Vertebrates (Lectures 10-12) tutorial
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for reviewing key concepts regarding the origin and evolution of vertebrates, specifically within the context of the course 'Animals and the Environment'.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What characterizes chordates?
Chordates have a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and post-anal tail.
What are deuterostomes?
Deuterostomes are animals where the blastopore develops into the anus, and they include echinoderms and chordates.
Describe the features of vertebrates.
Vertebrates are chordates that have a backbone .
What are gnathostomes?
Gnathostomes are vertebrates that have jaws.
What adaptations do tetrapods have?
Tetrapods are gnathostomes that have limbs.
What are amniotes?
Amniotes are tetrapods that possess a terrestrially adapted egg.
How are mammals characterized?
Mammals are amniotes that have hair and produce milk.
What are cyclostomes?
Cyclostomes are jawless vertebrates, including hagfishes and lampreys.
What is a notochord?
A notochord is a flexible rod-like structure that provides support in chordates.
How do vertebrates differ from invertebrates?
Vertebrates have a backbone, while invertebrates do not.
What are the four main characteristics of chordates?
Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and post-anal tail.
Describe the evolution of jawed vertebrates.
Jawed vertebrates are known as gnathostomes, believed to have evolved from early vertebrates.
What are the key evolutionary features of tetrapods?
Tetrapods exhibit features such as four limbs, a neck, and a fused pelvic girdle.
How does the amniotic egg benefit terrestrial life?
The amniotic egg protects the embryo and allows for reproduction in dry environments.
What are the major groups of extant mammals?
Monotremes, marsupials, and eutherians.
What is the significance of Hox genes?
Hox genes are involved in the body plan development of vertebrates.
How do amphibians regulate gas exchange?
Many amphibians have moist skin that functions in gas exchange.
Define 'synapsid'.
Synapsids are a clade of reptiles including mammals and their ancestors.
Differentiate between hagfishes and lampreys.
Hagfishes have reduced vertebrae and are mostly scavengers, while lampreys have cartilaginous vertebrate and are mostly parasitic.
What features restrict amphibians to moist habitats?
Amphibians' moist skin and reproduction strategies often restrict them to aquatic or moist terrestrial habitats.
What anatomical adaptations allow birds to fly?
Birds have lightweight bones, a fused sternum for muscle attachment, and specialized wing structures.
Describe the evolutionary significance of Archaeopteryx.
Archaeopteryx exhibits both avian and reptilian features, linking birds to their dinosaur ancestors.
What is the basic structure of chondrichthyans’ skeleton?
Chondrichthyans have a skeleton primarily made of cartilage.
What does the term 'osteichthyan' refer to?
Osteichthyans are bony fish characterized by a bony skeleton.
How do ray-finned fishes differ from lobe-finned fishes?
Ray-finned fishes have fins supported by rays, while lobe-finned fishes have muscular fins with rod-shaped bones.
What are the distinguishing features of the clade Amniota?
Amniotes possess an amniotic egg, which allows them to reproduce on land.
What adaptations do mammals have for respiration?
Mammals ventilate their lungs using a diaphragm, enhancing breathing efficiency.
What is bipedal locomotion?
Bipedal locomotion is walking on two legs, a defining characteristic of humans and some ancestors.
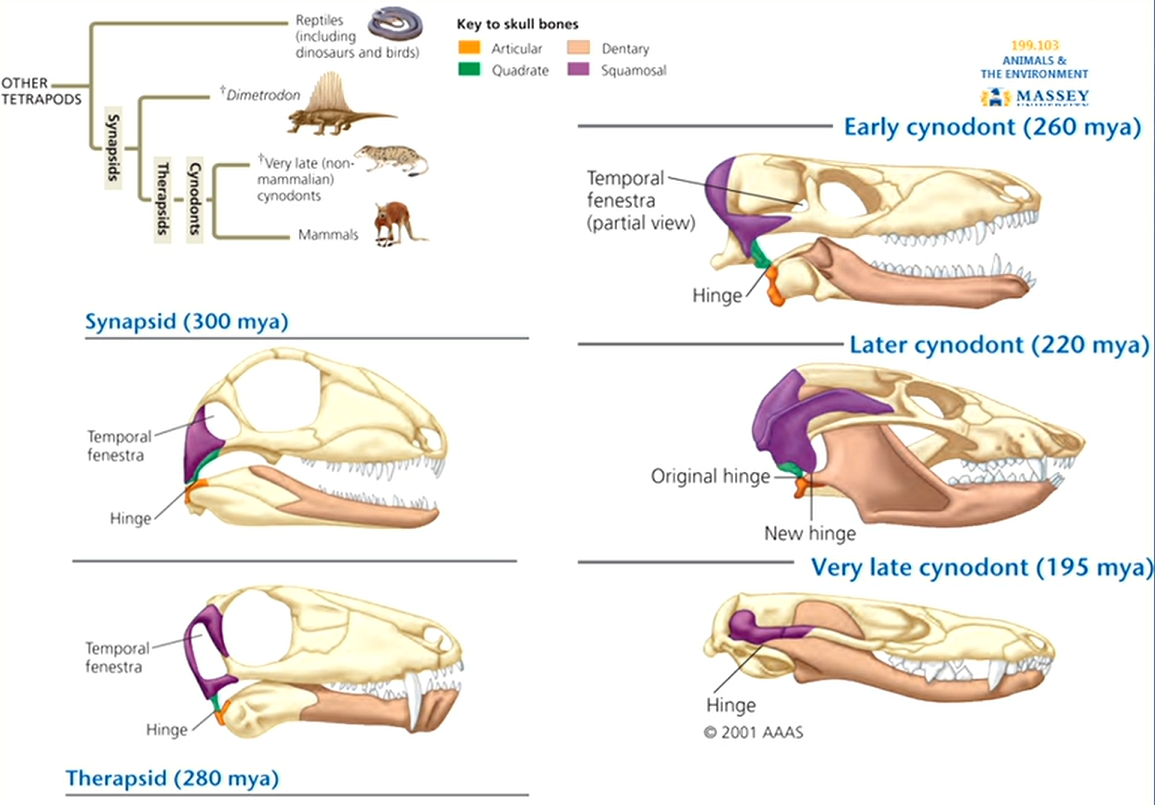
What is the significance of the temporal fenestra in synapsids?
The temporal fenestra allows for more muscle attachment around the jaw, aiding in stronger bites.
How do synapsids differ from diapsids?
Synapsids have one temporal fenestra, while diapsids have two, influencing skull structure and muscle attachment.
How do mammals' ear bones differ from other tetrapods?
Mammals have three middle ear bones derived from jaw bones, enhancing hearing.
What did the earliest mammals evolve from?
Earliest mammals evolved from synapsid ancestors.
How does the presence of jaws affect ecological interactions?
The evolution of jaws allowed for more diverse feeding strategies and predator-prey interactions.
What role did the notochord play in vertebrate evolution?
The notochord provides structural support and is critical in the development of the vertebrate spine.
What distinguishes tetrapod limbs from those of fish?
Tetrapod limbs are adapted for life on land, with fingers and toes for better locomotion.
How do the basal chordates differ from advanced vertebrates?
Basal chordates exhibit simpler structures and lack features such as a true backbone.
Describe the importance of rib cage ventilation in mammals.
Rib cage ventilation allows for more efficient breathing and greater oxygen intake compared to earlier vertebrates.
What is the evolutionary relationship between birds and reptiles?
Birds are considered a type of reptiles due to their evolutionary lineage and shared characteristics.
Identify characteristics of the first hominins.
Early hominins had small brains and likely walked upright, representing a key step in human evolution.
What evidence supports the evolutionary timeline of mammals?
Fossil records showing gradual changes in skull structure and limb adaptations provide evidence.
Explain the role of the pharyngeal slits in chordate development.
Pharyngeal slits are involved in the development of gill structures in aquatic vertebrates.
What defining features characterize mammals?
Mammals are characterized by hair, mammary glands, and complex ear structures.

Which feature of a developing embryo would allow it to be identified as deuterostome?
The presence of a blastopore that develops into the anus, with the mouth forming later.


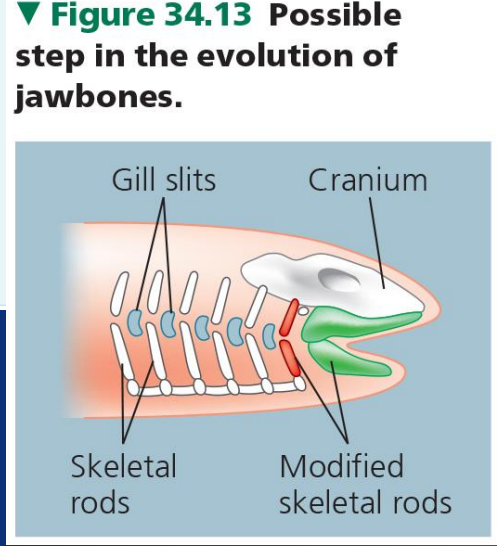
Think what are the features of chordates... which one evolved into the jaw of the gnathostomes.
The jaw evolved from the modifications of the first two pairs of pharyngeal arches/skeletal rods. Thus the answers is none of the above.
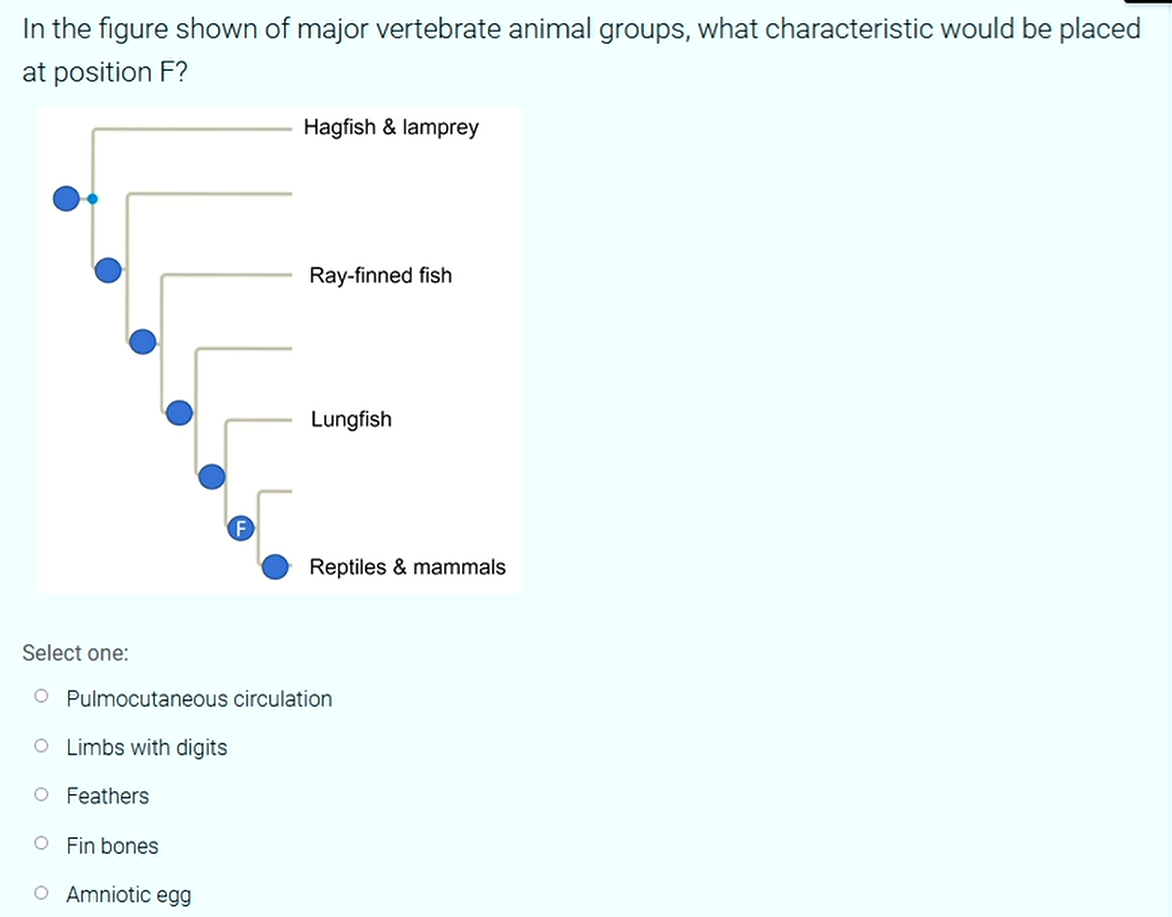
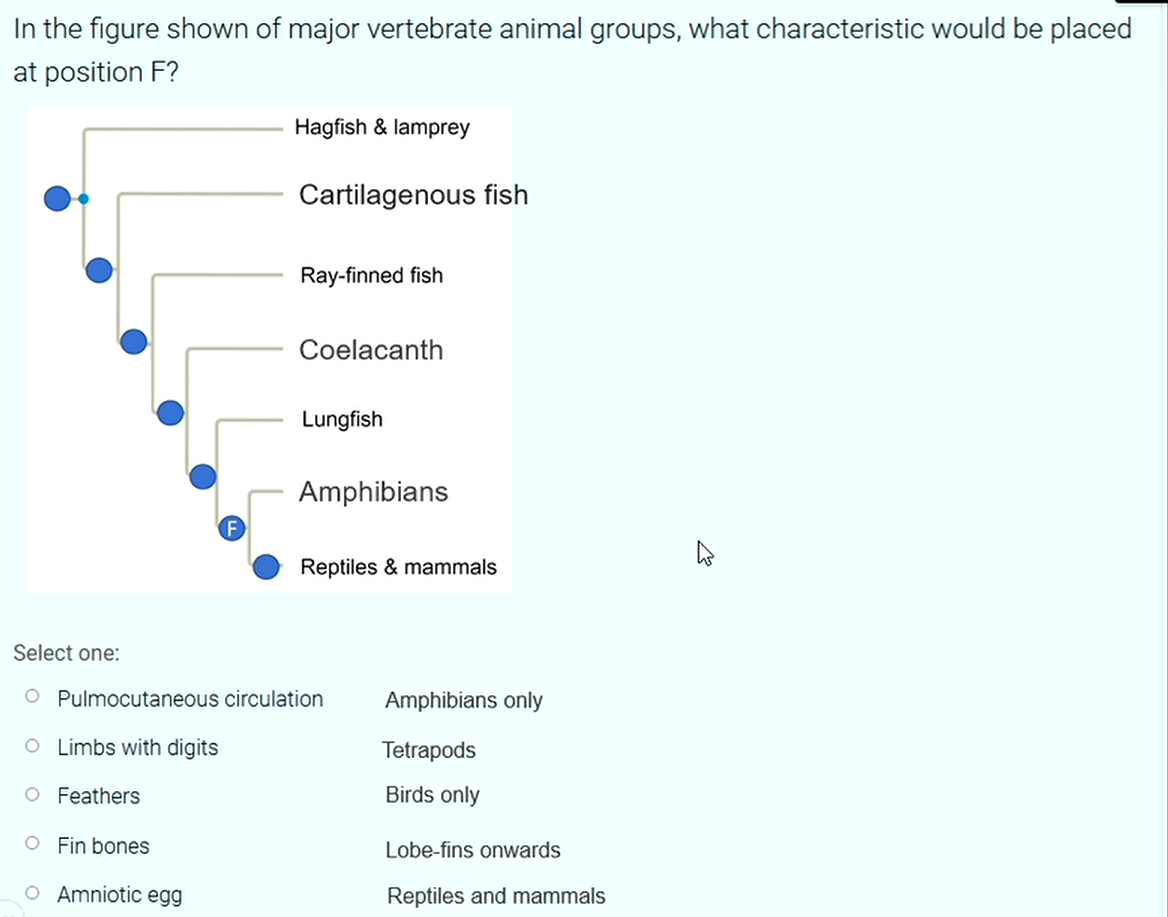
What is represented by point F in the image?
Answer is Limbs with Digits

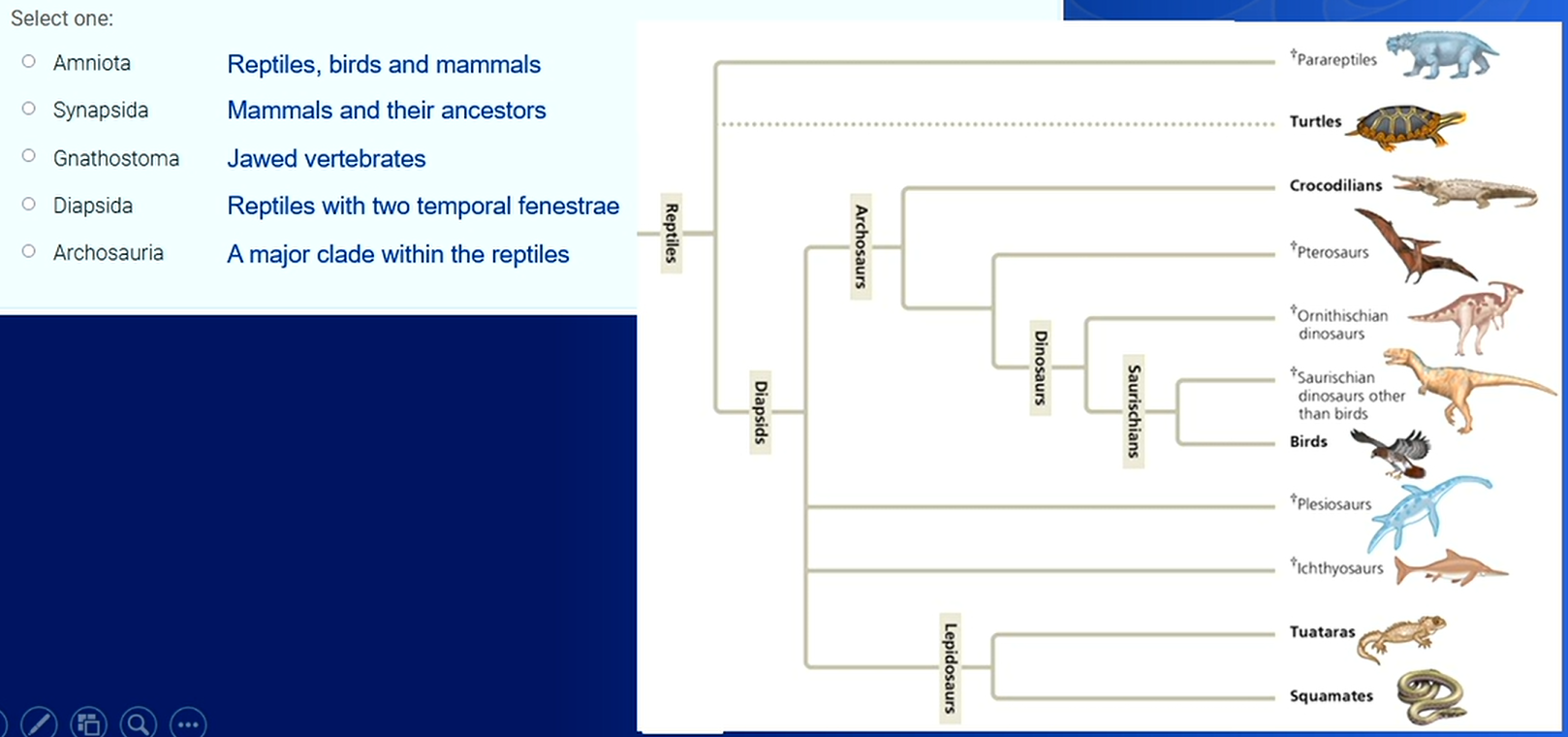
What is the name of the clad that includes lizards and birds but excludes mammals?
Can’t be Archosauria as it excludes the squamates where lizards are found thus the correct answer is the Diapsida.

Why do modern mammals have more bones in the middle ear than other Tetrapods?
Changes in jaw articulation shifted the skull-jaw hinge joint and two bones in the skull and jaw became incorporated into the ear.
(1 is wrong as it wasn’t two bones from the lower jaw it was one from the lower jaw and one from the skull)
(5 is wrong because this change didn’t occur for hearing rather this occurred due to diet and the better hearing was a bonus)