Important definitions
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
a measure of the amount of dissolvedoxygen required to break down theorganic material in a given volume ofwater through aerobic biological activity.An indirect measure of the amount oforganic matter within a sample
Environmental value system
Captive breeding
Captive breeding is the process of breeding animals in controlled environments, such as zoos, aquariums, or wildlife sanctuaries.
Carbon Sink
stores in a system containing a lot ofcarbon, e.g. a forest
CITIES
Convention in International Trade inEndangered Species of Wild Fauna andFlora.Aims to prevent species threatened with extinction because of international trade.Parties act by banning commercial international trade in an agreed list of endanged red species and by regulating and monitoring trade in others that might become endangered or whose trade needs to be regulated to ensure control over trade
Condensation
transformation of water vapour to water liquid
Dead zones
Dead zones in both oceans and freshwater can occur when there is not enough oxygen to support aquatic life
Edge effects
Edge effects occur at ecotones (where two habitats meet and there is a change near the boundary)
Environmental impact asessement
Include a baseline study to understand the environmental impact that the project might have before putting into place
Predict and evaluate the possible environmental impact and determine its sustainability
Suggest solution/mitigation strategies to address potential problems and minimize the adverse effects associated with the project development
Eutrophication
Factors for red list
population size, degree of specialization, distribution, reproductive potential and behavior, geographic range and degree of fragmentation, quality of habitat, trophic level, and the probability of extinction.
Fertile soil
require a significant time to develop through succession. they are considered a non-renewable resource.
Flows in Carbon cycle
consumption (feeding), death and decomposition, photosynthesis,respiration, dissolving and fossilization
Flows in nitrogen cycle
nitrogen fixation by bacteria and lightning ,absorption, assimilation, consumption(feeding), excretion, death and decomposition, denitrification by bacteria
Wildlife corridors
these are zones which link together protected areas. they may be physical bridges or simply wildlife friendly zones such as a hedge. They can increase the effective size of the habitat available to an organism
Highest rate of aquatic productivity
Occurs in coastal areas and upwelling zones, where nutrient availability is high, supporting diverse marine life.
Human activities affect carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle
burning fossil fuels, deforestation,urbanisation, agriculture
Human activites reduce fertility
deforestation, intensive grazing, urbanisation, certain agricultural practices such as irrigation and monocultures
Acid deposition on fish and plants
Increases solubility of metals such as aluminium which cause white froth to form in fish gills leading to suffocation
leaching of plant nutrients so soil has decreased fertility increasing the risk of erosion
Keystone species
plays a critical role in food chains or ecosystems. Includes exsitu (off site) efforts such as captive breeding, zoos, and reintroduction
Milenium ecosystem assessment (MEA)
Ecosystems have changed more rapidly in the past 50 years than in any previous period in history through human activities resulted in loss of diversity.
Changes have increased the poverty of some societies
The problems caused by ecosystem degradation will reduce the benefits for future generations
Human actions are diminishing Earth’s natural capital at a faster rate than it is being restored which is putting pressure on natural systems and the environment.
Ozone depleting substance (ODS)
halogenated organic gases such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are used in aerosols, gas-blown plastics, pesticides,flame redardants and refrigerants (e.g. in air conditioning units)
Pollution strategy - acid deposition
A - reducing use, or using alternatives to, fossil fuels; lobbying results in international agreements and national governments to reduce pollutant production.
B- regulating and monitoring release of pollutants, e.g. through use of scrubbers or catalytic converters that may remove sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen from coal burning power plants and cars
C- spreading limestone in acidified lakes or recolonisation of damaged systems but the scope of these measures is limited; repair and restoration of damaged limestone buildings
Pollution Management - Air pollution
A - consume less fossil fuels e.g. purchase of energy efficient technologies, use of public transport, walking or cycling
B- regulating and reducing pollutants at point of emission through government regulation or taxation; use of catalytic converters, regulating fuel quality by governments; pedestrian zones and charging for driving in city centres
C - reforestation, re greening and conservation areas to sequester carbon dioxide; cloud seeding to wash pollution out of atmosphere
Reduce fertility results from
soil erosion, toxification, salination and desertification
Sources of freshwater pollution
runoff, sewage, industrial discharge and solid domestic waste
Sucession
Succession is the process of change overtime in an ecosystem involving pioneer,intermediate and climax communities
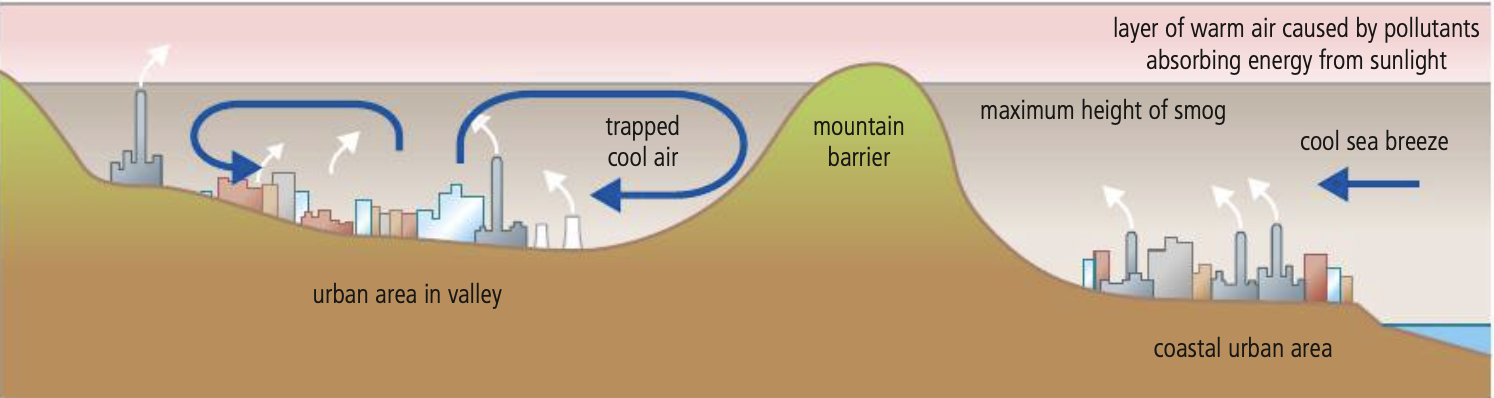
Thermal inversion
occur due to a lack of air movement when a layer of dense cool air is trapped beneath a layer of less dense, warm air.This causes concentrations of air pollutants to build up near the ground instead of being dissipated by "normal" air movement
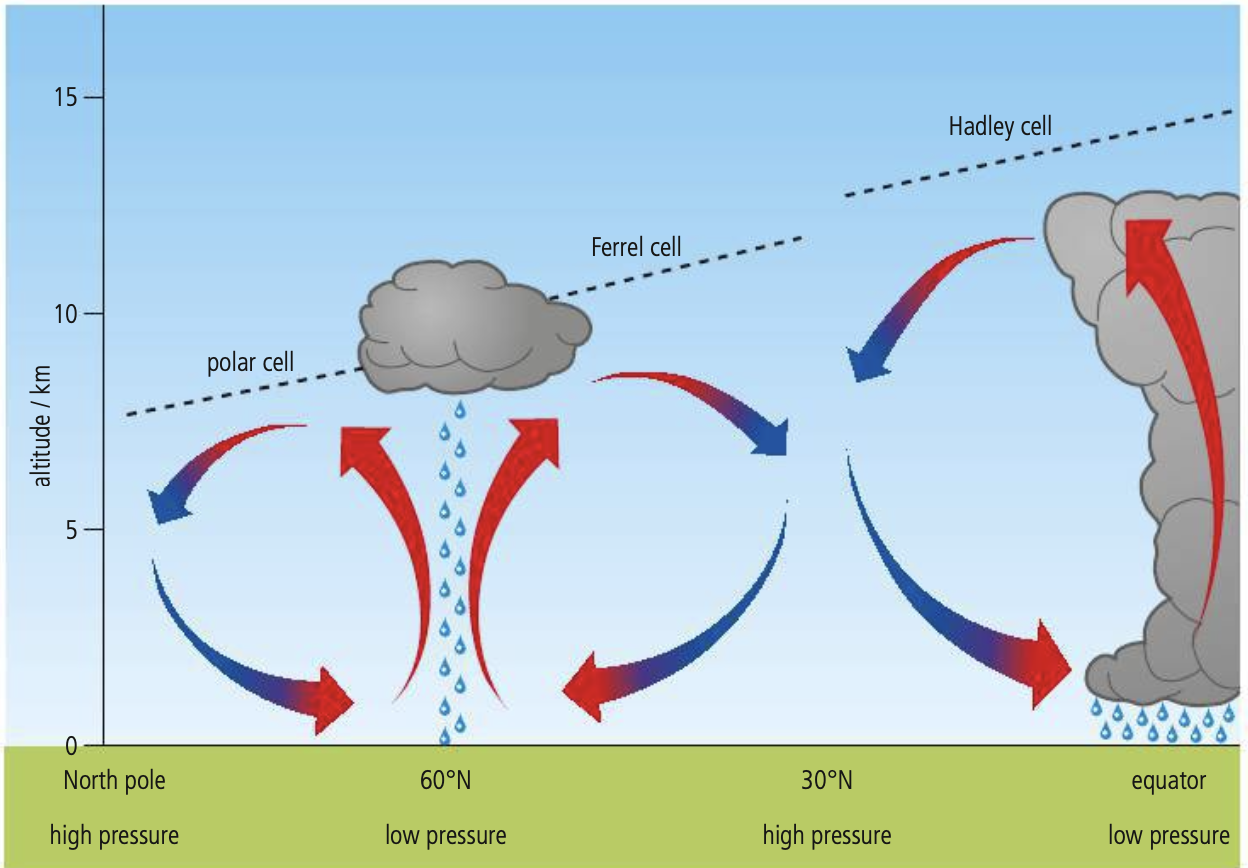
Tricellular model
hTe model which describes 3 large convection cells moving air from thee quator towards the poles in each hemisphere of the earth that explains the distribution of precipitation and temperature that influence structure and relative productivity of different terrestrial biome: explaining differences in atmospheric pressure belts, temperature, and precipitation that exist across the globe
UV radiation on humans
damages human living tissues, increasing the incidence of cataracts, mutation during cell division, skin cancer and others ubsequent effects on health
Water conservation strategies
drip irrigation, variable flush toilets, timed showers instead of baths, tap aerators to reduce water flow out of high pressure taps,use of grey water / storm runoff / reclaimed wastewater (already used for washing) for gardens and toilets, dry toilets, switching offtap while brushing teeth, metering water,fining companies for leaks and wasted water
Zonation
Zonation refers to changes in a community along an environmental gradient due to factors such as changes in altitude, latitude, tidal level or distance from shore (coverage by water).
Geoengineering
Climate engineering is the intentional large-scale alteration of the planetary environment to counteract anthropogenic climate change.