Psych Test 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:44 AM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
Yerkes Dodson Law
A moderate level of arousal is the best level for us to be motivated
\
(For example, you might do better at an athletic event if you are excited about participating or do better on an exam if you are somewhat anxious about your score)
\
(For example, you might do better at an athletic event if you are excited about participating or do better on an exam if you are somewhat anxious about your score)
2
New cards
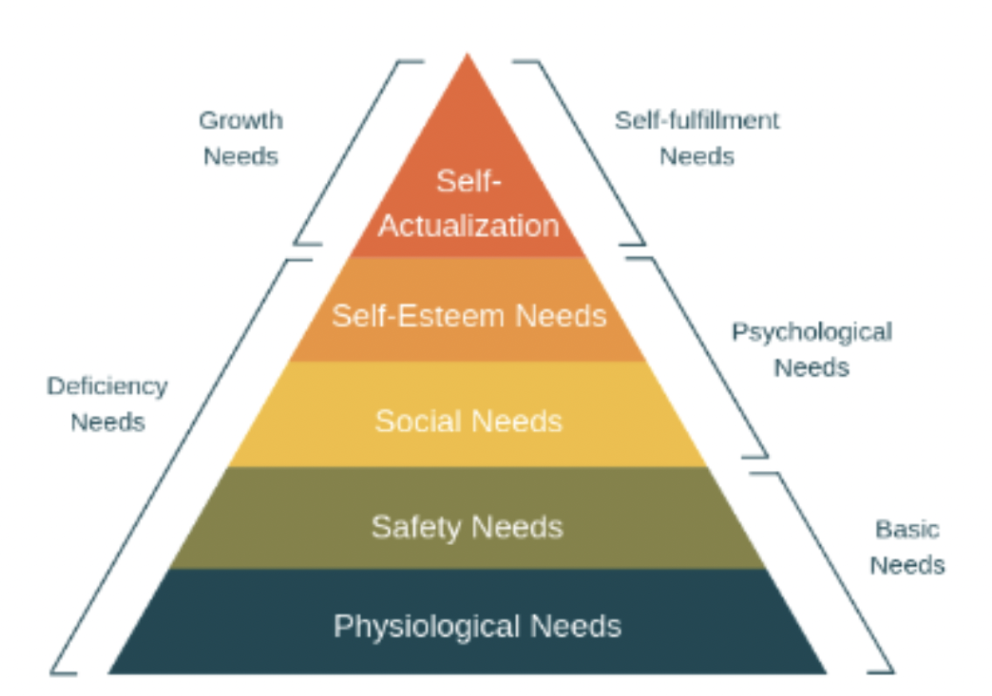
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
The idea that people are driven by many
needs
- Self actualization: when someone has achieved their personal dreams and aspirations
\
needs
- Self actualization: when someone has achieved their personal dreams and aspirations
\
3
New cards
What motivates eating?
* Hypothalamus
* Internal sensations (glucostatic hypothesis)
* Hormonal activity
* Insulin
* Ghrelin
* Leptin (lipostatic hypothesis)
* Times and taste
* Culture
* The reason, why we get hungry at specific times, is because of classical conditioning, not because we’re actually hungry (you can train your body not to get hungry at a specific time)
* Variety plays a role in if they’re still hungry
* Internal sensations (glucostatic hypothesis)
* Hormonal activity
* Insulin
* Ghrelin
* Leptin (lipostatic hypothesis)
* Times and taste
* Culture
* The reason, why we get hungry at specific times, is because of classical conditioning, not because we’re actually hungry (you can train your body not to get hungry at a specific time)
* Variety plays a role in if they’re still hungry
4
New cards
Obesity
* Thrifty-gene hypothesis: evolution has favored those with efficient metabolisms that maximize fat storage
* Dopamine reward system
* Environmental influences
* Increased abundance of fast and processed foods
* Widespread consumption of sugary, high-caloric soft drinks
* Decline in exercise
* Increase portion sizes
* Dopamine reward system
* Environmental influences
* Increased abundance of fast and processed foods
* Widespread consumption of sugary, high-caloric soft drinks
* Decline in exercise
* Increase portion sizes
5
New cards
Eating disorders
* Anorexia nervosa
* People who don’t consume enough calories but perceive themselves at being fat, they will restrict their caloric intake because of negative perception
* Risk of organ failure and brittle bones
* Bulimia nervosa
* Very much a western disorder, mostly because other countries don’t have a thin ideal
* People who don’t consume enough calories but perceive themselves at being fat, they will restrict their caloric intake because of negative perception
* Risk of organ failure and brittle bones
* Bulimia nervosa
* Very much a western disorder, mostly because other countries don’t have a thin ideal
6
New cards
Emotions vs moods
Emotions: an immediate and intense response to environmental changes or internal thoughts. An Emotion is an intense feeling that is short-term and is typically directed at a source. Emotions can often have indicative facial expressions and body language as well. A Mood is a state of mind that tends to be less intense than an emotion, and does not necessarily need a contextual stimulus. Moods: long-lasting, less intense emotional states
7
New cards
Primary Emotions
* Anger
* Fear
* Sadness
* Disgust
* Happiness
* Contempt
* Surprise
* Fear
* Sadness
* Disgust
* Happiness
* Contempt
* Surprise
8
New cards
Secondary Emotions
* Guilt
* Anticipation
* Embarrassment
* Jealousy
* Love
* Anticipation
* Embarrassment
* Jealousy
* Love
9
New cards
Classifying emotions
* Discrete emotional approach: definitive specific categories of emotions
* Dimensional approach: uses dimensions to make sense of emotions
* Alexithymia: difficulty identifying and labeling emotions
* Dimensional approach: uses dimensions to make sense of emotions
* Alexithymia: difficulty identifying and labeling emotions
10
New cards
Display rules
* Govern how and when people exhibit emotions
* Socialization
* Culture
* Emotion work: expression of emotion, often because of a role requirement, that a person doesn’t really feel
* Emotions strengthen interpersonal dynamics
* Guilt strengthens social bonds
* Embarrassment acknowledges social awkwardness
* Socialization
* Culture
* Emotion work: expression of emotion, often because of a role requirement, that a person doesn’t really feel
* Emotions strengthen interpersonal dynamics
* Guilt strengthens social bonds
* Embarrassment acknowledges social awkwardness
11
New cards
Emotions & Gender
* Emotions and gender:
* There are no differences in how men and women feel everyday emotions, only how they express them
* Women are more likely to express most emotions than men
* Men express anger more than women
* Early socialization plays a role
* Situational constraints
* Gender differences are not universal
* There are no differences in how men and women feel everyday emotions, only how they express them
* Women are more likely to express most emotions than men
* Men express anger more than women
* Early socialization plays a role
* Situational constraints
* Gender differences are not universal
12
New cards
Theories of emotion
* James Lange theory: how we interpret the situation determines how we feel
* Stimulus → arousal → emotion
* Cannon bard theory - arousal and emotion are separate but occur together
* Stimulus → arousal and emotion
* Schacter -singer two-factor theory: a cognitive appraisal of the situation influences how we feel
* Stimulus → arousal → label → emotion
* Stimulus → arousal → emotion
* Cannon bard theory - arousal and emotion are separate but occur together
* Stimulus → arousal and emotion
* Schacter -singer two-factor theory: a cognitive appraisal of the situation influences how we feel
* Stimulus → arousal → label → emotion
13
New cards
Misattribution of arousal
* Sometimes people misidentify the source of their arousal
* Excitation transfer: residual arousal from one event is transferred to a new stimulus
* Excitation transfer: residual arousal from one event is transferred to a new stimulus
14
New cards
Emotions and lie detector tests
* There is no physiological pattern of autonomic arousal that is specific to lying
* Polygraph results are inadmissible in most courts, even though they're still used
* Results may be used to promote false confessions
* Polygraph results are inadmissible in most courts, even though they're still used
* Results may be used to promote false confessions
15
New cards
What influences happiness?
* Happiness set point
* Life circumstances (adaptation)
* Intentional activities
* Real vs fake emotional expressions
* Life circumstances (adaptation)
* Intentional activities
* Real vs fake emotional expressions
16
New cards
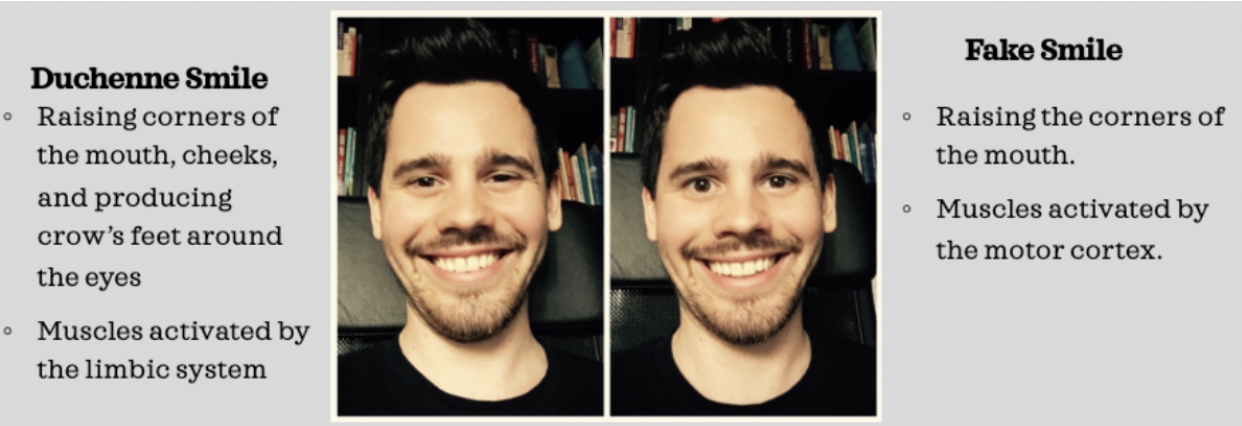
Duchenne smile vs fake smile
* Duchenne Smile - raising corners of the mouth, cheeks, and producing crows feet around the eyes (the muscles are activated by the limbic system)
* Fake Smile - Raising the corners of the mouth, muscles activated by the motor cortex
\
\
* Fake Smile - Raising the corners of the mouth, muscles activated by the motor cortex
\
\

17
New cards
What happens when we’re stressed? **General Adaptation Syndrome**
1. **Alarm phase:** the body mobilizes the sympathetic nervous system to meet an immediate threat
2. **Resistance phase:** The body attempts to resist or cope with a stressor that cannot be avoided
3. **Exhaustion phase:** persistent stress depletes the body of energy, thereby increasing vulnerability to physical problems and illness
18
New cards
What is stress
* A type of response that typically involves an unpleasant state
* When do we experience it?
* Uncertainty
* Lack of control
* Concern others will evaluate or treat us negatively
* When do we experience it?
* Uncertainty
* Lack of control
* Concern others will evaluate or treat us negatively
19
New cards
2 types of stress (Distress and Eustress)
* Distress is considered to be the bad kind of stress
* Beneficial stress (an example of this would be marriage, very stressful but we don’t view it as a bad event… same goes for moving, having a baby, etc)
* Both distress and eustress create strains on the body
* Beneficial stress (an example of this would be marriage, very stressful but we don’t view it as a bad event… same goes for moving, having a baby, etc)
* Both distress and eustress create strains on the body

20
New cards
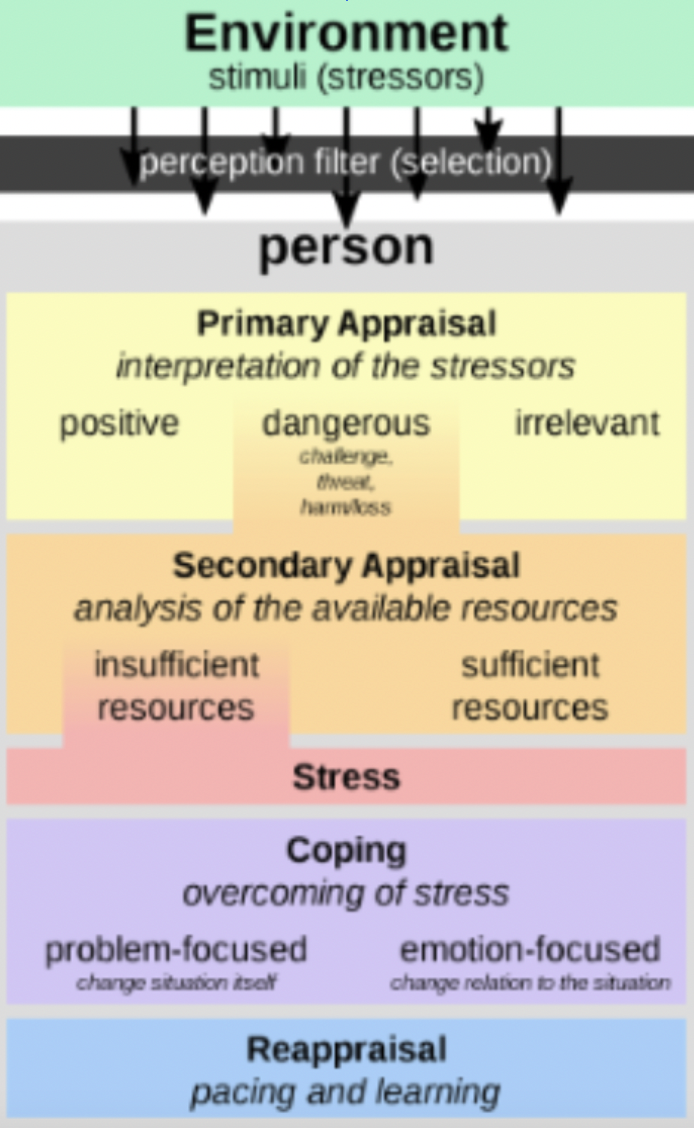
Stress Appraisal Theory
Stress appraisal refers to the process by which individuals evaluate and cope with a stressful event. Stress appraisal theory is concerned with individuals' evaluation of the event, rather than with the event per se. People differ in how they construe what is happening to them and their options for coping.
21
New cards
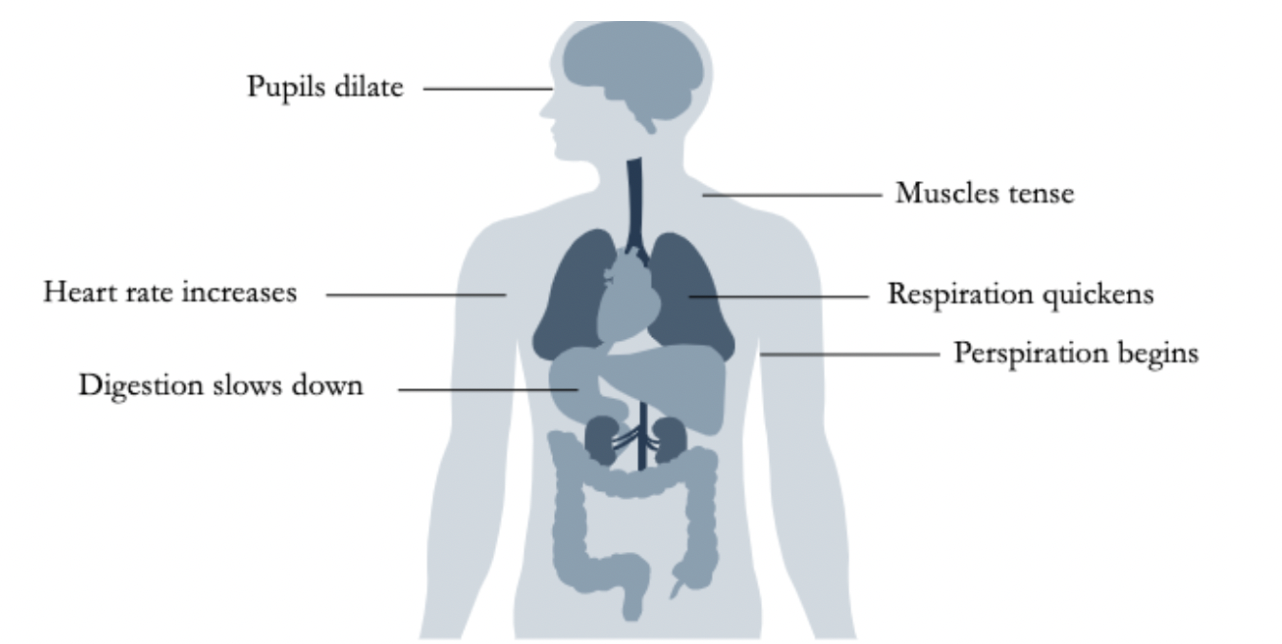
SAM Axis
* Being able to deal effectively with a stressor is important
* Physical and psychological responses that come with stress are important
* SAM Axis is basically the alarm phase
* Reactivity:
* Challenge reactivity
* Heart rate increases
* Blood vessels expand
* Enhanced performance
* Threat reactivity
* Heart rate increases
* Blood vessels constrict
* Inhibited performance
* Physical and psychological responses that come with stress are important
* SAM Axis is basically the alarm phase
* Reactivity:
* Challenge reactivity
* Heart rate increases
* Blood vessels expand
* Enhanced performance
* Threat reactivity
* Heart rate increases
* Blood vessels constrict
* Inhibited performance
22
New cards
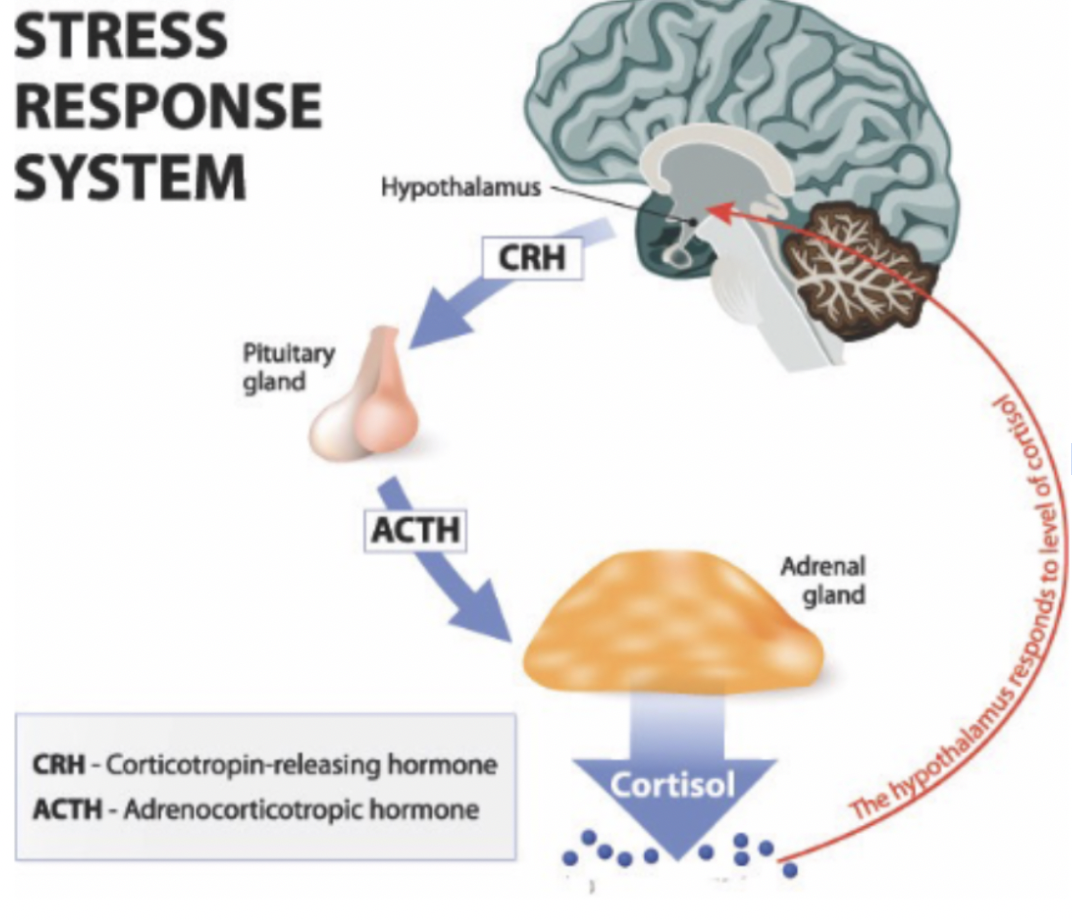
HPA Axis
One of the important stress responses our bodies experience
(tells your body when to go into fight or flight mode basically)
(tells your body when to go into fight or flight mode basically)
23
New cards
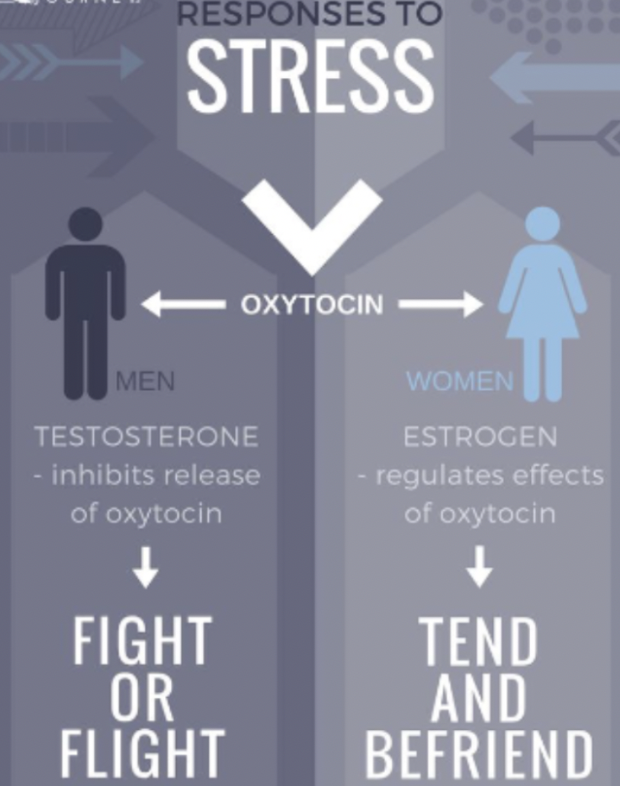
Sex differences in responses to stress
* Women may respond differently in stressful situations than men
* Tend and befriend response
* Oxytocin
* Men usually go for a fight or flight response
* Tend and befriend response
* Oxytocin
* Men usually go for a fight or flight response
24
New cards
Effects of stress
* Allostatic load: the sustained activation of many physiological systems in response to frequent or chronic stressors
* Chronic stress can lead to the progression of disease or illnesses
* Psychoneuroimmunology: stress disrupts the communication between the brain and the body which weakens the immune system
* Stress causes damage at the cellular level
* Shortening of telomeres (Tells the cell how long it has to live)
* Stress can make you look older, it affects the phenotype of your body
* Chronic stress can lead to the progression of disease or illnesses
* Psychoneuroimmunology: stress disrupts the communication between the brain and the body which weakens the immune system
* Stress causes damage at the cellular level
* Shortening of telomeres (Tells the cell how long it has to live)
* Stress can make you look older, it affects the phenotype of your body
25
New cards
Stress and the immune system
* Cortisol suppresses immune system’s effectiveness
* Reduces white blood cell count
* Lack of control over inflammation response
* Our heart is one of the major organs affected by stress
* Reduces white blood cell count
* Lack of control over inflammation response
* Our heart is one of the major organs affected by stress
26
New cards
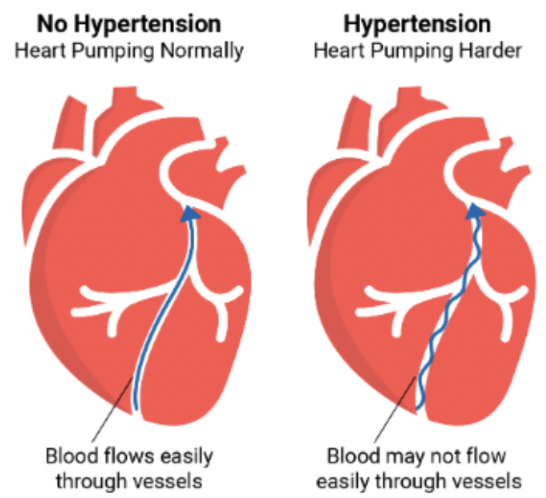
Emotions, stress, and cardiovascular problems
* Chronic stress increases your chance of developing a cardiovascular disease
* Cardiovascular issues:
* Hypertension
* Stress-induced
* Stress-induced Cardiomyopathy (Broken heart syndrome) - different from heart attack, no blocked arteries
* Women are more likely to experience cardiovascular issues
* Cardiovascular issues:
* Hypertension
* Stress-induced
* Stress-induced Cardiomyopathy (Broken heart syndrome) - different from heart attack, no blocked arteries
* Women are more likely to experience cardiovascular issues
27
New cards
Stress & The Mind
* Conscientiousness and feeling in control have been linked to better physical and psychological outcomes
* Optimism may be bad or good
* Unrealistic optimism vs realistic optimism
* Optimism may be bad or good
* Unrealistic optimism vs realistic optimism
28
New cards
Gene x environment interaction
* Diathesis-stress model
* Differential sensitivities hypothesis
* Epigenetics (reversable)
* Genetic predisposition for how you’re affected by traumatic events, you’re also more likely to benefit more from positive events
* People who are highly stressed can add that onto their genes and they’re likely to pass on a bad stress response
* Differential sensitivities hypothesis
* Epigenetics (reversable)
* Genetic predisposition for how you’re affected by traumatic events, you’re also more likely to benefit more from positive events
* People who are highly stressed can add that onto their genes and they’re likely to pass on a bad stress response
29
New cards
Coping styles
Coping styles:
* Problem-focused coping: attempting to manage or alter the stressor
* Emotion-focused coping: attempting to reduce the negative emotions associated with the stress
* In situations where we are unable to change what’s happening, we rethink the problem
Rethinking the problem:
1. Reappraising the situation
2. Learning from experience
3. Making social comparisons
* Upward social comparisons: comparing yourself to someone higher than you, could be good or bad
* Downward social comparison: people are more likely to make downward social comparisons when someone is going through something worse, which makes us feel better about ourselves
* Problem-focused coping: attempting to manage or alter the stressor
* Emotion-focused coping: attempting to reduce the negative emotions associated with the stress
* In situations where we are unable to change what’s happening, we rethink the problem
Rethinking the problem:
1. Reappraising the situation
2. Learning from experience
3. Making social comparisons
* Upward social comparisons: comparing yourself to someone higher than you, could be good or bad
* Downward social comparison: people are more likely to make downward social comparisons when someone is going through something worse, which makes us feel better about ourselves
30
New cards
Individual differences in coping
* Hardiness
* Commitment
* Challenge
* Control
* Commitment
* Challenge
* Control
31
New cards
Positivity and Health
* Positive psychology focuses on the strengths and virtues that help people thrive
* Positive affect linked to:
* Longer life
* Enhanced immune system functioning
* Positive affect linked to:
* Longer life
* Enhanced immune system functioning
32
New cards
Social Support:
* Individuals who have good social support are more likely to survive than those who have poor or no social support
* Good social support boosts the immune system
* People with a smaller social circle were more likely to die in a 9-year period than those who had more friends
* Good social support boosts the immune system
* People with a smaller social circle were more likely to die in a 9-year period than those who had more friends
33
New cards
Trust
* Trust is associated with better health and a longer life
* Oxytocin increases trust
* Increasing social bonds
* Oxytocin increases trust
* Increasing social bonds
34
New cards
Finding meaning
* Many people turn to religion to find a sense of meaning in the face of stress
* Can help people manage distress and maintain a sense of well-being
* Outcomes are often worse for those who find themselves questioning whether God has abandoned them or is punishing them
* Finding meaning in life is therapeutic
* Can help people manage distress and maintain a sense of well-being
* Outcomes are often worse for those who find themselves questioning whether God has abandoned them or is punishing them
* Finding meaning in life is therapeutic
35
New cards
To Inhibit or to Express
* Inhibition of thoughts and emotions is stressful
* Divulging thoughts and feelings reduces the effect of negative emotions
* Writing can produce insight and understanding
* Suppressing emotions is bad for you
* Divulging thoughts and feelings reduces the effect of negative emotions
* Writing can produce insight and understanding
* Suppressing emotions is bad for you
36
New cards
Staying healthy
* Precontemplation
* Contemplation
* Preparation
* Action
* Maintenance
* Contemplation
* Preparation
* Action
* Maintenance
37
New cards
Humor: broaden-and-build function
The idea that positive emotions evolved as a signal of safety, allowing for exploration and creativity
38
New cards
Personality
Old philosophers believed that the amount of blood in your body made you more or less sluggish
* Patterns of thought and behavior that make a person react to certain situations in relatively consistent ways
* Personality has both a biological and psychological aspect
* Patterns of thought and behavior that make a person react to certain situations in relatively consistent ways
* Personality has both a biological and psychological aspect
39
New cards
Psychodynamic theory
Psychodynamics, also known as psychodynamic psychology, in its broadest sense, is an approach to psychology that emphasizes systematic study of the psychological forces underlying human behavior, feelings, and emotions and how they might relate to early experience
40
New cards
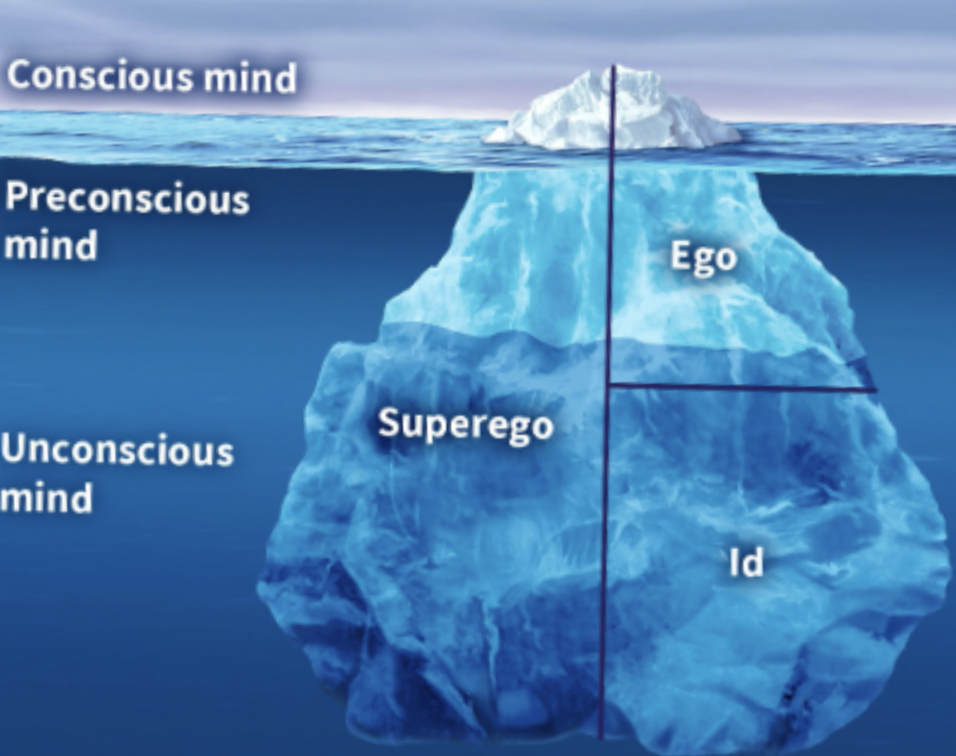
Psychodynamic Theory (Id, Ego, Superego)
* Id - the deepest level of thoughts, arousal, sexual
* + pleasure principle
* Ego - works on the ID and tries to decrease the want, keeps the ID in check
* Operates on a reality principle, serving as a referee between what the instincts want and what society demands of us
* Superego - basically just confirms what’s right and wrong
* The seat of moral conscious
* + pleasure principle
* Ego - works on the ID and tries to decrease the want, keeps the ID in check
* Operates on a reality principle, serving as a referee between what the instincts want and what society demands of us
* Superego - basically just confirms what’s right and wrong
* The seat of moral conscious
41
New cards
Defense mechanisms
Displacement, Projection, Repression, Denial
42
New cards
Displacement
Displacement: a defense mechanism in which the ego redirects the aggressive impulses of the id from their intended targets to more defenseless targets
* +current evidence supports
For example, a person who is angry at their boss may “take out” their anger on a family member by shouting at them.
* +current evidence supports
For example, a person who is angry at their boss may “take out” their anger on a family member by shouting at them.
43
New cards
Projection
Projection: a defense mechanism in which people, instead of acknowledging it in themselves, see others as possessing a disliked trait or feeling
* + current evidence supports
For example, the classroom bully who teases other children for crying but is quick to cry is an example of projection.
* + current evidence supports
For example, the classroom bully who teases other children for crying but is quick to cry is an example of projection.
44
New cards
Repression
a defense mechanism in which the ego keeps unwanted feelings, thoughts, and memories below the level of conscious awareness
* + current evidence does not fully support
Example: Jacob cannot remember certain painful memories as a child. To protect himself, he unconsciously represses these memories from his consciousness.
* + current evidence does not fully support
Example: Jacob cannot remember certain painful memories as a child. To protect himself, he unconsciously represses these memories from his consciousness.
45
New cards
Denial
A defense mechanism in which the ego prevents the perception of a painful or threatening reality as it is occurring.
* + Current evidence supports
Someone denies that they have an alcohol or substance use disorder because they can still function and go to work each day.
* + Current evidence supports
Someone denies that they have an alcohol or substance use disorder because they can still function and go to work each day.
46
New cards
Identifying central traits (Big 5 traits)
* Openness to experience
* Conscientiousness
* Extraversion
* Agreeableness
* Neuroticism
* Conscientiousness
* Extraversion
* Agreeableness
* Neuroticism
47
New cards
Trait Theory
* Gordon Allport was the first to pioneer the study of personality traits
* Cardinal: dominant trait
* Central: General dispositions
* Secondary: Relevant in certain contexts
* The traits shape how a person interprets the world and can lead people to behave in similar ways across different situations
* Functionally equivalent situations are those that cue a similar response from a person
* Cardinal: dominant trait
* Central: General dispositions
* Secondary: Relevant in certain contexts
* The traits shape how a person interprets the world and can lead people to behave in similar ways across different situations
* Functionally equivalent situations are those that cue a similar response from a person
48
New cards
The Dark Triad
(people who score a lot higher on the dark triad are more likely to seek revenge, exploit others, etc)

49
New cards
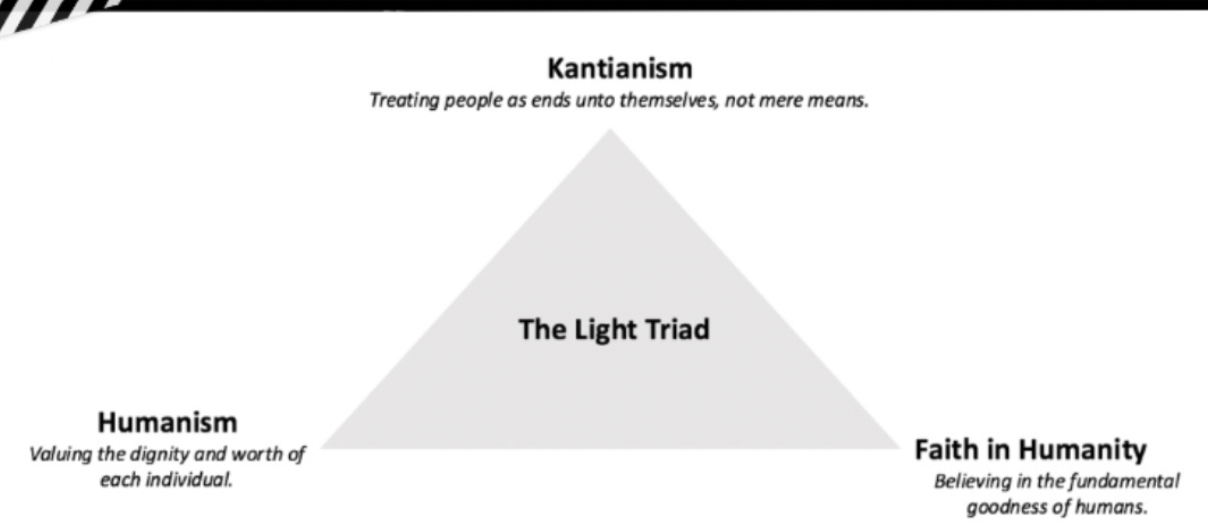
The Light Triad
The light triad was associated with being older, being female, less childhood unpredictability, as well as higher levels of religiosity, spirituality, life satisfaction, acceptance of others, belief that others are good, belief that one’s self is good, compassion, empathy, openness to experience, conscientiousness, positive enthusiasm, having a quiet ego and a belief that one can live on through nature and biosociality (having children) after one’s personal death.
50
New cards
Measuring personality
* Self-reports: questionnaires that involve reporting on one’s own personality traits
* MMPI and California Q-sort
* Advantages
* Quick and inexpensive
* Disadvantages
* Social desirability responding
* Projective tests: provides an ambiguous stimulus onto which the test taker “projects” his or her personality
* Rorschach Inkblot test and thematic apperception test
* Advantages
* Avoids social desirability concerns
* Disadvantages
* Poor validity and reliability, cultural bias
* Behavioral tests: gathering information about people's characteristics by assessing their overt behavior in highly standardized miniature situations
* Advantages
* Avoids social desirability to respond
* Disadvantages
* Lacks validity
* MMPI and California Q-sort
* Advantages
* Quick and inexpensive
* Disadvantages
* Social desirability responding
* Projective tests: provides an ambiguous stimulus onto which the test taker “projects” his or her personality
* Rorschach Inkblot test and thematic apperception test
* Advantages
* Avoids social desirability concerns
* Disadvantages
* Poor validity and reliability, cultural bias
* Behavioral tests: gathering information about people's characteristics by assessing their overt behavior in highly standardized miniature situations
* Advantages
* Avoids social desirability to respond
* Disadvantages
* Lacks validity
51
New cards
Why Myers-Briggs doesn’t work
* Developers had no training in psychometrics or psychological assessment
* It categorizes personality traits
* Lacking validity and reliability
* It is not related to any life outcomes
* It categorizes personality traits
* Lacking validity and reliability
* It is not related to any life outcomes
52
New cards
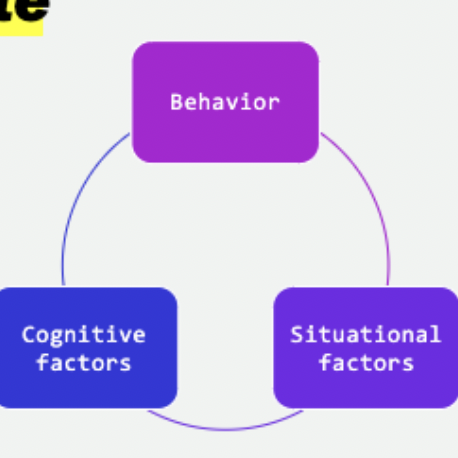
The person-situation debate
* Challenges to trait personality characteristics
1. Traits and behavior may not align
2. Consistency of traits
3. Traits are templates
* Reciprocal determinism: personality is shaped by the interaction of the environment and aspects of the individual
* Strong situations
* Weak situations
1. Traits and behavior may not align
2. Consistency of traits
3. Traits are templates
* Reciprocal determinism: personality is shaped by the interaction of the environment and aspects of the individual
* Strong situations
* Weak situations
53
New cards
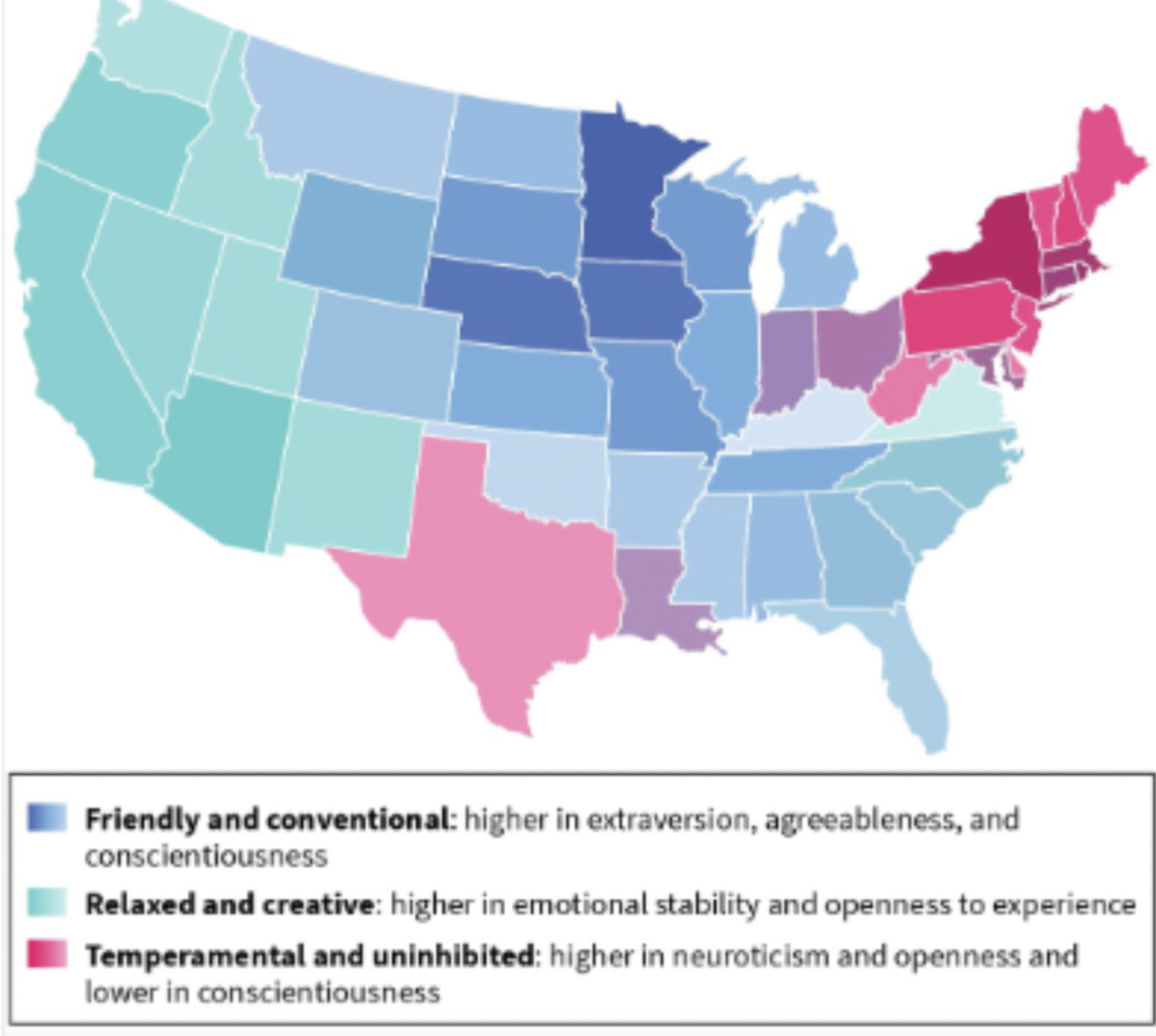
Cultural differences
* Differences exist in the average levels of traits across cultures
* Political and cultural forces also shape how someone perceives average trait levels in their own culture, which is not always accurate
* Regional differences have been found in America
* Political and cultural forces also shape how someone perceives average trait levels in their own culture, which is not always accurate
* Regional differences have been found in America
54
New cards
The Stability of Personality Traits
* Agreeableness and conscientiousness (more stable, usually older people)
* Neuroticism, extraversion, and openness to experiences (less stable, usually younger people)
* Neuroticism, extraversion, and openness to experiences (less stable, usually younger people)
55
New cards
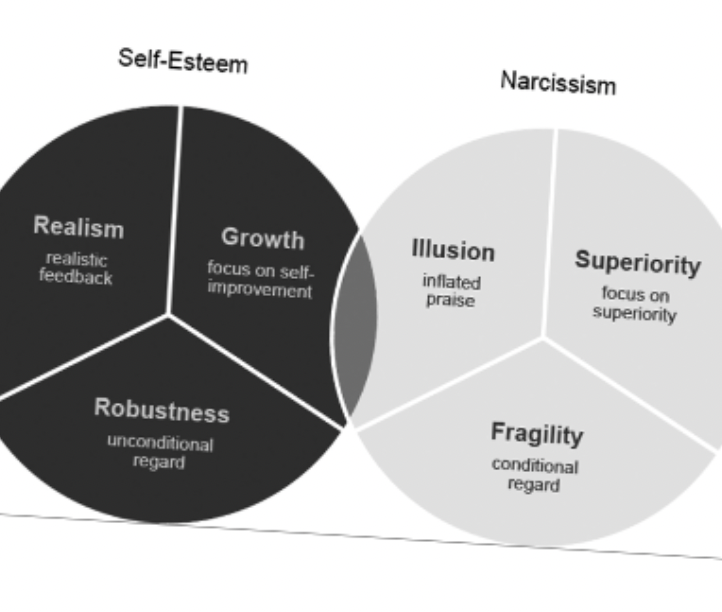
Sociometer theory
self- esteem serves as a measure of social appeal. Low self-esteem linked to a variety of issues. High self-esteem + Secure high self-esteem + Fragile high self-esteem
56
New cards
Perceiving personality
* The behavioral activation system (BAS): a biological system that governs people’s general tendencies towards approaching things that are rewarding
* Behavioral inhabitation system (BIS): A biological system that governs people’s general tendencies toward avoiding things that are threatening
* Behavioral inhabitation system (BIS): A biological system that governs people’s general tendencies toward avoiding things that are threatening
57
New cards
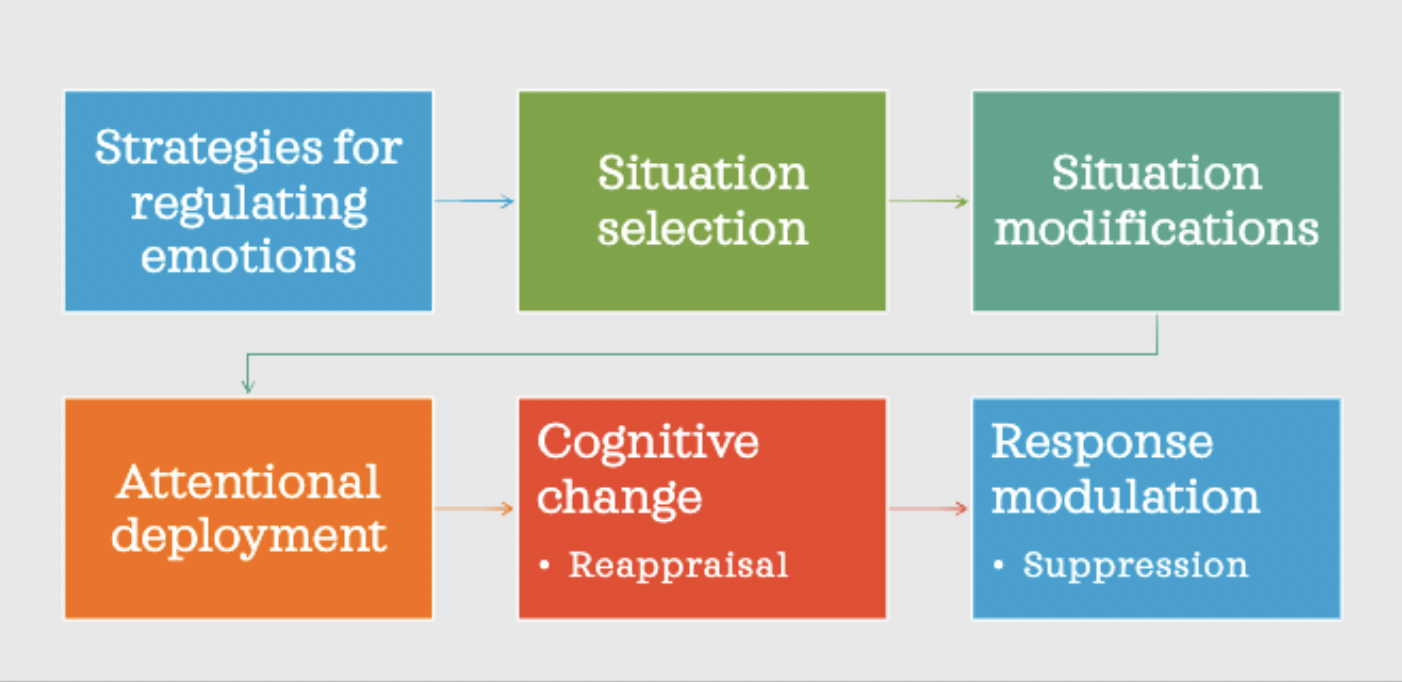
Emotion Regulation
term generally used to describe a person's ability to effectively manage and respond to an emotional experience.
58
New cards
Situation selection
Situation selection involves choosing situations based on their likely emotional impact and may be less cognitively taxing or challenging to implement compared to other strategies for regulating emotion, which require people to regulate their emotions 'in the moment'.
59
New cards
Situation modification
Situation modification involves direct efforts taken to change a situation in order to alter its emotional impact (Gross, 2008). This emotion regulation strategy deals with modifying external characteristics of the situation causing the emotion, not managing the emotion itself.
60
New cards
Attentional Deployment
Attentional deployment is an emotion regulation strategy that involves shifting attentional focus within an emotional scene in order to modulate emotional experience. Attentional deployment is widely used and effective at reducing negative affect, yet the supporting neural mechanisms are poorly understood.
61
New cards
Cognitive Change
This emotion regulation strategy involves using cognitive skills (e.g., perspective-taking, challenging interpretations, reframing the meaning of situations) to modify the meaning of a stimulus or situation that gives rise to emotional reactivity.
62
New cards
Response Modulation
Response modulation refers to efforts to modify an emotion after it has been fully generated. The most frequent form of this ER strategy is suppression, or volitional inhibition of verbal and behavioral expressions of emotions.