8. metabolism and exercise
5.0(1)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:09 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
aerobic exercise
exercise which increases heart rate/breathing rate for at least 20 mins, improves function and use of oxygen
2
New cards
recommended exercise
moderate activity 150 mins a week
3
New cards
adrenaline
causes initial increase in heart rate when you start exercising
4
New cards
divert blood flow
adrenaline causes vasodilation of arterioles in muscles and skin and vasoconstriction of arterioles in gut and non essential organs
5
New cards
nitric acid
secreted when oxygen levels drop in muscles causing vasodilation
6
New cards
stroke volume
increases as more blood returns to heart, therefore increases cardiac output
7
New cards
breathing
rate and depth increases allowing more carbon dioxide to be removed
8
New cards
carbon dioxide concentration increase
reacts with water forming carbonic acid which lowers blood pH
9
New cards
chemoreceptors
located in brain and aortic arch, they detect falling pH and trigger in increase in breathing via sympathetic nervous system
10
New cards
training
repeated short bouts of exercise over long term allowing the body to adapt to it
11
New cards
systems which adapt to long term exercise
circulatory system, respiratory system, muscular system
12
New cards
lower heart rate
effect of long term exercise as more blood returns to heart (vein compression), ventricles stretched more and contract more forcefully (sterlings law), ventricle muscle increases, higher stroke volume
13
New cards
recovery time
Time for heart to return to resting state
14
New cards
skeletal mucles
increase in cross sectional area, increase in number and size of mitochondria, more blood capillaries, more glycogen and myoglobin
15
New cards
aerobic fitness
how efficiently oxygen is used
16
New cards
contribute to aerobic fitness
age, gender, smoking, exercise program, nutrition
17
New cards
FITT factors
frequency, intensity type and intensity/duration of exercise
18
New cards
frequency of exercise
3-6 per week, strength and resilience training training for less to allow recovery
19
New cards
intensity of exercise
the effort put into et eg speed, distance, weight. moderate to high causes heart to increase to heart max
20
New cards
type of exercise
eg cardiovascular, running, swimming, cycling, aerobics, weightlifting
21
New cards
time/duration of exersise
shorter but more frequent or longer but less frequent, maintain elevated heart rate fir 20mins+
22
New cards
VO2 max
maximum rate which oxygen can be taken in, transported and utilised in exercise
23
New cards
VO2 max expressed
absolute rate eg litres of oxygen per min dm3 min-1
or relative rate eg millimetres of oxygen per kilogram of body mass per minute ml kg-1 min-1
or relative rate eg millimetres of oxygen per kilogram of body mass per minute ml kg-1 min-1
24
New cards
measure VO2 max
undertake graded exercise whilst ventilation oxygen and CO2 concentration of inhaled and exhaled air is measured, its reached when O2 consumption remains the same despite intensity increasing
25
New cards
precautions of carrying out VO2 max test
risk assessment of to determine existing health conditions, death suitable clothing, check equipment is in working order
26
New cards
measure aerobic fitness
indicated by time for heart rate to return to resting after exercise
27
New cards
Harvard step test
used to assess effect of FITT factors on aerobic fitness and indicate VO2 max
28
New cards
1, 5, 3, 4, 2, 6
order statements
1. using a 30-50cm high step, step up placing both feet on the step and step down placing both feet on floor
2. Convert pulse rates to beats per minute and add together
3. Wait 1 minute after stepping then measure pulse rate
4. Repeat pulse rate measurement at 2 minutes and 3 minutes after stepping
5. Each step cycle should take 2s and stepping is carried out for 300s
6. Calculate a score using the equation 100 x 300 / total beats per minute since 300s was the duration of stepping
1. using a 30-50cm high step, step up placing both feet on the step and step down placing both feet on floor
2. Convert pulse rates to beats per minute and add together
3. Wait 1 minute after stepping then measure pulse rate
4. Repeat pulse rate measurement at 2 minutes and 3 minutes after stepping
5. Each step cycle should take 2s and stepping is carried out for 300s
6. Calculate a score using the equation 100 x 300 / total beats per minute since 300s was the duration of stepping
29
New cards
measure pulse rate
use radial artery (wrist) or carotid artery (neck), use 2 fingers (not thumb) count for 30 seconds and multiply
30
New cards
measure effect of exercise
measure heart rate/pulse rate before, during and after, breathing rate, blood pressure, reaction times cognitive tasks
31
New cards
ethical and health safety issues for deciding someone can precipitate
give informed consent and know any potential health issues
32
New cards
factors to control when investigating activity
age, time of day, type and duration of exercise, sex, weight, height, fitness, BMI
33
New cards
oxygen deficit
when oxygen supply doens’t meet demand
34
New cards
excessive post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC)
period of increased oxygen consumption following vigorous exercise
35
New cards
oxygen dept
additional oxygen required to metabolise lactate
36
New cards
processes requiring oxygen after exercise
re-oxygenation of haemoglobin and myoglobin
oxidising lactate to pyruvate
regeneration of ATP and creatine phosphate
replenishing glycogen stores In muscle
meet increased metabolism rate due too been warmer and increased heart rate
cell repair
balancing hormones
oxidising lactate to pyruvate
regeneration of ATP and creatine phosphate
replenishing glycogen stores In muscle
meet increased metabolism rate due too been warmer and increased heart rate
cell repair
balancing hormones
37
New cards
oxygen deficit builds up at a start of exercise
takes time for heart rate and breathing rate to increase to meet demand
38
New cards
EPOC decreases with increased aerobic fitness
due to increased VO2 max due to increased stoke volume, more myoglobin and creatine phosphate
39
New cards
carbohydrate loading
aims to increase glycogen stores which can be hydrolysed to glucose for respiration
40
New cards
benefit from carbohydrate loading
endurance athletes not sprinters as it allows muscles to work for longer
41
New cards
carbohydrate loading regime
carbodepletion- less carbohydrates and more proteins/lipids from 10 days prior
carbohydrate loading- high carbohydrate diet diet 2-3 days prior to event
recovery- eat carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores
carbohydrate loading- high carbohydrate diet diet 2-3 days prior to event
recovery- eat carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores
42
New cards
athletic performance depends on
oxygen availability
carbohydrate availability
mass of muscles §
carbohydrate availability
mass of muscles §
43
New cards
blood doping
artificial increase in red blood cell concentration
44
New cards
methods of blood doping
use recombinant erythropoietin (RhEPO)
autologous blood doping
autologous blood doping
45
New cards
erythropoietin
protein secreted by cells surrounding capillaries in renal correct of kidney in response to low oxygen levels or reduced blood volume
46
New cards
train at high altitude
low partial pressure of oxygen stimulates production of erythropoietin which increases number of red blood cells- legal
47
New cards
inject recombinant erythropoietin
artificially increase number of red blood cells and therefore oxygen by a substance produced from genetically modified bacteria. illegal and may lead to kidney failure and increased chance of thrombosis
48
New cards
autologous blood doping
remove 1 dm3 of blood, which their body replenishes the inject their packed blood cells back into their body
49
New cards
anabolic
synthesise complex molecules from simple molecules
50
New cards
group of macromolecules with steroids
lipids
51
New cards
steroids synthesised form
cholesterol
52
New cards
steroids are able to pass through cell surface
due to them been non polar lipids
53
New cards
steroids cause
transcription and synthesis of new muscle protein
54
New cards
transcription factor
molecule which binds to DNA and determines which genes are expressed
55
New cards
anabolic steroids
eg nandrolone and stanozolol, are artificially produced and injected into muscles to music action of hormones like testosterone which increase protein synthesis
56
New cards
anabolic steroids effet
promote growth and repair allowing more muscle building, train for longer and recover faster. also increase erythrocyte production and therefore VO2 max
57
New cards
why anabolic steroids are banned
enhance perforce giving an unfair advantage, health risks
58
New cards
health risks of anabolic steroids
altered behaviour eg aggression and mood swings
liver dammage
infertility and altered sexual characteristics
liver dammage
infertility and altered sexual characteristics
59
New cards
creatine phosphate
legal performance enhancer found in many foods and naturally synthesised by the body
60
New cards
creatine phosphate
can lose its phosphate group to phosphorylate ADP to ATP
61
New cards
respiratory pigments
haemoglobin
myoglobin
myoglobin
62
New cards
haemoglobin
found in erythrocytes to transport oxygen
63
New cards
myoglobin
found in muscle tissue to store oxygen
64
New cards
haemoglobin structure
quaternary protein containing 4 polypeptide chains with a haem prosthetic group (Fe2+ which binds to oxygen)
65
New cards
saturated
when 4 oxygen bind to haemoglobin
66
New cards
associate
when oxygen bind to haemoglobin
67
New cards
dissociation
release of oxygen from haemoglobin
68
New cards
oxygen realsed
haemoglobin response to increase of carbon dioxide and drop in oxygen in respiring tissues
69
New cards
myoglobin structure
a tertiary protein containing one ham group
70
New cards
haemoglobin function
carry oxygen (oxyghaemoglobin HbO8)
carry carbon dioxide (carboaminohaemoglobin)
act as a buffer
carry carbon dioxide (carboaminohaemoglobin)
act as a buffer
71
New cards
partial pressure of oxygen
pO2 is a measure of relative pressure oxygen contributes to a mixture of gases
72
New cards
lungs
area with high partial pressure where haemoglobin becomes fully saturated
73
New cards
respiring tissues
low partial pressure where haemoglobin becomes half saturated
74
New cards
s shaped curve
oxygen dissociation curve, due to co-operative binding, once one oxygen binds it is easier for more to, hard to achieve 100 saturation
75
New cards
myoglobin oxygen affinity
higher affinity for oxygen than Hb so only releases oxygen at low pO2
76
New cards
fetal haemoglobin
able to bind to oxygen at a lower affinity where adult haemoglobin dissociates. this is due to its higher affinity for oxygen
77
New cards
fetal haemoglobin
quaternary structure made of 2 alpha and 2 gamma globin chains
78
New cards
adult haemoglobin
quaternary structure made of 2 alpha and 2 beta chains
79
New cards
carbon dioxide transport in blood
5% dissolves in plasma
10% combines with Hb to form carbaminohaemoglobin
85% transported as HCO3- in plasma
10% combines with Hb to form carbaminohaemoglobin
85% transported as HCO3- in plasma
80
New cards
carbonic anhydrase
enzyme which catalyses reaction of CO2 and water to form carbonic acid. within red blood cells
81
New cards
carbonic acid
produced from CO2 and dissociates to H+ and hydrogencarbonate (HCO3)-
82
New cards
chloride ions
inward movement of ions to balance outward movement of hydrogencarbonate into plasma from red blood cells
83
New cards
H+ ions
cause oxyhemoglobin to dissociate and release oxygen, due to it binding and forming haemoglobinic acid, this prevents a change in pH
84
New cards
greater affinity for oxygen
dissociation curve shifts to left
85
New cards
lower affinity for oxygen
dissociation curve shifts to right
86
New cards
Bohr effect
increase in CO2 causes dissociation curve to shift to right, due to more H+ ions causing dissociation of oxygen
87
New cards
pH
decrease causes dissociation curve to shift to right, due to anaerobic respiration producing lactic acid and therefore H+
88
New cards
temperature
raise causes dissociation curve to shift to right, due to it effecting H and ionic bonds in haemoglobin and association between oxygen and haemoglobin
89
New cards
types of muscle
cardiac muscle
skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
90
New cards
smooth muscle
involuntary, found in walls of arteries and intestines and controls blood flow, moves food and controls pupil size, contracts slowly without fatigue, spindle unstriped fibre appearance.
91
New cards
cardiac muscle
forms part of heart, contracts continuously to pump blood, connected to intercalated disks to allow transmission of action potential, some are myogenic, contracts rhythmically without fatigue, striated
92
New cards
skeletal muscle
voluntary muscle, attached to skeleton via tendons, contracts to move bones at joints, striated, contracts rapidly and powerfully but fatigues quickly
93
New cards
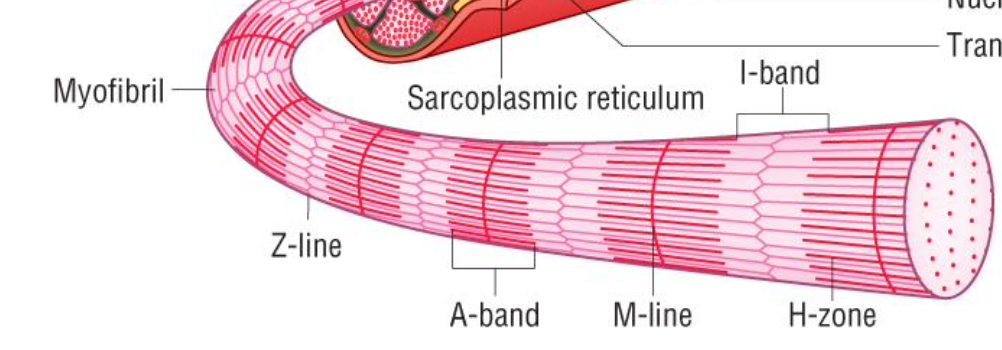
cause of striped muscles
due arrangement of protein filaments in myofibrils
94
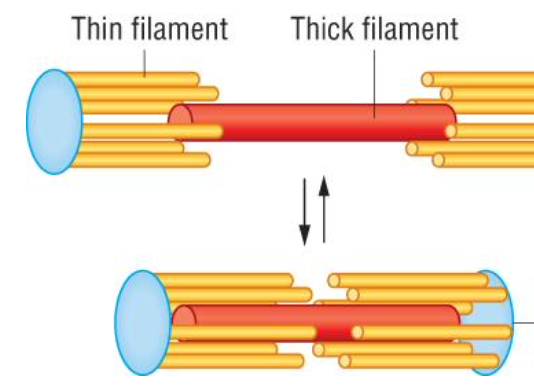
New cards
thick protein filamnet
composed of myosin, surrounded by 6 other filaments
95
New cards
think protein filament
composed of actin, troponin and tropomyosin, around 1 filament
96
New cards
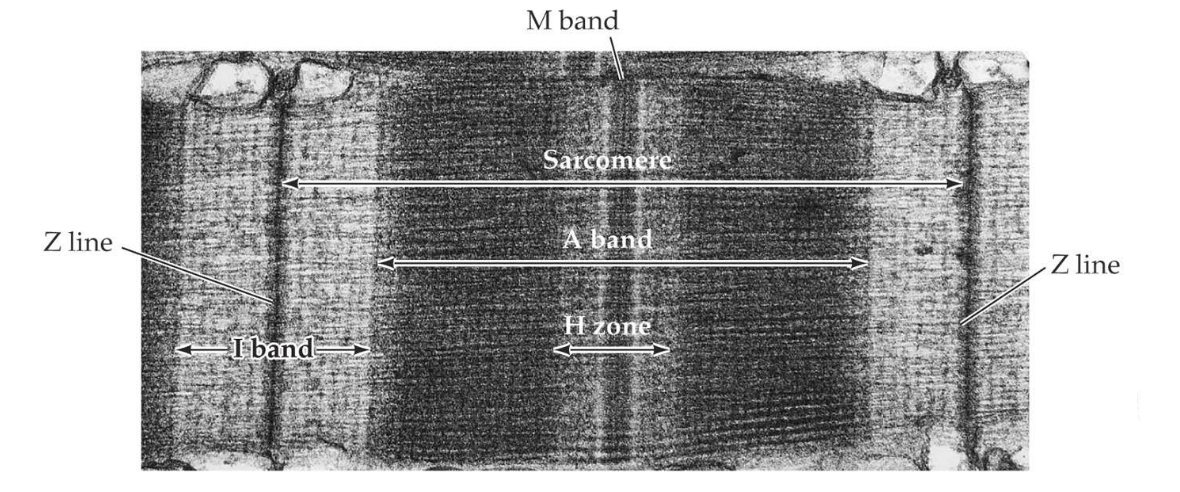
z line
are the thin filaments anchor to with the distance between been called a sarcomere, move closer together with muscle contraction
97
New cards
sarcomere
distance between 2 z lines, approximately 2.5µm in length when relaxed, and shortens when muscles contract as the filaments slide past each other,
98
New cards
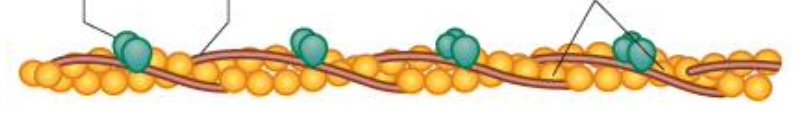
G actin
2 chains of globular subunits twisted together
99
New cards
tropomyosin
hides a myosin binding site on the actin subunits
100
New cards
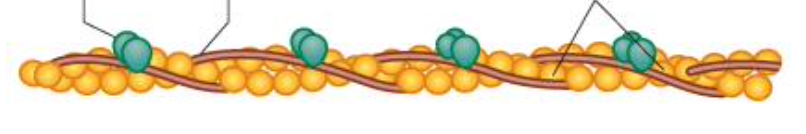
troponin
found at intervals with 3 subunits, one binds to tropomyosin, one to actin, one to Ca2+