"Other Rhythms" from Conduction Disorders
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
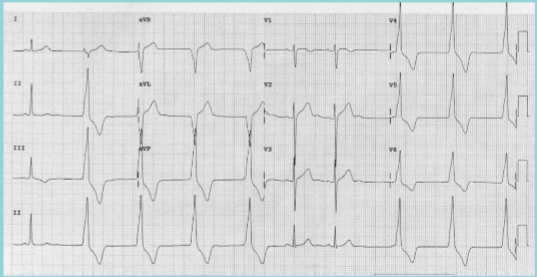
ventricular, 20-40, QRS, P, 50-100
Idioventricular Escape Rhythm
AKA _________ Escape Rhythm
Criteria
Ventricular rate of __-__ bpm
Wide ___ complex and no _ wave
Morphology similar to PVC
If rate is __-___ bpm, rhythm is accelerated idioventricular rhythm
(accelerated) idioventricular escape rhythm
What is this?
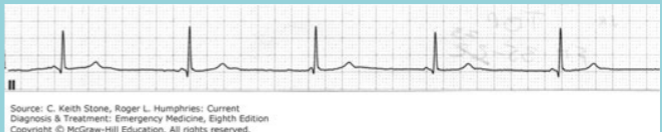
generation, P, 40-60, narrow, 61-130
Junctional Rhythm
Occurs when there is failure of impulse __________ from the sinus node or atrial myocardium
Criteria
Retrograde/absent _ wave
Ventricular rate of __-__ bpm
______ QRS complex
If rate is __-___ bpm, rhythm is accelerated AV junctional rhythm
Junctional Escape Rhythm (Junctional Rhythm)
What is this?
0.47, 0.48, medications, poly, torsades, all, outpatient, holter, telemetry
Prolonged QT Interval
> _.__ seconds in males
> _.__ seconds in females
Can be acquired or congenital
Acquired is most commonly d/t __________
Increased risk of ____morphic v-tach and _______ de pointes
Treatment
Treat any underlying etiology of prolonged QT in ___ patients
Address electrolyte imbalances, d/c offending agents
Asymptomatic Patients
Closely monitor in the outpatient setting with _________ testing
Patient with Palpitations
______ monitoring
Patients with Syncope
Admit for _________ observation
Prolonged QT
What is this?
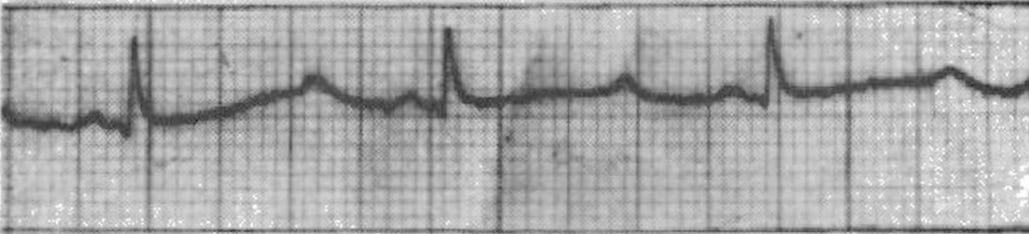
poly, QT, twisting, death, Mg, defibrillation
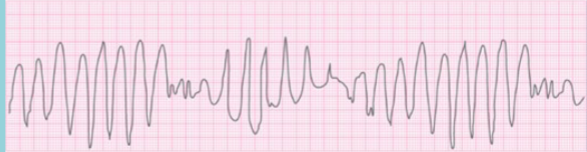
Torsades de Pointes
____morphic VT that occurs in the setting of __ prolongation
Pts will usually go into v.fib then potentially die
Heart rate is usually 160-250 bpm
Characteristic “________ on a point” appearance
Can be short-lived/self terminating OR cause hemodynamic instability and _____
Treatment
Stable
IV __ (low magnesium usually the cause)
Address underlying etiology
Unstable
Immediate ___________
Torsades de Pointes
What is this?
atria, sinus, sinus, no, avoid, b-blocker, catheter ablation
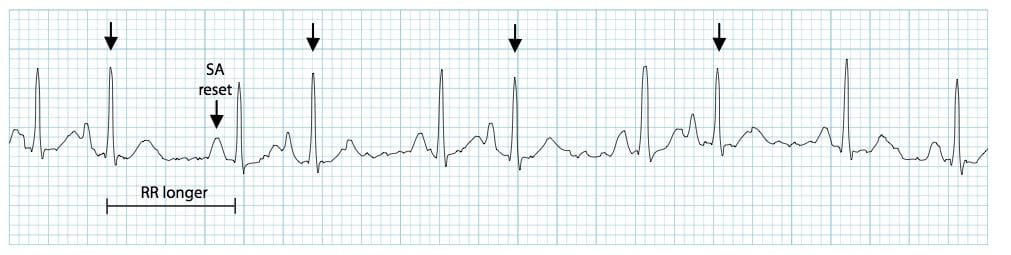
Premature Atrial Contractions
Premature beat originating anywhere in the _____
Except in the _____ node
Very common in younger and older pts
Criteria
P wave with different morphology and axis from the _____ P wave
Etiology
Idiopathic
Lifestyle
Structural Heart Disease
Treatment
Asx pts: __ therapy required
Symptomatic pts:
Patient education
_____ precipitants of PAC
_-_______
If patient has evidence of heart disease - further testing indicated
If PACs trigger a-fib - _________ _______ is indicated
bigeminy
occurs every other beat
trigeminy
occurs every 3rd beat
quadrigeminy
occurs every 4th beat
couplet
2 consecutive PACs/PVCs
Triplet
3 consecutive PACs/PVCs
Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
What is this?
Purkinje, wide, T, pattern
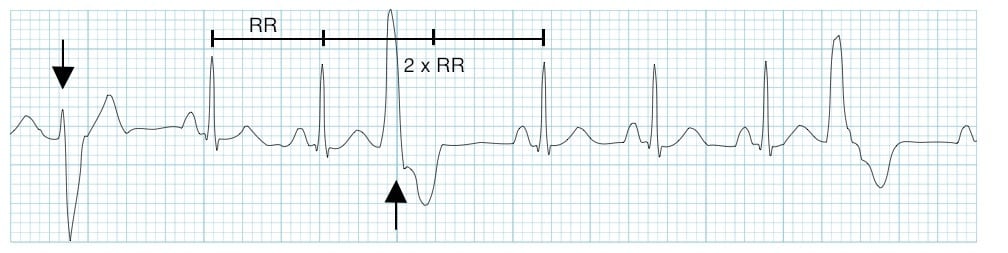
Premature Ventricular Contractions
Originates in the ventricular myocardium or terminal ________ fibers
Produces a ____ QRS complex
Secondary _ wave abnormalities directed opposite of the dominant R wave
Mechanism (any of these):
Automaticity
Reentry
Triggered activity
Can occur alone, grouped repetitively, or in a ________
common, r, K, digitalis, 10-15, stimulants, b-blocker
PVCs
VERY ______
Cardiac / non-cardiac etiologies can cause / exacerbate PVC
Cardiac
LVH
MI
HF_EF
myocarditis
cardiac sarcoidosis
cardiomyopathy
Non-cardiac
COPD
Pulmonary HTN
Hypo_
HypoMg
_________ toxicity
High-risk features:
Frequent (>__-__%), long QRS duration, interpolated or complex PVC, highly variable coupling intervals
No treatment needed
Patient education → avoid _________ may be helpful
Pharmacotherapy
_-_______
CCB
(multifocal) Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVC)
What is this?
ventricle, V1, V2, wider, ST, T, structural, pacemaker
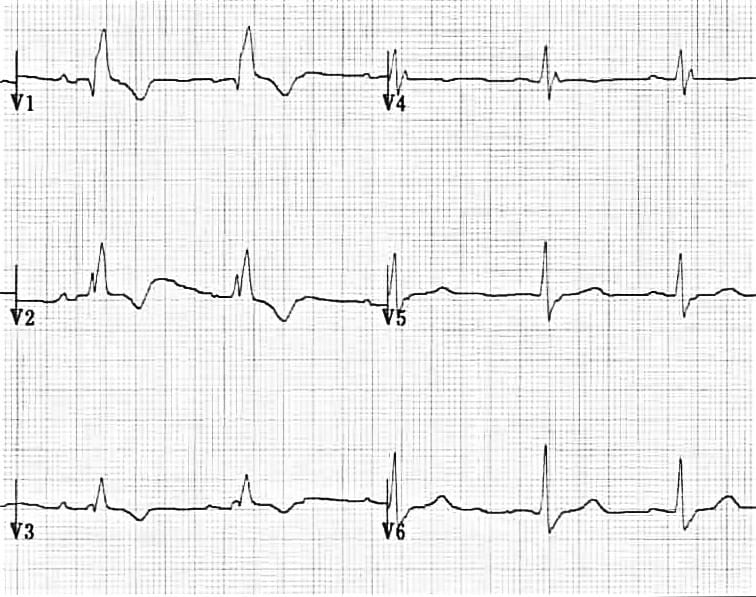
Right Branch Bundle Block
Delay in depolarization of the right ________
Criteria
Rsr’, rsR’, rSR’, or M shaped pattern on __ or __
Secondary R' wave is usually _____ and of greater amplitude than initial r wave
Secondary __ segment and _ wave abnormalities in right precordial leads directed opposite of that dominant R wave
Etiology
________ Heart Disease → cor pulmonale, MI, myocarditis
Iatrogenic → right heart cath
Treatment
Asx: no therapy required
Sx: _________
Right Bundle Branch Block
What is this?
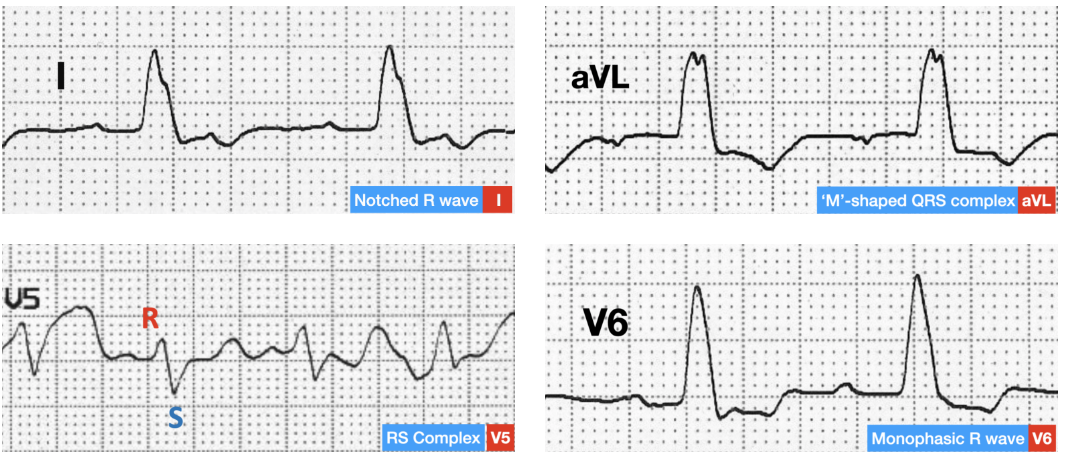
ventricle, R, I, 5, 6, Q, aVL, ST, T, structural, pacemaker
Left Bundle Branch Block
Delay in depolarization of the left ________
Criteria
Broad, notched, or slurred waves (rR’, RR’) in leads , aVL, and V_-V_
Absent _ waves in leads I, V5-V6
May be present in lead ___
Secondary __ segment and _ wave abnormalities in left precordial leads directed opposite to that of the dominant R wave
Etiology
________ Heart Disease: acute anterior MI, endocarditis, myocarditis
Iatrogenic: septal myectomy
Treatment
Asx: no specific therapy required
Sx pts with AV Block: __________
Left Bundle Branch Block
What is this?