AP Africa American Studies: Unit 1 MCQ
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP African American Studies is an interdisciplinary course that examines the diversity of African American experiences through direct encounters with varied sources. Students explore key topics that extend from early African kingdoms to the ongoing challenges and achievements of the contemporary moment. Given the interdisciplinary character of African American Studies, students in the course will develop skills across multiple fields, with an emphasis on developing historical, literary, visual, and data analysis skills. This course foregrounds a study of the diversity of Black communities in the United States within the broader context of Africa and the African diaspora. Unit 1 in APAAS focuses on the Origins of the African Diaspora, exploring how ancient African kingdoms impacted the continent and society overall, from the historical trade and migration patterns of indigenous peoples that led to the dispersion of various cultures, languages, and religions to the influence that African technological and agricultural innovations had on the emergence of early societies and its connections to the global world.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Which of the following is the traditional African model in which African American studies build from?
A. Maat
B. Sesh
C. Oliko
D. Nika
B. Sesh
Explanation: African American studies builds from an important model derived from African tradition, known as Sesh, who is socially conscious.
Which of the following correctly pairs the two movements of the 1960s that more directly contributed to the Student movement?
A. Civil Rights Movement and Feminist Movement
B. Black Power Movement and Free Speech Movement
C. Anti-Vietnam War Movement and Civil Rights Movement
D. Free Speech Movement and Anti-Vietnam War Movement
D. Free Speech Movement and Anti-Vietnam War Movement
Explanation: The Free Speech Movement and Anti-Vietnam War movement more directly contributed to the overall thrust of the Student Movement because it challenged University authority, demonstrating student power and the criticalness of being seen in history and in institutions of higher education.
Which of the following is NOT one of the many goals of the Black Campus movement?
A. Incorporate Africans and those of African descent in history while recognizing their contributions to society
B. Force Universities to adopt the idea of a relevant education which adequately depicts diverse peoples and their struggles
C. Overturn the established order in society which did not allow minorities to attend universities with white students
D. Pressure universities to have diversity in their faculty and staff
C. Overturn the established order in society which did not allow minorities to attend universities with white students
Explanation: The Black Campus Movement lasted from 1965 to 1972 and is directly the result of black students entering PWI’s for the first time in history, meaning that C. could not be the answer as minorities were allowed in these institutions after the passing of Brown v. Board of Education in 1954.
At which of the following universities did Black Studies emerge as both a discipline and movement?
A. University of California Berkeley
B. San Francisco State College
C. Hunter College
D. University of North Carolina
B. San Francisco State College
Explanation: Black studies emerged as a discipline and movement at San Francisco State College where students striked and clashed with police after the university refused to offer black studies causing the movement to diffuse to colleges across the nation and ultimately force most colleges to adopt a black studies after 1969.

This document reflects the success of which of the following movements?
A. Black Campus Movement
B. Free Speech Movement
C. Anti-Vietnam War Movement
D. The Diversity Movement
A. Black Campus Movement
Explanation: This document, a “Schedule of Courses for Black and Puerto Rican Studies” at Hunter College in the fall of 1972 is the result of the Black Campus movement where students fought to be seen in history.
Which of the following is NOT a major climate zone of Africa?
A. Desert
B. Tropical Rainforest
C. Tundra
D. Mediterranean
C. Tundra
Explanation: The five major climate zones of Africa are Desert (Sahara), Semiarid (Sahel), Savanna Grasslands, Tropical Rainforest and Mediterranean.
Which of the following items was traded in the Sahel climate zone?
A. Livestock
B. Grain
C. Yams
D. Jewelry
A. Livestock
Which of the following is one of the 5 major rivers in Africa that supported the emergence of early societies?
A. Limpopo River
B. Senegal River
C. Blue Nile River
D. Orange River
D. Orange River
Explanation: The 5 major rivers that supported the emergence of early societies include: Niger River, Congo River, Zambezi River, Orange River and the Nile River.
Which of the following is the percentage of Africans that are Bantu?
A. 30%
B. 25%
C. 35%
D. 70%
A. 30%
Explanation: 30% (350 million) of Africans are Bantu. The Bantu people originated in Africa then migrated throughout east, west and south Africa.
Between which of the following two countries did the Bantu people originate?
A. Mauritania and Mali
B. Cameroon and Western Nigeria
C. Ivory Coast and Togo
D. Angola and Zambia
B. Cameroon and Western Nigeria
Which modern day countries did the first group of Bantus migrate to after they split from West Africa?
A. Mozambique, Malawi and Zimbabwe
B. Angola, Zambia and Congo
C. Ethiopia, Eritrea and Somalia
D. Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria
B. Angola, Zambia and Congo
Explanation: After the Bantu people expanded out of Western Africa between 3000 and 1000 B.C. and established themselves just North of the Congo River they split, the first group migrating southward into modern-day Angola, Zambia and Congo while the second group migrated east to occupy the Great lakes.
For how long did the Great Migration of the Bantu people last?
A.1,500 years
B. 700 years
C. 2,000 years
D. 5,000 years
C. 2,000 years
Explanation: The Bantu migration lasted over 2,000 years, initially moving because their rulers wanted to expand and create new kingdoms.
Which of the following statements explains the historical significance of the Bantu Tribe?
A. Contributed to the linguistic diversity of Africa with the diffusion of hundreds of languages spoken throughout West, Central and South Africa that are still in use today
B. Made technological advancements in iron smelting around the continent replacing the long used stone tools
C. Supported population growth through agricultural innovations with the introduction and popularization of the yam and banana to other regions of Africa
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
Which of the following is one of the main language groups that developed in South Africa?
A. Sotho-Tswana
B. Xhosa
C. Swazi
D. Mguni
A. Sotho-Tswana
Explanation: The two main language groups that developed in South Africa were the Sotho-Tswana in the interior plateau and Nguni (Xhosa, Zulu, Swazi) in the eastern coastal plains.
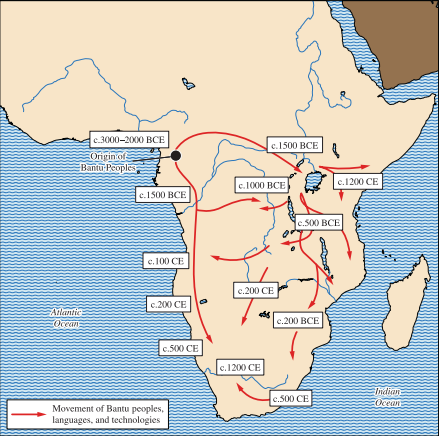
Based on the map above, which of the following explains why the Bantu people did not migrate further north?
A. Lack of weapons to fight northern empires
B. Unable to pay fares that allowed them to travel north
C. The Sahara Desert acted as a geographical barrier
D. The Bantu people did not understand the languages of Northern Africans
C. The Sahara Desert acted as a geographical barrier
Which of the following rivers did ancient societies Egypt and Nubia emerge along?
A. Nile River
B. Orange River
C. Zambezi River
D. Blue Nile River
A. Nile River
Which of the following items did Egypt source from Nubia that led to constant conflict between the two societies?
A. Gold and Luxury items
B. Silver and fur
C. Goat and salt
D. Fruit and steel
A. Gold and Luxury items
Which of the following explains how the 25th dynasty of black pharaohs was established?
A. Economic decline of Egypt after Nubia ended all trade relations
B. Through the conquering of the Egyptians by the Nubians
C. The spread of Christianity which increased the power of the Nubians
D. The uniting of both Egypt and Nubia which created the greatest kingdom of its time
B. Through the conquering of the Egyptians by the Nubians
Explanation: After constant conflict with one another as Nubia was the source of Egypt’s gold and luxury items, around 750 BCE the Nubians conquered Egypt establishing the 25th dynasty of Black pharaohs who ruled for a century.
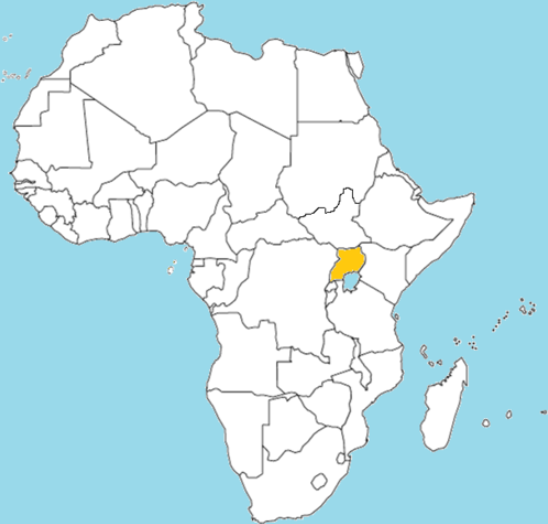
Which of the following countries is labeled on the map?
A. Rwanda
B. Ugandi
C. Burundi
D. Uganda
D. Uganda
The Aksumite Empire was located in which of the following modern day African country’s?
A. Djibouti
B. Eritea
C. Egypt
D. Somalia
B. Eritea
Which of the following is NOT an attribute of the Aksumite Empire’s success?
A. Access to major maritime trade networks through the Mediterranean sea
B. The creation of their own currency
C. The conquering of several West African kingdoms
D. Its establishment as a Christian kingdom
C. The conquering of several West African kingdoms
Which of the following industries was the Nok society most known for?
A. Salt mining
B. Cotton farming
C. Iron working
D. Coal mining
C. Ironworking
Explanation: The Nok society was one of west Africa’s earliest societies to develop iron working around 500 BCE.
In which of the following modern day countries did the Nok society emerge?
A. Nigeria
B. Ghana
C. Mali
D. Niger
A. Nigeria
Which of the following Sudanic empires lasted the longest?
A. Songhai
B. Mali
C. Ashanti
D. Ghana
D. Ghana
Explanation: Songhai lasted for 100 years, Mali lasted for 400 years and the Ashanti empire lasted for 200 years while Ghana lasted from 700 CE to 1300 CE making it the longest lasting sudanic empire.
Which of the following is NOT a contributor to the success of the Sudanic empires?
A. Portuguese introduction of Atlantic trade
B. The production of steel weapons
C. Diffusion of Islam
D. Trans-Saharan commerce
A. Portuguese introduction of Atlantic trade
Explanation: Portuguese exploration along the west coast of Africa caused trade routes to shift from Trans-Saharan commerce to Atlantic trade which diminished Songhai’s wealth and ultimately led to its decline not success.
Which of the following regions is the origin of the majority of enslaved Africans transported directly to North Amercia?
A. East Africa
B. North Africa
C. West and West central Africa
D. South and Central Africa
C. West and West central Africa
Which of the following Kings established the Mali Empire as a center for trade, learning and cultural exchange in the 1400s?
A. King Ezana
B. Mansa Musa
C. King Piankhi
D. Suni Ali
B. Mansa Musa
Which of the following climate zones was the Songhai empire located in?
A. Semi-arid
B. Tropical rainforest
C. Desert
D. Meditrranean
C. Desert
Which of the following explains how the Kingdom of Mali extended power over their neighbors?
A. Requesting other Sudanic empires to integrate with Mali as they would benefit from their wealth
B. Use of their wealth and access to trade routes to cross-breed powerful North African horses and purchase steel weapons to conquer their neighbors
C. Spreading their wealth in a pilgrimage to neighboring countries which caused inflation and better allowed them to conquer these kingdoms
D. Spread of Islam from Mali throughout the region which forced surrounding neighbors to subjugate to Mali
B. Use of their wealth and access to trade routes to cross-breed powerful North African horses and purchase steel weapons to conquer their neighbors
Which of the following is the climate zone of Kenya?
A. Semi-arid
B. Desert
C. Grasslands
D. Tundra
A. Semi-arid
Which of the following European countries initiated the trade of enslaved Africans, and turned islands on Africa’s Atlantic coast into large-scale plantation camps?
A. United Kingdom
B. Spain
C. Portugal
D. France
C. Portugal
Which of the following is the primary religion of the Aksumite Empire?
A. Christianity
B. Voodoo
C. Animalism
D. Islam
A. Christianity
Explanation: The Aksumite Empire was the first African society to adopt Christianity while under the leadership of King Ezana
The Nok people were known for making which of the following types of art?
A. Ceramic sculptures
B. Terracotta sculptures
C. Stone pots
D. Silver jewelry
B. Terracotta sculptures
Which of the following types of crops were grown in the Savanna grasslands?
A. Tobacco
B. Cotton
C. Corn
D. Grain
D. Grain
In Timbuktu, Mali, the flourishing of book trade, universities and learning centers attracted which of the following types of people?
A. Architects
B. Jurists
C. Astronomers
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
In the tropical regions of Africa which of the following two main crops were grown?
A. Rice and beans
B. Mango and Pineapple
C. Banana and cabbage
D. Yams and kola trees
D. Yams and Kola Trees
Which of the following provides an accurate description of Griots?
A. Storytellers that preserve a community’s history, traditions and cultural practices
B. Architects who design and build culturally significant cities
C. Dancers that perform rituals for God’s blessing of good harvests
D. Historians who keep cultural knowledge and historical events from outsiders for elites
A. Storytellers that preserve a community’s history, traditions and cultural practices
As the world’s second largest continent, Africa is a mass landscape consisting of several different climate zones and surrounded by various seas and oceans.
Which of the following is NOT an ocean or sea that borders the continent of Africa?
A. Indian Ocean
B. Red Sea
C. Bohol Sea
D. Atlantic Ocean
C. Bohol Sea
Which of the following defines syncretism?
A. The breaking up of a religion, culture or school of thought into a new sect
B. A combination of different religions, cultures or schools of thought
C. The forced introduction of a religion or culture upon a different group of people
D. The diffusion of a religion, culture or school of thought through synchronized dance
B. A combination of different religions, cultures or schools of thought
Which of the following explains how syncretic practices from early West African societies were carried forward in African descended communities in the Americas?
A. Communities in the Americas willingly accepted the diverse religious practices of African descendants of West African societies.
B. Religious books, texts and scripts from West Africa were brought to the Americas by enslaved Africans which sustained their culture.
C. Descendants of West African societies who blended local spiritual practices with Islam and Christianity brought their syncretic practices to the Americas.
D. None of the above, West African cultural practices were taboo in the Americas and descendants of West Africa were indoctrinated with Christianity.
C. Descendants of West African societies who blended local spiritual practices with Islam and Christianity brought their syncretic practices to the Americas.
Which of the following is the percentage of enslaved Africans brought to North America that came from Christian and Muslim societies in West Africa?
A. 25% Christian and 25% Muslim
B. 75% Christian and 25% Muslim
C. 25% Muslim and 75% Christian
D. 35% Muslim and 50% Christian
A. 25% Christian and 25% Muslim
Which of the following is a syncretic practice brought by enslaved Africans in the Americas that can be traced back to West Africa?
A. Catholicism in Cuba
B. Islam in the United States
C. Vodou in Haiti
D. Mormonism in the United States
C. Vodou in Haiti
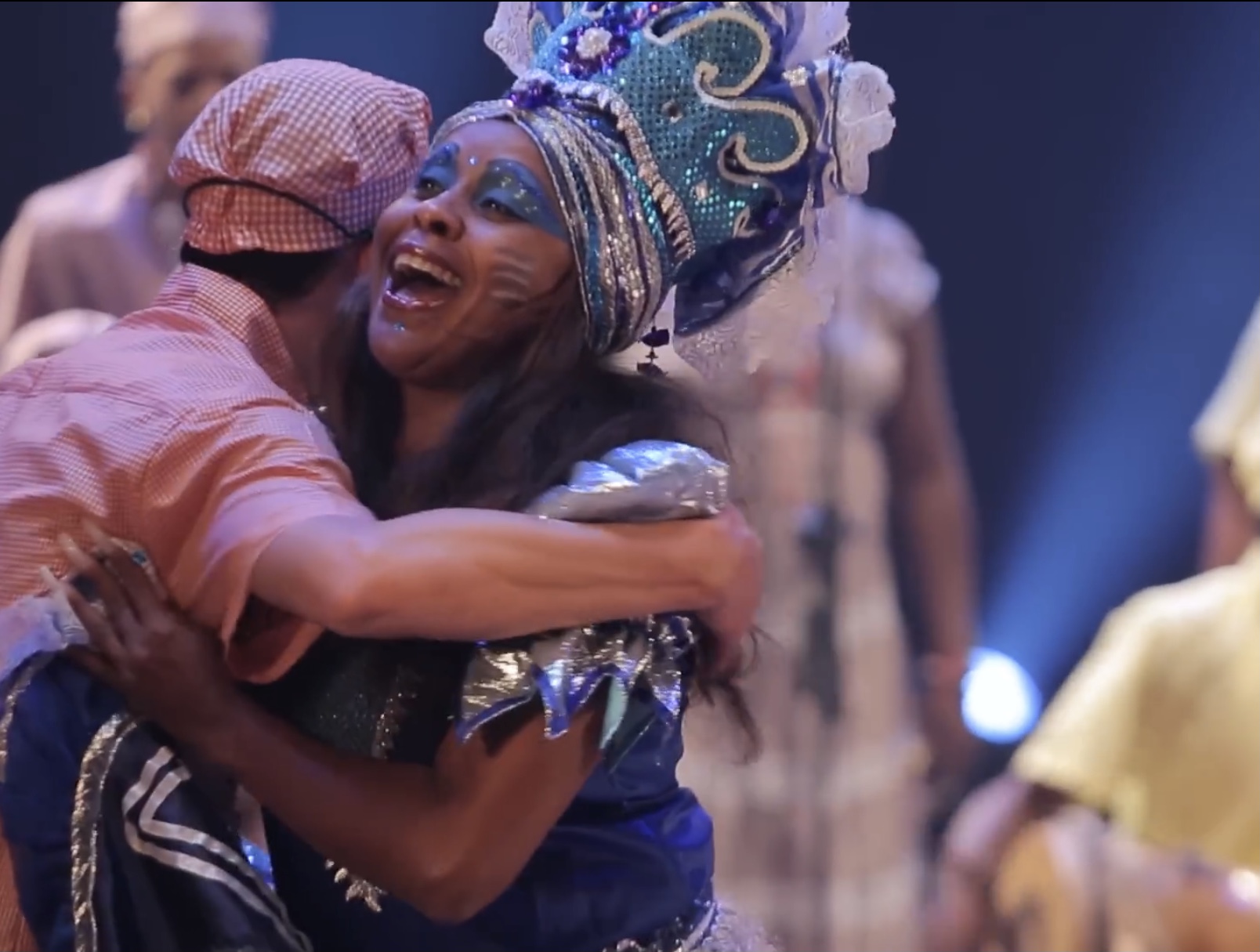

The performance “Osain del Monte” is a syncretic practice deriving from which of the following two cultures?
A. African and Portuguese
B. Puerto Rican and French
C. African and Cuban
D. Colombian and African
C. African and Cuban
Explanation: “Osain del Monte” is an Afro-Cuban performance where aspects of African and Cuban religions are combined into new forms of song and dance.

In which of the following countries was the Yoruba Oshe Shango used in ceremonies to honor the Orisha deity Shango?
A. Ghana
B. Namibia
C. Zimbabwe
D. Nigeria
D. Nigeria
The Shona people of Zimbabwe became wealthy from which of the following resources through trade on the Swahili Coast?
A. Cattle
B. Gold
C. Ivory
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
Great Zimbabwe was mostly known for which of the following developments?
A. Steel weapons
B. Large stone architecture
C. Massive Pyramids
D. Large gold temples
B. Large stone architecture
Zimbabwe and Great Zimbabwe flourished in South Africa during which of following time periods?
A. 1200s to 1500s
B. 1500s to 1700s
C. 1300s to 1600s
D. 1200s to 1400s
A. 1200s to 1500s
Which of the following trade communities were NOT linked to the city-states along the Swahili Coast in Africa?
A. Slavic
B. Persian
C. Chinese
D. Indian
A. Slavic
Explanation: The Swahili Coast stretches from Somalia to Mozambique, its city states linking Africa’s interior to Arab, Persian, Indian and Chinese trading communities.
Which of the following European countries took control of Indian Ocean trade by establishing settlements in the city-states along the Swahili Coast?
A. France
B. Britain
C. Belgium
D. Portugal
D. Portugal
Which of the following sources best demonstrates the complex connections and presence that early African societies had in the global world?
A. Catalan Atlas by Abraham Cresques, 1375
B. “Osain Del Monte”
C. Map of Indian Ocean trade routes from Swahili Coast
D. Statue of Black Madonna of Regla, Cuba
C. Map of Indian Ocean trade routes from Swahili Coast
Which of the following religions did King Nzinga and his son, Nzing, convert the Kingdom of Kongo to in 1491?
A. Catholicism
B. Islam
C. Voodoo
D. Judaism
A. Catholicism
True or False.
The Kingdom of Kongo increased its wealth by voluntarily converting to Roman Catholicism.
A. True
B. False
A. True
Explanation: King Nzinga and his son voluntarily converted the Kingdom of Kongo to Roman Catholicism which strengthened its trade relationship with Portugal, ultimately increasing Kongo’s wealth.
Which of the following was NOT one of the primary goods traded by the Kingdom of Kongo in the 15th century?
A. Textiles
B. Salt
C. Ivory
D. Cattle
D. Cattle
Which of the following explains how the conversion to Roman Catholicism in the Kingdom of Kongo gained mass acceptance?
A. King Nzinga’s tax cut to those who converted
B. Nobility’s voluntary conversion to the faith
C. The totalitarian government’s use of military forces to mandate the religion
D. King Nzinga’s implementation of Catholic teachings in schools
B. Nobility’s voluntary conversion to the faith
Explanation: After King Nzinga converted the Kingdom of Kongo to Roman Catholicism all nobles voluntarily converted which led to the hierarchical diffusion of the faith resulting in everyone throughout the kingdom to follow suit.
After Portugal demanded access to the trade of enslaved people in the Kingdom of Kongo, King Nzinga had a rule only permitting the enslavement of which of the following groups of people?
A. Muslims
B. Lower Class
C. Foreigners
D. Educators
C. Foreigners
Explanation: The King of Kongo had a rule that only foreigners—those not of Kongolese origin—could be enslaved by Portugal to be sent to the Americas.
Which of the following explains how Africans of Kongo descent in the Americas maintained lineage ties?
A. By naming children after saints or according to the day of the week which they were born
B. Creating schools in the Americas that taught Kongo history and culture
C. By hosting spiritual festivals in the Americas that celebrated their culture
D. None of the above, the Portuguese did not allow enslaved Africans to practice their culture or speak their native language in the Americas
A. By naming children after saints or according to the day of the week which they were born
In King Nzinga’s letter to Portuguese King Joao lll in 1526, he uses which of the following terms to describe what is happening to his Kingdom?
A. “Indoctrination”
B. “Depopulation”
C. “Corruption”
D. “Balkanization”
B. “Depopulation”
Explanation: In King Nzinga’s letter he sends to the King of Portugal he states, “Sir, is the corruption and licentiousness that our country is being completely depopulated.” King Nzinga is complaining to the Portuguese king about how his merchants are kidnapping all of his people to the point of depopulation after he told the King they could only enslave foreigners for trade which was ignored by the Portuguese.
Which of the following is NOT one of the various roles that women had in West and Central African societies?
A. Educators
B. Spiritual leaders
C. Political advisors
D. Blacksmiths
D. Blacksmiths
In the 1400s Queen Idia became the first Iyoba of which of the following Kingdoms?
A. Kingdom of Mali
B. Kingdom of Songhai
C. Kingdom of Benin
D. Kingdom of Kongo
C. Kingdom of Benin
Explanation: Queen Idia was the first Iyoba (Queen mother) in the Kingdom of Benin (modern-day Nigeria) in the 1400s, serving as her son’s political advisor.
Queen Njinga was leader of which of the following modern day countries in Africa?
A. Benin
B. Cameroon
C. Namibia
D. Angola
D. Angola
Explanation: Queen Njinga was queen of Ndongo which is located in modern day Angola and was where one of the first large group of enslaved Africans were transported from to the Americas in the 1600s.
Queen Njinga’s reign as a skilled political and military leader throughout the diaspora led to which of the following?
A. 100 years of women rulers in Matamba
B. The establishment of trade opportunities with Europe that would last hundreds of years
C. Becoming the wealthiest Queen in Angolan history from transatlantic slave trade
D. The increasing life expectancy of her entire tribe from curing several diseases
A. 100 years of women rulers in Matamba
Explanation: Queen Njinga was a brave and strong leader of Ndongo, standing up to European colonizers to protect her people and ultimately creating opportunities for other women to lead 100 years later.
The growth of Portuguese and West African trade in the 1500s led to which of the following?
A. An increase of European presence in West Africa
B. An increase in the population of sub-Saharan Africans in Iberian port cities
C. The bypassing of trans-Saharan trade by Transatlantic slave trade
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
The Portuguese colonized islands off the coast of west Africa to be used for which of the following?
A. Banana Plantations
B. Corn plantations
C. Indigo plantations
D. Rubber plantations
C. Indigo Plantations
Explanation: In the mid-1500s, the Portuguese colonized the Atlantic islands of Cabo Verde and São Tomé where they established cotton, indigo and sugar plantations using labor from enslaved Africans not corn, banana or rubber plantations.
True or False.
The Atlantic Islands of Cabo Verde and São Tomé off the coast of West Africa were used as models for slave labor based economies in the Americas.
A. True
B. False
A. True