6. Functions of Language
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 6. Functions of Language
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
functions of language
Communicative
Self-regulatory
Representational
Language as a tool for communication
social & communicative activities
initiation & development essential within family context
need to communicate begins
child is around 18 months old.
Communication is the process by which a
sender & a receiver exchange information (messages) through various forms
oral, written
aim of interacting with others
Language
communication tool
composed: arbitrary signs → must be socially established
allow for communication with others & with themselves.
Propose a model of communication with key elements
dual process of codification & decoding
codification
transformation of ideas into words and their subsequent production
decoding
words by the receiver and their transformation into mental representations, a process of recognition.
In order to use language appropriately, the child must be
able to
Encode & decode messages quickly
Recognise all sounds
Avoid using meaningless words
Language development is
inevitably linked to the fact that the child needs to learn how to communicate.
language should be a tool that
Facilitates interactions between people
allowing express information, feelings, & emotions.
Sender
creator of the message
encoded the message
code
set of symbols or signs
a shared system of symbols or signs used by sender & receiver.
message
the content being communicated
Channel
the medium through which the message is sent.
context
environment in which both sender & receiver exists
providing background
the situation or environment that affects how the message is interpreted.
Receiver / recipent
the person who receives and decodes the message
Human language is articulate allowing →
unlimited number of messages & meaningful dialogue between sender and receiver.
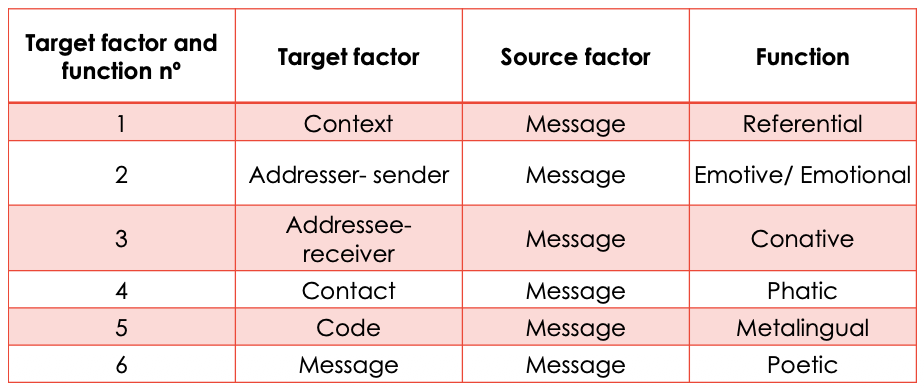
Jakobson's Communication Model
communication theory
both material & immaterial elements → functions
six constitutive factors (terms) & functions
six constitutive factors (terms) & functions
Addresser- sender
Context (referential)
Message (poetic)
Contact (phatic)
Code (metalinguistic)
Addressee- receiver
Addresser- sender
emotional or expressive
Addressee- receiver
(conative)
context
subject that represents a cultural or physical reality
sender
encodes a message using rules of language → can be received & interpreted by the receiver.
communication model includes
oral & written communication
message
Constructed with a specific intention
transmitted through a channel
within a particular context
Factors of Jakobson's Communication Model
Context
Addresser (Sender)
Addressee (Receiver)
Contact
Code
Message
Context
The co-text (other verbal signs within the same message)
the world in which the message occurs, encompassing the physical & cultural realities the message may refer to.
Addresser (Sender)
The individual who performs a linguistic act with intention & organization.
Addressee (Receiver)
The person to whom the message is directed, who interprets it & determines its function.
Contact
The physical & psychological channel that connects the addresser & addressee, enabling communication.
Code
The shared language or system of signs used by both the sender & receiver.
Message
A combination of signs organized according to specific rules to convey meaning.
Illustration
The Referential Function
emphasizing the context factor.
allows transmission of knowledge
he Emotional or Expressive Function
sender to convey their attitudes, feelings, & moods, as well as their desires, wishes
The Conative Function
receiver
act according to the message, often through commands, requests, or questions.
The Phatic Function
Establish, maintain, or end communication
Check if contact is still active
The Metalinguistic or Metalingual Function
language refers to itself
establishing a mutual understanding of the code.
The Poetic Function
qualities that make a verbal message a work of art.
aesthetic qualities of language → “poetry”
Note
Several alternative terms have been proposed for the same factors & functions.
function of context
referential
adresser-sender
emotive /emotional
addresser-receiver
conative
contact
Phatic
Code
Metalingual
message
poetic
an order
conative function
a comment on a novel
indicate metalinguistic function
physical space where the communication takes place
referential function
a rhyme
poetic function
a call to capture the listener´s attention
phatic function
expressive emotion
emotional function
Are linguistic functions (Jakobson) completely distinct from one another
No.
Linguistic functions are not fully distinct.
When one function is accentuated, others tend to be deemphasized, but they are still present.
Functions often interact & merge, rather than operate in isolation.
Which linguistic functions show the strongest inverse relationship, and why is this important?
The strongest pairings are:
Expressive ↔ Conative
Referential ↔ Poetic
Important of referential vs. poetic:
Poetic function dominates, reference is not removed but becomes ambiguous (Jakobson).
Shows a struggle for dominance, not mutual exclusion.