Solar System | Quizlet
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Planet
any of the celestial bodies that revolves a star and has large enough to have become rounded by its own gravity, and has cleared its path in orbit
Star
a celestial body of hot gases that radiates energy derived from nuclear reactions in the core

Solar System
sun, planets, and all the other objects that revolve around the sun due to the sun's gravitational pull
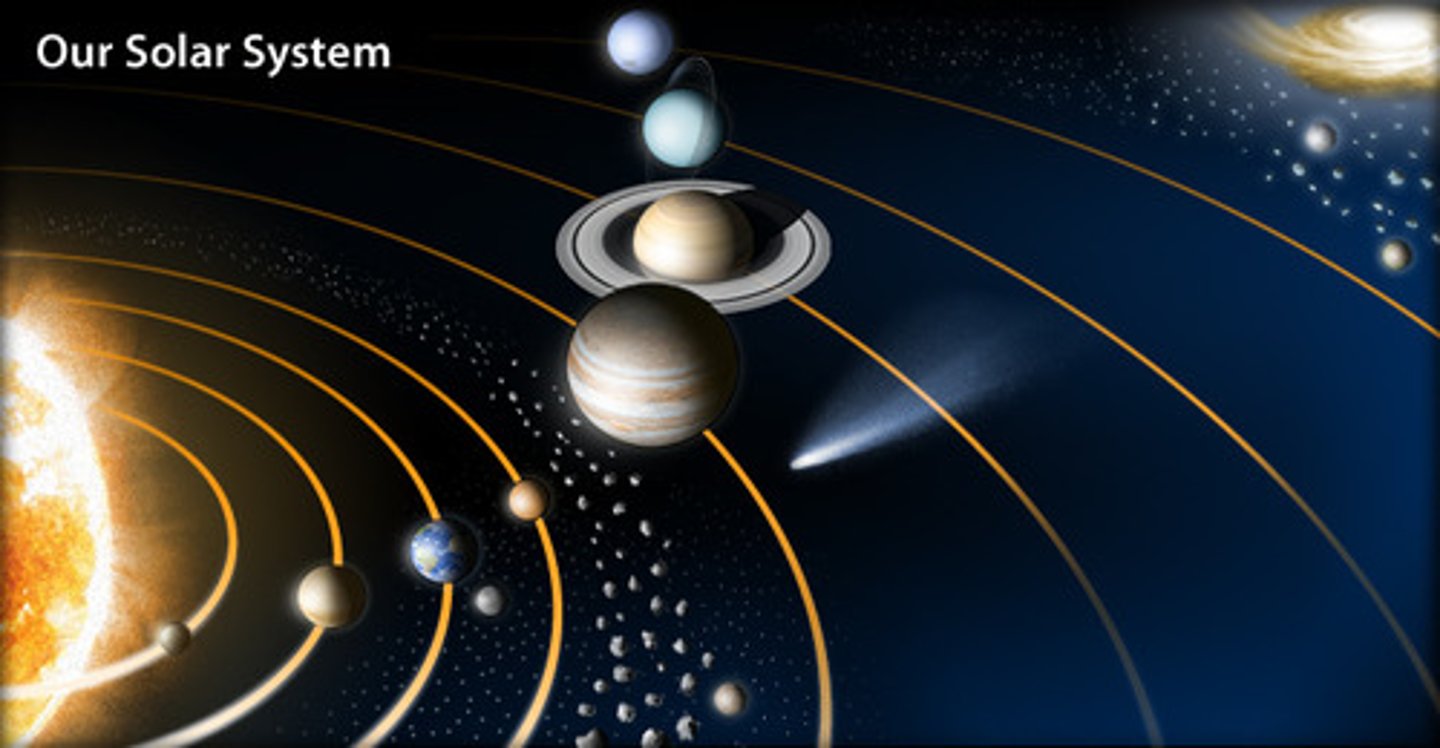
Inner Planets
Planets that are: rocky, high densities, revolve around the sun quickly, thin atmospheres, relatively warm, rotate on axis slowly, few if any moons, terrestrial, no rings

Asteroid Belt
the region of the solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, where many asteroids are found

Outer Planets
Planets that are: rotate on own axis quickly, revolve around the sun slowly, low densities, huge gas giants, thick gaseous atmospheres, cold, all have rings, all have MANY moons

Inertia
the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion
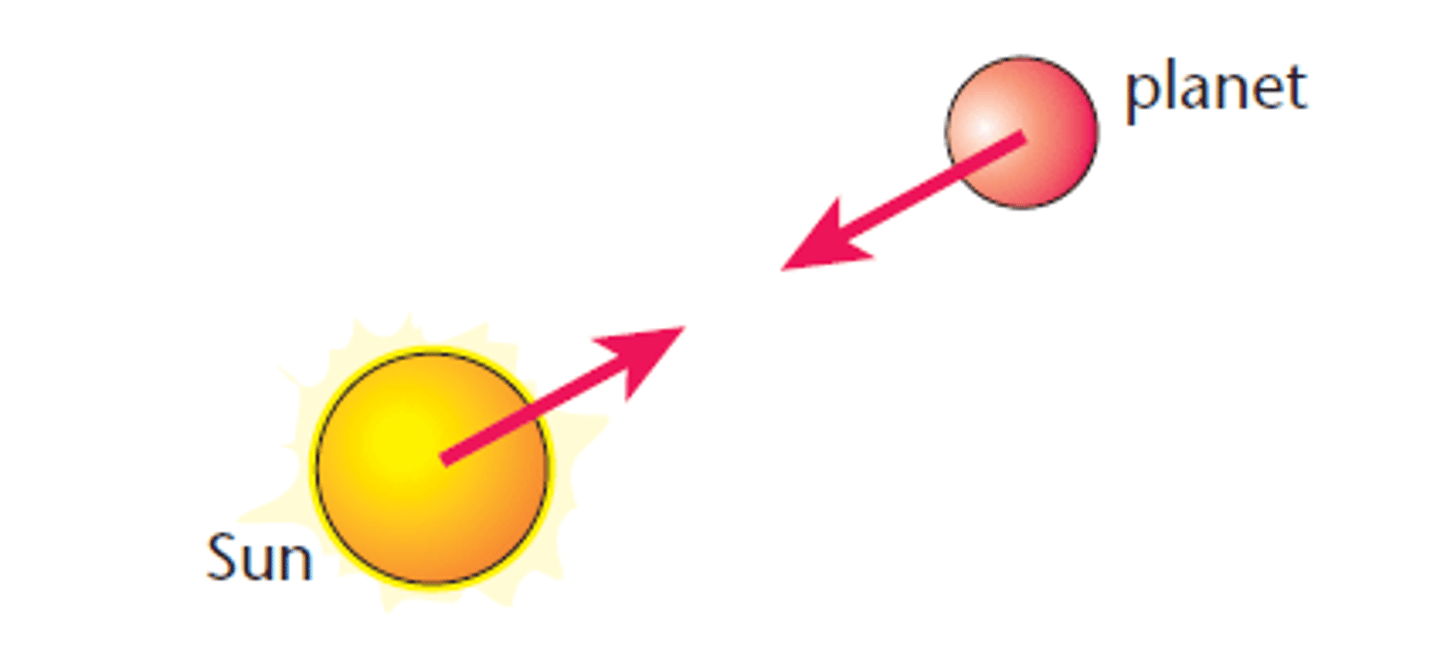
Gravitational Force
an attractive force that acts between any two objects
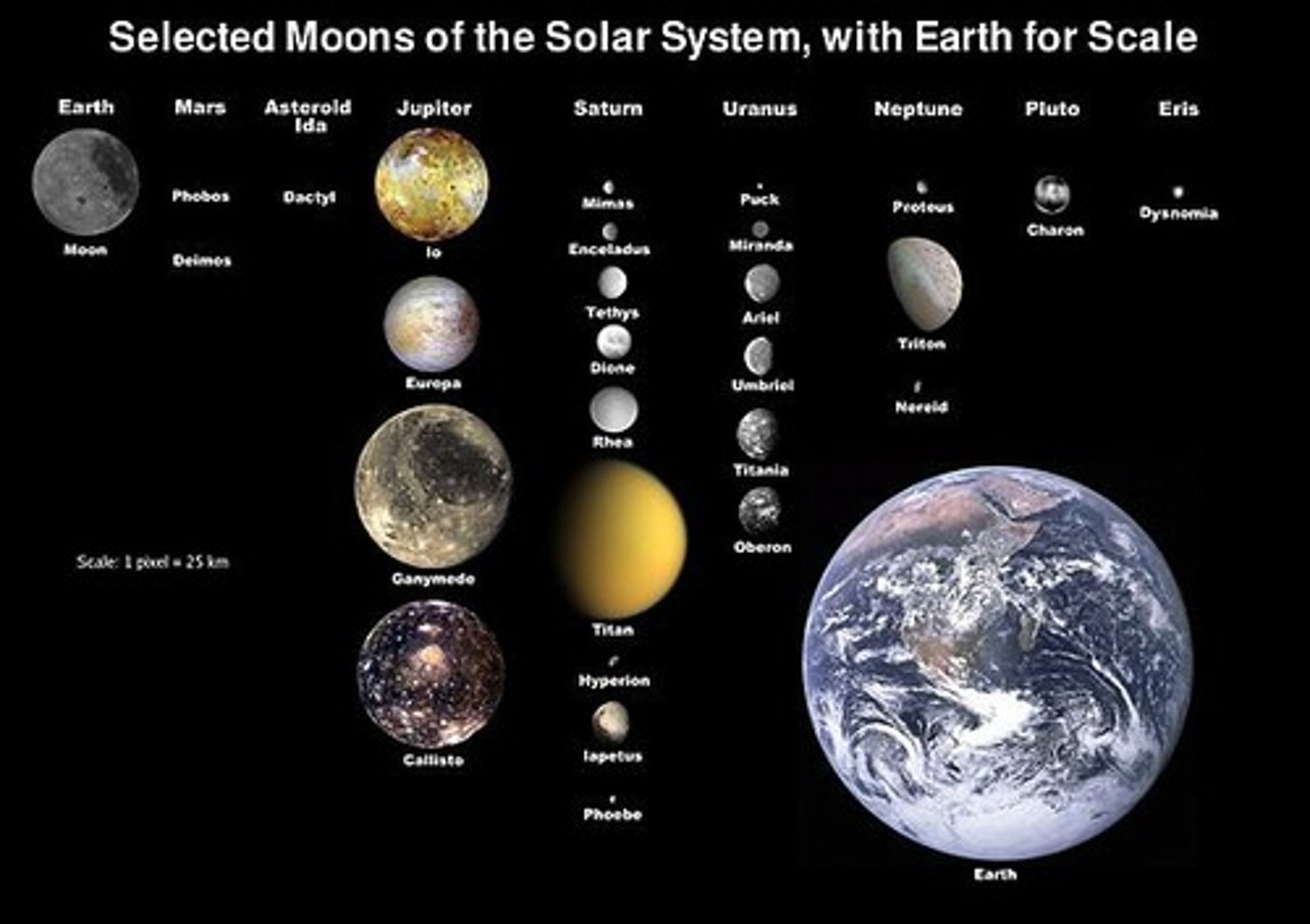
Natural Satellites
moons
What keeps any planet from flying off into outer space?
The gravitational pull of the sun
Mercury
smallest planet, only other inner planet with magnetic field (beside Earth), The "Incredible Shrinking" planet
Venus
second planet from the Sun; the hottest planet in our solar system, similar to Earth in mass and size; Earth's "Evil Twin," has a thick atmosphere of carbon dioxide gas and a surface with craters and over 1,500 volcanoes
Earth
third planet from the sun; has an atmosphere that protects life and surface temperatures that allow water to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas; the "Water Planet"
Mars
has two moons, reddish in color due to iron oxide (rust), the "Red" planet
Retrograde rotation
the clockwise spin of a planet or moon as seen from above the planet's or moon's north pole; also causes day and night to occur
Rotation
the counter-clockwise spinning of a planet or moon; example: the Earth's spinning on its imaginary axis, which takes about 24 hours to complete and causes day and night to occur
Revolution
The movement of an object around another object (a year)
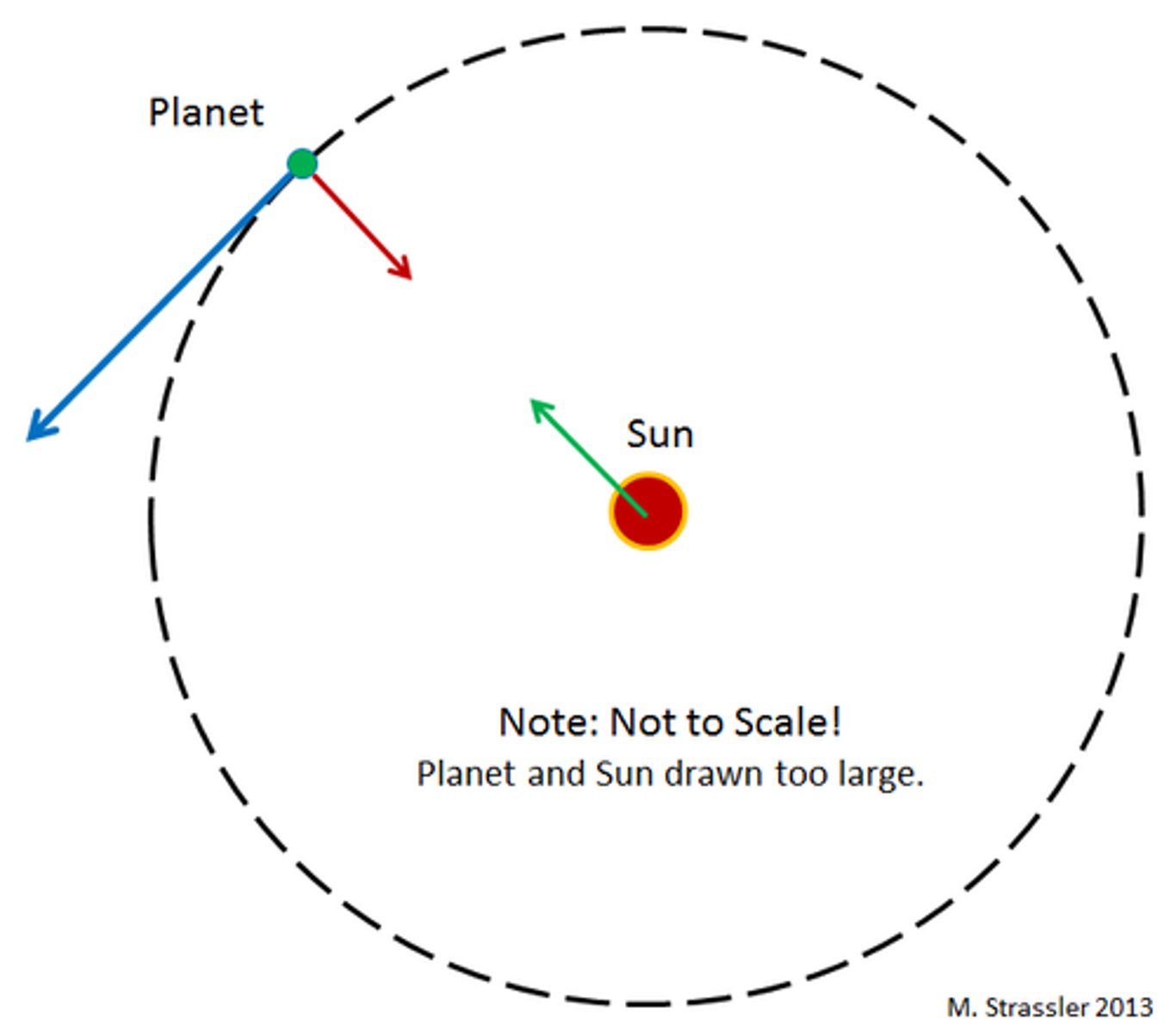
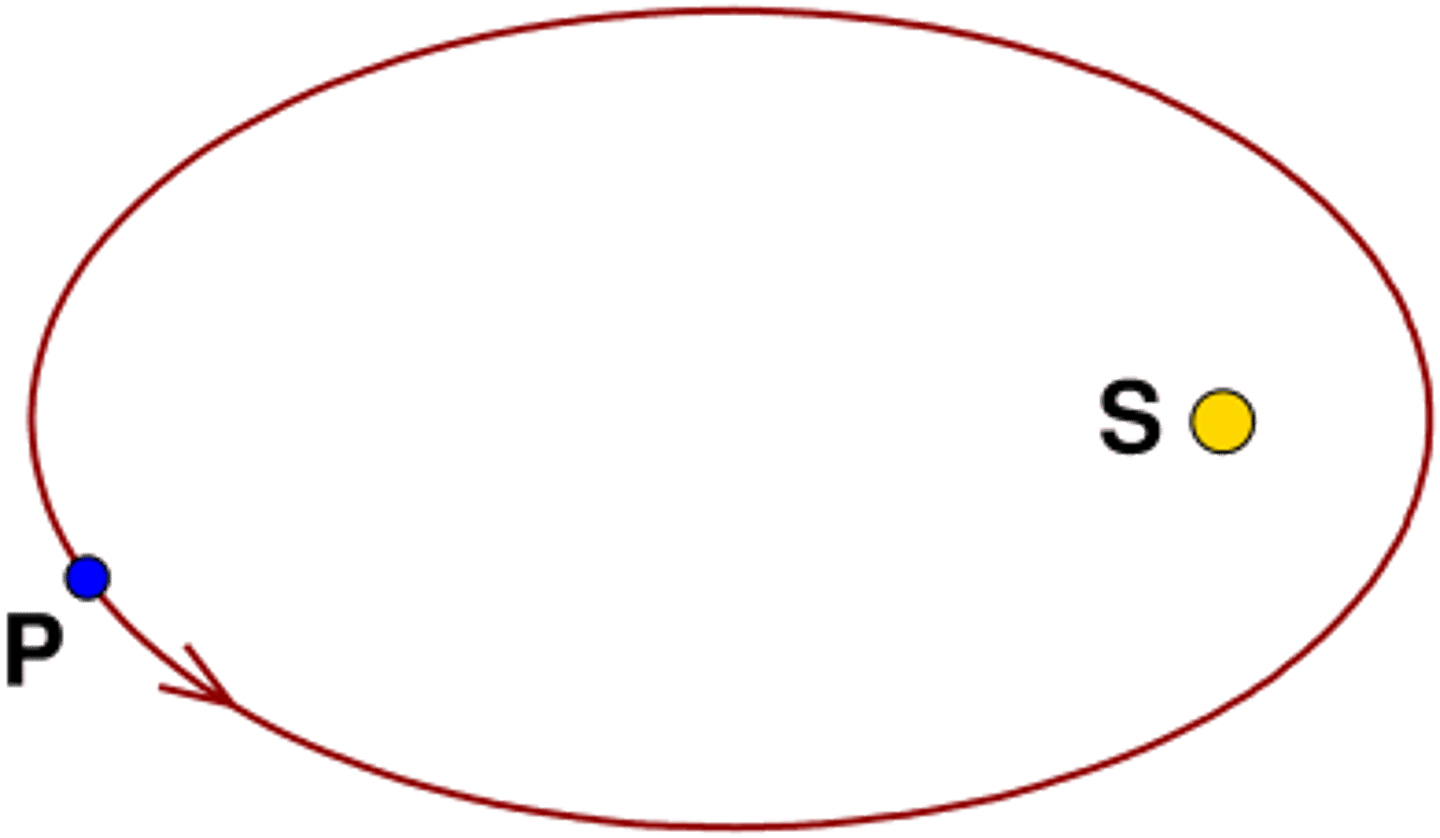
Orbit
the path of an object as it revolves around another object in space; usually the shape of an ellipse
Ellipse
A elongated circle, or oval shape, the shape of the planets orbit.l
Heliocentric Model
the accepted model of our solar system with the sun in the center
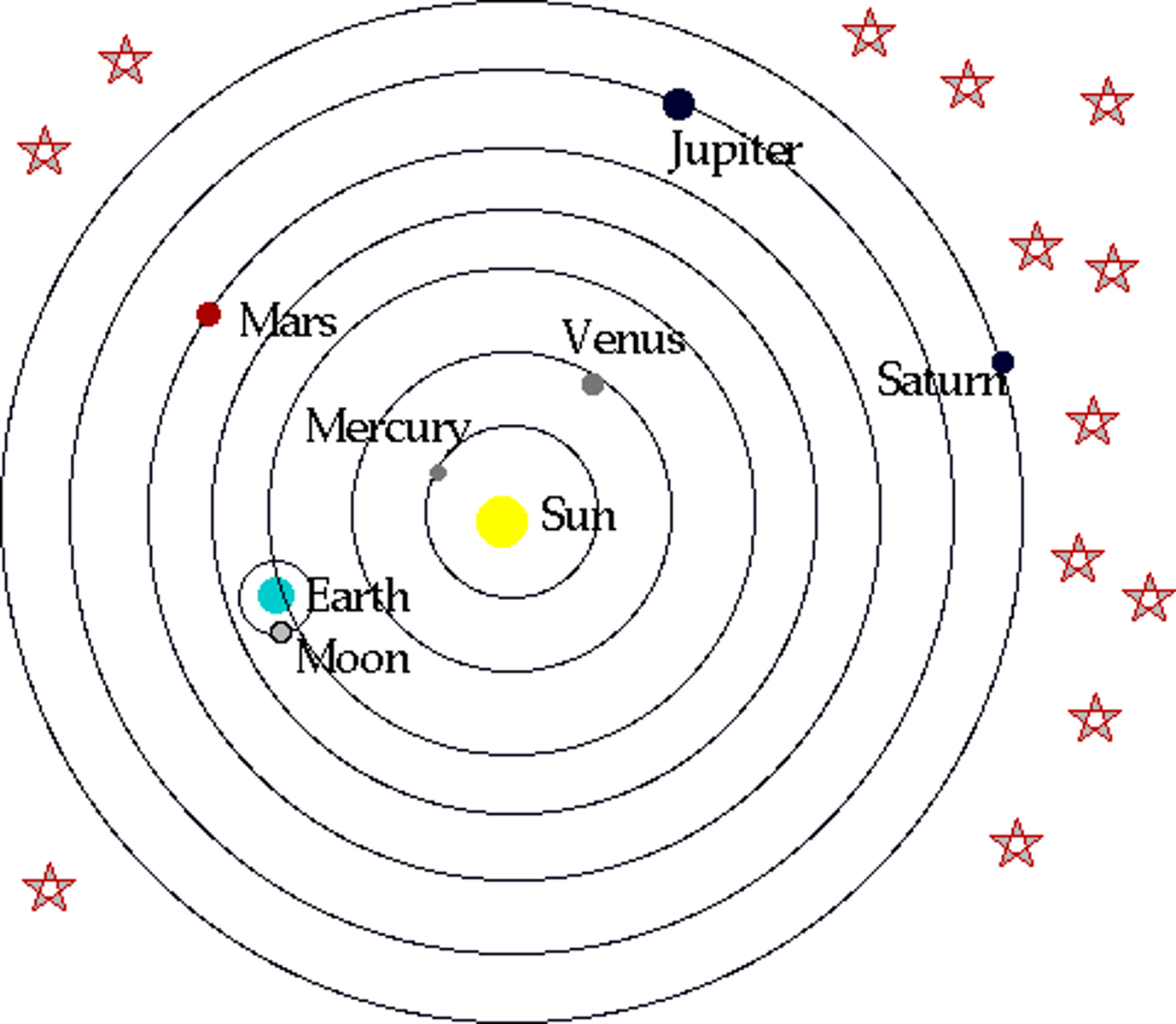
Geocentric Model
the early, incorrect model of our solar system with the earth in the center
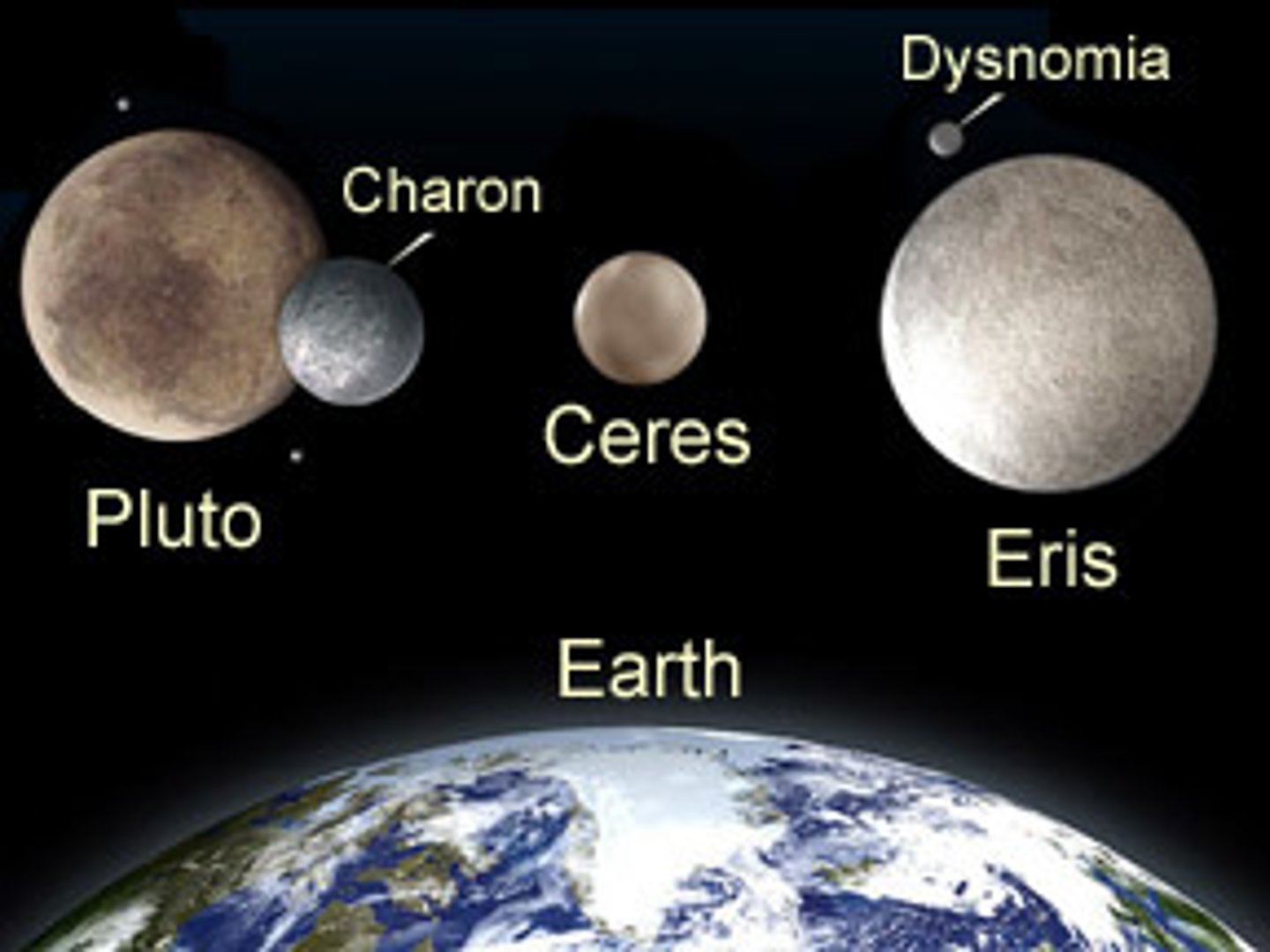
Dwarf planets
Small round bodies that orbit the sun but have not cleared the area around their orbits of other orbiting bodies;Pluto, Eris, Ceres
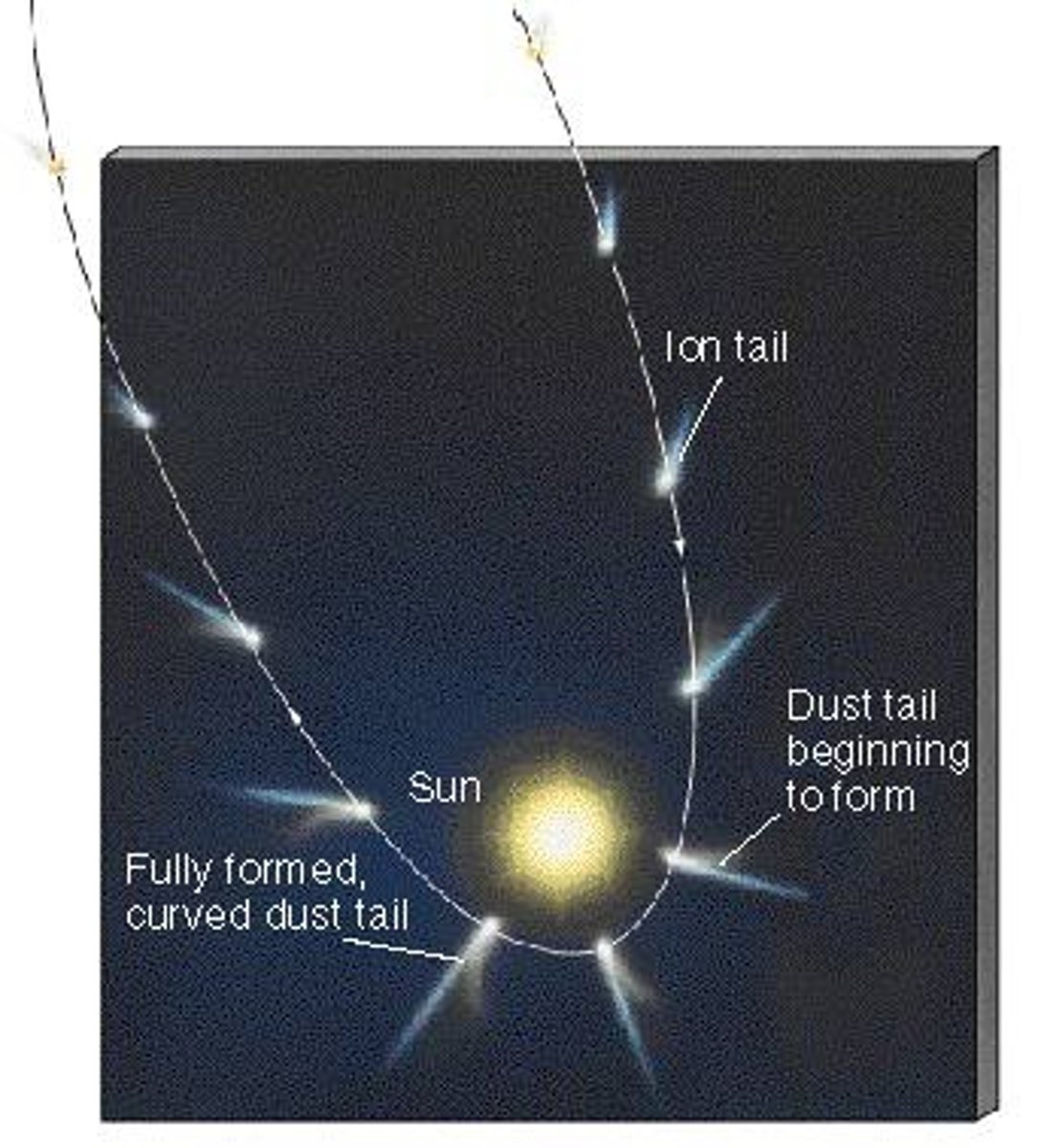
Comets
large clumps of ice, dust and frozen gases that travel around the Sun in long elliptical orbits; only have a tail when they are close to the sun; tail always points away from the sun
Asteroids
rocky metallic objects that orbit the sun but are too small to be considered planets

Meteroid
a chunk of rock or dust that moves through outer space

Meteor
a streak of light in the sky that happens when a meteoroid hits the earth's atmosphere and air friction causes the meteoroid to melt or vaporize or explode

Meteorite
a meteoroid that does not completely burn up in the atmosphere and strikes the surface of a moon or planet

Jupiter
the largest planet and the 5th from the sun; over 63 moons
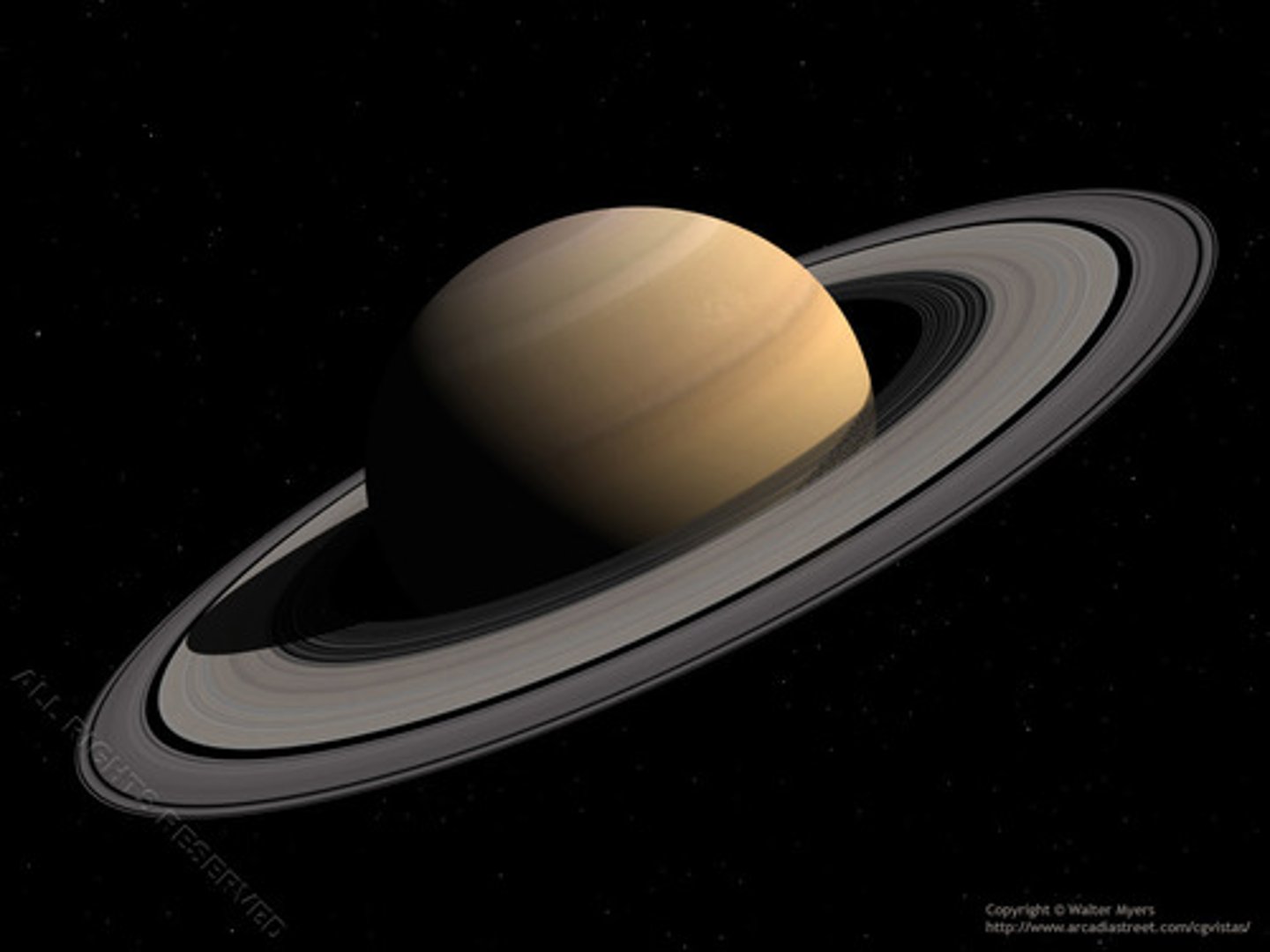
Saturn
the planet that could float on water, due to the fact it is primarily hydrogen; over 60 moons and many rings
Uranus
Seventh planet from the Sun; is large and gaseous with thin, dark rings and rotates tilted on its side; over 27 moons
Neptune
large, gaseous planet with rings, dark-colored storms, and over 13 moons; has a distinctive blue-green color; 8th planet from our sun
Galileo Galilei
This scientist proved Copernicus' theory was correct that the sun was the center of the solar system and developed the modern experimental method. With his telescope he saw that Venus had phases similar to our moon's phases, and he saw the four large moons of Jupiter orbiting Jupiter and not Earth!
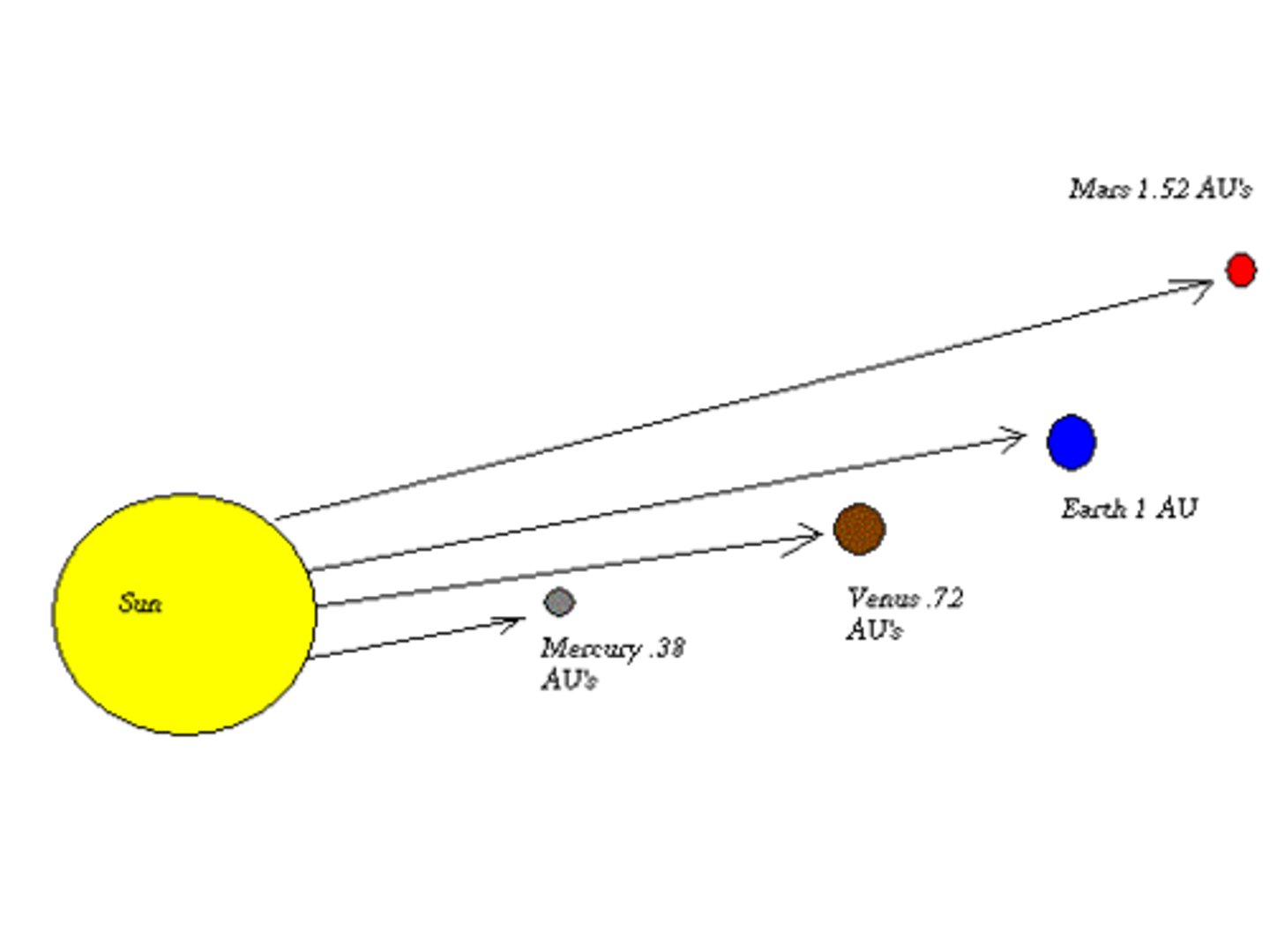
Astronomical Unit
A unit of length used for distances within the solar system; 1 AU = the average distance from the Earth to the Sun
🌞Distance from earth to sun
Average distance: 93 million miles
Or 150 million kilometers
easy way to convert miles to km
1 mile
1.6 km
so a simple way to convert is multiply by 16 then divide 10
ex: 15 miles
15 × 16 = 240 / 10 = 24 km
ex: 24km
24 × 10 = 240 / 16 = 15 miles
🌙 Distance from Earth to the Moon
Average distance: 238,000 miles
Or 384,000 kilometers