptic vesicles
anatomy of a synapse:
spherical structures that contain the chemical messengers
neurotransmitter molecules
anatomy of a synapse:
chemical messengers used for communication between the presynaptic membrane and postsynaptic membrane
synaptic gap (cleft)
anatomy of a synapse:
space between presynaptic and postsynaptic membrane
presynaptic membrane
anatomy of a synapse:
at the very end of the terminal button; place from which chemical messengers are released from the presynaptic neuron
postsynaptic membrane
anatomy of a synapse:
the place on the postsynaptic neuron that recieves chemical messengers
postsynaptic receptors
anatomy of a synapse:
protein complexes embedded in the postsynaptic membrane; contain binding sites for chemical messengers
reuptake transporters
anatomy of a synapse:
proteins embedded in the postsynaptic membrane; each contain a channel (pore) through which chemical messengers are brought back into the presynaptic neuron after brief exposure in the synaptic gap
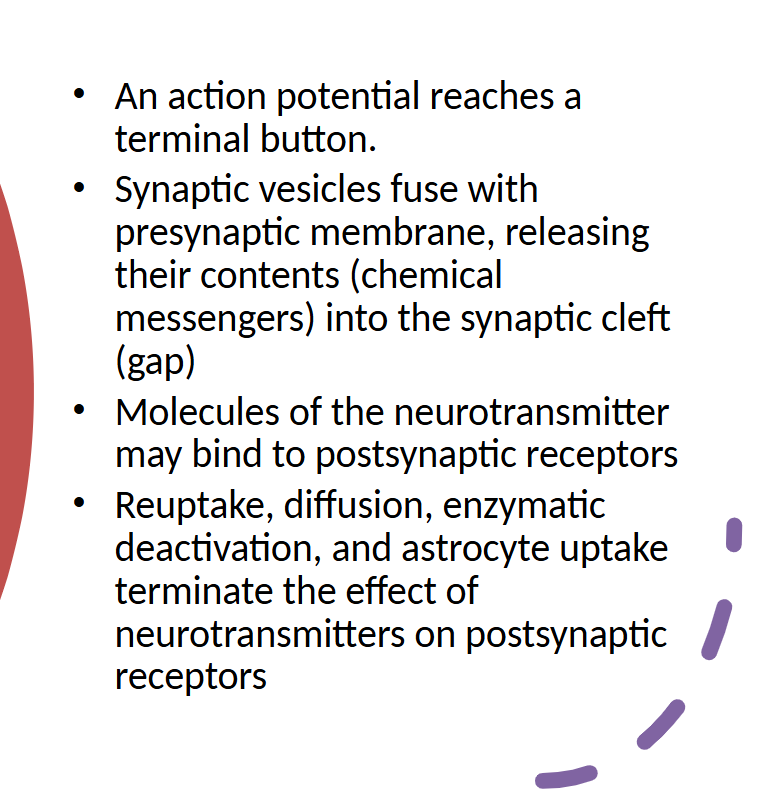
steps of a synaptic transmisson
neural integration
refers to the combining of excititory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) by the dendrites and somas of postsynaptic neurons
whether or not an action potential occurs in the axon of a postsynaptic neuron
What does the result of neural integration determine?
postsynaptic potentials
________ are graded potentials occuring in the postsynaptic membrane (of a postsynaptic neuron)
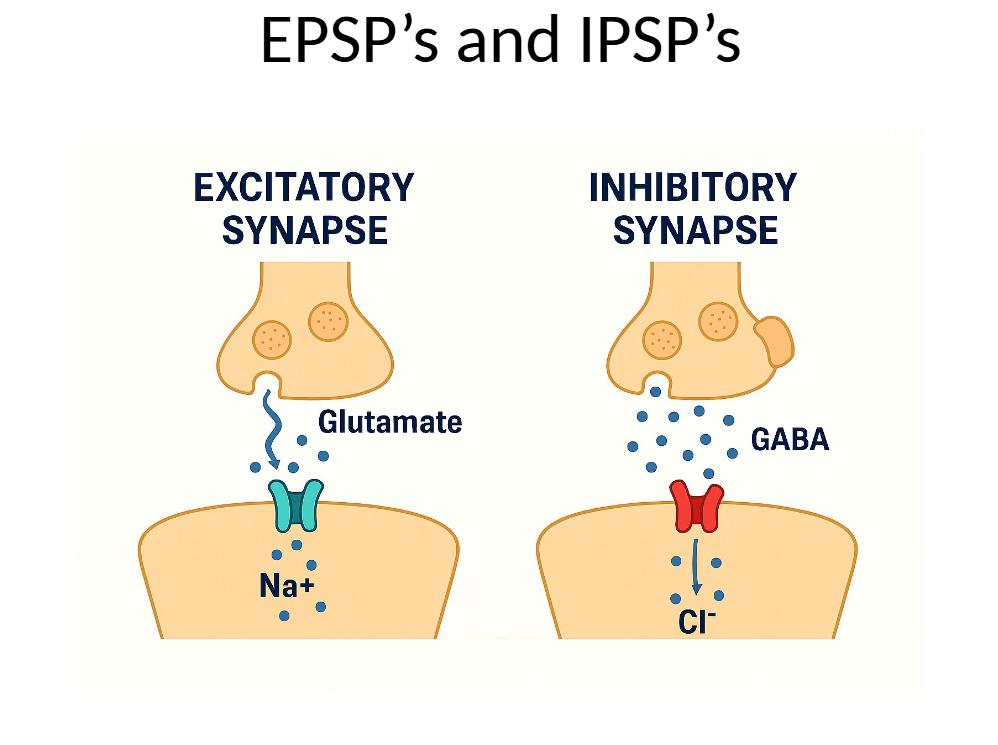
excititory postsynaptic potenials (EPSPs)
associated with the opening of ion channels that allow for the flow of sodium (Na+) ions to the inside of the cell, producing a decrease in the membrane potential (less lenagtive than before)
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs)
associated with the opening of ion channels to allow for the flow of potassium (K+) to the outside of the cell, or ion channels that allow for the flow of chloride (Cl-) ions to the inside of the cell, producing increase in membrane potenial (more negative than before)
efficacy
maximum effect obtainable, with additional doses producing no effect
affinity
how tightly a drug binds to its receptor
agonist
mimics a neurotransmitter; acts like the neurotransmitter it replaces
antagonist
blocks neuro transmitter function
blindsight
exhibit cortical blindness (are not conciously aware of what they see) due to damage in area V1 in the occipital lobe
Balint’s syndrome
person may exhibit a wide variety of difficulties related to spatial cognition