MDC 4 NUR2755 FINAL EXAM
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Alzheimer's Mild Stage
-Forgets names; misplaces household items
-Has short-term memory loss and difficulty recalling new information
-Shows subtle changes in personality and behavior
Alzheimer's Moderate Stage
-Is disoriented to time, place, and event
-Has difficulty driving and gets lost
-Incontinent
-Psychotic behaviors, such as delusions, hallucinations, and paranoia
-Episodes of wandering, trouble sleeping
Alzheimer's Late Stage
-Totally incapacitated; bedridden
-Totally dependent in ADLs
-Has agnosia
-Hallucinations
-Incontinence
-Difficulty eating
Apraxia
Difficulty with motor planning to perform tasks or movements
Aphasia
Inability to speak or understand language
Anomia
Inability to recall the names of everyday objects
Agnosia
Loss of sensory comprehension, including facial recognition
Alzheimer's diagnostics
-No laboratory test can confirm the diagnosis of AD
-Definitive diagnosis is made on the basis of brain tissue examination at autopsy, which confirms the presence of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques
Alzheimer's medications
Cholinesterase inhibitors- Donepezil, galantamine
NMDA receptor antagonists- Memantine
Parkinson's symptoms
-Slow, shuffling, and propulsive gait
-RESTING tremors
-Muscle rigidity
-Bradykinesia/akinesia (loss of ability to move muscles voluntarily)
-Mask Like face
-Drooling
-Postural instability
Parkinson's diagnostics
-Diagnosis typically made based on manifestations, their progression, and by ruling out other disease
-Analysis of CSF may show a decrease in dopamine levels
Parkinson's medications
Carbidopa/Levodopa (Sinemet)
Parkinson's surgical interventions
Stereotactic pallidotomy or thalamotomy
Migraine triggers
-Caffeine
-Red wine
-MSG
-Foods high in tyramine (aged cheeses, cultured food like yogurt)
Migraine abortive therapy
Acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen, triptans, ergotamine derivatives
Migraine preventative therapy
Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiepileptics, Botox
Migraine surgical treatment
Trigeminal nerve resection
Aura symptoms
-Visual disturbances
-Flashing lights/lines/spots
-Numbness of lips or tongue
-Acute confused state
-Aphasia
-Vertigo
-Unilateral weakness*
-Offensive smell
-"Deja vu" feeling
Multiple sclerosis clinical manifestations
-Muscle weakness and spasticity
-Intention tremors (tremor when performing an activity)
-Diplopia (double vision)
-Nystagmus (an involuntary condition in which the eyes make repetitive uncontrolled movements)
-Depression/labile
Multiple sclerosis diagnosis
MRI of the brain and spinal cord demonstrates the presence of plaques in at least 2 areas
Multiple sclerosis medications
-Baclofen
-Disease-modifying therapies
-Interferon beta-1a and beta-1b
-Corticosteroids
Meningitis clinical manifestations
-Nuchal rigidity
-Kernig Sign
-Brudzinski Sign
-Decreased level of consciousness
-Photosensitivity
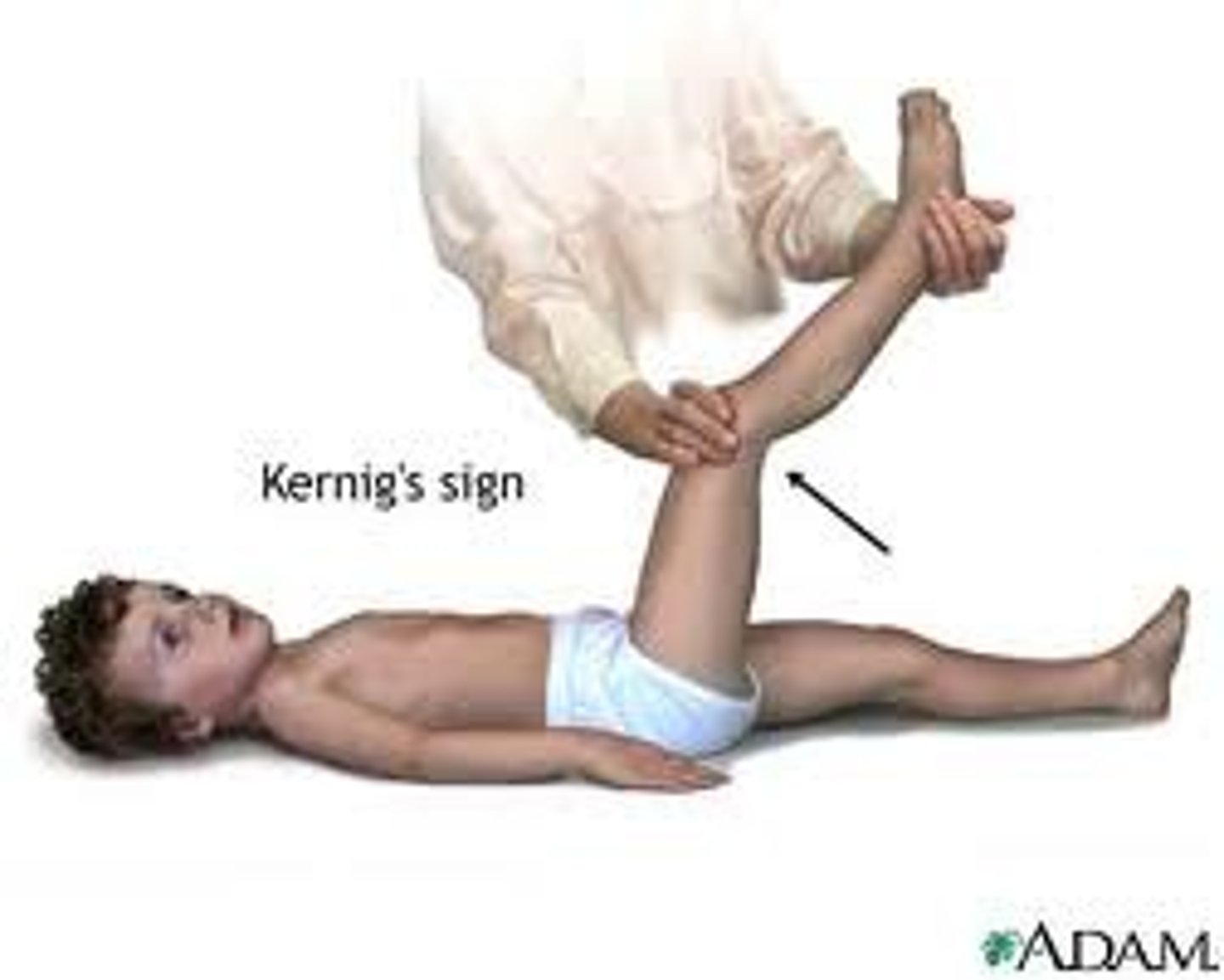
Kernig Sign
Resistance and pain with extension of the client's leg from a flexed position
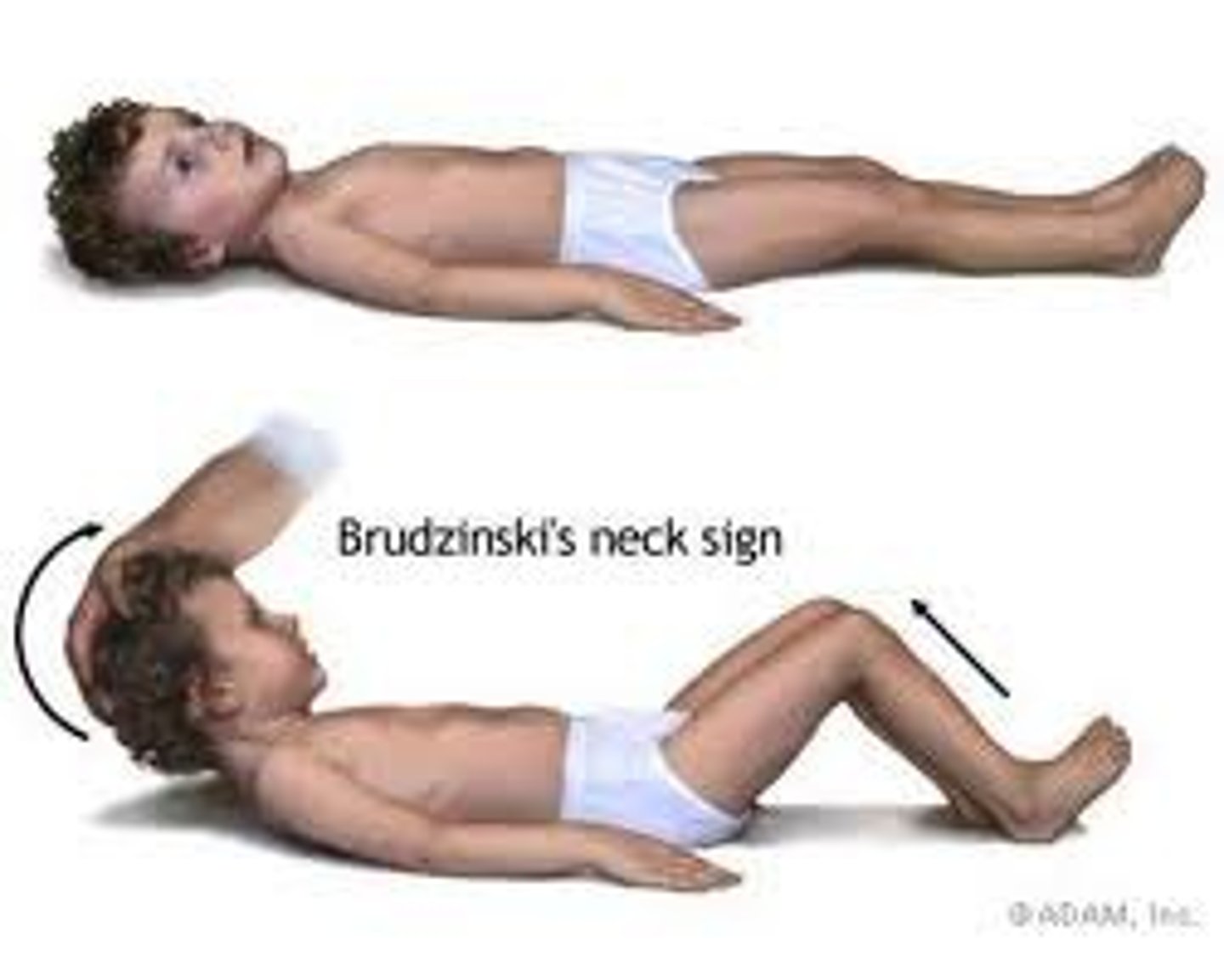
Brudzinski Sign
Flexion of the knees and hips occurring with deliberate flexion of the client's neck
Meningitis diagnostics
Lumbar puncture
Appearance of CSF: cloudy (bacterial) or clear (viral)
Prevention of meningitis
Meningococcal vaccine
Droplet precautions
-Private room
-Stay at least 3 feet away from the patient unless wearing a mask
-Patients who are transported outside the room should wear a mask
-Health care personnel should wear gloves, gown, and mask
Tonic-clonic seizure
Generalized seizure in which the patient loses consciousness and has both stiffening of the muscles (tonic) and rhythmic jerking of the extremities (clonic)
Tonic seizure
Clients suddenly lose consciousness and experience sudden increased muscle tone, loss of consciousness, and have autonomic manifestations
Clonic seizure
Only the clonic phase is experienced (rhythmic jerking of the extremities)
Myoclonic seizure
Lasting only seconds, myoclonic seizures consist of brief jerking or stiffening of the extremities, which can be symmetrical or asymmetrical
Atonic or akinetic seizure
Characterized by a few seconds in which muscle tone is lost
Complex partial seizure
-Seizures associated with automatisms (behaviors that the client is unaware of, such as lip smacking or picking at clothes)
-Can cause loss of consciousness
Simple partial seizure
Seizure where consciousness is maintained
Seizure diagnostics
-Electroencephalogram (EEG)
-CT/MRI
Seizure interventions
-Turn the patient on their side
-Remove objects that may injure the patient
-Suction as needed
-Oxygen
-Padded side rails
-IV access (saline lock)
-Bed in lowest position
-Nothing in mouth
-Loosen or remove restrictive clothing
Seizure medications
-Lorazepam or diazepam IV push to stop a seizure (4 mg over a 2 minute period)
-Phenytoin (therapeutic range 10 to 20 mcg/ml)
Earliest sign of increased intracranial pressure
Decreased level of consciousness
Increased intracranial pressure early signs
-EARLIEST SIGN: Decreased level of consciousness
-Restlessness
-Changes in speech
-Confusion
-Headache
-Nausea and vomiting → projectile
Increased intracranial pressure late signs
-Pupillary changes → can mean herniation
-Cranial nerve dysfunction
-Ataxia
-Cushing's triad (very late sign)
Increased intracranial pressure interventions
-Low stimulation
-Semi-fowlers → 30 degrees
-Head in neutral position
-Do not cluster activities
-Suction only as needed
-Teach patient not to cough or blow their nose
-Dim lighting
-Stool softeners
-Do not bend or bare down
Increased intracranial pressure treatment
IV mannitol given through a filter because it crystallizes at room temperature
Cushing's triad
Severe hypertension, widened pulse pressure (difference between the systolic and diastolic blood pressure), bradycardia, irregular respirations
Pulse pressure
Difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
Ischemic stroke
Caused by the occlusion of a cerebral artery by either a thrombus or an embolus.
Thrombotic stroke
Occur secondary to the development of a blood clot on an atherosclerotic plaque in a cerebral artery that gradually shuts off the artery and causes ischemia distal to the occlusion
Embolic stroke
Caused by an embolus traveling from another part of the body to a cerebral artery. Blood to the brain distal to the occlusion is immediately shut off causing neurologic deficits or a loss of consciousness to instantly occur.
Hemorrhagic stroke
Occur secondary to a ruptured artery or aneurysm. The prognosis for a client who has experienced a hemorrhagic stroke is poor due to the amount of ischemia and increased ICP caused by the expanding collection of blood. Patients will complain of the "worst headache of my life".
Alexia
Inability to understand written words
Stroke diagnostics
A non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scan (WITHOUT CONTRAST) is the initial diagnostic test and should be performed within 25 minutes from the time of client arrival to the emergency department
Homonymous hemianopsia interventions
-Instruct them to use a scanning technique (turning head from the direction of the unaffected side to the affected side) when eating and ambulating
-Rotate their plate so that they can see it
-Talk to them on their good side
Ischemic stroke treatment
-Give thrombolytics within 4.5 hours of initial manifestations
-Low-dose aspirin is given within 24-48 hours following an ischemic stroke to prevent further clot formation
Stroke prevention
-Smoking cessation
-Heart-healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low in saturated fats
-Regular activity, including planned exercise; example: walking at least 30 minutes most days of the week
-Reduction in alcohol consumption
-Reduction of salt in diet
Post-stroke feeding interventions
-An RN should provide the initial feeding and intervene if choking occurs. Some clients require an eating environment without distractions to prevent choking.
-Chin tuck when swallowing
-Watch for pocketing
-Put food on the unaffected side
-Aid cannot feed unless they are stable
-Do not rush the patient while they are eating
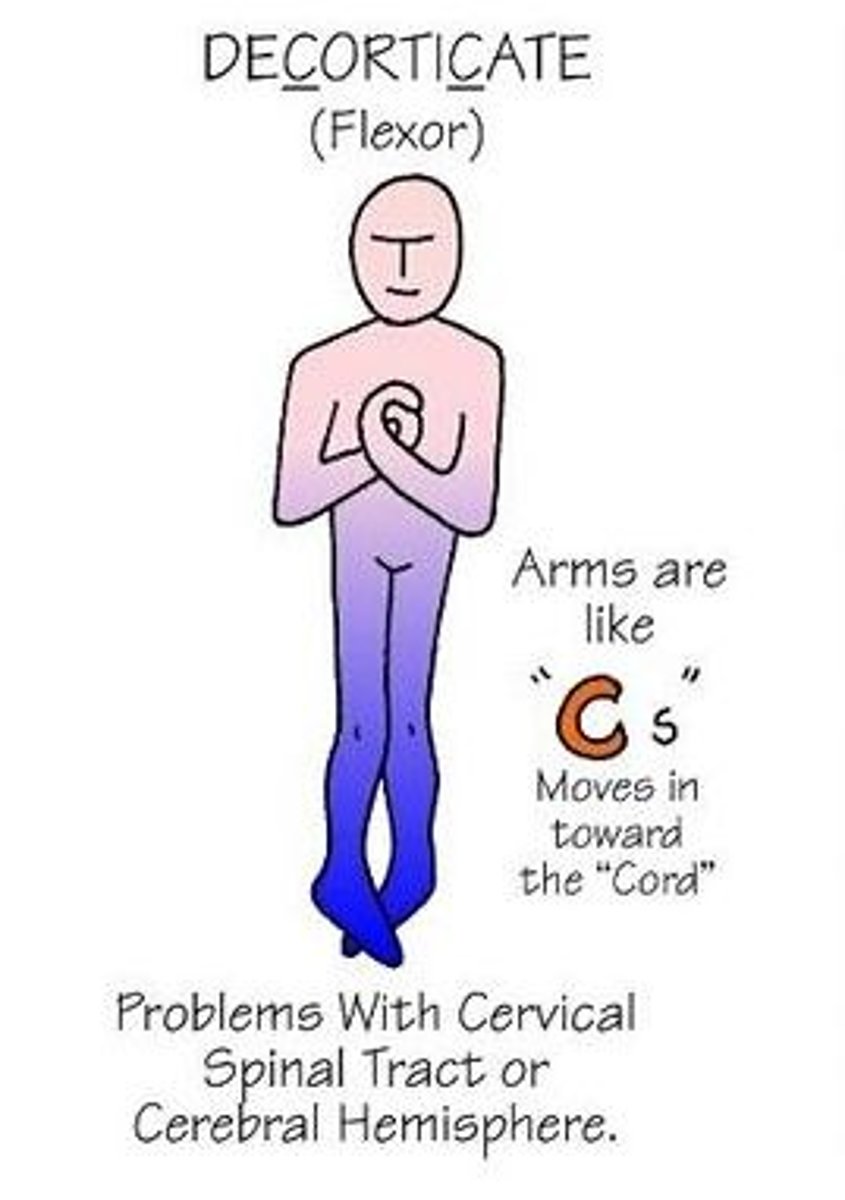
Decorticate posturing
Hands towards the CORE
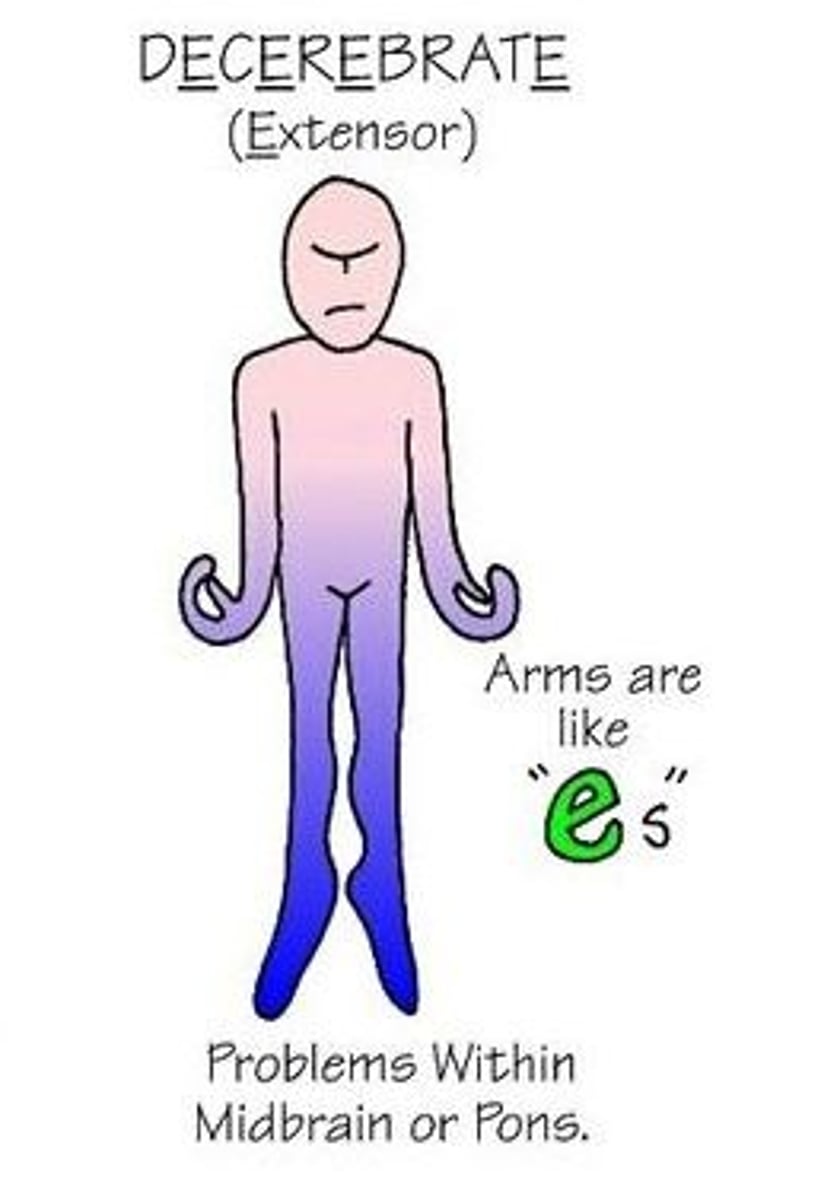
Decerebrate posturing
Hands OUT ("to celebrate")
ICP can be increased by
-Hypercarbia, which leads to cerebral vasodilation
-Endotracheal or oral tracheal suctioning
-Coughing
-Extreme neck or hip flexion/extension
-HOB at less than 30 degrees
-Increasing intra-abdominal pressure (restrictive clothing, Valsalva maneuver)
Ways to decrease ICP
-Elevate HOB to at least 30 degrees
-Maintain patent airway
-Administer oxygen to maintain PAO2 greater than 60 mmHg
-Limit visitors, minimize noise
Brain death diagnosis prerequisites
-Coma of known cause as established by history, clinical examination, laboratory testing, and neuroimaging
-Normal or near-normal core body temperature (higher than 96.8°F (36°C)
-Normal systolic blood pressure (higher than or equal to 100 mm Hg)
-At least one neurologic examination (many U.S. states and health care systems require two)
Spinal shock
Physiologic response that occurs between 30 and 60 minutes after trauma to the spinal cord and can last up to several weeks. Spinal shock presents with total flaccid paralysis and loss of all reflexes below the level of injury. Paralytic ileus can also occur.
Autonomic dysreflexia clinical manifestations
-Sudden, significant rise in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, accompanied by bradycardia
-Headache
-High temperature
-Profuse sweating/flushing (redness) above the level of the lesion
-Pale skin below the level of the lesion
-Blurred vision
-Nasal congestion
Autonomic dysreflexia interventions
-Sit the client up (90 degrees) to decrease blood pressure secondary to postural hypotension (first priority!)
-Determine and treat the cause (kinked cath, fecal impaction, restrictive clothing)
-Administer antihypertensives (nitrates or hydralazine)
Myasthenia gravis pathophysiology
Acquired autoimmune disease characterized by muscle weakness that is proximal to distal
Myasthenia gravis clinical manifestations
-Progressive (proximal to distal) muscle weakness that worsens with repetitive use and usually improves with rest
-Ptosis (incomplete eyelid closure)
-Diplopia
-Respiratory compromise
-Incontinence
-Fatigue
Myasthenia gravis treatment
Cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitor drugs are the first-line management of MG. Ex: pyridostigmine.
Cholinergic crisis
-The patient has received too much cholinesterase inhibitor drug
-Muscle tone DOES NOT improve after giving Tensilon
-Give atropine
Myasthenic crisis
-The patient has received too little cholinesterase inhibitor drug
-Muscle tone DOES improve after giving Tensilon
Gullian-Barre Syndrome clinical manifestations
-Ascending symmetric muscle weakness (legs and up)
-Decreased or absent deep tendon reflexes
-Respiratory compromise
-Ataxia
-Dysphagia
-Diplopia
Gullian-Barre causes
-Often associated with bacterial infection, especially with Campylobacter jejuni. Influenza, Epstein-Barr, and cytomegalovirus (CMG) viral infections have also been associated with GBS
-Zika Virus
-Vaccines
-Autoimmune response
Gullian-Barre treatment
-Plasmapheresis
(Removes the circulating antibodies thought to be responsible for the disease)
-IV immunoglobulin
(Reduces production of antibodies)
Bell's Palsy clinical manifestations
-RULE OUT STROKE FIRST
-Most severe at 48 hours
-The patient cannot lose his or her eye, wrinkle the forehead, smile, whistle, or grimace
-Tearing may stop or become excessive
-Taste is usually impaired to some degree
-Tinnitus
Bell's Palsy treatment
-Corticosteroids 30-60 mg daily for the first few days
-Antiviral drugs
-Eye drops due to eyes not closing properly
Implied consent
Type of consent in which a patient who is unable to give consent is given treatment under the legal assumption that he or she would want treatment.
Informed consent
Nurse’s responsibilities:
Witness informed consent
-Ensure that the provider gave the client the necessary information
-Ensure that the client understood the information and is competent to give informed consent
-Notify the provider if the client has more questions or appears to not understand any of the information provided
-Have the client sign the informed consent document
Informed consent and minors
Only MARRIED or EMANCIPATED minors can give informed consent
Pre-op labs
-Urinalysis
-Blood type and crossmatch
-CBC or hemoglobin level and hematocrit
-Clotting studies (PT, INR, aPTT)
-Electrolyte levels (especially potassium)
-Serum creatinine level
-Pregnancy test
NPO before surgery
-Ensure that the patient remains NPO for at least 6 hours for solid foods and 2 hours for clear liquids before surgery with general anesthesia to avoid aspiration
-Note on the chart the last time the client ate or drank
Surgery: prophylactic antibiotics
Prophylactic antibiotics are administered within 1 hour of surgical incision
Latex allergies: Also check for allergies to
-Shellfish
-Eggs/peanuts/soy → may interfere with propofol
-Avocados
-Bananas
-Kiwi
-Strawberries
-Check if they've had over-exposure to latex; this can create an allergy
Circulator RN
NOT STERILE
-Initiates the TIME OUT procedure
-Sets up OR, gather supplies, inspects equipment, monitor asepsis
-Monitors room traffic in and out of room
Scrub RN
STERILE
-Sponge count
-In charge of sterile field
Malignant hyperthermia symptoms
-High body temperature
-Muscle rigidity of the jaw and upper chest
-Tachycardia
-Tachypnea
-Hypotension
-Cyanosis
Malignant hyperthermia treatment
Dantrolene
Dehiscence
Bursting open of a wound, especially a surgical abdominal wound.
If dehiscence (wound opening) occurs, apply a sterile non adherent or saline dressing to the wound and notify the surgeon.
Evisceration
MEDICAL EMERGENCY
-Call for another nurse to notify the surgeon and/or Rapid Response Team (RRT)
-Stay with the patient
-Place the patient in a supine position with the hips and knees bent.
-Raise the head of the bed 15 to 20 degrees.
-Place dressings moistened with sterile saline over the exposed viscera.
-Do not attempt to reinsert the protruding organ or viscera.
DVT/PE prevention
Compression stockings
Ambulate ASAP
Ted hose
Enoxaparin
Wound infection symptoms
-Redness/erythema
-Oozing → purulent and smelly drainage
-Warm to the touch
-Swollen, hard skin
-Severe pain
Atelectasis
Collapsed lung; incomplete expansion of alveoli. Can happen after surgery as a result of anesthesia
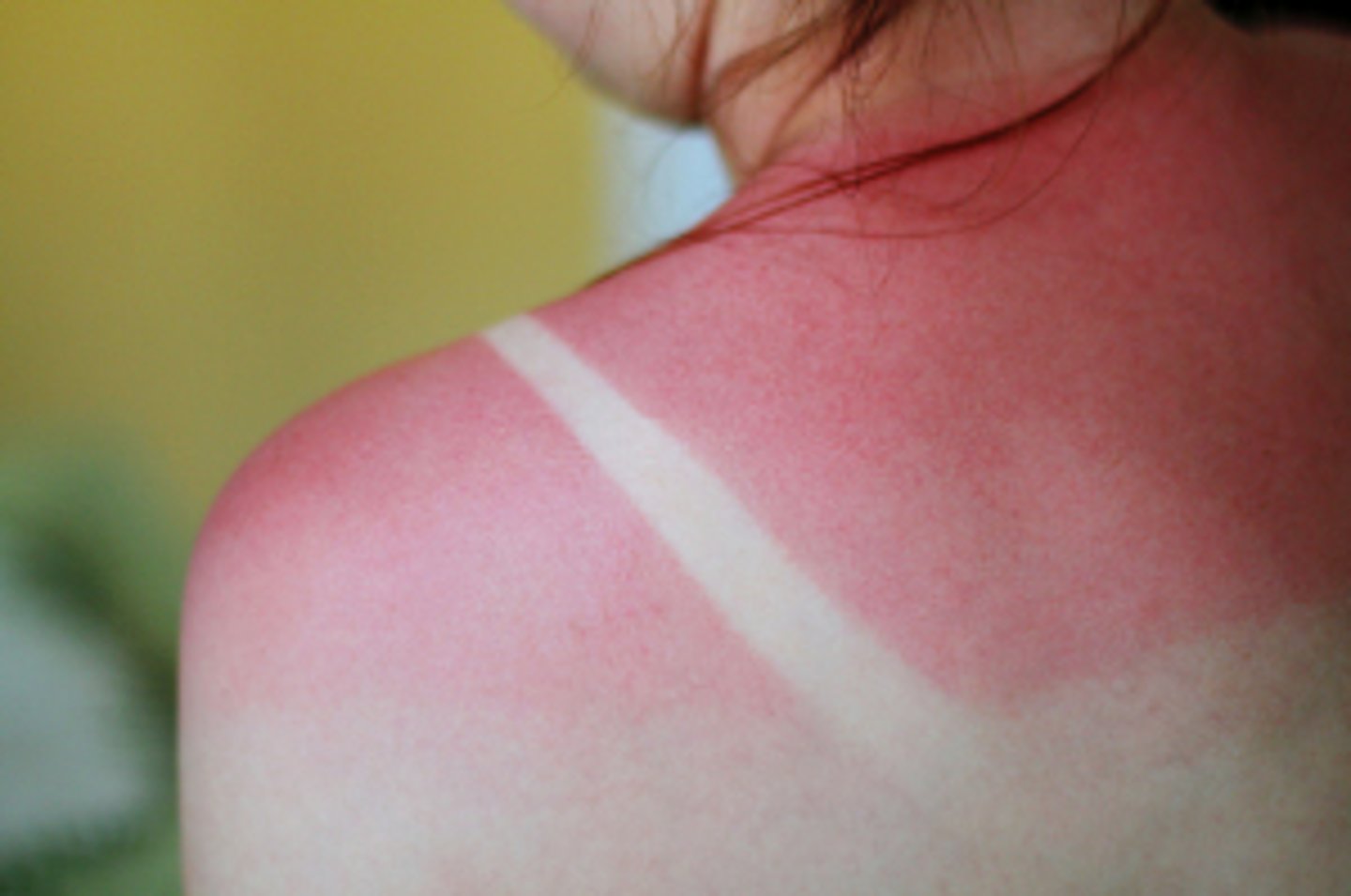
Superficial burns (1st degree)
-Damage to the epidermis
-Dry, pink to red
-NO edema, blistering, or eschar
-Painful
-Healing time is about 1 week

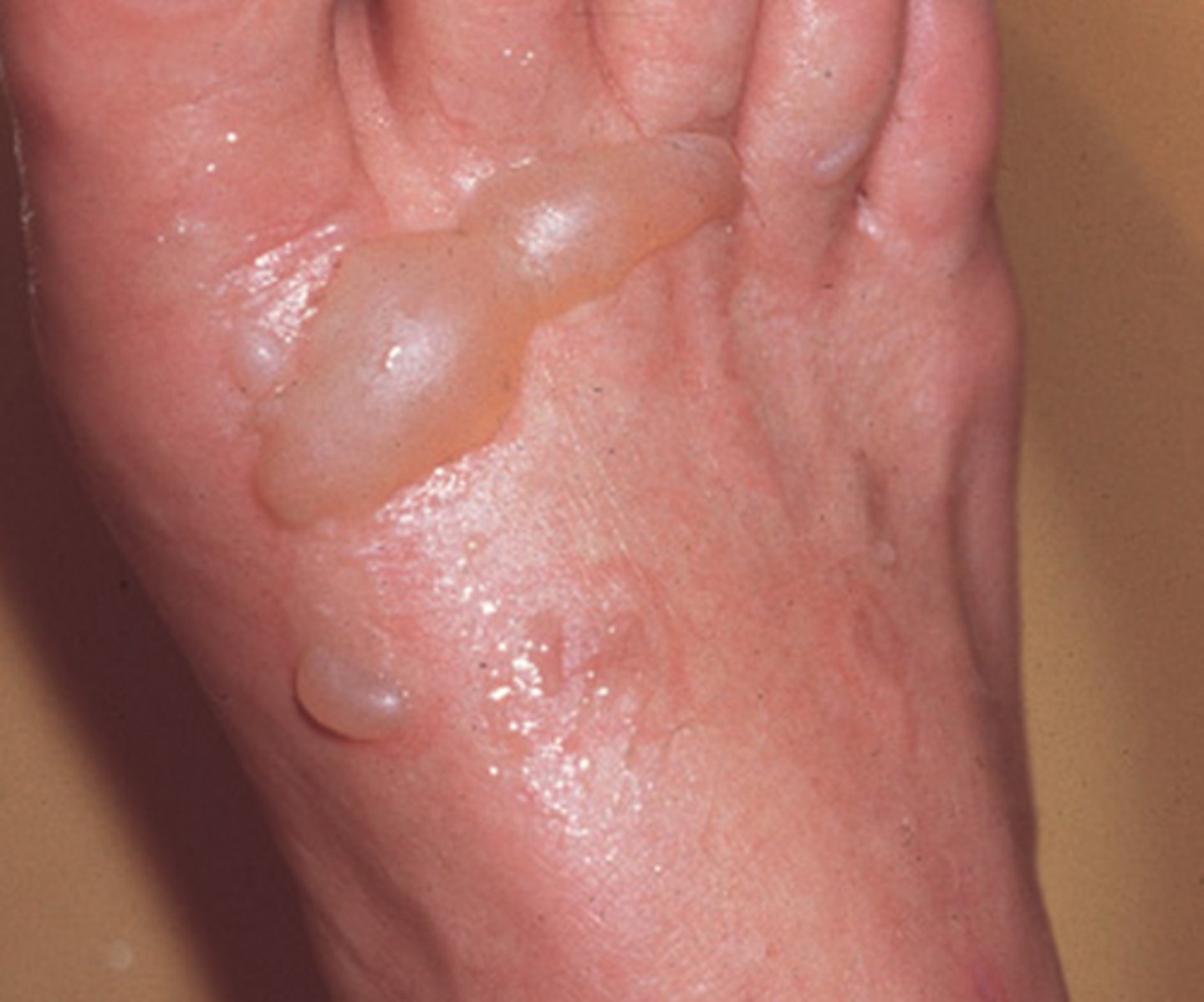
Superficial partial-thickness burns (2nd degree)
-Damage extends into the dermis
-Moist, red, blanching, blistering
-Mild to moderate edema
-Blisters
-Extensive pain
-NO eschar
-Healing time about 2 weeks
Deep partial-thickness burns (2nd degree)
-Epidermis and into the dermis, can vary in depth
-Less moist, less blanching, less painful
-Moderate edema
-Blisters rare
-Some pain
-Soft and dry eschar
-Healing time about 2-4 weeks
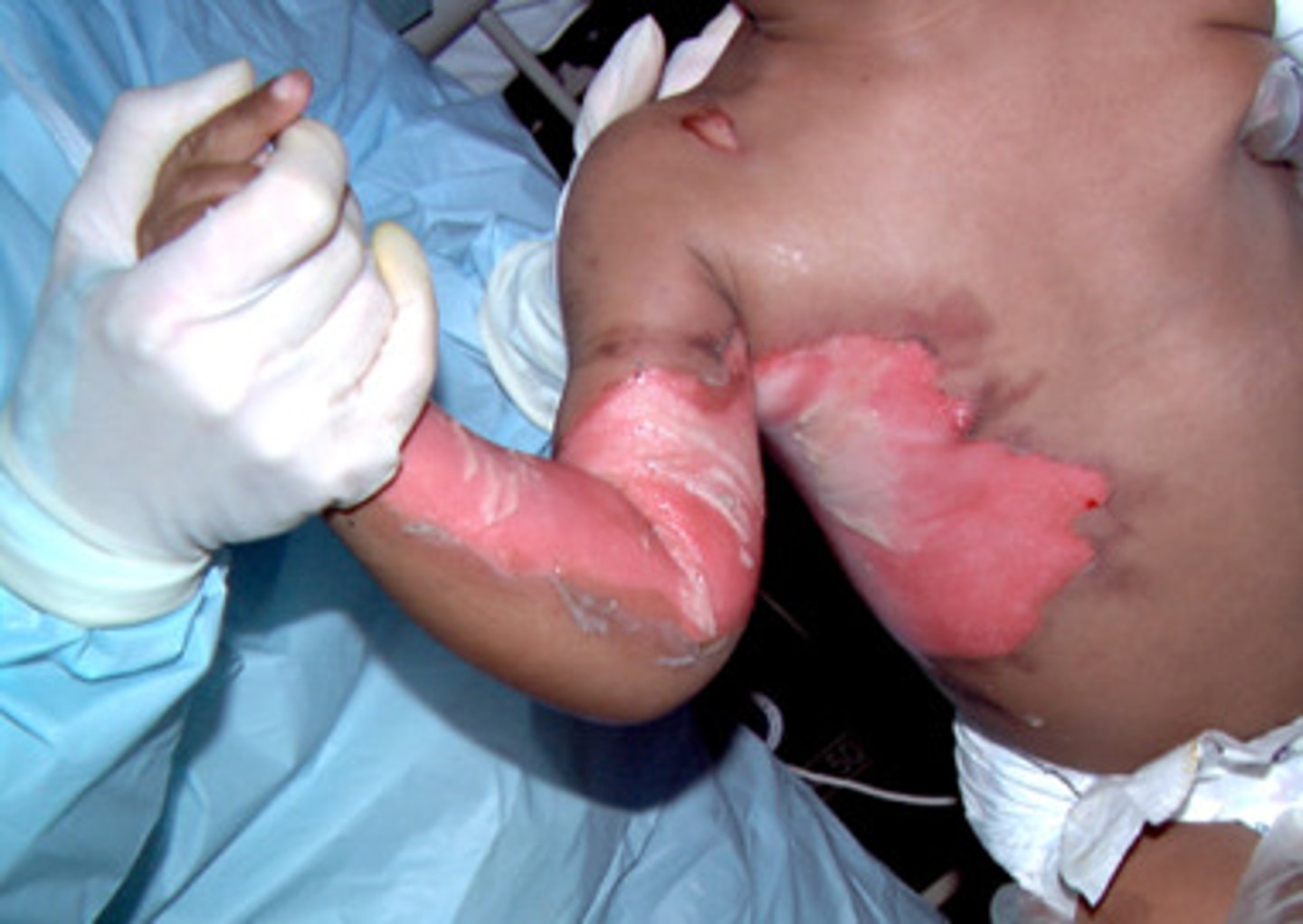
Full-thickness burns (3rd degree)
-Entire thickness of skin destroyed, into subcutaneous tissue
-Black, red, yellow, brown, white
-Severe edema
-NO blisters
-NO pain
-Eschar hard and inelastic
-Healing time weeks to months
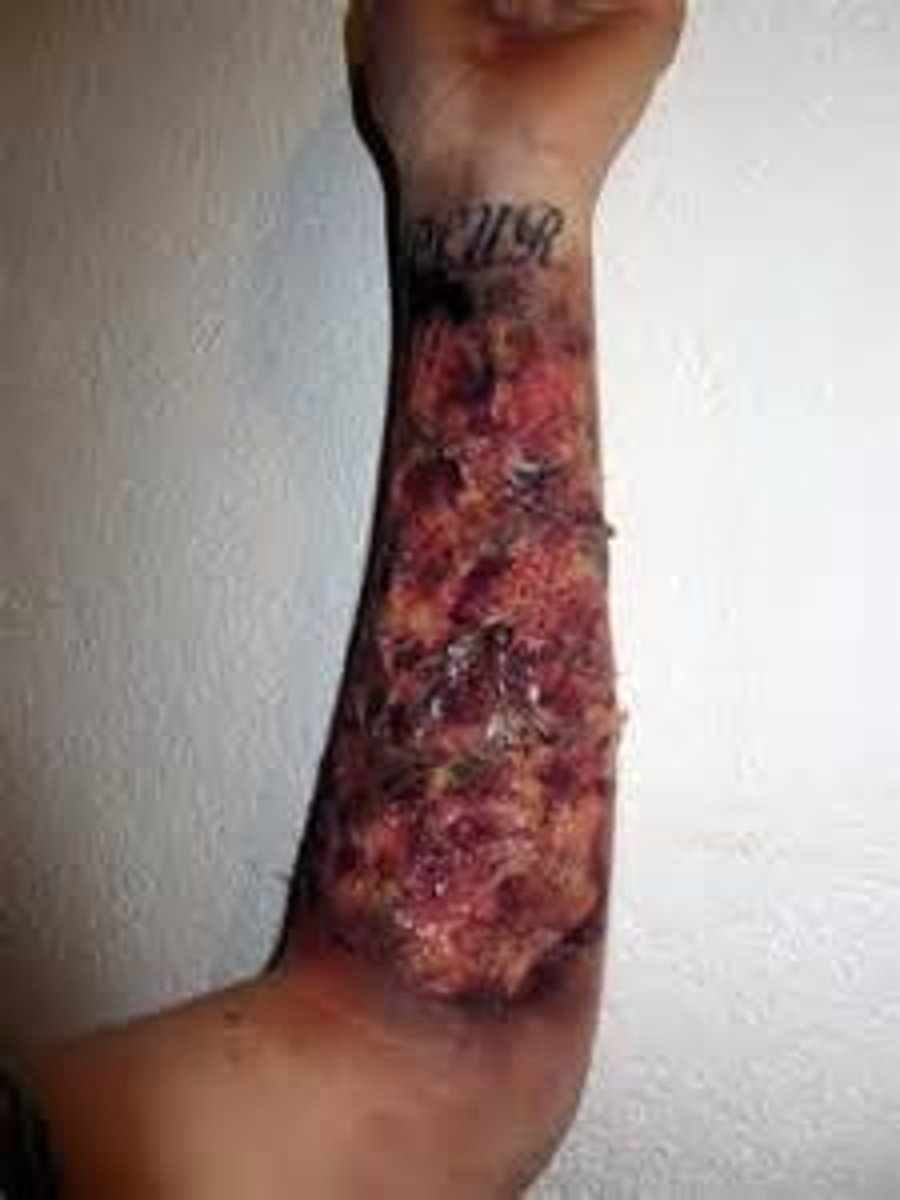
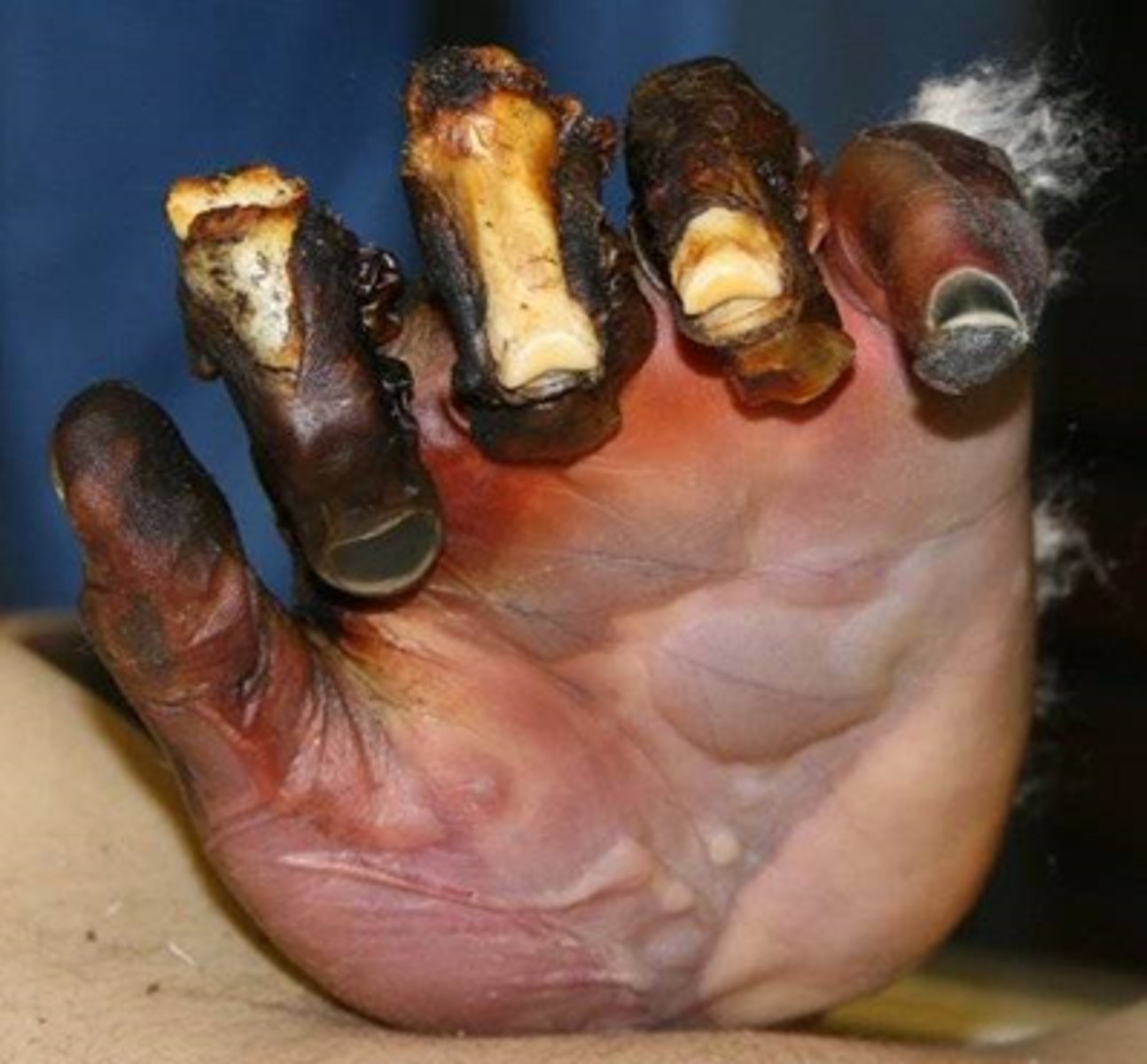
Deep full-thickness burns (4th degree)
-Damage extends into muscle, tendon, bone
-Black
-Severe edema
-NO blisters
-NO pain
-Eschar
-Healing time weeks to months, if at all
Resuscitation phase labs
-Increased glucose
-Increased BUN
-Increased Ht and Hgb
-Decreased sodium
-Increased potassium
-Increased chloride
-Increased CO2
(More than 10% strongly indicates smoke inhalation)
-Decreased protein
-Decreased albumin
(Normal range 3.4 - 5.4 g/dl)
-Metabolic acidosis
Fluid remobilization labs
-Decreased Hgb and Hct
-Decreased sodium
-Decreased potassium
-Increased and then decreased WBC
-Increased glucose
-Decreased protein
-Decreased albumin
Minor burns interventions
-Cleanse with mild soap and tepid water
-Use antimicrobial agent
-Avoid greasy lotions or butter on the burn
-Determine need for tetanus immunization
Burns expected manifestations during the initial phase
-Tachycardia
-Increased RR
-Decreased GI motility
-Increased glucose
Fluid of choice for burn fluid resuscitation
Lactated ringers is fluid of choice, can also infuse 0.9% sodium chloride
General burns interventions
-Provide humidified oxygen
-A tracheotomy when long-term intubation is expected
-Suction every hour as needed
-Initiate IV access using a large-bore needle
-Use IV route for medications
-Keep pt's room warm
-Restrict plants and flowers
-Limit visitors
-Use strict asepsis with wound care
-Large burn areas crease a hypermetabolic state, requiring 5000 calories/day
-Facilitate position changes to prevent contractures
-Assist with ambulation as soon as the client is stable
Burn compression stockings
Wear compression dressings as prescribed (usually 23 hours a day) to minimize scarring and prevent difficulty with mobility