Wave-Particle Duality
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What were Newton’s corpuscles?
Light is a stream of tiny particles, hits a mirror it reflects as Normal component switches 180 degrees
He thought if you enter a denser medium the particles will speed up and thats why they bend to the normal, this was not true
What is Huygen’s principle?
Each point in a wavefront is a source of wavelets - these superpowers and interfere to form future waveforms
What did Huygen assume?
Light travels slower in glass but he was not believed as Newton was more respected
What were some reasons people didn’t believe Huygen?
He couldn’t measure speed of light in glass
He couldn’t explain polarisation
He wasn’t Isaac Newton
Why did Youngs double slit disprove Newton?
If light was a particle then we would have two continuous fringes
What did James Clark Maxwell find?
As I changes it causes a magnetic field which causes an electric field which creates a magnetic field and so on
What is permittivity of free space?
Measure of how an electric field is transmitted
What is permeability of free space?
A measure of the amount of resistance encountered when forming a magnetic field in a classical vacuum
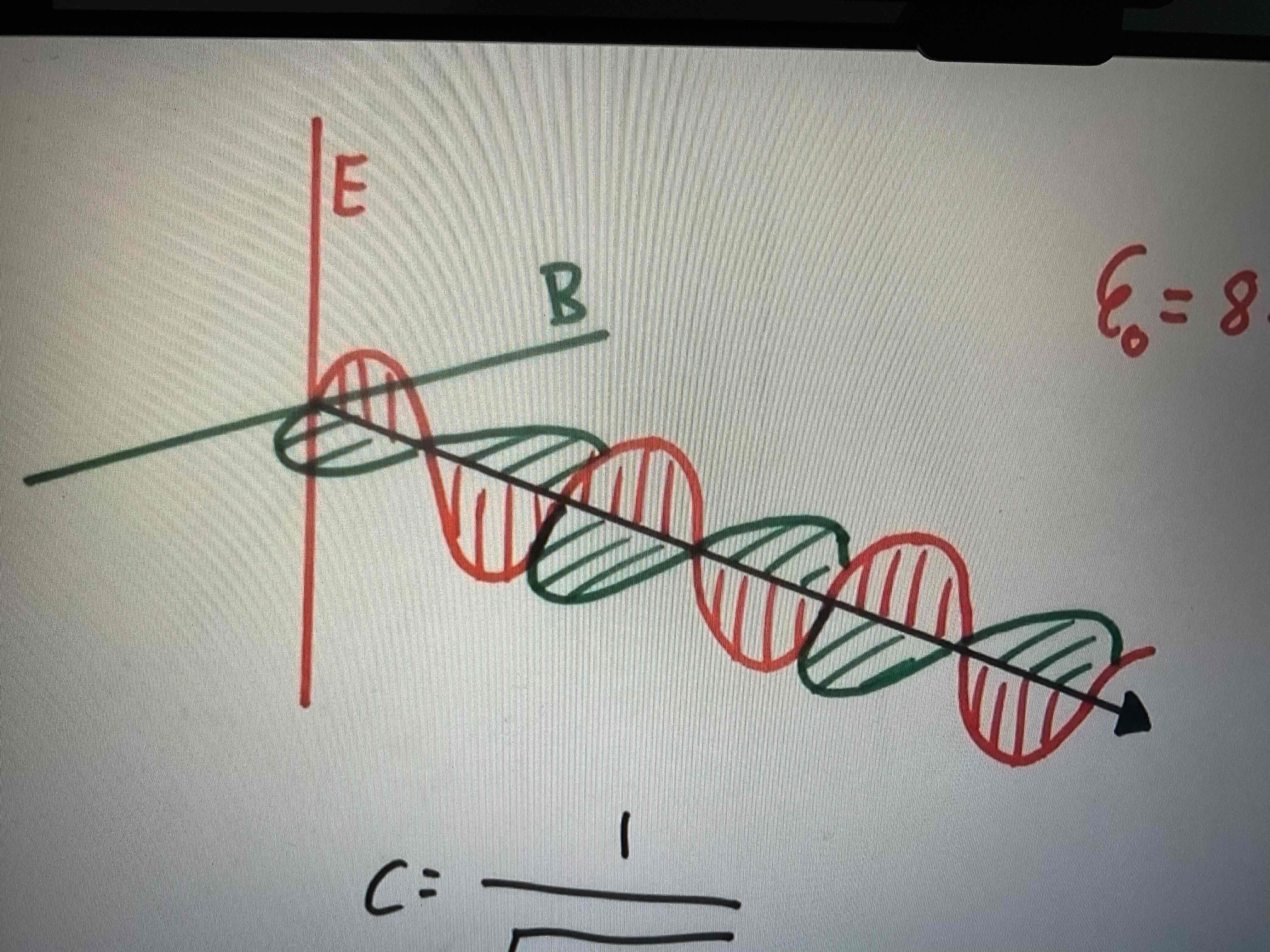
What does this graph show?
The direction the wave is moving and how its effected by electric fields and magnetic fields
What was found using c=1/root mu0 x epislon0?
Speed of light is 2.9986×10^8 which is our value today
What did Heinrich Hertz do?
Applied p.d across 2 pieces of metal and observed a small spark, a spark was detected in a circular piece of metal detector. Found that radio waves could be stopped by metal between transmitter and receiver.
He set his detector at different points between his induced p.d metal and a reflective surface. He had points with max and min signal which were the nodes of about 33cm, wavelength was 66cm. Through this he could find the speed of radio waves which was equal to the speed of light
What is the only way of explaining the photoelectric effect?
That light behaves like a particle, that depending on the energy of each photon effects the liberation of electrons which shows particle like features.
What did De Broglie look at?
Looked at wavelength of matter which was dependent on momentum so we got lambda=h/mv
What is wave-particle duality?
Waves can have particle like behaviour whilst particles can have wave like behaivour
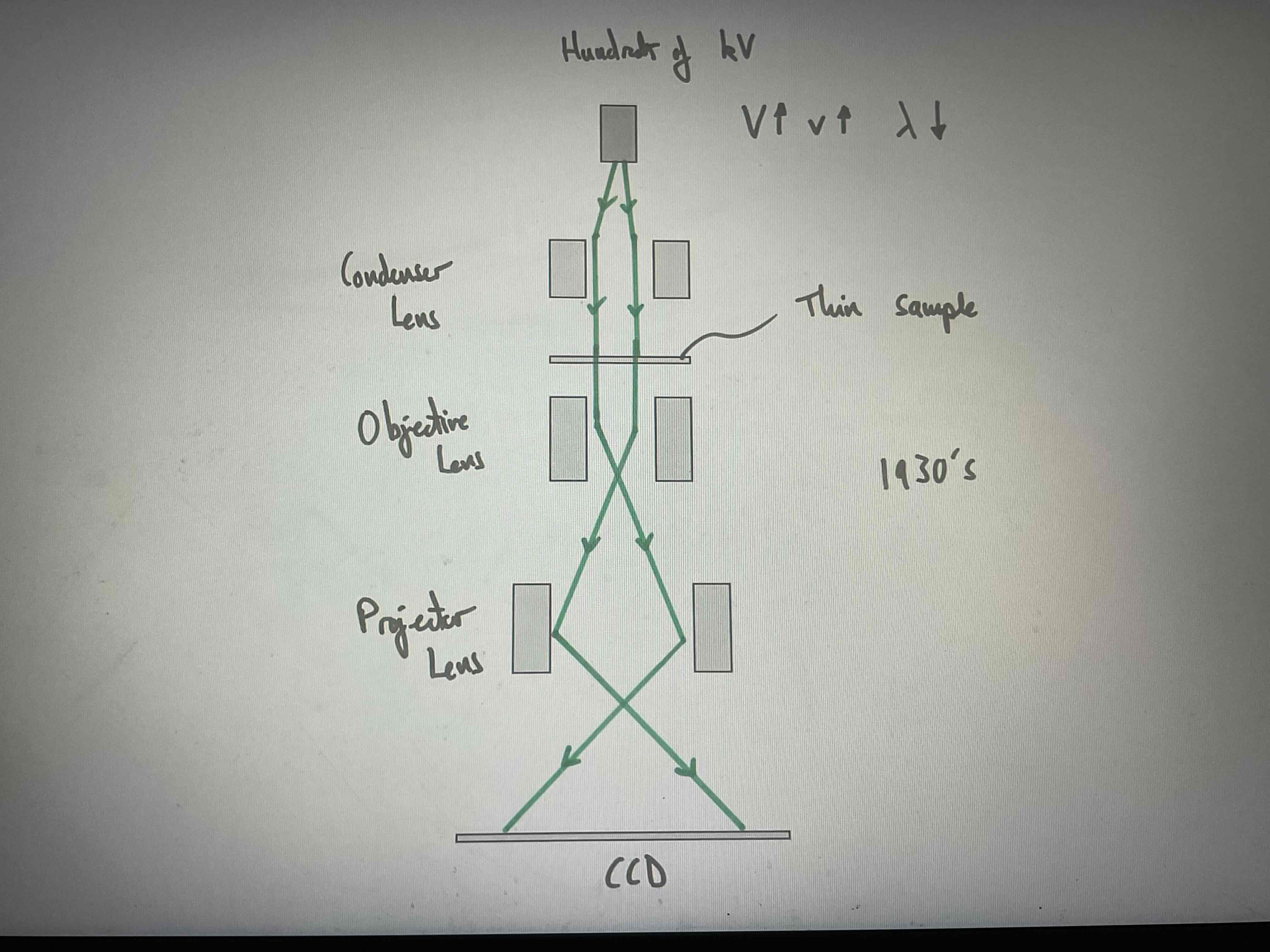
What is A TEM?
Transmission Electron Microscope
Accelerates electrons with high p.d so they have high velocity and high momentum, so wavelength is smaller and resolution becomes larger.
Can use lenses with magnets to change the electrons directions, condenser lens makes them travel parallel and then use a very thin sample (50nm e.g). Electrons go through and are bent by objective lens then again by projector lens where they are enlarged at the bottom.
What is a STM?
Surface Transmission Microscope, uses quantum tunnelling which is when there is a probability of particles Amplitude squared is proportional to probability of electron at a certain position. The further we get away the smaller the wave function gets. With a smaller amplitude there is less chance of an electron being away from that material.
Scans the surface of something that is conducting, can detect change of tunnelling current so with a smaller gap there is a higher current and vice versa due t the probability of an electron being present. Will scan in a zigzag pattern to show picture of surface of a material