A2.3 Viruses
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Virus (+draw)
non living
non cellular
fixed size → do not grow
no cytoplasm, no enzyme → no metabolism
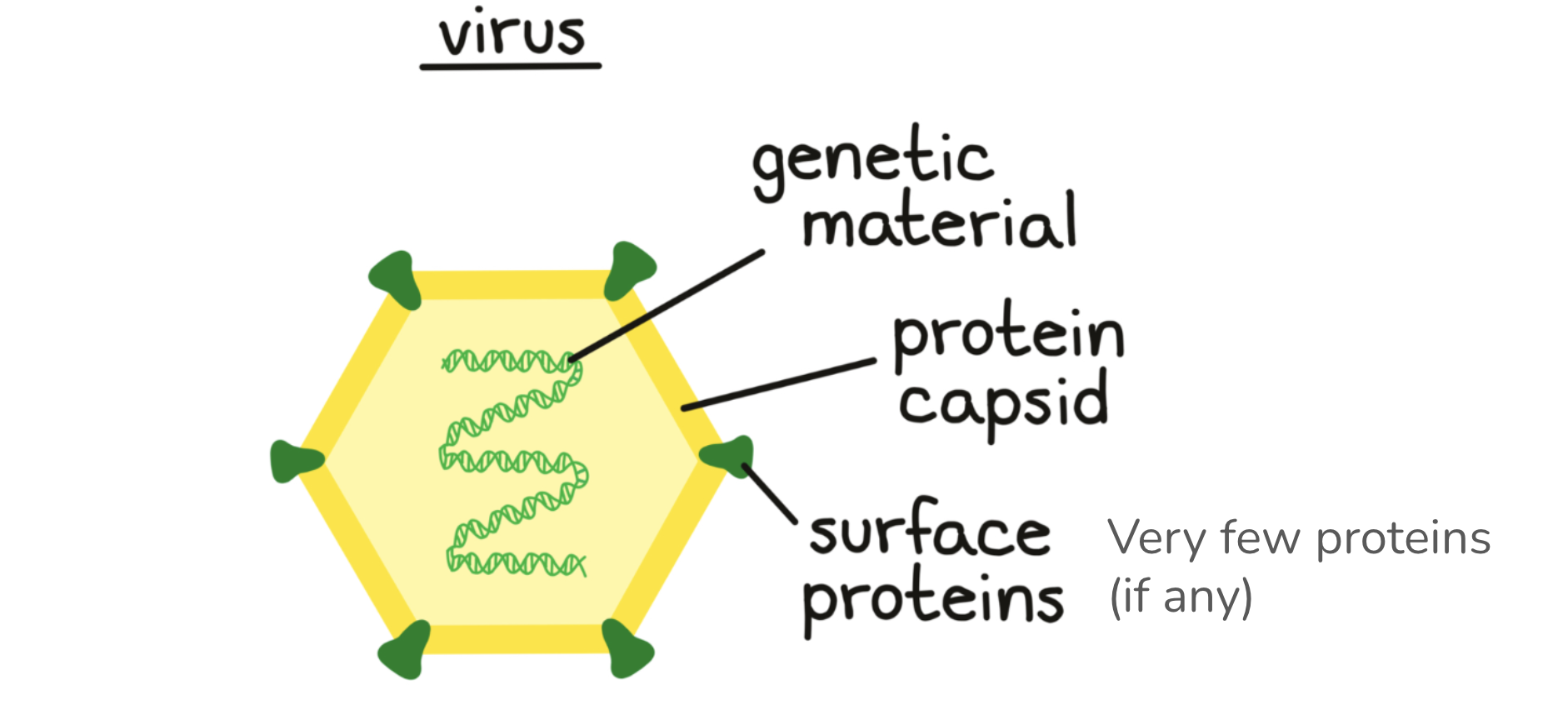
Diversity in Virus
Genetic material - DNA or RNA; single- or double-stranded
Membrane envelope - present or absent
envelope: outer lipid membrane is not coded for by the viral genes, as it forms from the host cell membrane when the virus bursts out of the host cell, but it may have viral proteins embedded in it.
Genome size
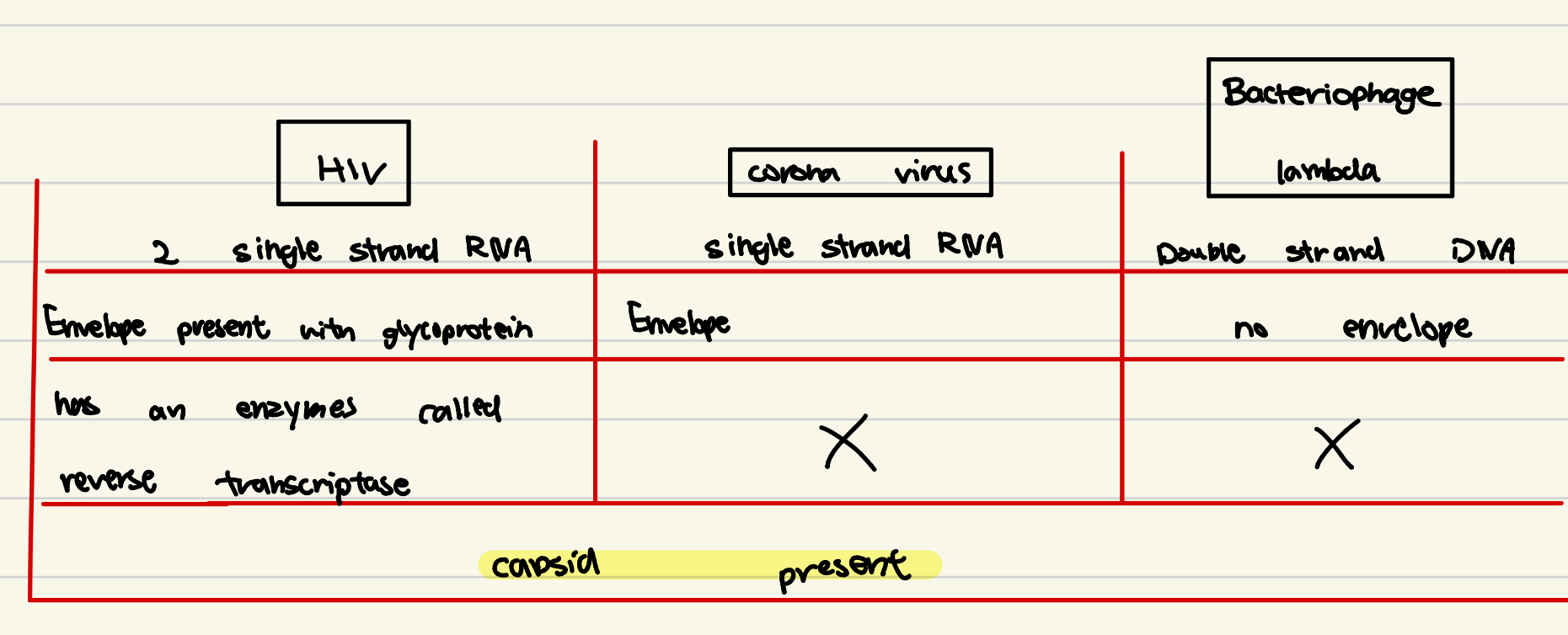
Comparison of Viruses
Obligate Intracellular Parasite → Virus
restricted to one function
Inside a cell
uses host to survive, at the expense of host
virus rely on host cell to
replicate
metabolism : site of energy
Nutrition : obtain amino acid, nucleotide for replication
reproduction : obtain ribosome, enzyme for replication
movement : move around the cell / spread to other cells
Lytic cycle
Attachment : Bacteriophage attach on host cell after recognising the antigen
Penetration : Bacteriophage penetrates host cell, inject DNA
Biosynthesis : destroys host dna, Virus replicate its genetic material, synthesis viral protein
Assembly : new phage assembles into virions
Release : Host cell lyses, new virions are released
Lysogenic cycle
Attachment : Bacteriophage attach on host cell after recognising the antigen
Penetration : Bacteriophage penetrates host cell, inject DNA
Integration : phage DNA integrates with the bacteria chromosome by recombination→ Prophage
Cell division : lysogenic bacteria reproduce normally
Excision: prophage may excise from bacteria chromosome → enter lytic cycle
Evidence for virus evolving from cells
Viruses are obligate parasites; they need a host cell to survive
Viruses use the same genetic code as living organisms, suggesting that viruses evolved from cells
Origin of virus
Genetic material that ‘escaped’ from a cell, becoming a virus
A cell that lost the ability to carry out the functions of life and became a virus
From basic self-replicating molecules, which became encased in protein coats
Convergent evolution
The process by which similar features evolve separately due to similar selective pressures
Rapid evolution of virus
short & high replication times → many new viruses produced in a short time span
High mutation rate → mechanism used to replicate
(mutation → change in genetic material)
Horizontal gene transfer (the non-parent-to-offspring movement of genetic material between organisms) → viruses exchange genetic information to acquire new traits
Reassortment : Influenza and its mechanisms in mutation
Antigenic shift - reassortment of genes, where two viruses infect the same cell and exchange genetic information, resulting in a new virus.
Antigenic drift - where the error-prone methods of replication cause changes to the shape of the surface proteins (antigens)
(virus with segmented genome swap genome)
Recombination : HIV and its mechanisms in mutation
HIV has highest known mutation rate of any virus.
HIV reproduces very quickly, using error-prone reverse transcriptase.
High replication rate + error-prone methods = high mutation rate.
Not all mutations will be beneficial to the virus, but because of the high rate, some will be.
HIV can also exchange genetic material with other viruses or its host cell in a process called recombination.
This leads to even greater variability in the virus.
(gene pair together, exchange sequences)
How does mutation affect treatment
Our immune system, and vaccines, rely on identifying the antigens on the surface of pathogens.
higher mutation rate of pathogen → difficult to treat