BIOL 2460 - chapter 17 - PARKS - MICROBIOLOGY
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parks UTA
Last updated 7:34 AM on 12/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
Physical barriers
prevent pathogen from reaching target tissue site
- Cells create tight junctions, desmosomes, or gap junctions
- Cells create tight junctions, desmosomes, or gap junctions
2
New cards
gap junctions
selective access to certain molecules
3
New cards
Shedding of _________ cells help shed microbes
epidermis
4
New cards
Mucous membranes
protect via tight junction
- Nose, mouth, lungs, urinary, and digestive
- Nose, mouth, lungs, urinary, and digestive
5
New cards
Mucus
may also contain antimicrobial peptides
6
New cards
Mucociliary escalator
ciliated epithelial cells of the upper respiratory system move debris-laden mucus out of the lungs
7
New cards
Endothelia
tightly packed epithelial cells lining blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, urogenital track and others
* Endothelia of blood-brain barrier protects CNS (tight
junctions)
* Endothelia of blood-brain barrier protects CNS (tight
junctions)
8
New cards
Mechanical Innate Defense
physically remove; urine, feces, blinking, cilia, shedding, and mucus
9
New cards
Microbiome Innate Defense
microbiome competition of beneficial microbes inhibits growth of potential pathogens; secrete own defenses; EX: resident flora of vaginal area keeps C. albicans in check
10
New cards
Chemical Mediators
produced to inhibit microbial growth; can be produced by host (endogenous) or resident microbiota (exogenous)
11
New cards
chemical defenses
1. Body fluids
2. Antimicrobial peptides
3. Plasma protein mediators
4. Cytokines
5. Inflammation eliciting mediators
2. Antimicrobial peptides
3. Plasma protein mediators
4. Cytokines
5. Inflammation eliciting mediators
12
New cards
endogenous examples
- sebum oil produced by sebaceous gland to seal off pores
- saliva produced in oral cavity
- In the digestive system stomach acid, pancreatic and intestinal enzymes, cryptins, liver bile, Paneth cells eliminate most pathogens
- tear production
- saliva produced in oral cavity
- In the digestive system stomach acid, pancreatic and intestinal enzymes, cryptins, liver bile, Paneth cells eliminate most pathogens
- tear production
13
New cards
exogenous examples
- Propionibacterium acnes digest sebum to produce oleic acid (olay) and lower skin pH
- Lactobacilli in the vagina ferment glycogen to produce lactate, lowering pH
- Lactobacilli in the vagina ferment glycogen to produce lactate, lowering pH
14
New cards
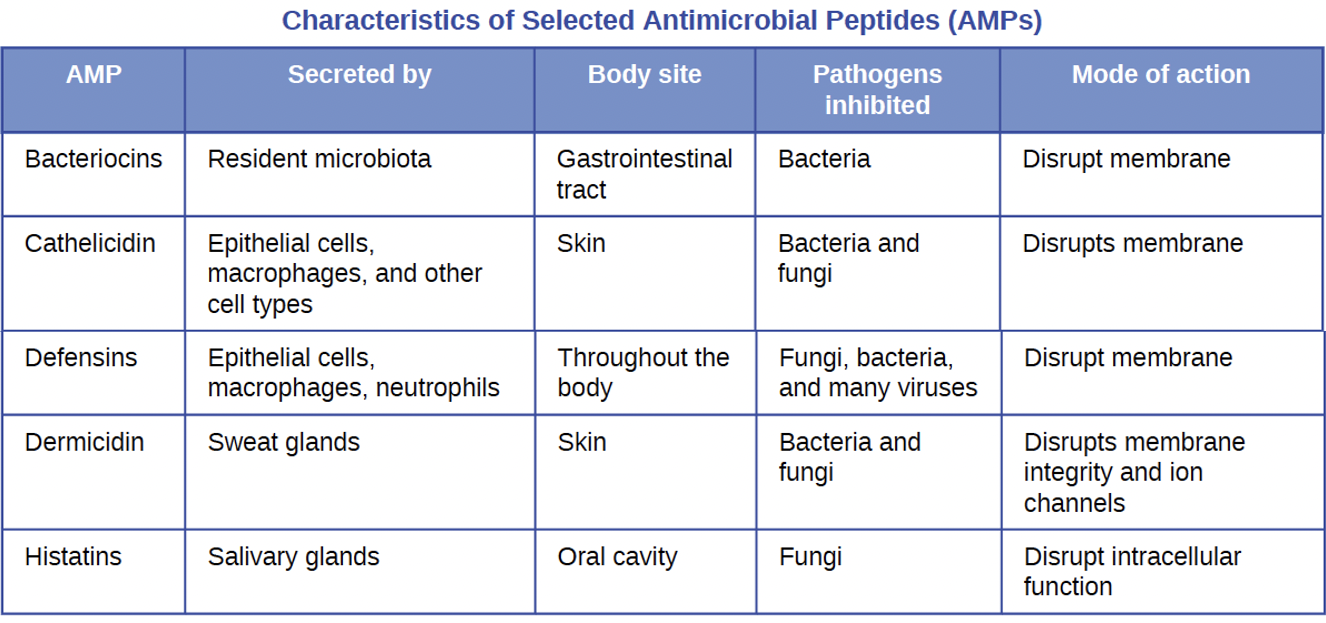
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)
cell-derived mediators with broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties; AMPs can damage membranes, destroy DNA/RNA, or cell wall synthesis; Some are specific to Gram (+) or Gram (-); others broad-range (bacteria fungi, protozoa, viruses)
EX: Bacteriocins and Defensins
EX: Bacteriocins and Defensins
15
New cards
Plasma Mediators
Acute phase proteins (liver -> blood)
Complement proteins (lectin, alt, classical, opsonization (phagocytized later), MAC)
Cytokines (chem messengers for long distance, interleukins, chemokines, interferons)
Complement proteins (lectin, alt, classical, opsonization (phagocytized later), MAC)
Cytokines (chem messengers for long distance, interleukins, chemokines, interferons)
16
New cards
Mannose-binding lectin
activates complete cascade
17
New cards
Precursor proteins float in blood until _________ ________.
complement activation
18
New cards
Classical
antibody-antigen complex C1
19
New cards
Lectin
Acute-Phase Proteins (APPs); inflammatory response; mannose-binding lectin
C4-->Carbohydrates
C4-->Carbohydrates
20
New cards
Alternative
Spontaneous Activation; C3b and C3a
21
New cards
Though complement activation initiation is __________, protective outcomes are the __________
different; same
22
New cards
Opsonization
coating of a pathogen by a chem substance (opsonin) to be phagocytized more easily (binding)
23
New cards
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
complex C6, C7, C8, C9; forms pores in the membranes of G-
- Water, ions, etc. move through pores leading to cell lysis and death
- Cannot penetrate thick peptidoglycan of G+
- Water, ions, etc. move through pores leading to cell lysis and death
- Cannot penetrate thick peptidoglycan of G+
24
New cards
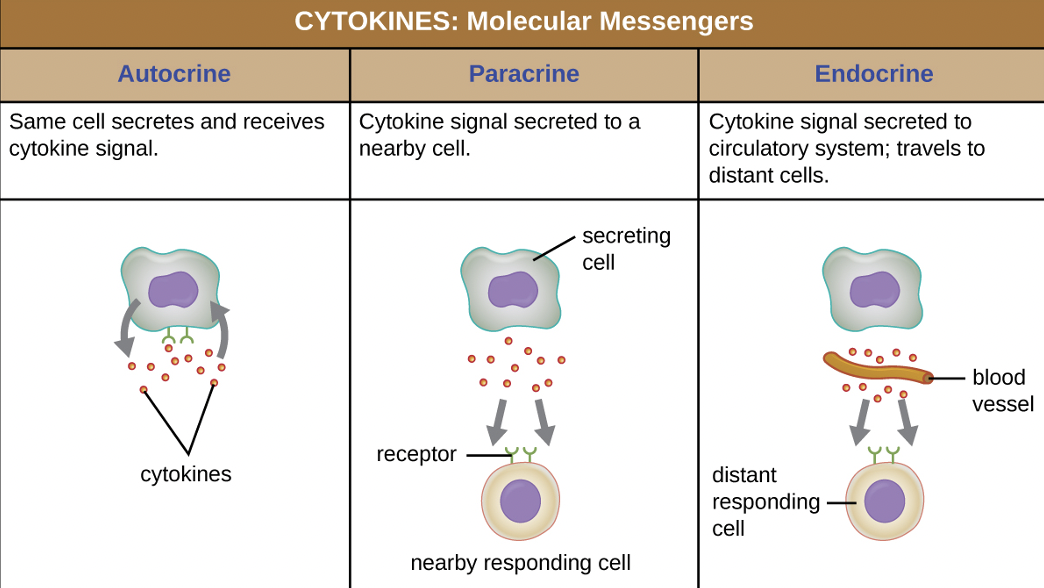
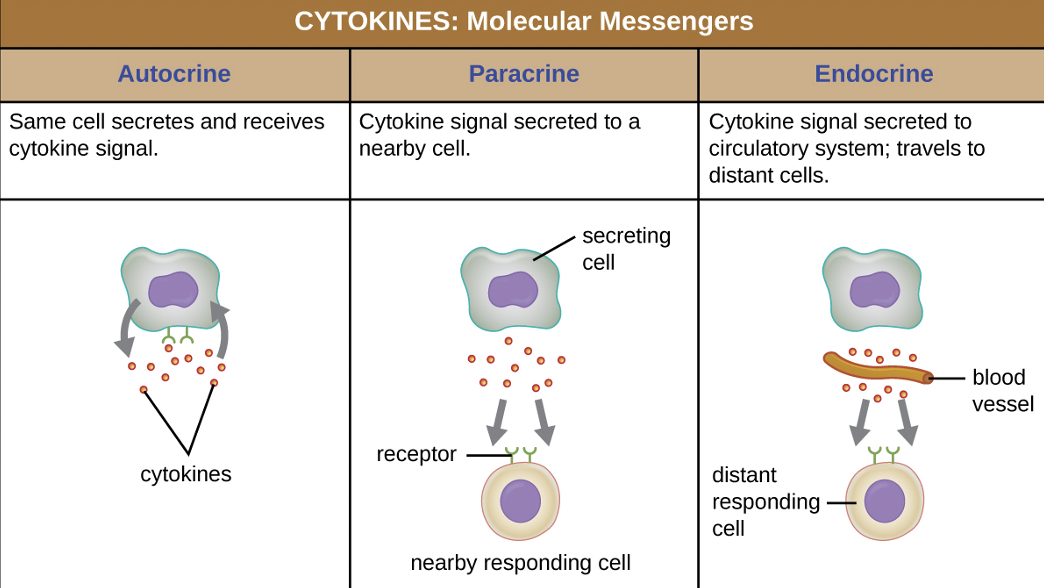
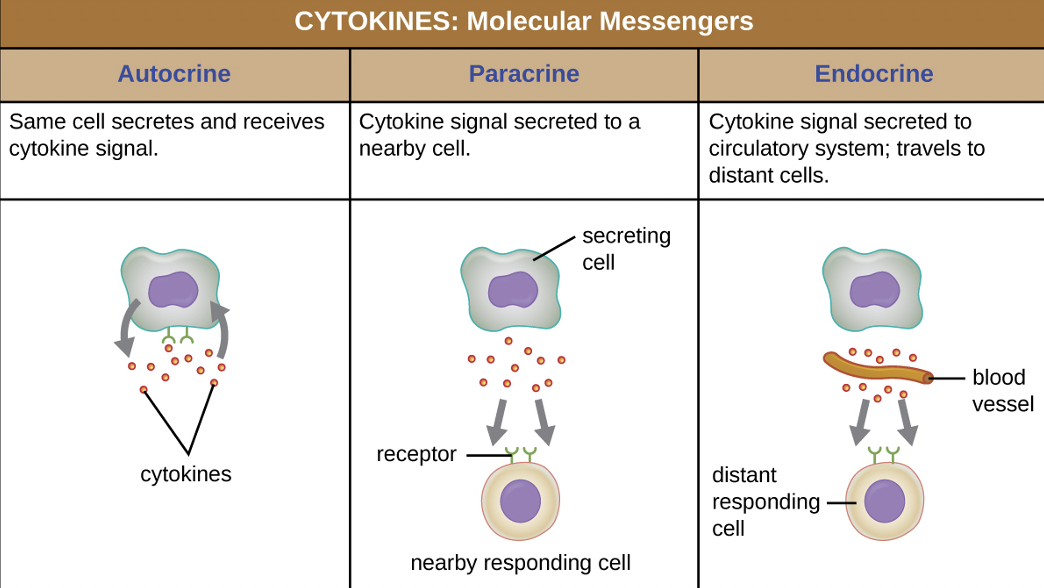
Cytokines
communication proteins that can stimulate immune cells to produce chemical defenses
25
New cards
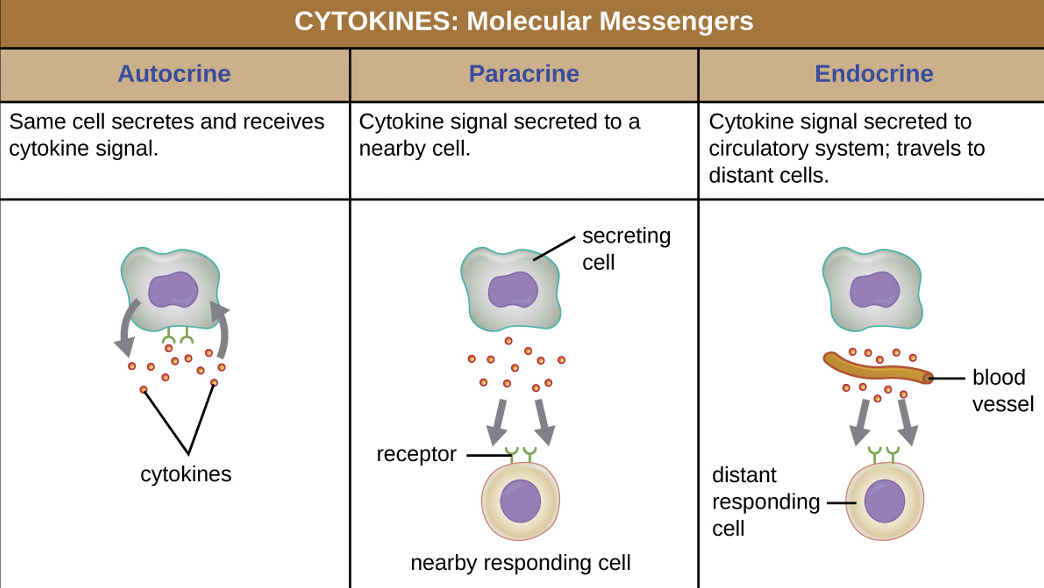
Autocrine
same cell secretes and receives cytokine signals (positive-feedback loop)
26
New cards
Paracrine
cytokine signal secreted to a nearby cell (neighbor)
27
New cards
Endocrine
cytokine signal secreted to circulatory system; travels to distant cells (roundtrip)
28
New cards
Cytokine classes
Interleukins, Chemokines, Interferons
29
New cards
Interleukins
help recruit immune cells to infection site
30
New cards
Chemokines
help recruit specific leukocytes
31
New cards
Interferons
released by cells with viral infection to recruit immune cells
32
New cards
Cytokine Inflammatory Mediators
Histamine, Leukotrienes, Prostaglandins, Bradykinin
33
New cards
Histamine
to cause bronchoconstriction (coughing)
34
New cards
Leukotrienes
to induce coughing, vomiting, diarrhea
35
New cards
Prostaglandins
to induce fever
36
New cards
Bradykinin
induce permeability in capillaries; contributing to edema (acute) (swelling)
37
New cards
Hematopoiesis
differentiation of blood cells from bone marrow stem cells
38
New cards
Granulocytes – innate WBCs
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
39
New cards
Agranulocyte exception: Natural killer cells
- Lymphocytes (adaptive)
- Monocytes (adaptive)
- Monocytes (adaptive)
40
New cards
Neutrophils
most abundant, pus formation, NET (mesh of chromatin w/ AMPs to trap pathogens), defensins & hydrolytic enzyme
41
New cards
Eosinophils
protection against protozoa & helminths, histamine, MBP, degradative enzymes
42
New cards
Basophils
complement cascade degranulation, allergies and edema, histamine and cytokines
43
New cards
Lymphocytes
B & T cells, seek out and find abnormalities to kill
44
New cards
Monocytes
largest constituent; macrophages (tissues) and dendritic cells (skin and mucus) (mononuclear phagocyte system); adaptive immunity
45
New cards
Mast Cells
same source as neutrophils and eosinophils; same function as basophils; leave blood and reside in surrounding tissue; associated w/ blood vessels and nerves or found close to surface structures (i.e. skin and mucus membranes)
46
New cards
Natural Killer Cells
Seek out non-self
markers (i.e. tumors and viral infected
host cells); Can express cytokines & cytotoxic molecules stored in granules to kill non-self cell
** Use perforin (punches a hole into the cell) and granzymes to induce apoptosis in target cells
** Use perforin (punches a hole into the cell) and granzymes to induce apoptosis in target cells
47
New cards
Leukocytes
phagocytes that travel to infection site; Site is entered through diapedesis, initiated by complement factor 5a and cytokines
48
New cards
Diapedesis or extravasation
process of leukocytes passing through capillary walls to tissues
- cannot go through arterioles/arteries or venioles/veins bc these are thick and the process occurs in thin capillaries
- cannot go through arterioles/arteries or venioles/veins bc these are thick and the process occurs in thin capillaries
49
New cards
Transendothelial migration
flattening out and squeezing through cellular junction after “rolling adhesion”
50
New cards
PAMPs
auto recognition for
pathogen-associated molecular patterns
Peptidoglycan
LPS
Flagellin
Microbial DNA/RNA
lipopeptides
Peptidoglycan
LPS
Flagellin
Microbial DNA/RNA
lipopeptides
51
New cards
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
structures that allow phagocytic cells to detect PAMPs (external surface of leukocytes); phagocyte surface or embedded internally
-PRRs on macrophages also respond to chemical distress signals from damaged or stressed cells; inflammatory response
-PRRs on macrophages also respond to chemical distress signals from damaged or stressed cells; inflammatory response
52
New cards
Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
bind to PAMPs and communicate with phagocyte nucleus to elicit a response
53
New cards
Phagocytosis Stages
1. Pathogen engulfment (phagocytosis)
2. Formation of phagosome (digestion)
3. Formation of phagolysosome and pathogen particle degradation
4. Expulsion of debris
2. Formation of phagosome (digestion)
3. Formation of phagolysosome and pathogen particle degradation
4. Expulsion of debris
54
New cards
Pathogen Recognition
When PAMP is recognized, phagocyte activates genes for phagocytosis, cell proliferation, interferon production, and/or cytokines
55
New cards
Inflammation
- Recruitment of immune cells
- Additional elimination tactic of dead/damaged cells
- Initiate repair of host damage
- Additional elimination tactic of dead/damaged cells
- Initiate repair of host damage
56
New cards
Acute
immediate response to breach in physical barrier. Induces erythema (redness), edema (swelling), heat, pain, and altered function
57
New cards
Chronic
occurs when short term (acute) inflammation is not enough. Infections sites may be walled off with WBCs (granulomas)
58
New cards
Fever
Systemic inflammatory response that raises overall body temperature
- Enhances innate immune defenses; mesophiles are inhibited and increases WBC
- Vasoconstriction and shivering
- Enhances innate immune defenses; mesophiles are inhibited and increases WBC
- Vasoconstriction and shivering
59
New cards
Pyrogens
produced by pathogens that alter hypothalamus (regulator of body temp)
- exogenous (LPS) or endogenous (interleukins)
- exogenous (LPS) or endogenous (interleukins)
60
New cards
Crisis phase
fever breaks; vasodilation and sweating