ABDOMINAL - RENAL
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
renal arterial supply
aorta
main renal artery
segmental
interlobar
arcuate
intralobar
afferent arterioles
the lra originates from the _____ aspect of the aorta
posterolateral
the rra originates from the _____ aspect of the aorta
anterolateral
the rra courses _____ to the ivc to reach the kidney
posterior
renal arteries normally course _____ to the renal veins
posterior
_____% of patients have duplicated renal arteries
30
how can lumbar arteries be differentiated from accessory renal arteries
they are very high resistance and renal arteries are not
low resistance flow with a low ri is considered _____ for the renals
normal
what ri is considered abnormal for the renal arteries
over .7
parenchymal ri values under .5 can indicate
proximal renal artery stenosis and renal ischemia
a difference in length of greater than _____ cm between the kidneys can mean renal disease or ras
2
serum BUN and creatinine levels will be _____ with decreased renal perfusion/function
increased
how does renovascular htn work
kidney receives less blood flow due to arterial stenosis
kidneys perceive this as body having an overall low blood pressure
renal response is the angio-tensin aldosterone response to raise pressure to increase flow to the kidneys, leading to systemic htn
ras is most commonly caused by
atherosclerosis
second most common cause of ras
fibromuscular dysplasia
fibromuscular dysplasia most commonly affects what part of the renal arteries
mid-distal
gold standard in diagnosis of renal stenosis
angiography
a kidney length of under _____ cm is considered abnormal
9
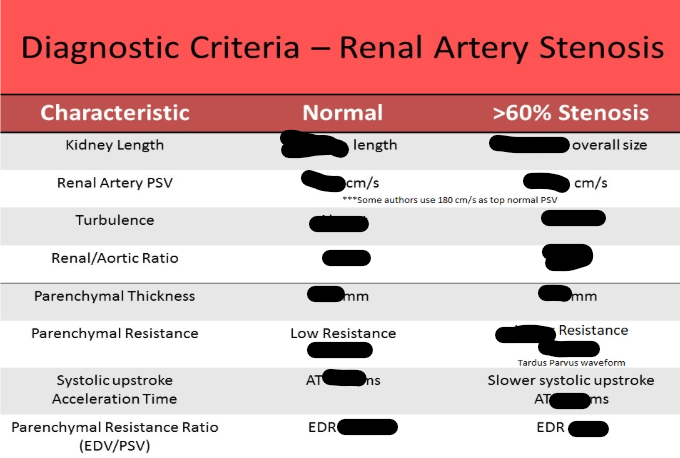
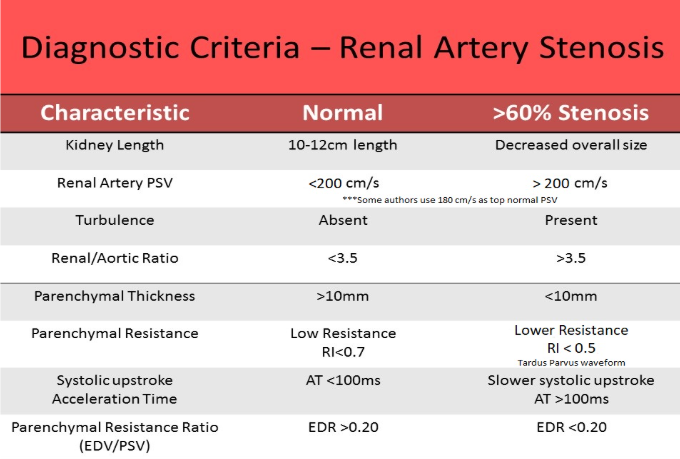
how is edr calculated and what does it evaluate
edv/psv, evaluates parenchymal resistance
when is the renal/aortic ratio invalid in patients
when they have aaa or aortic stenosis, which can artificially reduce velocities
increased resistance in the renal arteries can indicate
distal stenosis or kidney disease
stenosis causes the _____ to disappear, making the waveform more rounded
early systolic peak
renal artery occlusion will cause the echogenicity of the kidney to
increase
renal artery occlusion will cause the contralateral kidney to _____ in size
increase
renal artery occlusion will cause the affected kidney to _____ in size
decrease
renal transplant is the gold standard for patients with
end stage renal disease
most common site for renal transplant
right iliac fossa
most common sites for renal arterial and venous anastomosis in renal transplant
external iliac artery and vein (internals are used as an alternative)
how to calculate velocity ratio for transplanted kidney
psv of main renal artery of allograft / native iliac artery psv
#1 acute cause of allograft failure
acute tubular necrosis
causes of allograft failure
infection
vascular thrombosis/stenosis
rejection
drug toxicity
signs of allograft failure
oliguria
elevated BUN
elevated creatinine
acute vs chronic rejection
acute is within 1-3 weeks
chronic starts after 3 months, is progressive decrease