Class 5 Restorations Subgingival CORD Isolation
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
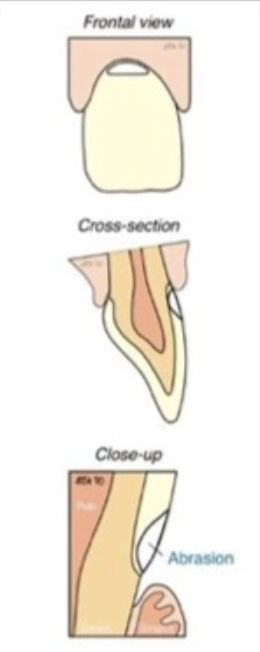
What is abrasion?
Cause: Mechanical wear (toothbrush habit)
Affects: Teeth in groups (often unilateral)
Treatment: Composite (hybrid or flowable)
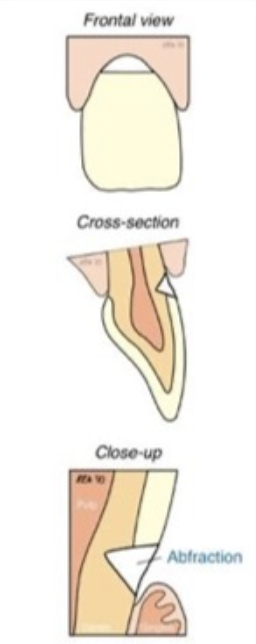
What is abfraction?
Cause: Stress corrosion (occlusion related)
Affects: Single teeth (often upper premolars first)
Treatment: Composite (hybrid or flowable), Light-cured GIC
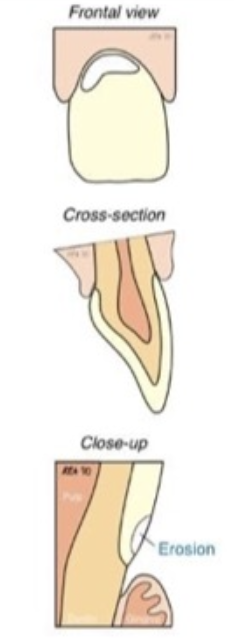
What is erosion?
Cause: Chemical erosion (gastric causes)
Affects: Teeth in groups (lingual upper/buccal lowers)
Treatment: Composite (hybrid or flowable)
What is the Basic Erosive Wear Examination (BEWE)?
A simple, quick index for screening a patient’s erosion status used to assess the level of erosion
How does the Basic Erosive Wear Examination (BEWE) work?
The mouth is divided into 6 distinct areas and uses the criteria for sextant scores from 0 to 3. THe surface with the highest score is recorded for each sextant. The scores are summed to obtain a cumulative score that is the basis for determining interventions.
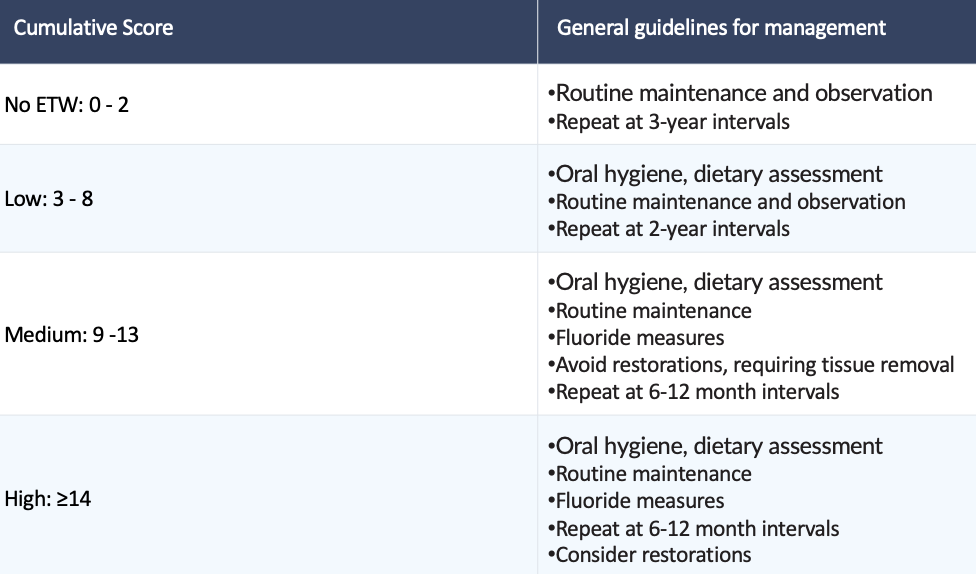
What are some management challenges for ETW?
Early diagnosis of erosive lesions
Initiation of preventive strategies and behavioral changes
Early intervention with minimally-invasive restorative procedures
What should early diagnosis include for the management of Erosive Wear Examination?
Charting of erosive lesions
Sensitive teeth
Staining
Making note of areas of exposed dentin
What are some preventive habits that reduce the risk of ETW?
Staying hydrated
Rinsing with water before brushing
Brushing with fluoride toothpaste
Not brushing for at least 1-2 hours after an acid challenge
What is the bottom line in the management of ETW?
Early diagnosis
Initiation of preventive measures
Early intervention to avoid the need for extensive and invasive care
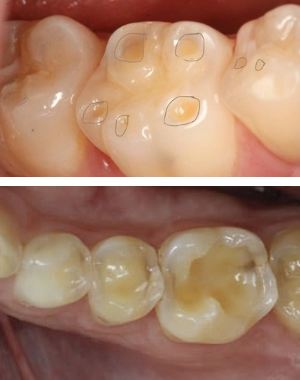
Scoring criteria
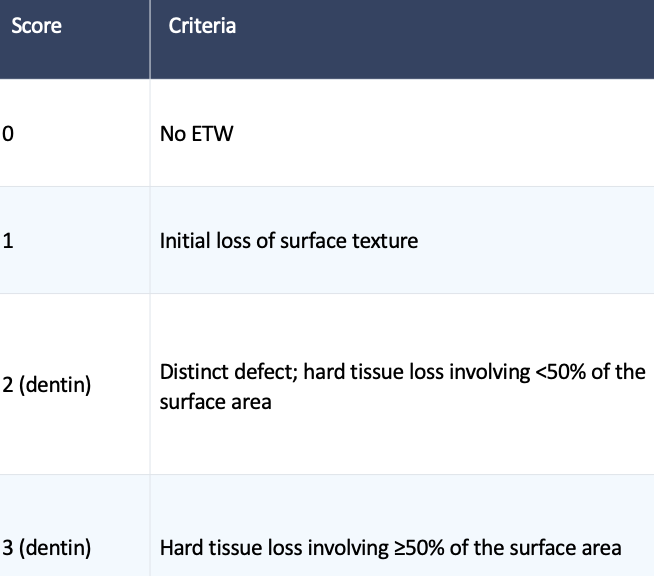
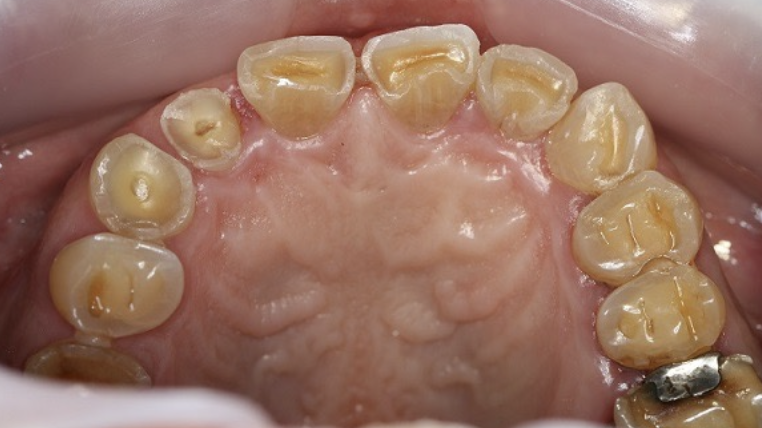
What is this caused by? What would you grade it?
Erosion; 3 on all sextants
Guidelines for management
What are the multi-factorial components of tooth surface lesions
Stress (abfraction)
Friction (wear)
Biocorrosion (chemical, biochemical and electrochemical degradation)
What are some causes of stress (abfraction)?
Endogenous
Parafunction
Occlusion
Deglutition
Exogenous
Mastication
Habits
Occupations
Dental appliances
Types of stress
Static
Fatigue (cyclic)
What are some causes of friction (wear)?
Endogenous (attrition)
Parafunction
Deglutition
Endogenous (abrasion)
Mastication
Action of tongue
Exogenous
Dental hygiene
Habits
Occupations
Dental appliances
Erosion (flow of liquids)
What are some causes of biocorrosion (chemical, biochemical and electrochemical degradation)?
Endogenous (acid)
Plaque (caries)
Gingival crevicular fluid
Gastric HCl
Exogenous
Diet
Occupations
Miscellaneous
Proteolysis
Enzymatic lysis (caries)
Proteases (pepsin and trypsin)
Crevicular fluid
Electrochemical
(Piezoelectric effect on dentin)
What are some examples of noninvasive therapeutic options?
Desensitizer
Fluoride varnish
When should you restore non-cervical carious lesions?
Active cavitated carious lesions associated with the lesions
Cervical margins subgingival precluding plaque control increasing caries, biocorrosion and periodontal disease risk
Extensive tooth structure loss, which compromises the integrity of the tooth
Defect is in close proximity to the pulp, or the pulp has been exposed
Persistent dentinal hypersensitivity in which non invasive therapeutic options have failed
Prosthetic abutment
Esthetic demands: by patient request
What are some techniques to use for cervical isolation: buccal retraction
Butterfly clamp
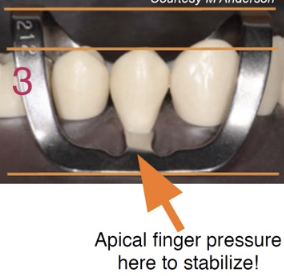

What does the B4 clamp do?
It’s like a half 212: The B4 clamp aids in isolation by retracting tissue without harming surrounding gingival tissue
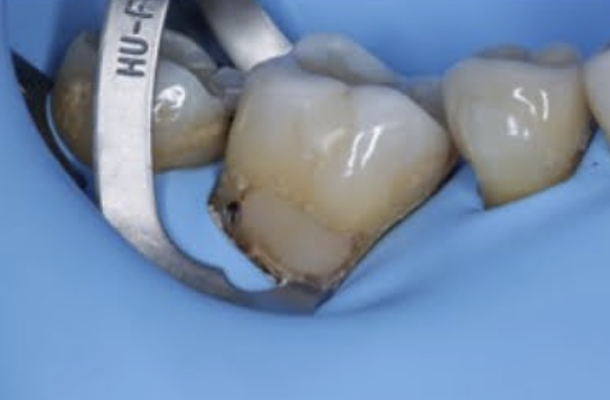
Which clamps are used to provide access if Rubber Dam is used?
B4, 212
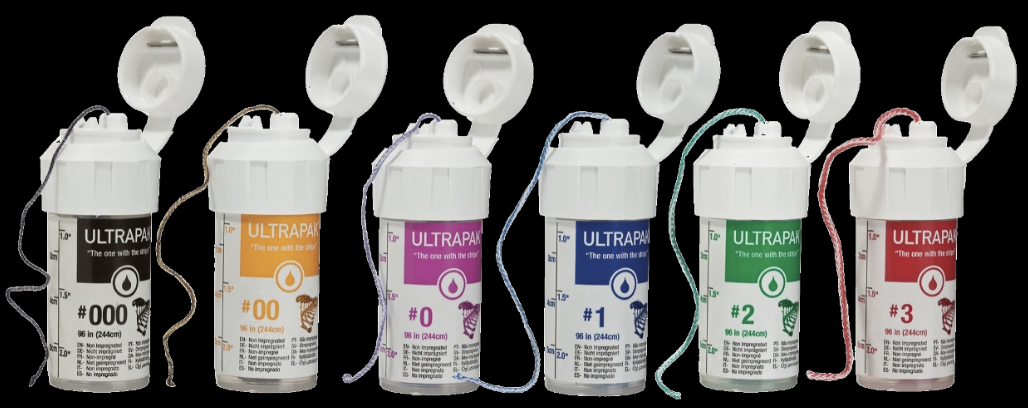
Retraction cords

Instruments for packing retraction cord
Cord packer, plastic

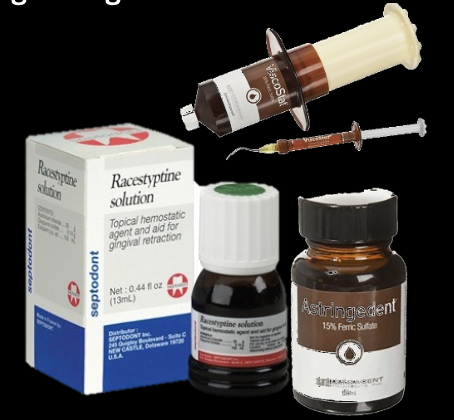
What do astringents/homeostatic agents do?
Cause a contraction-retraction of the tissues; the hemostatic agents constrict blood flow through coagulation
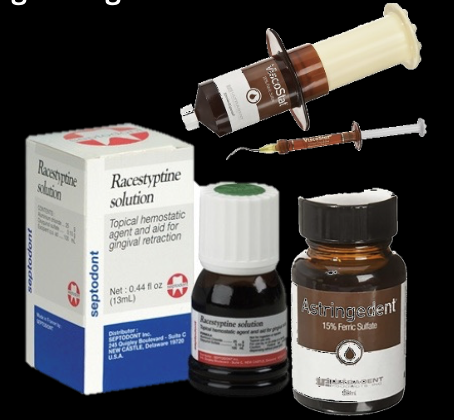
What are some common astringent/hemostatic compounds
Ferric sulfate 15-20%: Viscostat
Aluminum potassium sulfate
Aluminum sulfate
Aluminum chloride 20-25%
Racemic epinephrine 4-8%
What are the clinical steps for cord isolation?
Before preparation, or before restorative material placement
Evaluate the health of the gingiva and the depth of the sulcus to select the proper cord (single or double)
Soak the cord in astringent/hemostat (recommended), avoid excess of the solution
Loop the cord around the tooth, depending on the preparation area. Adjust the length to cover M to D
Repeat the process for a second cord if needed
At the time of removal (using after finish or polish) the cord should be wetted with water so it won’t grab and tear the tissues when it is removed, creating more bleeding.
Once the cord is removed, the retraction is maintained for about 30 seconds. Use this time for further subgingival finish if needed
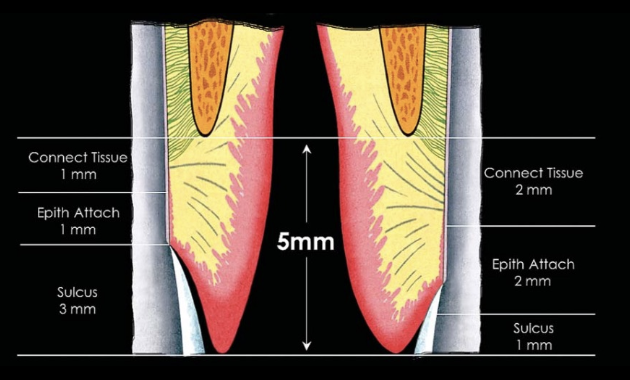
Where is cord actually packed?
Sulcus

Make sure you are going into the sulcus; start packing from the distal