Exam 2: Pediatric Health and wellness
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Pediatrics
branch of medicine dealing with the health and medical care of infants, children, and adolescents from birth to 18yrs
(note: not always 18yrs)
Pediatrics is a __________________ specialty that encompasses children's _______________, ______________, ______________ and ___________________
- multifaceted
- physical
- psychosocial
- developmental
- mental health
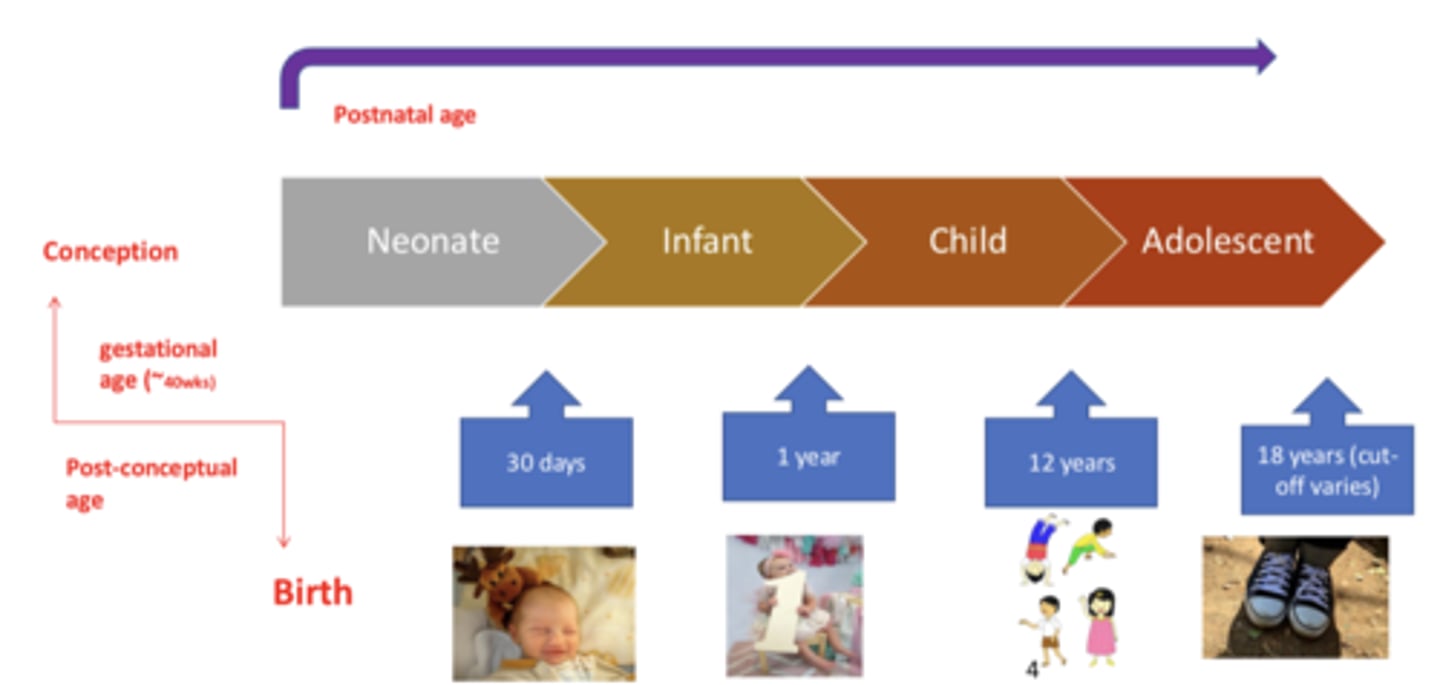
Gestational age
the time from conception to birth
- 40 weeks
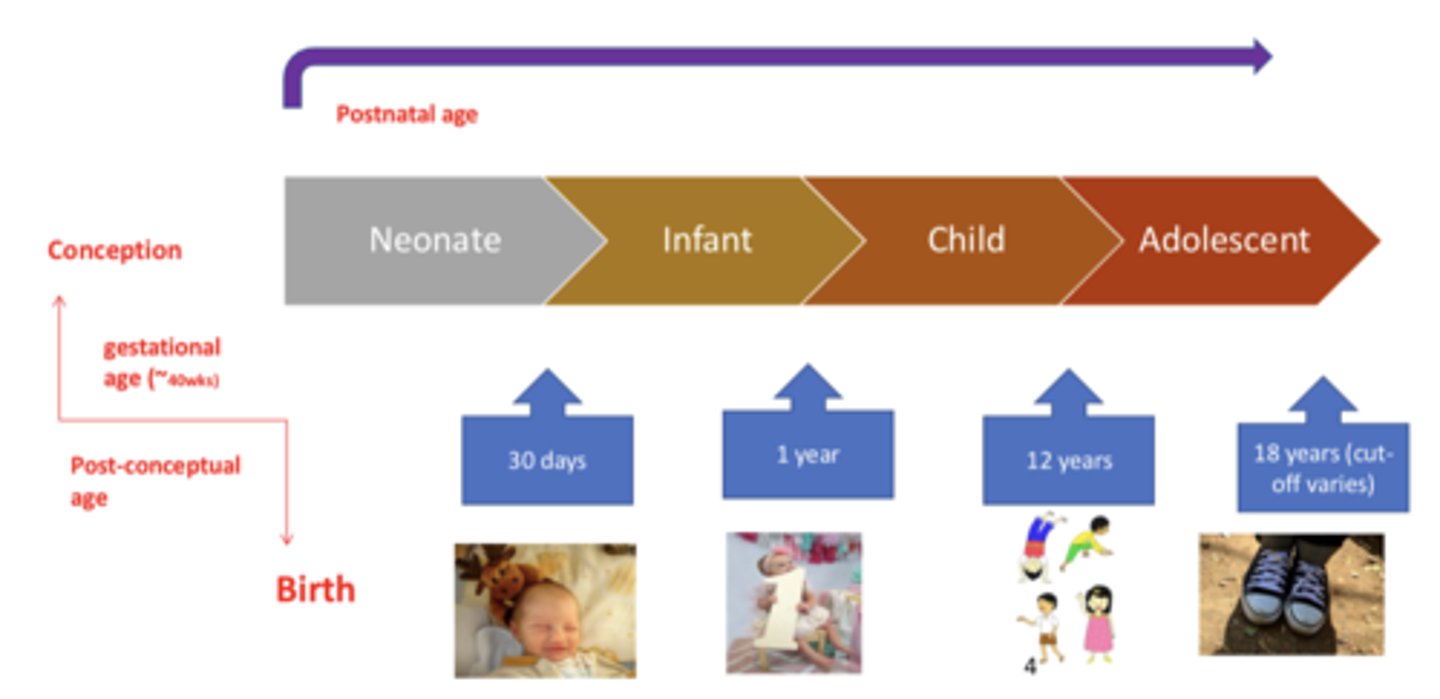
Postnatal age
time elapsed after birth
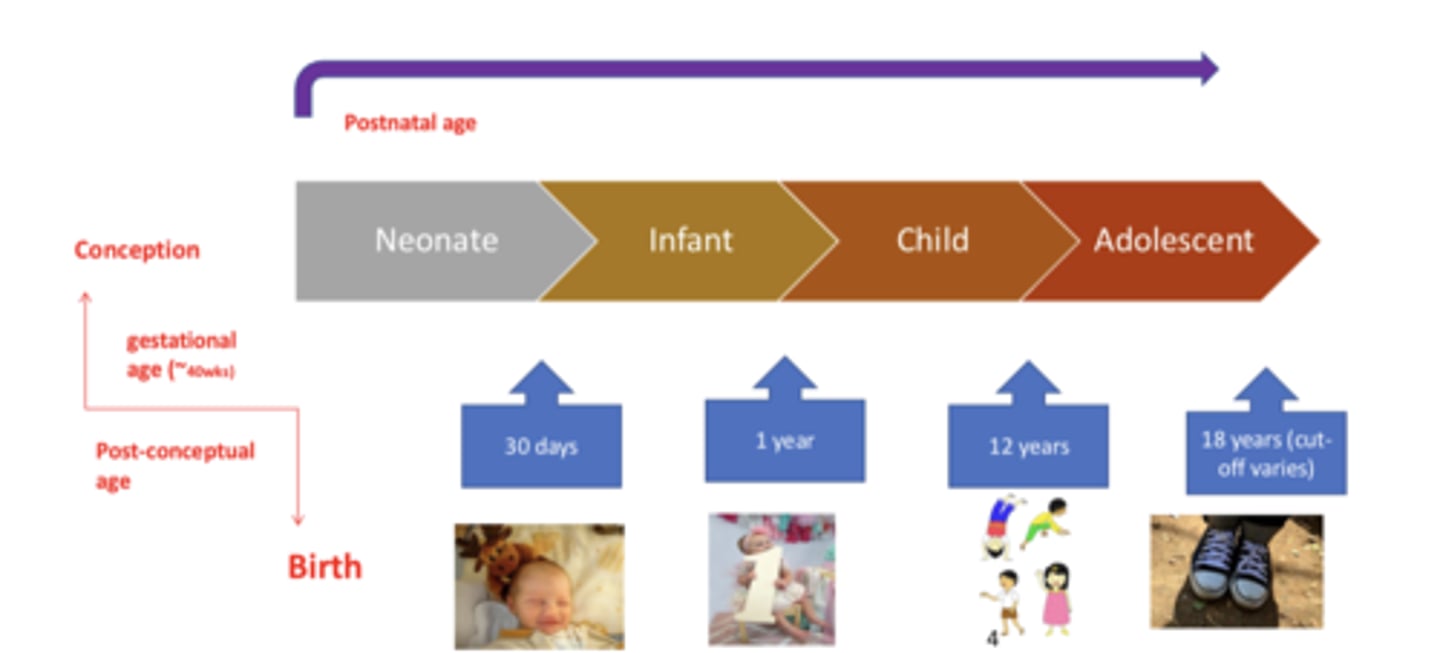
Neonate
from birth to 30 days

Infant
from 30 days to 1 year
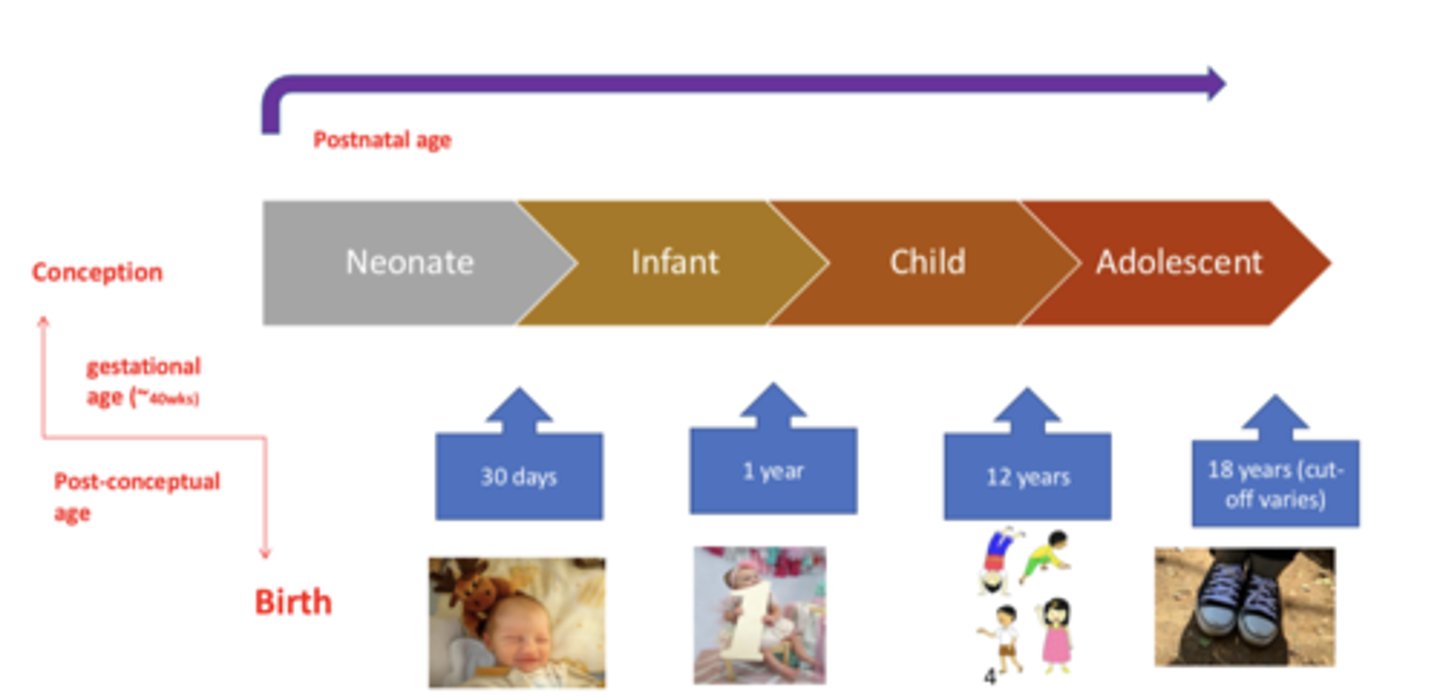
Child
from 1 year to 12 years
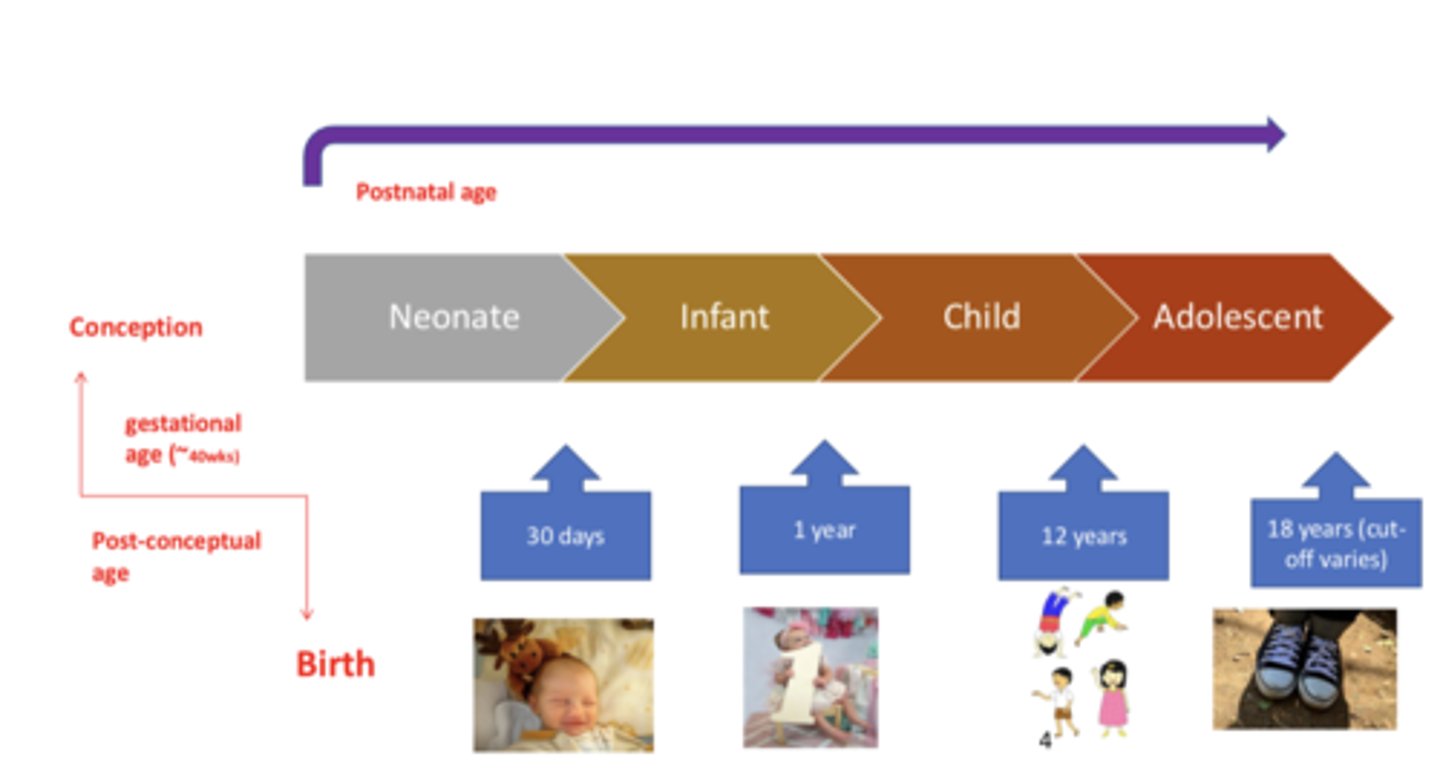
Adolescent
18 years (cut off caries)
Preventive Care
screenings, check-ups (well-child visits), patient counseling used to prevent illnesses, disease, and other health problems, or to detect illness at early stages
Pediatric health and wellness includes: (2)
- obtaining preventive services
- education regarding healthy lifestyle choices (e.g., promote nutrition, exercise, sleep, mental/behavioral health)
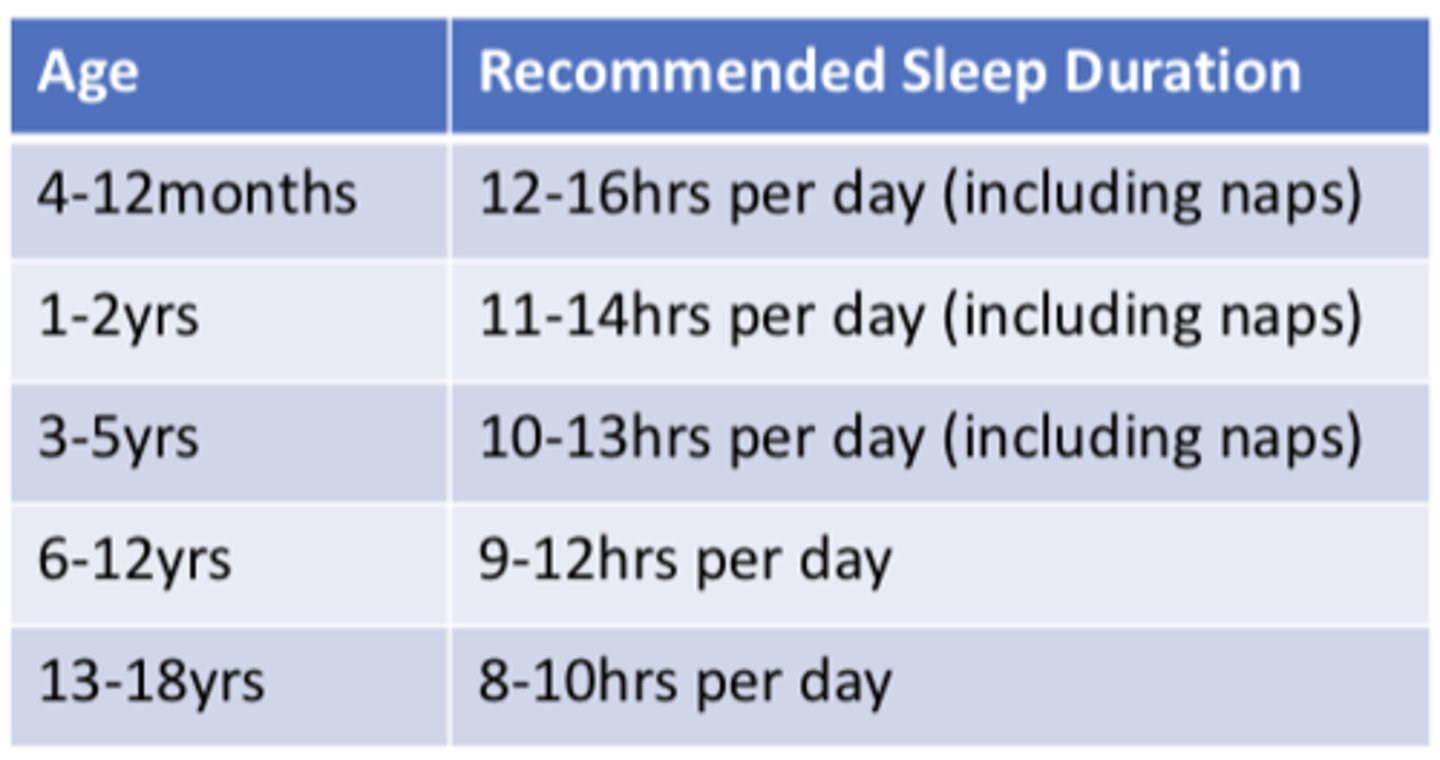
Sleep recommendations in children
4-12 months:
1-2 yrs:
3-5 yrs:
6-12 yrs:
13-18 yrs:
4-12 months: 12-16 hrs per day (including naps)
1-2 yrs: 11-14 hrs per day (including naps)
3-5 yrs: 10-13 hrs per day (including naps)
6-12 yrs: 9-12 hrs per day
13-18 yrs: 8-10 hrs per day
children 3-5 yrs should be encouraged to engage in active/play/structured movement including.....
what is the daily goal?
- light, moderate, and vigorous activity
- 3 hrs per day
Children and adolescents ages 6-17 yrs should do ______________ or more of ____________-to_________________ physical activity daily
- 60 minutes (1 hour)
- moderate-to-vigorous
3 components of pediatric health surveillance visits ***
- Disease detection (screenings)
- Disease prevention
- Health promotion and safety
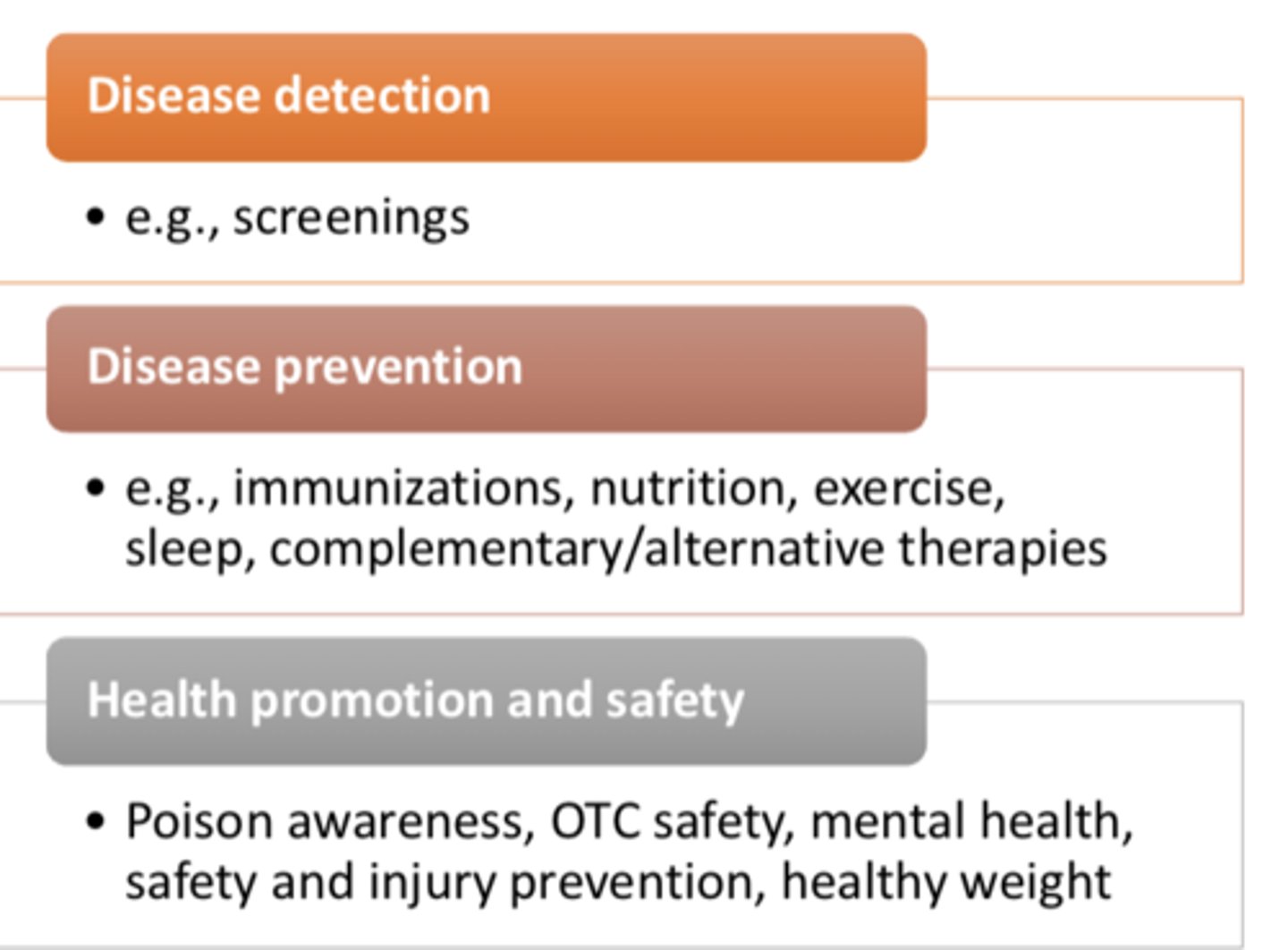
Disease prevention examples (5)
- immunizations
- nutrition
- exercise
- sleep
- complementary/alternative therapies
Health promotion and safety examples (5)
- poison awareness
- OTC safety
- mental health
- safety & injury prevention
- healthy weight
Bright futures
a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
Bright futures guidelines provide _________________, _________________________ for all preventive care screening and well-child visits
- theory-based
- evidence-driven guidance
What is the goal of Bright futures?
to support primary care practices in providing well-child and adolescent care across settings
Settings bright futures applies to: (6)
• Private practice
• Hospital-based or hospital-affiliated clinics
• School-based health centers
• Public health clinics
• Community health centers
• Pharmacies!
Healthy People 2030
sets data-driven national objectives to improve health and well-being over the next decade
Leading Health Indicators (LHIs)
a small subset of high-priority Healthy People 2030 objectives selected to drive action toward improving health and well-being
Healthy People 2030 includes 23 LHIs:
• 5 of these are specific to _______________
• Additionally, 10 of these affect people across the ___________________________
- infants and children
- lifespan (including children)
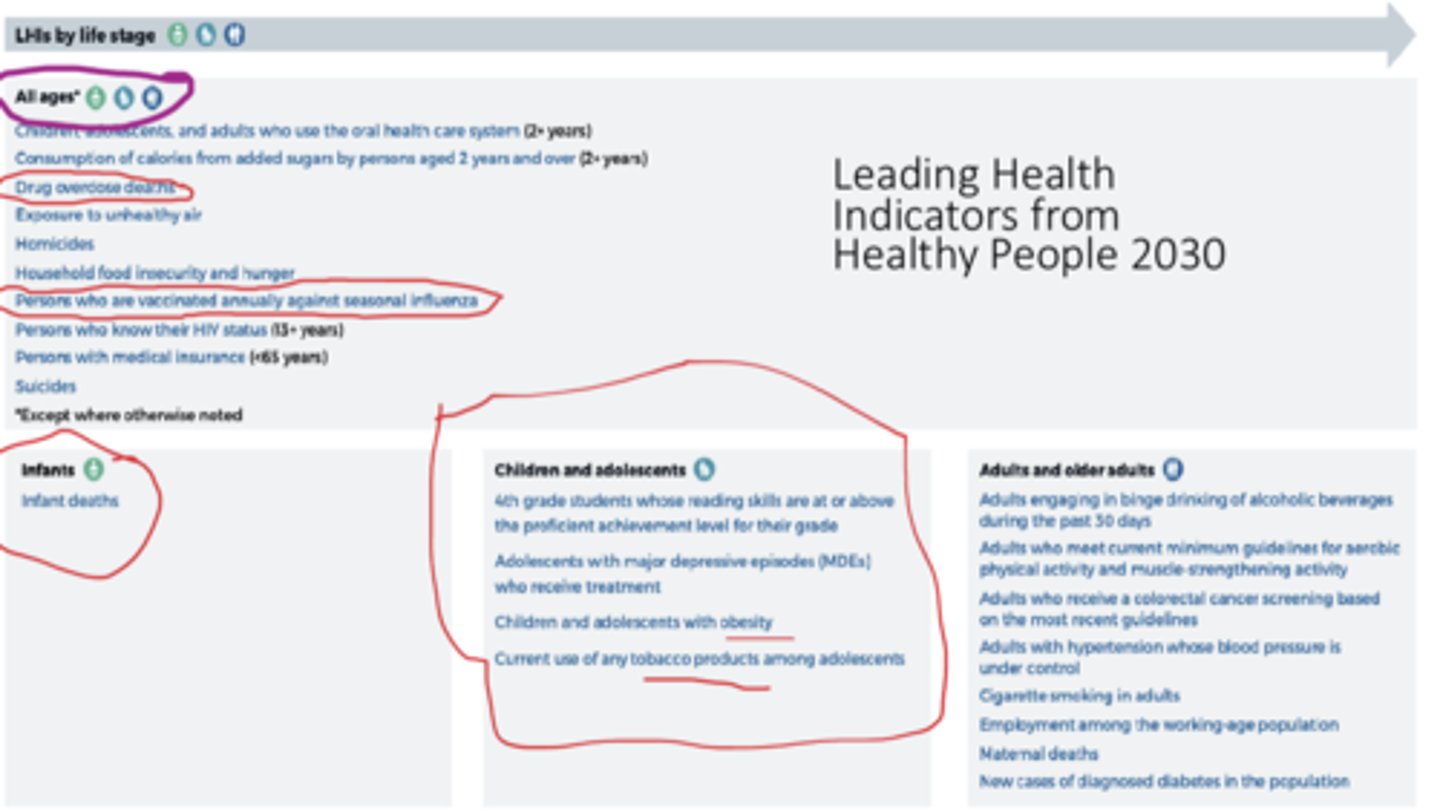
Healthy people 2030 leading health indicators for all ages
- drug overdose deaths
- persons who are vaccinated annually against seasonal influenza
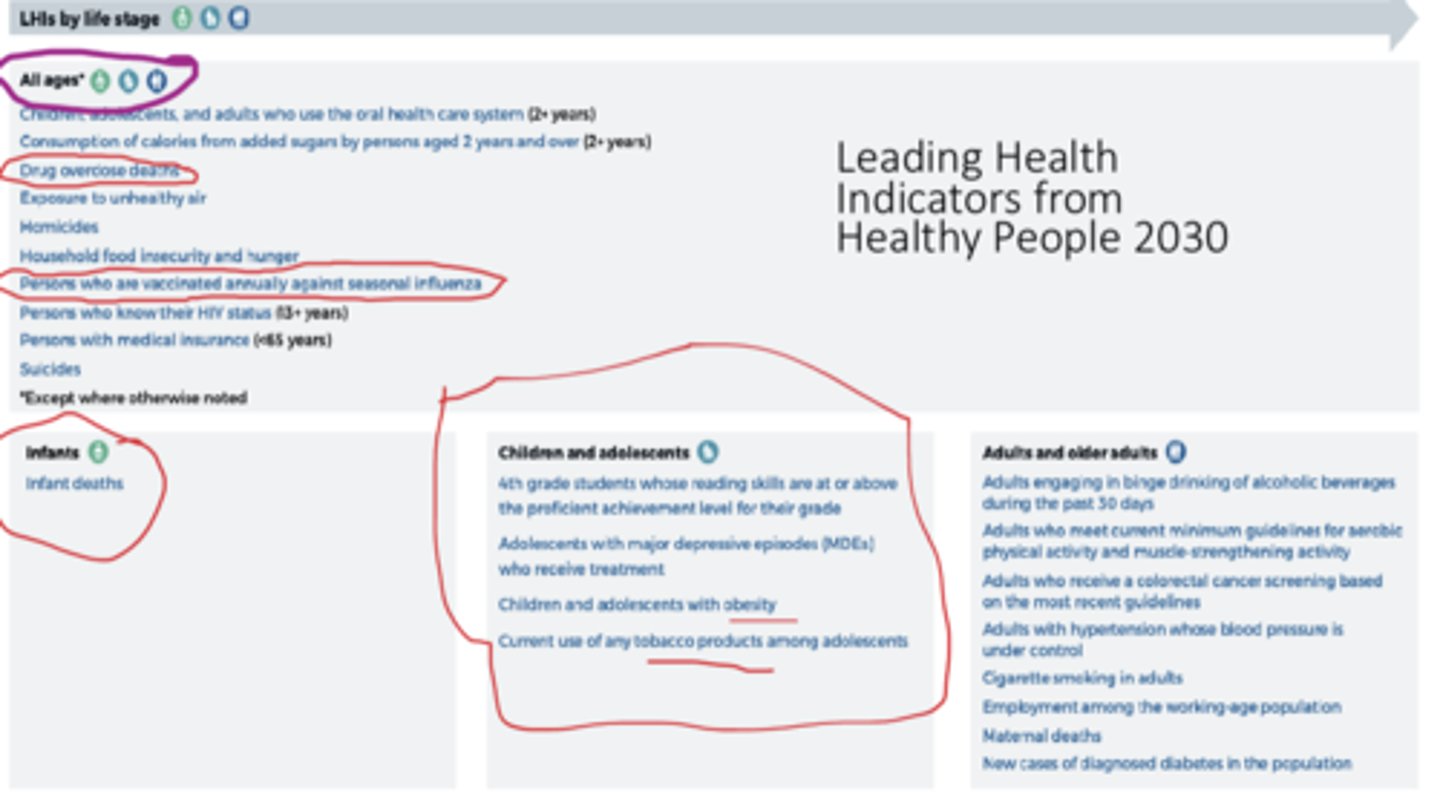
Healthy people 2030 leading health indicators for infants
infant death
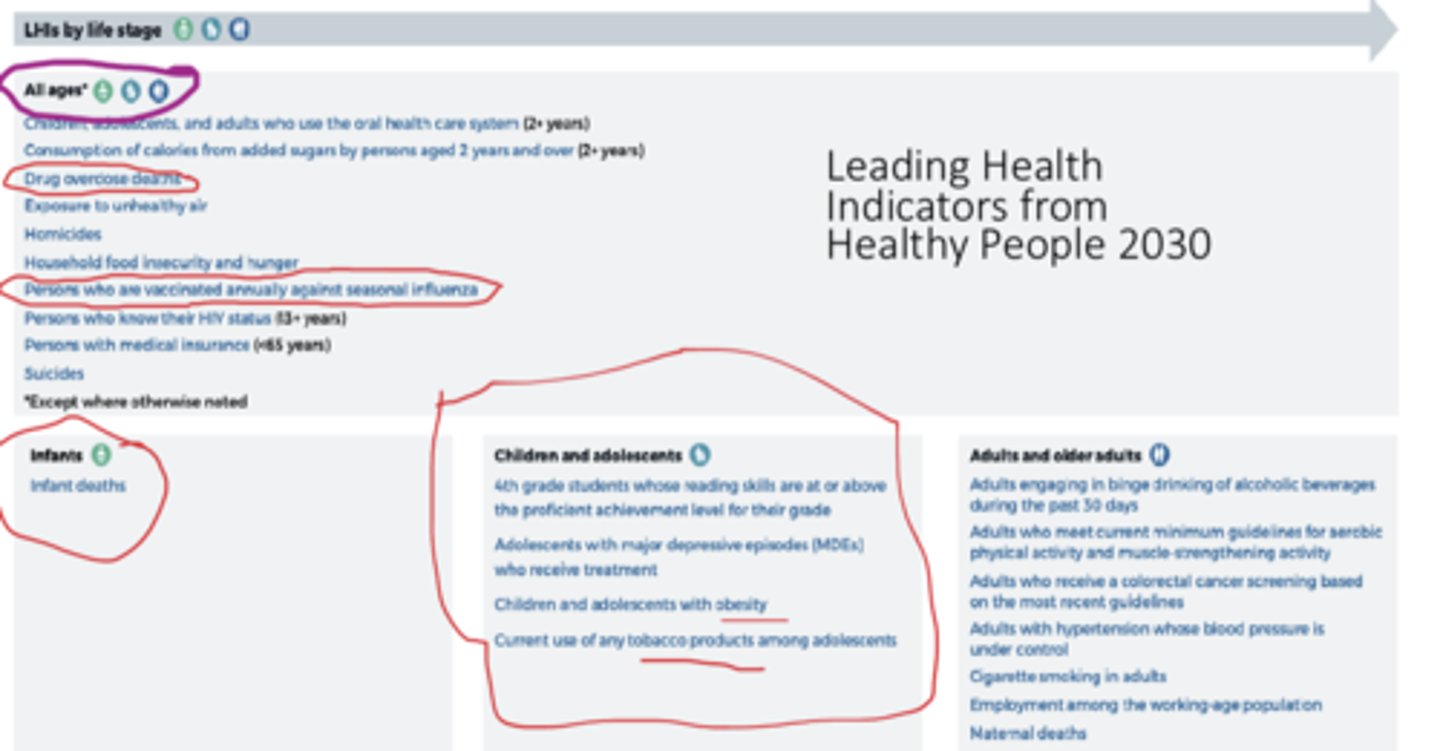
Healthy people 2030 leading health indicators for children and adolescents
- 4th grade students whose reading skills are at or above the proficient achievement level for their grade
- adolescents with major depressive episodes (MDEs) who receive treatment
- children and adolescents with obesity
- current use of any tobacco products among adolescents
Components of Preventive Pediatric Health w/Examples (6)
• Measurements- length, weight, height, BMI
• Sensory screening– vision, hearing
• Developmental/Behavioral health screenings– autism spectrum disorder screening; tobacco, alcohol, or drug use screening; depression screening
• Physical examinations
• Procedures- immunizations
• Oral health
T/F: The components of preventive pediatric health help address many of the Healthy People 2030 Leading Health indicator objectives
TRUE
How to make vaccine recommendations for a child using CDC immunization guide (5)
1. Determine needed vaccines based on PT age
2. Determine appropriate interval for catch-up, if needed
3. Assess for medical conditions and other indications
4. Review special situations
5. Review contraindications & precautions to vaccination s
How to respond to an immunization refusal: Provide CLEAR info. about the immunization and the _________ being prevented, the ____________, the ________ of _________, and the ______________ to child/family
- disease being prevented
- efficacy
- duration of action
- benefit to child/family
Other ways to respond to immunization refusals: (2)
- discuss COMMON adverse effects
- unhurried conversations with opportunities for questions
What falls under health promotion and safety (4)
• Accidents/Unintentional injury
• Intentional injury
• Environment
• Prevnetion
Examples of accidents/Unintentional injury (7)
- poisoning
- prescription/OTC or drug overdose
- drowning
- firearms
- heatstroke
- sports injury/concussion
- sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Examples of intentional injury (3)
- suicide
- violence
- tobacco/alcohol/drug abuse
Example of environment (health promotion and safety)
tobacco exposure
Examples of prevention: (5)
- water safety
- car seat safety
- sleep safety
- parent CPR
- protective sports gear
What was developed in an effort to create a standard of care for the safe use of medications in children?
Key Potentially Inappropriate Drugs in Pediatrics (the KIDs list)
After critical analysis, peer review, and public review, how many drugs/or drug classes does the final KIDs list contain?
how many excipients?
- 67 drugs and/or drug classes
- 10 excipients
T/F: Most drugs on the KIDs list do not require a prescription
FALSE
most do require a prescription
Potentially inappropriate medications are defined as "medications/medication classes that should generally be avoided in children <18 years because....
they pose an unnecessarily high risk for children and a safer alternative is available
T/F: Drug effectiveness is NOT a criteria for the KIDs list
TRUE
What is the primary target audience of the KIDs list?
In what settings? (4)
- health care professionals caring for PTs younger than 18 yrs
- acute & chronic institutional setting, ambulatory, and community settings
The KIDs List is intended to be a guide, and the recommendations DO NOT....
suggest absolute contraindication of any drug in any pediatric patient
The KIDs list is meant to serve as a clinical tool and is NOT MEANT to replace...
clinical judement
Once medicine leaves the pharmacy, it is the responsibility of the...
parent to appropriately dose and administer
Studies and documents phone calls to poison control centers indicate many unintentional overdoses each year due to...
OTC and prescription med errors
For children <= 5 years, highest the scenario for therapeutic errors is...
10-fold dosing error
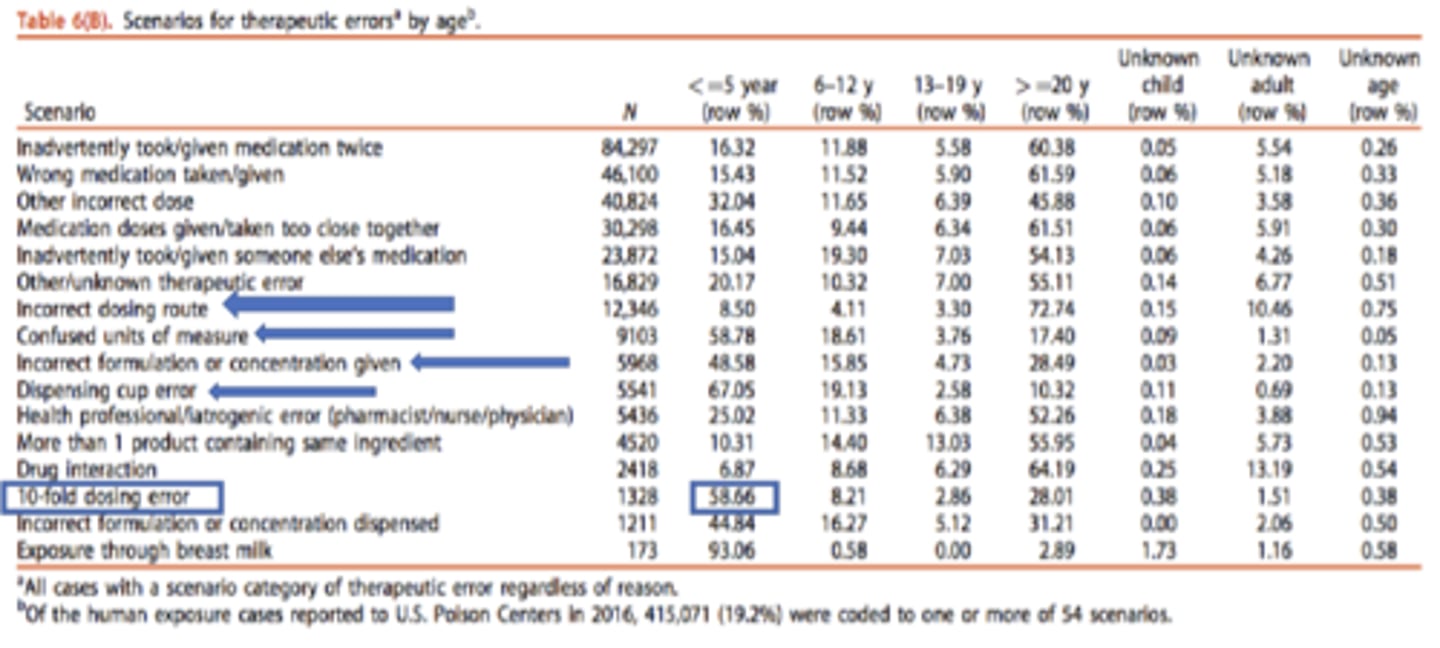
Steps to properly use OTC meds in children (7)
1. Check Label - what it's for, how to use it, what is in it, what to watch out for
2. Check chart on label (weight-based preferred when available)
3. Check for safe age range to use in as an OTC product
4. Check for other medications being taken
5. Check for allergies
6. Watch for signs of adverse/allergic reaction
7. Counsel appropriately (what does this mean to you?)
During 2004-2005 ____________ children <2 yrs old were treated in the US ED for adverse events/overdoses associated with _________________________
- ~1,519 children
- cold & cough medications
What are downsides to cold and cough medications in children? (2)
- little evidence for efficacy in children <12 yrs
- reports of serious side effects resulted in labeling changes
How have manufacturers voluntarily changed labeling instructions for cough & cold medications in children?
• removed OTC infant cough/cold products intended for children <2yrs
• changed labeling on products to state "do not use" in childrenunder 4 years of age
the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends avoiding cough and cold medications in children ________________ years unless recommended by doctor/health care provider
4-6 years
REMEMBER: When giving children >/=7yrs old a cough and cold product, OTC cough/cold products can be harmful if: (3)
• more than the recommended amount is used
• they are given too often
• more than one product containing the same drug is being used
A cold is _______________; most patients will get better on their own without needing __________________
- self-limited
- medications
For older children, some OTC medicines can help relieve the symptoms, however they won't change the.....
natural course of the cold or make it go away faster
T/F: Coughs are a normal symptom of a cold and can serve a purpose
TRUE
they can help the body clear the mucus out of the airway
Alternative Options for Cough/Cold in Children (8)
• Drinking plenty of liquids (water, chicken soup, broths)
• For cough, mix 1 to 2 teaspoons of honey in warm lemon water. Do NOT give honey to children <1 year old
• Plenty of sleep
• Cool mist humidifier helps nasal passages shrink and allow easier breathing
• For sore throat (older child)-non-medicated lozenges or gargle with warm salt water (mix 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon of table salt in 8 ounces of warm water)
• Saline nose drops/spray
• Nasal suctioning with a bulb syringe -- with or without saline nose drops
• Acetaminophen or ibuprofen- used to reduce fever, aches and pains
When to call a doctor for cough/cold (9)
• Rectal temperature of ________________ in an infant __________________
• ____________________________ in a child
• Signs of ____________________ (nostrils widening with each breath, wheezing, fast breathing, the ribs showing with each breath)
• ___________ lips
• Not ___________ or ________________, with signs of __________________________
• _______ pain
• Excessive _______________ or ______________
• If the cough lasts for more than _________________
• If the child is __________________
• Rectal temperature of 100.4F (38C) in an infant 3 months or younger
• Uncontrolled fever in a child
• Signs of labored breathing (nostrils widening with each breath, wheezing, fast breathing, the ribs showing with each breath)
• Blue lips
• Not eating or drinking, with signs of dehydration
• Ear pain
• Excessive crankiness or sleepiness
• If the cough lasts for more than three weeks
• If the child is getting worse
OTC Medication use in children: Antihistamines (2)
• Can cause drowsiness in some children; can cause fussiness/restlessness in some children
• Some children may need benefit (usually select non-drowsy)
OTC Medication use in children: Decongestants/Decongestant nose drops (3)
• Avoid use in infants & young children
• For older children, never use more than 2-3 days
• ALWAYS check label for dosing and age range (use clinical judgment)
OTC Ibuprofen is not to be used in children younger than......
younger than 6 months
- OTC labeling states 2-11 yrs
What can ibuprofen cause?
kidney disease, asthma, ulcer, or chronic illness
- ask doctor before giving ibuprofen
CAUTION with acetaminophen and ibuprofen:
contained in many OTC products for children
- counsel and check for duplication of therapy
T/F: Aspirin is typically used as an OTC med in children
FALSE
aspirin is typically NOT used in children, causes reye's syndrome
What is Reye's Syndrome and what is its association toaspirin use in children?
causes swelling/damage to the brain and liver often following a viral infection
- has been linked to aspirin use
What strength is liquid children's acetaminophen available as?
160 mg/5 mL
Acetaminophen: for a child under 3 months with fever...
call doctor
Acetaminophen: for a child under 2 years...
contact pediatrician prior to using
Acetaminophen: for a child greater than or equal to 2 yrs...
check label for dosing (weight-based preferred IF known)
Acetaminophen: avoid multi-ingredient in products in...
<6 yrs of age
Acetaminophen:
_____________________ are more accurate than _________________________
- dosing syringes
- household utensils
T/F: Household spoons are reliable
FALSE
are NOT reliable
- lead to inadvertent under- or over-dose
What measuring device should be used?
use syringe or device that comes with medication
- ask pharmacist if dosing device not included (pharmacist: BE PROACTIVE)
How often can acetaminophen be used? no more than how many times per day?
- can be used q4-6hrs prn
- no more than 5x a day
Fever in a child:
Rectal, tympanic, temporal:
Oral:
Axillary:
Rectal, tympanic, temporal: 100.4°F (38°C)
Oral: 100°F (37.8°C)
Axillary: 99°F (37.2°C)
A doctor should be called when a child is younger than _______________ and has a temperature of ___________________ or higher
- 3 months (12 weeks)
- 100.4°F (38.0°C)
Fever in a child: when to call a doctor (8)
• Looks very ______, is unusually __________, or is very _________
• Has been in a _______________, such as an overheated car
• Has other symptoms, such as a ___________ neck, severe _____________, severe _____________, severe ______________, _____________ difficulty, an unexplained ________, or repeated __________ or ________________
• Has _______________________ problems, such as sickle cell disease or cancer, or is taking _____________ or other medicines that could affect their _______________
• Has_______________________ that may affect how she tolerates a fever and increased ______________________ as a result of the fever
• Has had a ____________
• Is younger than ___________________ and has a temperature of _______________ or higher
• Temperature rises above _____________ repeatedly for a child of any age
• Looks very ill, is unusually drowsy, or is very fussy
• Has been in a very hot place, such as an overheated car
• Has other symptoms, such as a stiff neck, severe headache, severe sore throat, severe ear pain, breathing difficulty, an unexplained rash, or repeated vomiting or diarrhea
• Has immune system problems, such as sickle cell disease or cancer, or is taking steroids or other medicines that could affect their immune system
• Has heart problems that may affect how she tolerates a fever and increased heart rate as a result of the fever
• Has had a seizure
• Is younger than 3 months (12 weeks) and has a temperature of 100.4°F (38.0°C) or higher
• Temperature rises above 104°F (40°C) repeatedly for a child of any age
Using the acetaminophen dosing chart provided, how much liquid acetaminophen (per dose) should you give to a child who weighs 36 lbs?
Please list correct dose in mL AND mg
7.5 mL
240 mg
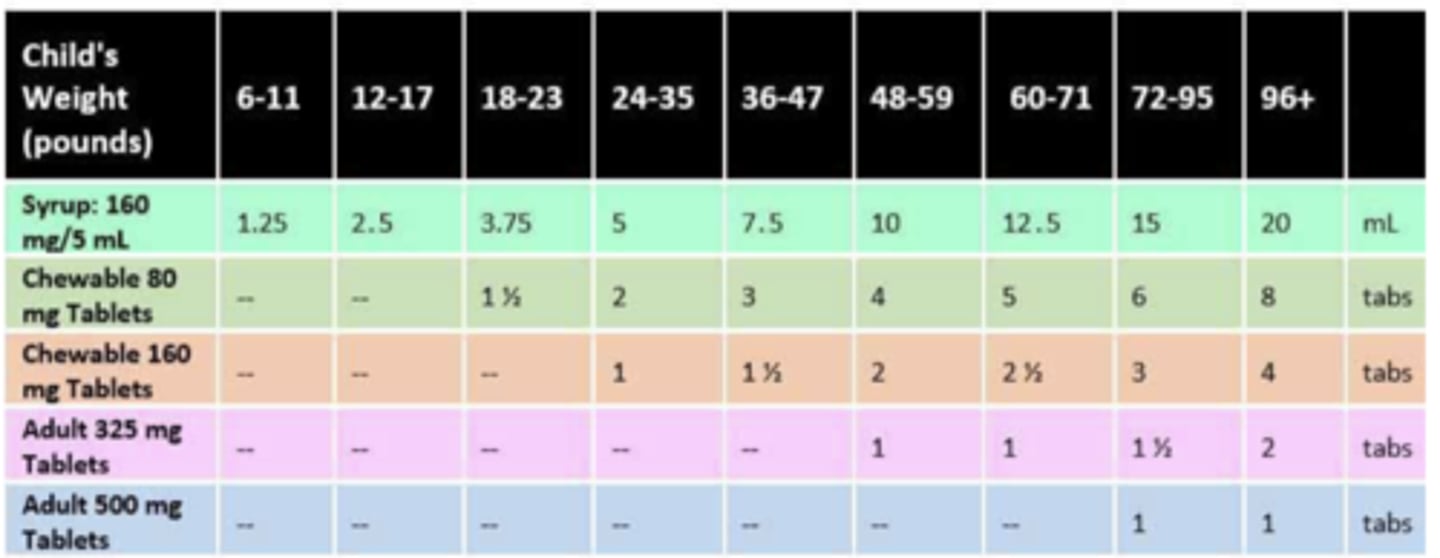
How much liquid acetaminophen should you give to a child who weighs 9 kg? Please list correct dose in mL AND mg
3.75 mL
120 mg
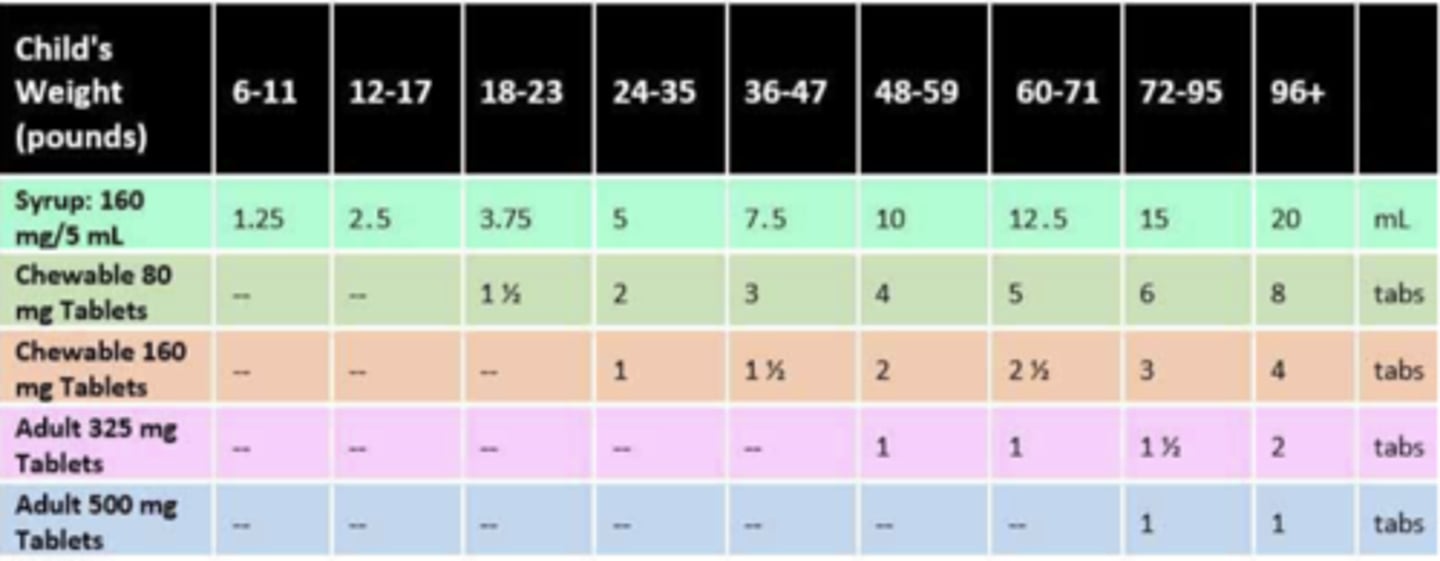
Medication Safety Reminders (3)
- Keep all medicines out of the reach of children
- Use only the dosing device that comes with the product (do not use a household teaspoon)
- If you think your child has taken too much of this or any medicine, call poison control at 800.222.1222
Pediatric Tobacco and Nicotine Use (5)
- Youth use tobacco products, including e-cigarettes at high rates
- Adolescents are uniquely vulnerable to nicotine dependence
- Evidence base for youth tobacco cessation is limited
- Effective strategies to promote youth tobacco cessation are urgently needed
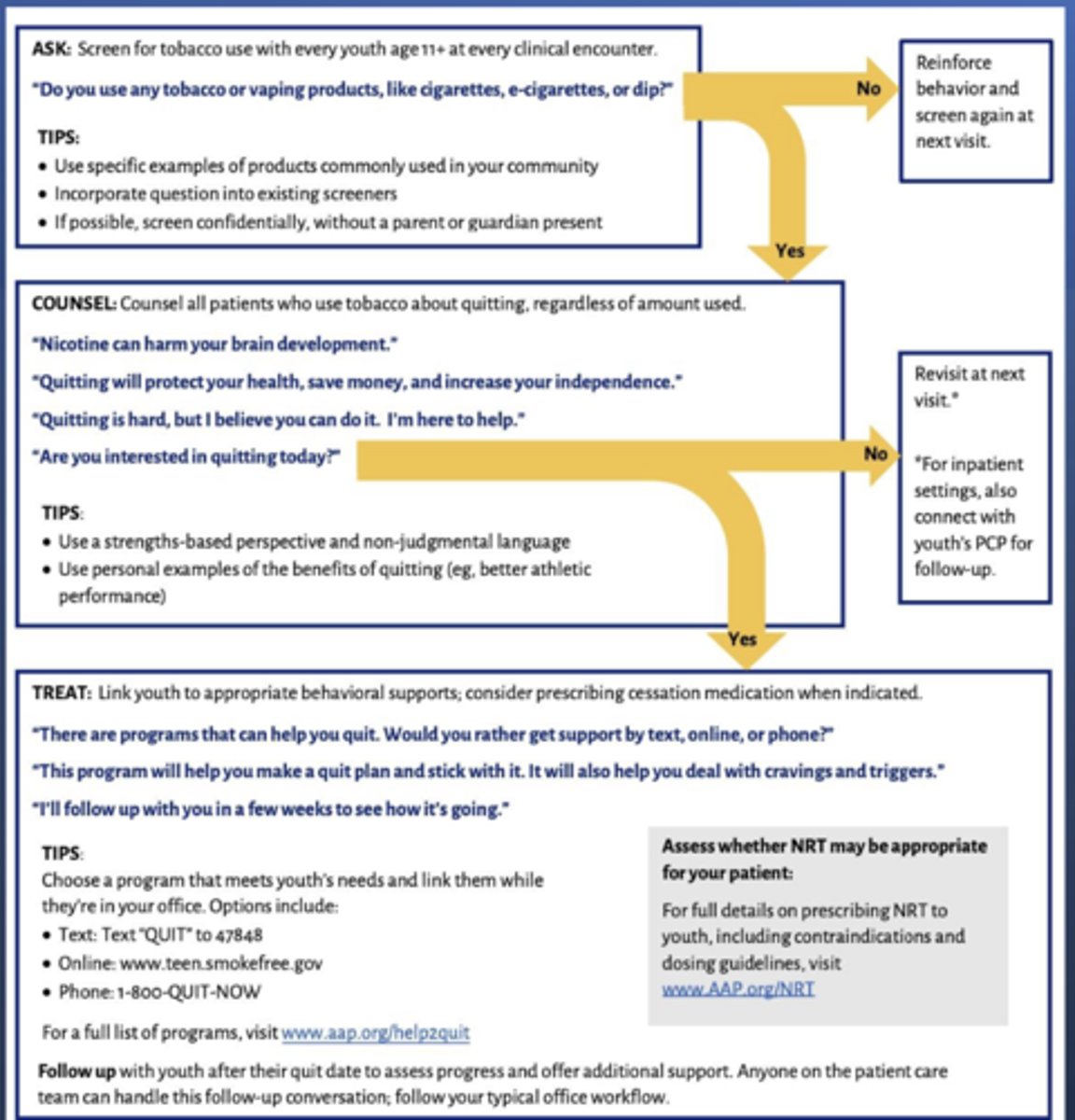
- The AAP provides an Ask-Counsel-Treat (ACT) Model for youth cessation
Ask-Counsel-Treat (ACT) Model for youth cessation
Poisoning is the __________ leading cause of unintentional injury death among ages 1 to 19 years
third leading
- poison prevention awareness & education, safe medication use
What is the leading cause of child poisoning?
medicines
Poison center number
1-800-222-1222
When to call 911 or local emergency number if child is...
unresponsive, having trouble breathing, twitching/shaking, acting strange
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
unexpected and unexplained deaths that occur in infants younger than 1 year
SIDS is leading cause of death in...
infancy beyond the neonatal period
Besides SIDs, what else is on the rise?
accidental suffocation or strangulation (ASSB) in bed
(form of SIDS)
Independent risk factors of SIDS
Young maternal age, maternal smoking during pregnancy, inadequate prenatal care, low birth weight, prematurity, overheated infant, prone sleep position, infant sleeping on soft surface, bedding in infant sleep area, infant sleeping on cushioned surface, bed sharing
T/F: Evidence exists that links immunizations to SIDS
FALSE
no evidence exists
_________________ leading cause of injury-related death among children ages 1-4 and the _________ leading cause of unintentional injury-related death among children 19 and under
- drowning
- third
Ways to prevent drowning
learn to swim, water survival, CPR, physically barriers around pools, water safety advocacy/awareness/education
Role of the pediatric healthcare provider
Uniquely positioned to assess health and development of children over time due to regular well-child visits (plus sick visits)