Artificial Intelligence Exam 1
5.0(2)Studied by 8 people
Card Sorting
1/121
Earn XP
Last updated 11:11 PM on 2/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
1
New cards
popular definition of AI
involves using methods based on the intelligent behavior of humans and other animals to solve complex problems
2
New cards
strong AI
* if given sufficient processing power and enough intelligence
* it can literally think and is conscious about the behavior it is performing
* it can literally think and is conscious about the behavior it is performing
3
New cards
weak AI
* intelligent behavior can be modeled and followed by computers to solve complex problems
* just because a computer behaves intelligently, it doesn’t mean that it’s actually intelligent like a human
* just because a computer behaves intelligently, it doesn’t mean that it’s actually intelligent like a human
4
New cards
weak methods
* uses logic, automated, and other general structures of systems
* can be applied to wide range of problems
* does not necessarily have any real knowledge about the problem domain
* focus on inferencing
* can be applied to wide range of problems
* does not necessarily have any real knowledge about the problem domain
* focus on inferencing
5
New cards
Newell and Simon’s General Problem Solver (GPS)
an attempt to use weak methods to solve a wide range of general problems
* failed but led to realization that problem solving needed more
* knowledge was key ingredient
* failed but led to realization that problem solving needed more
* knowledge was key ingredient
6
New cards
strong methods
* depend on a system being given a great deal of domain knowledge
* focus on knowledge representation
* depend on the weak methods
* focus on knowledge representation
* depend on the weak methods
7
New cards
weak method, strong method
Production systems use __________ expert system shells to perform inference but use _________ rules to encode their knowledge.
8
New cards
syllogism
a disclosure in which certain things having been
stated, something else follows of necessity from
their being so
stated, something else follows of necessity from
their being so
9
New cards
Aristotle
The propositional and predicate logic for logical reasoning are based on the logic invented by _________________
10
New cards
Dialectica
* a treatise on logic
* the first real study of logic written by Peter Abelard in the 12th century
* the first real study of logic written by Peter Abelard in the 12th century
11
New cards
Gottfried Leibniz
* German mathematician and philosopher who thought of developing a formal mathematical language for reasoning
* allowed us to express problems to go about solving them
* allowed us to express problems to go about solving them
12
New cards
Boolean algebra
developed by English mathematician George Bool
* for expressing concepts such as A is true and A is true \n but B is false
* for expressing concepts such as A is true and A is true \n but B is false
13
New cards
Analytic Engine
* the world’s first computer invented by Charles Babbage
* his logical design was used to build working digital \n computers around 1950s
* his logical design was used to build working digital \n computers around 1950s
14
New cards
Alan Turing
* worked on the possibility of building a computer that could think
* published a paper in 1950, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” one of the first papers on this subject
* published a paper in 1950, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” one of the first papers on this subject
15
New cards
Turing test
* an interrogator is given access to two individuals
* a human and a computer
* the interrogator can ask two individual questions but can not see them
* questions are entered into a computer via a keyboard and the responses appear on the computer screen
* the human is intended to help the interrogator
* if the computer is smart enough, it should be able to fool the interrogator
* to be uncertain about which is the computer and which is the human
* a human and a computer
* the interrogator can ask two individual questions but can not see them
* questions are entered into a computer via a keyboard and the responses appear on the computer screen
* the human is intended to help the interrogator
* if the computer is smart enough, it should be able to fool the interrogator
* to be uncertain about which is the computer and which is the human
16
New cards
John McCarthy
first to use the term “Artificial Intelligence” at a conference in Dartmouth College, New Hampshire 1956
17
New cards
General Problem Solver (GPS)
* invented to solve almost any logical problem
* works well on simple problems, but could not be applied in a general way
* works well on simple problems, but could not be applied in a general way
18
New cards
LISP
a programming language invented by McCarthy which is still widely used today in AI research
19
New cards
algorithm
claimed by Socrates that it could be defined to describe the behavior of humans and determine whether a person’s behavior was good or bad
20
New cards
dualism
* Rene Descartes was a strong believer in this
* the universe consists of two entirely separate things
* mind and matter
* the mind was entirely separate from the physical body and not constrained by it in any way
* the universe consists of two entirely separate things
* mind and matter
* the mind was entirely separate from the physical body and not constrained by it in any way
21
New cards
Syntactic Structures
* theory proposed by Noam Chomsky
* a formal theory of the structure of human language
* a formal theory of the structure of human language
22
New cards
cognitive psychology
based on the idea that the human brain can solve problems, make decisions, draw conclusions, and carry out other intelligent acts
23
New cards
electronic neurons
* made by McCulloch and Pitt
* used today to build neural networks
* based on the function of human brain neurons
* used today to build neural networks
* based on the function of human brain neurons
24
New cards
a) Linguistics, b) Biology, c) Philosophy, d) Psychology
What areas of study had a great deal of influence and vital roles in the development of AI?
a) Linguistics
b) Biology
c) Philosophy
d) Psychology
e) Chemistry
a) Linguistics
b) Biology
c) Philosophy
d) Psychology
e) Chemistry
25
New cards
PROLOG, LISP
two programming languages that have features particularly useful for AI projects
26
New cards
PROLOG (PROgramming in LOGic)
* designed to enable programmers to build databases of facts and rules
* have the system answer questions by process of logical deduction using the databases’ facts and rules
* have the system answer questions by process of logical deduction using the databases’ facts and rules
27
New cards
LISP (LISt Programming)
* a language more similar to C++ and Pascal
* uses list to represent both data and programs
* a program can be treated as data
* writing self-modifying programs is possible
* uses list to represent both data and programs
* a program can be treated as data
* writing self-modifying programs is possible
28
New cards
B :- A
“if A is true, then B is true” or “A implies B”
29
New cards
“if cheese is made from milk and milk contains calcium, then cheese contains calcium”
What is this example of a rule in PROLOG written in human language?
contains(cheese, calcium) :- made_from(cheese, milk), contains(milk, calcium)
contains(cheese, calcium) :- made_from(cheese, milk), contains(milk, calcium)
30
New cards
Chinese Room
\n Designed by the American philosopher Jon Searle to argue against the proponents of strong AI
31
New cards
Chinese Room experiment components
* an English-speaking human placed inside a room
* the human can speak only English and has no ability to read, speak, or understand Chinese
* inside the room with the human are
* a set of cards showing printed Chinese symbols
* a set of instructions written in English
* the human can speak only English and has no ability to read, speak, or understand Chinese
* inside the room with the human are
* a set of cards showing printed Chinese symbols
* a set of instructions written in English
32
New cards
Chinese Room experiment
* a story in Chinese is fed into the room through a slot along with a set of questions about the story
* by following the cards and instructions the human has to answer these questions
* pass the answers back to the questioner through the slot
* if the system were set up properly
* would be able to make an observer believe that the room or person inside truly understood the story, the questions, and the answers it gave
* by following the cards and instructions the human has to answer these questions
* pass the answers back to the questioner through the slot
* if the system were set up properly
* would be able to make an observer believe that the room or person inside truly understood the story, the questions, and the answers it gave
33
New cards
after the Chinese Room experiment
* the man in the room does not understand Chinese
* the pieces of cards do not understand Chinese
* the room itself does not understand Chinese
* in other words
* a computer program that behaves in an intelligent way does not necessarily produce understanding, consciousness, or real intelligence
* the pieces of cards do not understand Chinese
* the room itself does not understand Chinese
* in other words
* a computer program that behaves in an intelligent way does not necessarily produce understanding, consciousness, or real intelligence
34
New cards
fuzzy logic
widely used in washing machines, cars, and elevator control mechanisms
35
New cards
intelligent agents
widely used to
* solve problems while using our computers
* search the Internet for documents that might be of interest
* solve problems while using our computers
* search the Internet for documents that might be of interest
36
New cards
robots
are widely used
* as the physical embodiment of agents
* to explore the oceans and other worlds
* to travel in environments inhospitable to humans
* as the physical embodiment of agents
* to explore the oceans and other worlds
* to travel in environments inhospitable to humans
37
New cards
expert systems
are used by doctors to prescribed treatment in cases where even human experts have difficulty
38
New cards
a) the variables it uses, c) the operators applied to those variables
The way a computer represents a problem involves
a) the variables it uses
b) the problem definition
c) the operators applied to those variables
d) the variable created for the computer
a) the variables it uses
b) the problem definition
c) the operators applied to those variables
d) the variable created for the computer
39
New cards
b) search of solutions
There are a wide range of representations used in AI. A good representation is vital for the
a) research development
b) search of solutions
c) creation of software systems
d) solution modeling
a) research development
b) search of solutions
c) creation of software systems
d) solution modeling
40
New cards
semantic nets
a graph consisting of nodes that are connected by edges (links)
* nodes represent objects
* links between nodes represent relationships between those objects
* the links are usually labeled to indicate the nature of the relationship
* nodes represent objects
* links between nodes represent relationships between those objects
* the links are usually labeled to indicate the nature of the relationship
41
New cards
represent knowledge
Semantic nets provide a very intuitive way to ___________________ about objects and their relationships.
42
New cards
true
(T/F) The links in a semantic net are directional.
43
New cards
false
(T/F) The links in a semantic net are not directional.
44
New cards
true
(T/F) The data in semantic nets can be reasoned about, such as the ability to represent negations.
45
New cards
instances
Objects are referred to as ___________ of a particular class.
46
New cards
frames
an object-oriented representation that can be used to build expert systems
* each of this describes either an instance or a class
\
* each of this describes either an instance or a class
\
47
New cards
slots, slot values
Each frame has one or more ____________ that are assigned ________________.
48
New cards
true
(T/F) An instance could be a physical object, a property, a place, a situation, or a feeling.
49
New cards
relationship
Each ______________ is expressed by a value being placed in a slot.
50
New cards
generalization
using the is-a relationship to express membership of classes
51
New cards
true
(T/F) In frame-based systems, all information about a particular object is stored in one place.
52
New cards
why frames are useful
in frame-based systems
* all information about a particular object is stored in one place
in a rule-based system
* information about an object might be stored in a number of unrelated rules
* if the object changes, or a deduction needs to be made about the object
* time may be wasted examining irrelevant rules and facts
* all information about a particular object is stored in one place
in a rule-based system
* information about an object might be stored in a number of unrelated rules
* if the object changes, or a deduction needs to be made about the object
* time may be wasted examining irrelevant rules and facts
53
New cards
inheritance
a relation that can be particularly useful in AI
* can define a subclass which inherits the properties of its super class
* can define a subclass which inherits the properties of its super class
54
New cards
exceptions
Inheritance needs to express __________ in some cases.
55
New cards
true
(T/F) In some cases of inheritance, the default value in the super class is overridden in the subclass.
56
New cards
false
(T/F) In the cases of inheritance, the default value in the super class is always overridden in the subclass.
57
New cards
true
(T/F) It is possible to express a range of values that a slot can take.
58
New cards
false
(T/F) It is not possible to express a range of values that a slot can take.
59
New cards
multiple inheritance
* an object can be an instance of more than one class
* a frame can inherit properties from more than one other frame
* a frame can inherit properties from more than one other frame
60
New cards
contradictory information
Multiple inheritance might lead to ____________________ about a frame.
61
New cards
procedures
a set of instructions associated with a frame that can be executed on request
62
New cards
WHEN-NEEDED procedures
procedures that are called when needed
63
New cards
demon
a particular type of procedure
* run automatically whenever a particular value changes or when a particular event occurs
* run automatically whenever a particular value changes or when a particular event occurs
64
New cards
WHEN-READ demon
are called automatically when a slot value is read
* can calculate the value to be returned to the user
* can calculate the value to be returned to the user
65
New cards
WHEN-CHANGED demon
are run automatically when a slot value is changed
* also known as WHEN-WRITTEN demon
* can be used to ensure that values assigned to a slot meet the constrains
* also known as WHEN-WRITTEN demon
* can be used to ensure that values assigned to a slot meet the constrains
66
New cards
search space
consist of a set of states, connected by paths that represent actions
* many search problems can be represented by this
* many search problems can be represented by this
67
New cards
goal states
one or more states of the desired results
68
New cards
aim of search procedures
* to identify one or more goals and then find the paths to those goals
* usually interested in the shortest path, or the path with least cost
* usually interested in the shortest path, or the path with least cost
69
New cards
state transitions
For a robot that lives in an environment with three rooms (room A, B, C) and a block that can be moved from room to room.
The arrows between states represent
The arrows between states represent
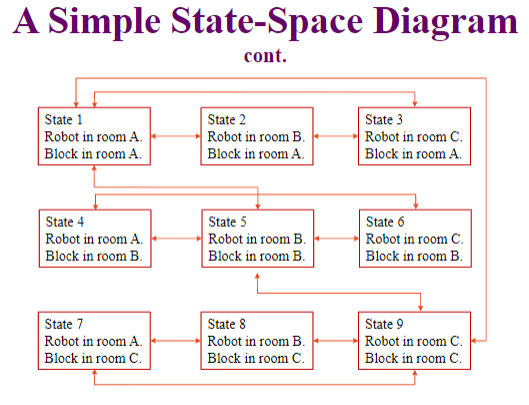
70
New cards
search tree
a kind of search space with the following properties
* one node has no predecessors called the root node
* each node (except for root node) has exactly ne predecessor (parent) and one or more successors (children)
* some nodes have no successors called leaf nodes
* one or more leaf nodes are called goal nodes that represent a state where the search has succeeded
* one node has no predecessors called the root node
* each node (except for root node) has exactly ne predecessor (parent) and one or more successors (children)
* some nodes have no successors called leaf nodes
* one or more leaf nodes are called goal nodes that represent a state where the search has succeeded
71
New cards
root node
a node in a search tree that has no predecessors
72
New cards
leaf nodes
nodes in a search tree that have no successors
73
New cards
goal nodes
one or more leaf nodes that represent a state where the search has succeeded
74
New cards
ancestor
A ___________ of a node is a node further up the tree in some path.
75
New cards
descendent
A _______________ comes after a node in a path in the tree.
76
New cards
complete path
a path that leads from the root node to a goal node
77
New cards
partial path
a path that leads from the root node to a leaf node that is not a goal node
78
New cards
branching factor
If a node has n successors, that node has a ________________ of n
79
New cards
true
(T/F) A tree that has branching factor of n means the average branching factor of all the nodes is n.
80
New cards
false
(T/F) A tree that has branching factor of n means the average branching factor of all the nodes is n/2.
81
New cards
cycles are allowed in any path, construct the tree in a top-down and right-left manner, after reaching the first goal state the construction is stopped
Select which of the following are NOT guidelines to constructing a search tree
* cycles are allowed in any path
* start from the root (initial state)
* the shortest path from the root to a goal state is the best solution
* construct the tree in a top-down and right-left manner
* no repeated state in the tree
* after reaching the first goal state the construction is stopped
* cycles are allowed in any path
* start from the root (initial state)
* the shortest path from the root to a goal state is the best solution
* construct the tree in a top-down and right-left manner
* no repeated state in the tree
* after reaching the first goal state the construction is stopped
82
New cards
problem solving as search
a set of actions that can be taken to lead from the initial state to the goal state
* during the search
* keep checking if the current state has reached the desired result or not
* during the search
* keep checking if the current state has reached the desired result or not
83
New cards
data-driven search
* start from an initial state and use actions to move forward until a goal is reached
* a top-down approach
* also known as forward chaining
* a top-down approach
* also known as forward chaining
84
New cards
goal-driven search
* start at the goal state and work back toward an initial state
* a bottom-up approach
* also known as backward chaining
* a bottom-up approach
* also known as backward chaining
85
New cards
when the goal can be clearly specified
When is the goal-driven search particularly useful?
86
New cards
when the initial data is provided but its not clear what the goal is
When is the data-driven search particularly useful?
87
New cards
succeeded, moves on to the next node
Generate each node in the search space and test it to see if it is a goal node
* If yes, the search has _____________
* If no, the procedure ____________________________
* If yes, the search has _____________
* If no, the procedure ____________________________
88
New cards
generate and test
* is the simplest form of brute-force search
* also known as exhaustive search or blind search
* assume no additional knowledge other than
* how to traverse the search tree and how to identify leaf nodes and goal nodes
* also known as exhaustive search or blind search
* assume no additional knowledge other than
* how to traverse the search tree and how to identify leaf nodes and goal nodes
89
New cards
depth-first search
* follow each path to its greatest depth before moving on the next path
* start from the left side and work toward the right
* work all the way down the left-most path in the tree until a leaf node is reached
* if it is a goal node, the search is successfully completed
* if not, search backtracks up to the next highest node that has an unexplored path
* start from the left side and work toward the right
* work all the way down the left-most path in the tree until a leaf node is reached
* if it is a goal node, the search is successfully completed
* if not, search backtracks up to the next highest node that has an unexplored path
90
New cards
chronological backtracking
Depth-first search uses a method called ____________________ to move back up the search tree.
91
New cards
breadth-first search
* start by examining all nodes one level down from the root node
* if a goal state is reached, success is reported
* otherwise, continue to search all the nodes in the current level then go down to the next level
* if a goal state is reached, success is reported
* otherwise, continue to search all the nodes in the current level then go down to the next level
92
New cards
when the tree has very deep paths, when the goal node is in a shallower part of the tree
When is breadth-first search good to use?
a) when the branching factor is extremely high
b) when the tree has very deep paths
c) when the goal node is in a shallower part of the tree
d) when there is more than one goal node
a) when the branching factor is extremely high
b) when the tree has very deep paths
c) when the goal node is in a shallower part of the tree
d) when there is more than one goal node
93
New cards
a) when the branching factor is extremely high
When is breadth-first search NOT good to use?
a) when the branching factor is extremely high
b) when the tree has very deep paths
c) when the goal node is in a shallower part of the tree
d) when there is more than one goal node
a) when the branching factor is extremely high
b) when the tree has very deep paths
c) when the goal node is in a shallower part of the tree
d) when there is more than one goal node
94
New cards
less memory
Depth-first search requires ____________ than breadth-first search
95
New cards
current path, all paths that reach the current depth
* Depth-first search needs to store info about the _________________
* Breadth-first search needs to store info about _______________________
* Breadth-first search needs to store info about _______________________
96
New cards
depth threshold
The problem of infinite paths can be avoided by applying ________________________
* some goals might be missed but all branches will be explored within reasonable time
* some goals might be missed but all branches will be explored within reasonable time
97
New cards
properties of search methods
* complexity
* completeness
* optimality
* admissibility
* irrevocability
* monotonicity
* completeness
* optimality
* admissibility
* irrevocability
* monotonicity
98
New cards
complexity
to describe how efficient is the method
* by using big-O notation
* by using big-O notation
99
New cards
time complexity
related to the length of time that the method would take to find a goal state
100
New cards
space complexity
related to the amount of memory that the method needs to use