Fungus
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:11 PM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
What does heterotroph mean
no photosynthesis
2
New cards
Complete the sentence: Fungi can reporoduce sexually and asexually with the production of **……..**
spores
3
New cards
What is the cell wall of fungi primarily made of?
chitin
4
New cards
Give 2 species of **yeast** of medical importance
1. *Candida albicans*
2. *Cryptococcus neoformans*
5
New cards
Give 2 species of **aseptate** **molds** of medical importance
1\. *Rhizopus sp.*
*2.Mucor sp.*
*2.Mucor sp.*
6
New cards
Give 2 species of **Dematiaceous** **molds** of medical importance
1\.*Rhinocladiella aquaspersa*
2\.*Madurella mycetomatis*
2\.*Madurella mycetomatis*
7
New cards
Give 2 species of **Hyaline septate** **molds** of medical importance
1\.aspergillus fumigatous.
2\.aspergillus clavatus
2\.aspergillus clavatus
8
New cards
Give 2 species of **Dimorphic molds** of medical importance
1\.histoplasm capsulatum
2\.
2\.
9
New cards
Mold are …….. and yeast are …… types of organism
Mold are **multicelllular** and yeast are **unicellular** types of organism
10
New cards
Yeast, mold and dermatophytes are all……?
Saprobes
11
New cards
Describe the clinical manifestations of candidiasis
Caused by species of candida, it can manifest in oral thrush (white paste on tongue), vagina, skin and nails and can rarely invade the body in cases of immunocompromised patients.
12
New cards
What can cryptococcus neoformans cause in immunocompromised
It can be invasive and cause complications such as meningitis and encephalitis
13
New cards
What are the ways in which we can classify fungi?
1. mode of nutrition (saprobes, parasites)
2. mode of reproduction
3. by pathologies caused (cutan, sub-cutan, invasive)
4. phylogenic classification
14
New cards
What are the 5 major groups of fungi?
1. **CHYTRIDIOMYCOTA**
2. **ZYGOMYCOTA**
3. **GLOMEROMYCOTA**
4. **ASCOMYCOTA**
5. **BASIDIOMYCOTA**
15
New cards
Briefly draw the fungi classification tree
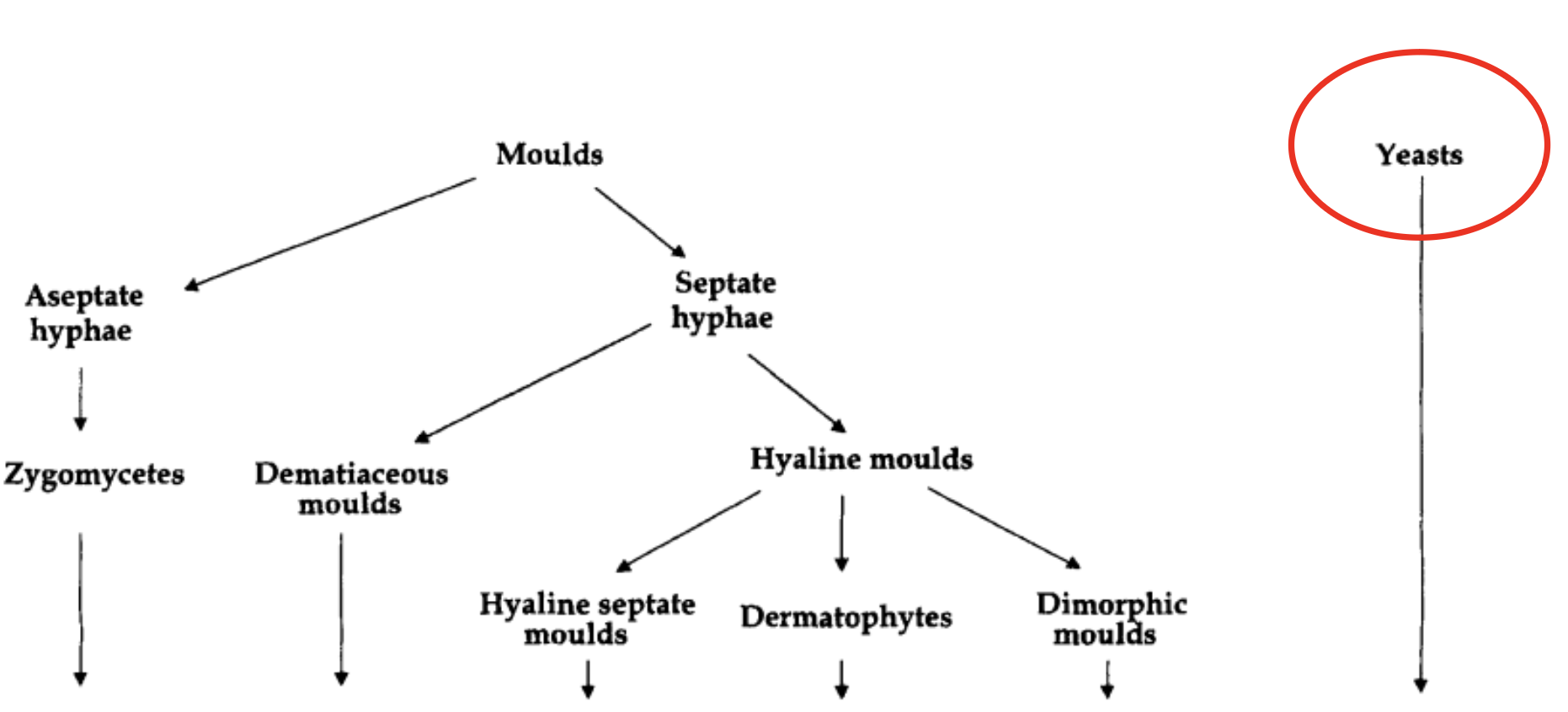
16
New cards
What are the clinical manifestations of an **aspergillus** infection?
It can cause localized infections in immunocompetent people, but can cause disseminated infections in immunocompromised patients. It can cause **Allergic BronchoPulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) ; sub acute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, invasive pulmonary apsergillosis** and even more severe like c**erebral aspergillosis and meningitis.** It can also manifest in a chronic way in **Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis.**
17
New cards
What are the clinical manifestations of an **fusarium** infection?
It typically causes lesions on the foot such as tinea pedis and pustules in immunocompetent people. In immunocompromised individuals, it can also cause skin lesions and pneumonia, sinusitis.
18
New cards
What is a mycellium?
group of hyphae
19
New cards
What is a dimorphic fungus?
It can live in the soil but can also become a pathogen
20
New cards
What is the difference between **anamorph** and **teleomorph**?
**anamorph**=asexual stage of reproduction
**teleomorph**=sexual stage of reproduction
**teleomorph**=sexual stage of reproduction
21
New cards
What are the three types (shapes) of spores?
1\.Ascus (sac-like)
2\.basidium (club-like)
3\.zygospore
2\.basidium (club-like)
3\.zygospore
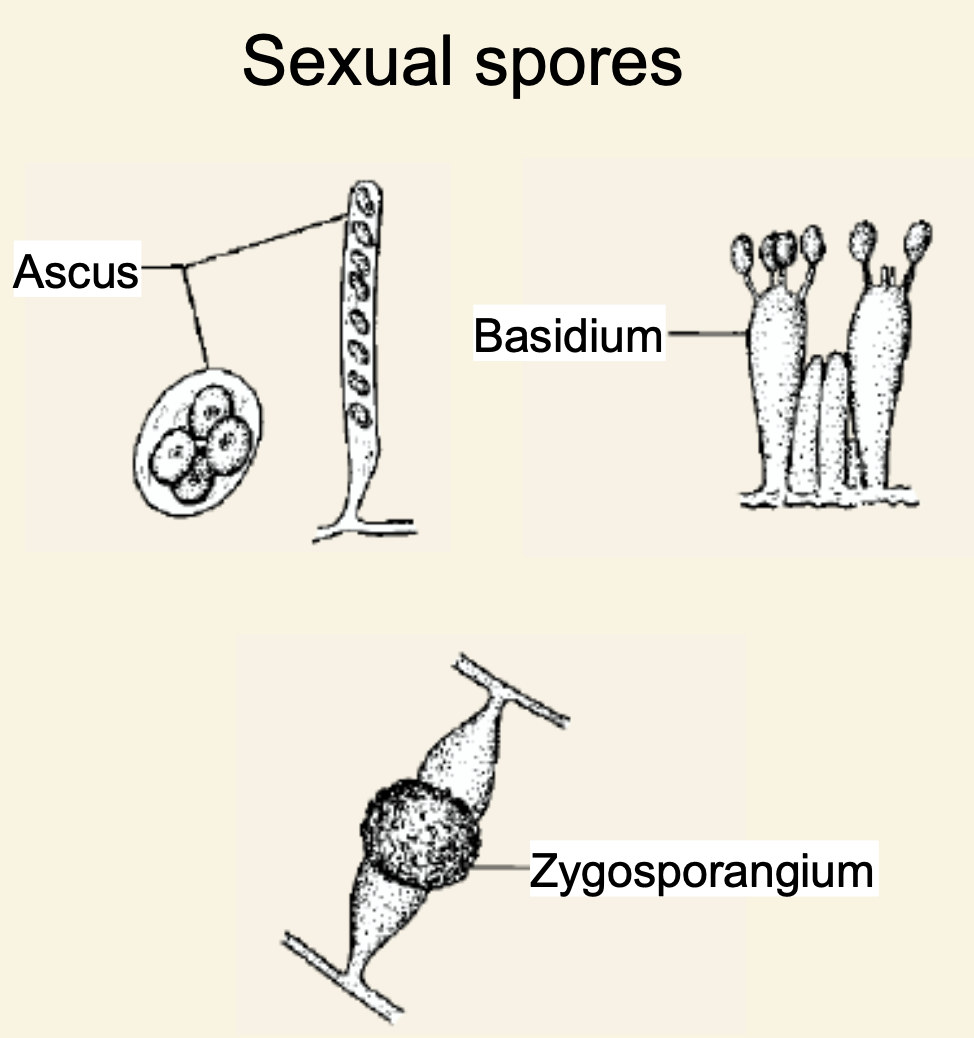
22
New cards
Name the 5 families of antifungals
1. Polyenes
2. Echinocandins
3. Azoles
4. Pyrimidine
5. Allyamines
23
New cards
Name a drug from the **polyenes** family
Amphotercin B
24
New cards
Name a drug from the **Echinocandins** family
Caspofungin
25
New cards
Name a drug from the **Azoles** family
Fluconazole
26
New cards
Name a drug from the **Pyrimidine** family
Flucytosine
27
New cards
Name a drug from the **Allyamines** family
Terbinafine
28
New cards
Explain the MOA of **polyenes**
Forms a complex with ergosterol which is found on the cell membrane of the fungus. Leads to the formation of pores leading to a mass leakage of ions (K+)→ death
\
Fungicide on yeasts and filamentous fungi
\
Fungicide on yeasts and filamentous fungi
29
New cards
Explain the MOA of **echinocandins**
Competitive inhibition of 1,3-β-D glucane synthase, leads to the destabilization of the fungal cell wall→ death
30
New cards
Explain the MOA of **Azoles**
Inhibits the conversion of Lanosterol into ergosterol by inhibiting the converting enzyme called 14α-demethylase. This leads to inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis and therefore the membrane is altered leading to the accumulatoin of toxic methylated sterols→ death
31
New cards
What is an advantage with **echinocandins**?
They are active on biofilms!
32
New cards
Explain the MOA of **Pyrimidines (Flucytosine)**
Flucytosine is converted to the antimetabolite 5-fluorouracil in fungal but not human cells. 5-Fluorouracil inhibits thymidylate synthetase and thus DNA synthesis.
33
New cards
Explain the MOA of **Allyamines**
Inhibition of squalene epoxidase (ERG1) leading to the accumulation of squalene (toxic) and therefore inhibition of ergosterol synthesis→ death
34
New cards
What are some limitations with amphotercin B?
renal toxicity, not absorbed in digestive tract, Induces production of IL-1 & TNF-a, and it has no activity in dermatophytes
35
New cards