1 Lec 14 Exam 2: Cysts of the Jaw
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
radiolucent
Most cysts present what radiodensity?
odontogenic
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Radicular cyst
well-defined/corticated
Describe the periphery of MOST cysts:
displacement of teeth
root resorption
displacement of cortical boundaries
osseous expansion /erosion
Describe the effect that cysts have on adjacent structures:
above
In relation to the IAN canal, where will odontogenic cysts present?
non-vital
radicular cysts are associated with what tooth vitality?
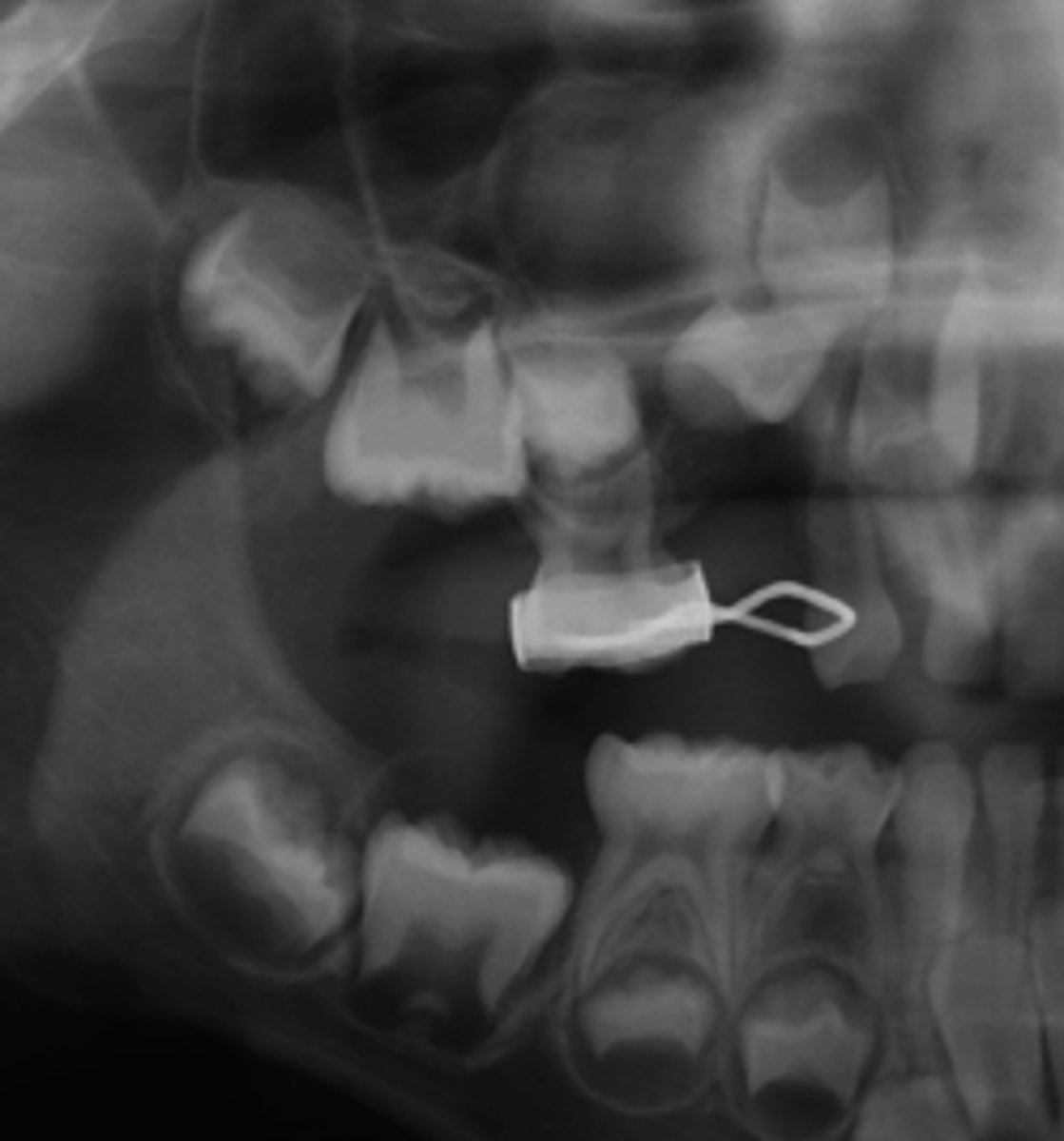
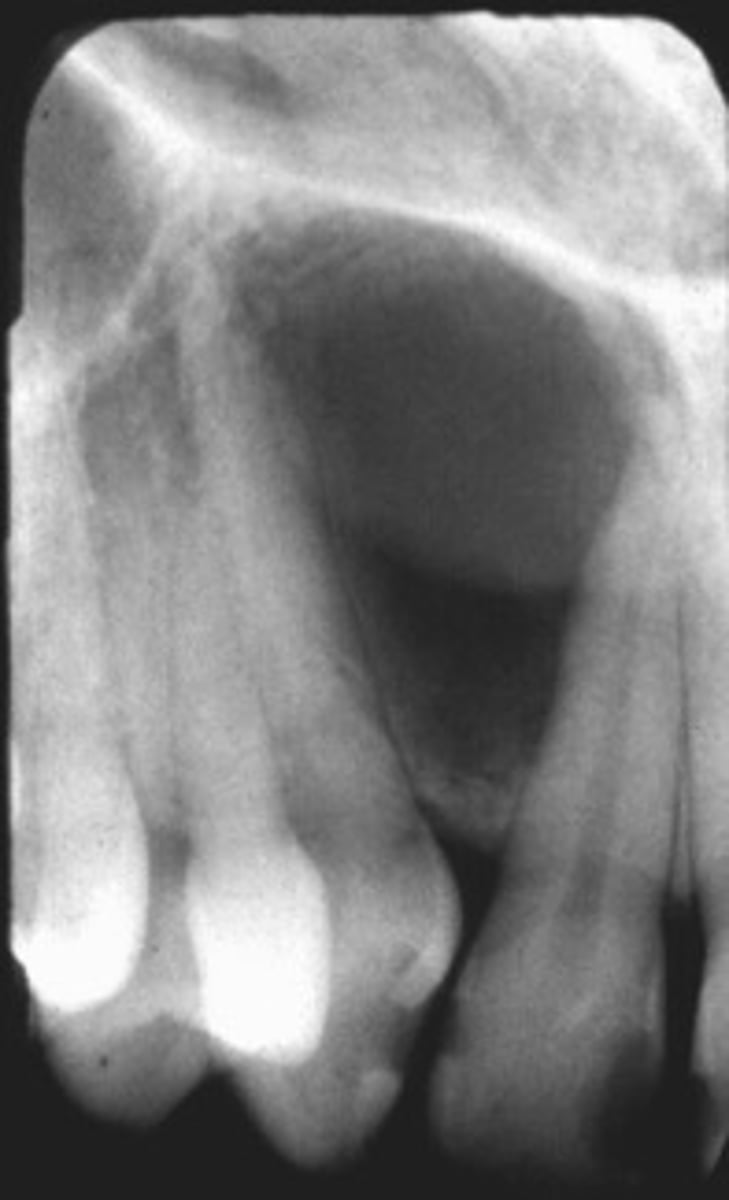
Maxillary Radicular Cyst
ID the cyst:
- Well-defined corticated lesion
- radiolucent
-LOSS of lamina dura
- displaces floor of maxillary sinus
Radicular Cyst
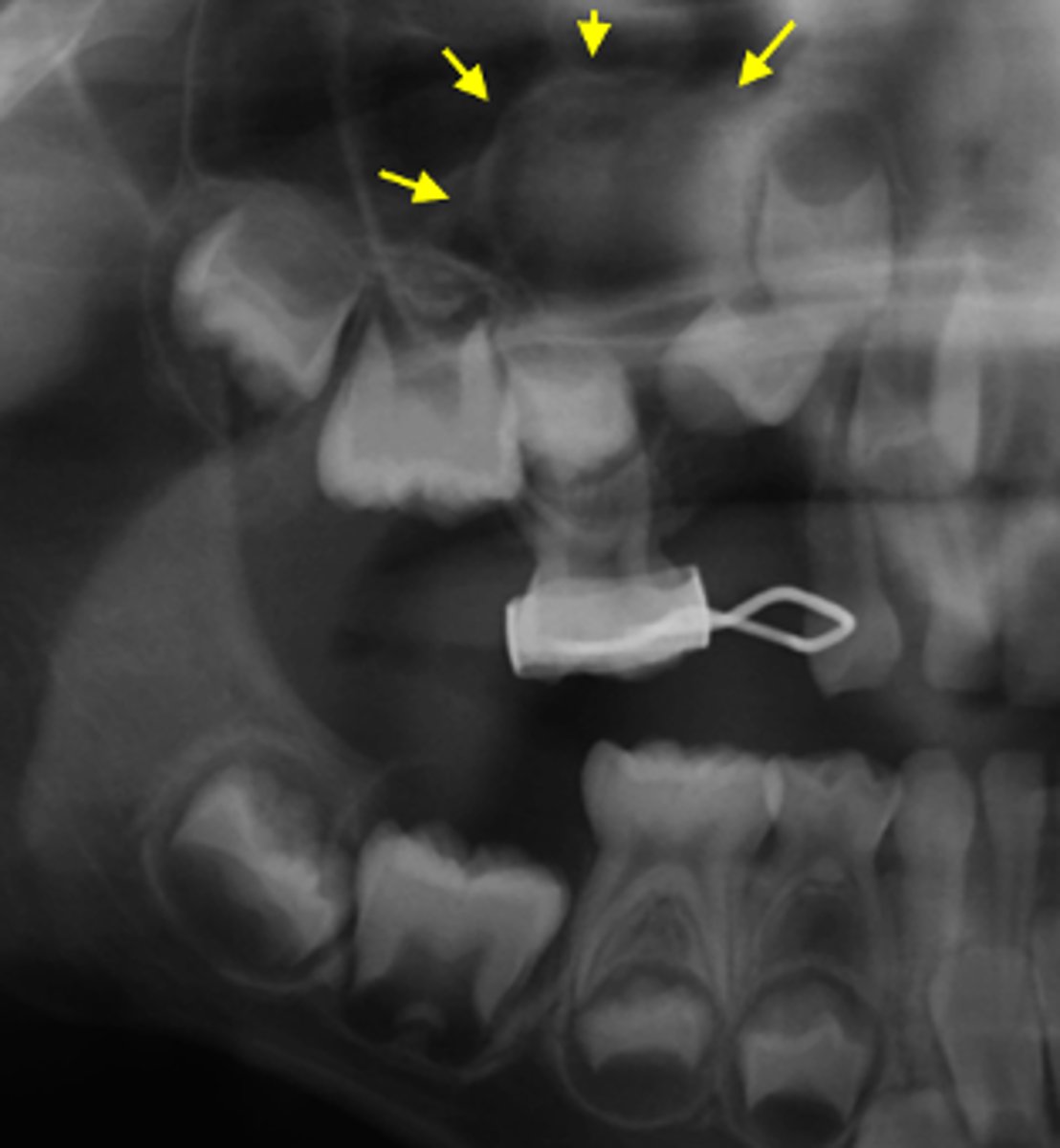
ID the cyst:
•Radiolucent lesion
•Well defined, corticated borders
•Hydraulic/round
•Periapical in location (apex of a non vital tooth)
Radicular Cyst
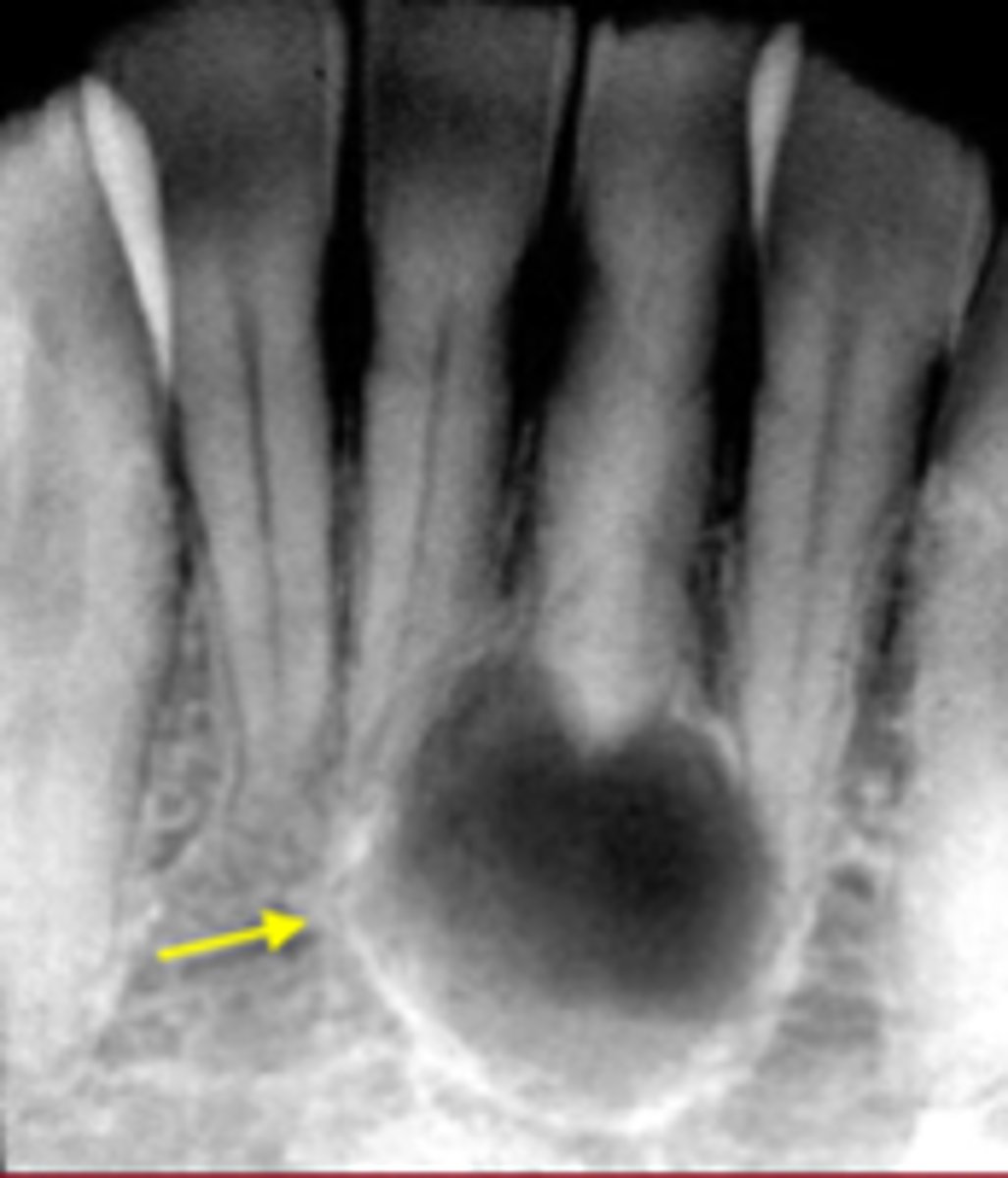
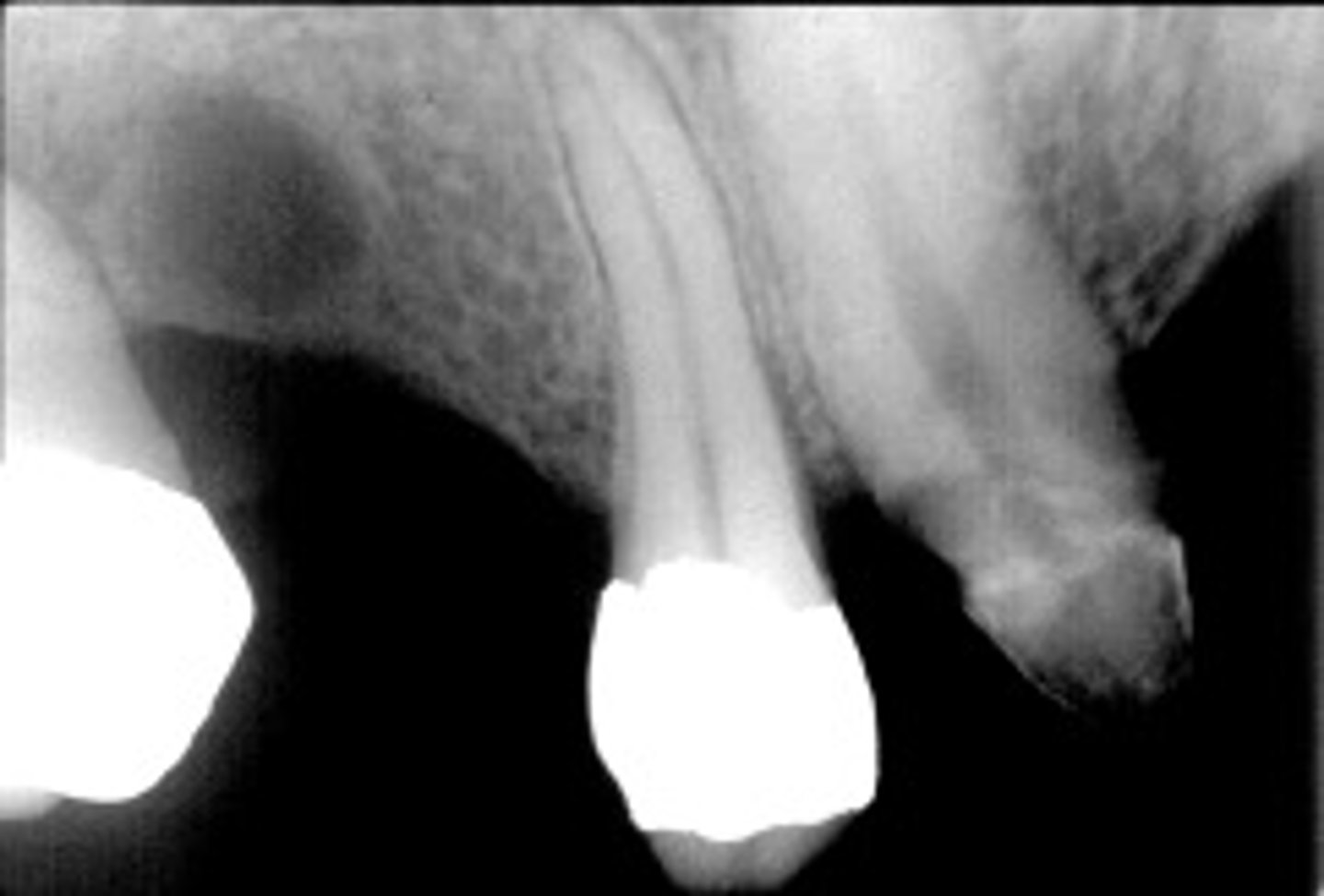
ID the cyst:
this image has intact PDL and lamina dura
How do you know this is NOT a radicular cyst?
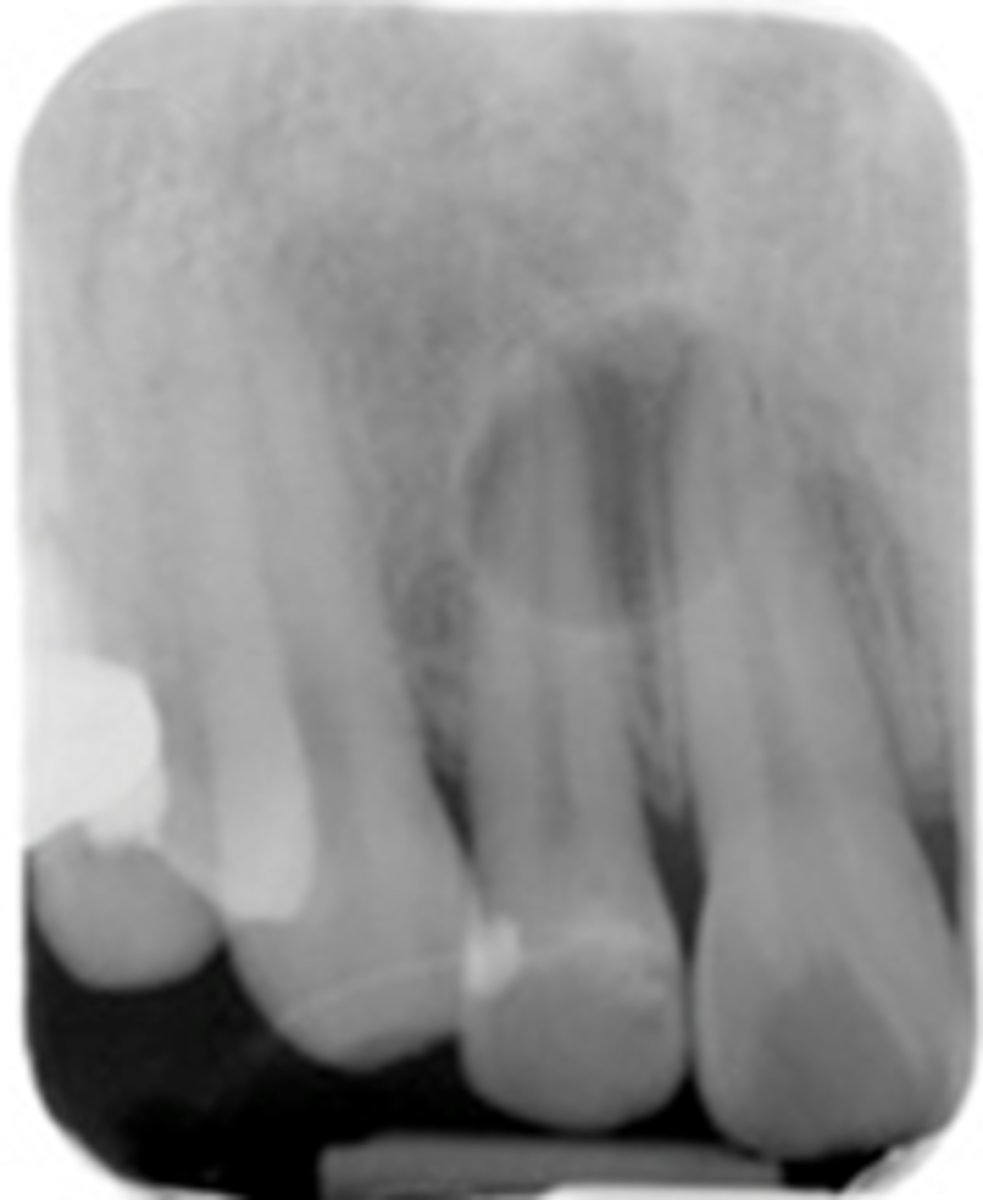
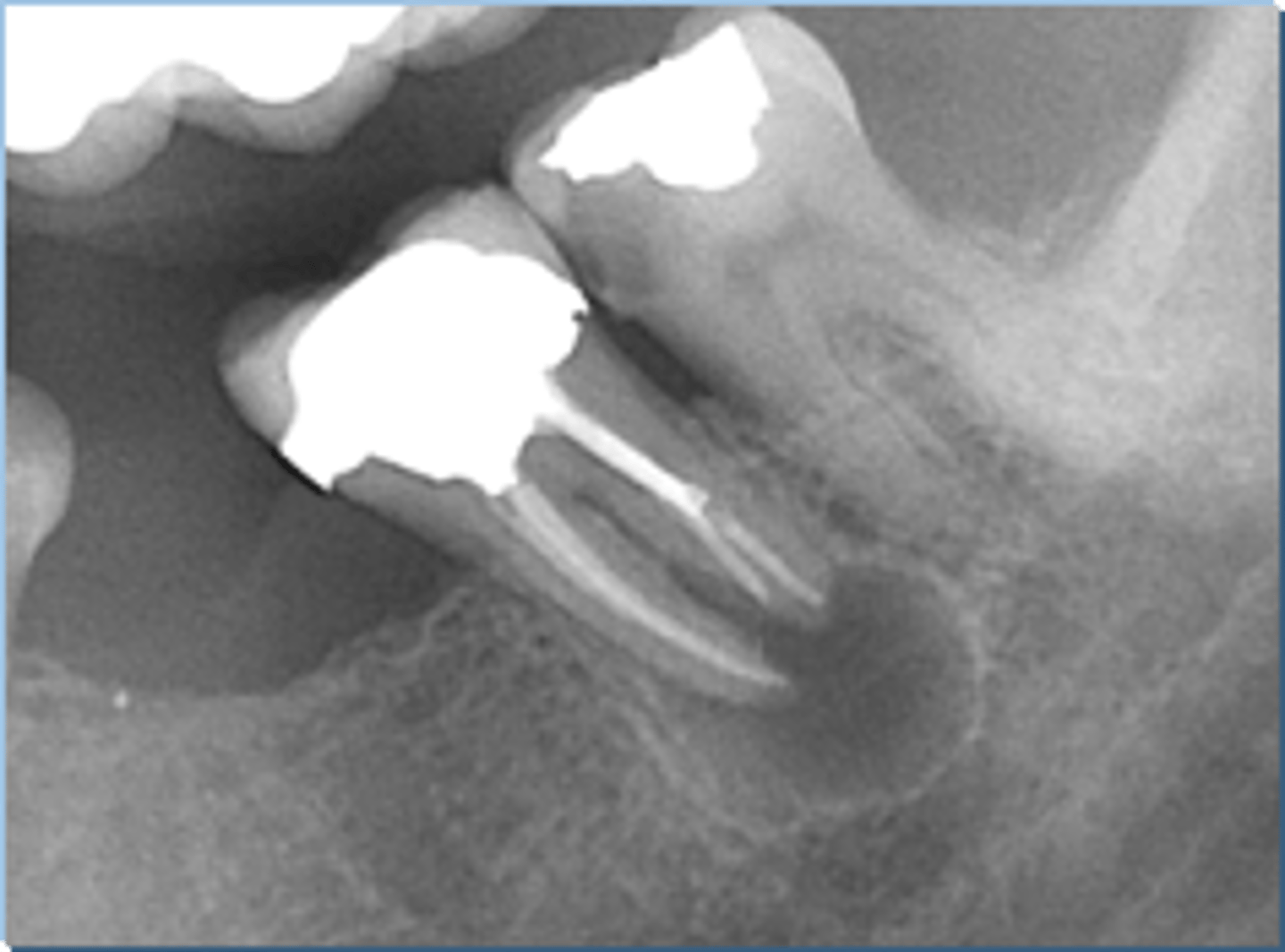
Lateral Radicular Cyst
ID the cyst (tooth is non-vital):
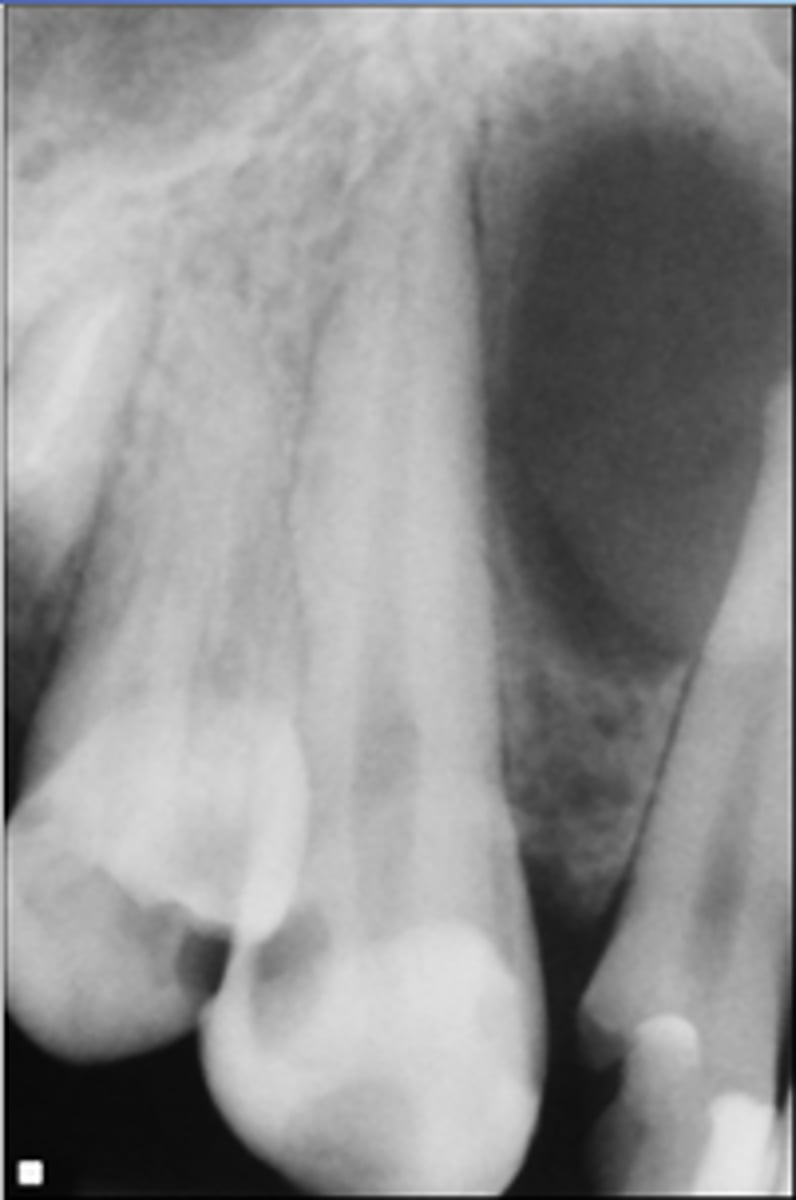
odontogenic
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Lateral Radicular cyst
non-vital
Lateral Radicular Cyst are associated with what vitality of teeth?
this image has intact PDL and lamina dura
which of these reasons prove that this cysts is NOT associated with the roots of teeth?
Periapical radiolucent lesion
Well defined
Corticated
Hydraulic/round
lamina dura
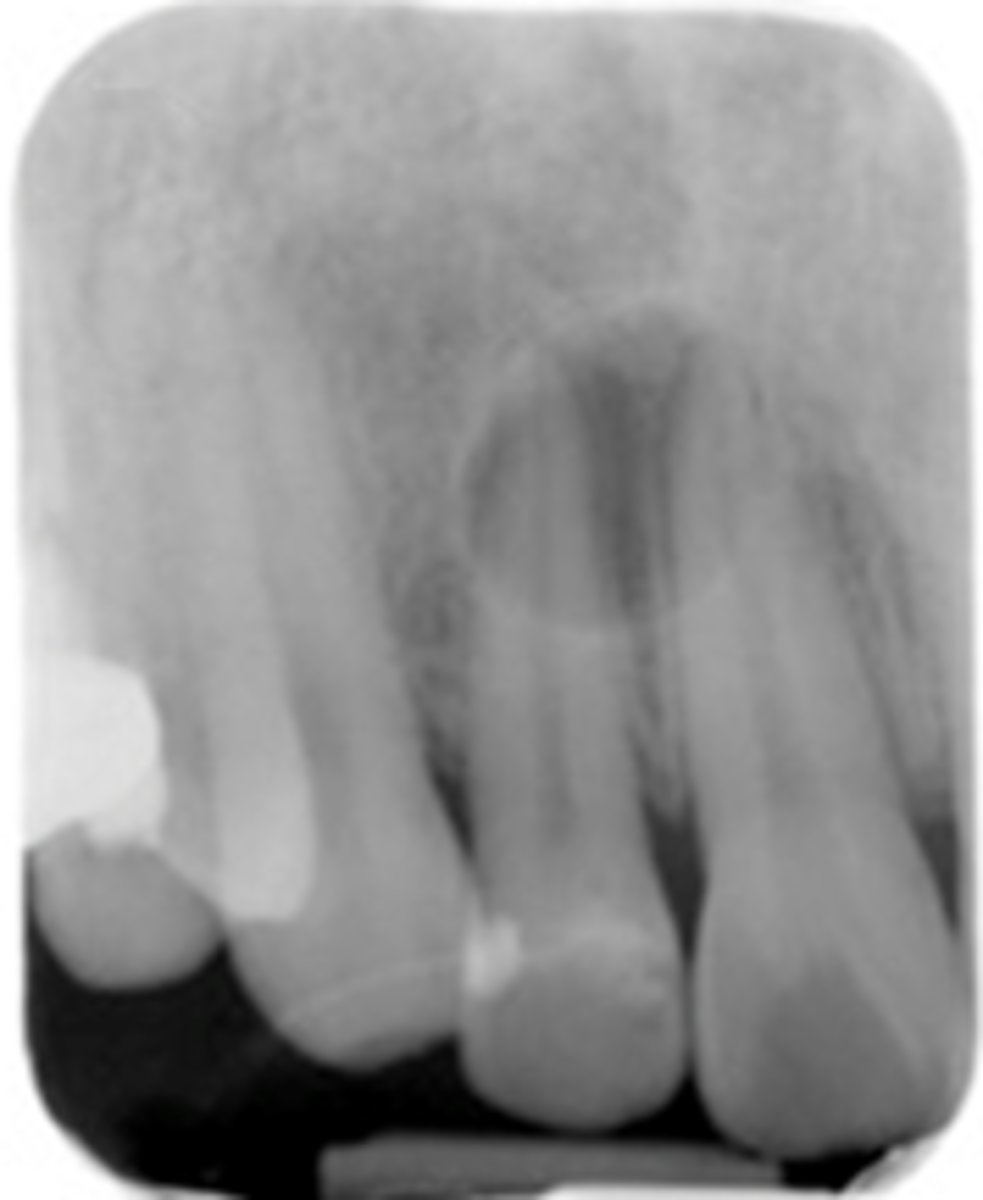
Residual Cyst
ID the cyst:
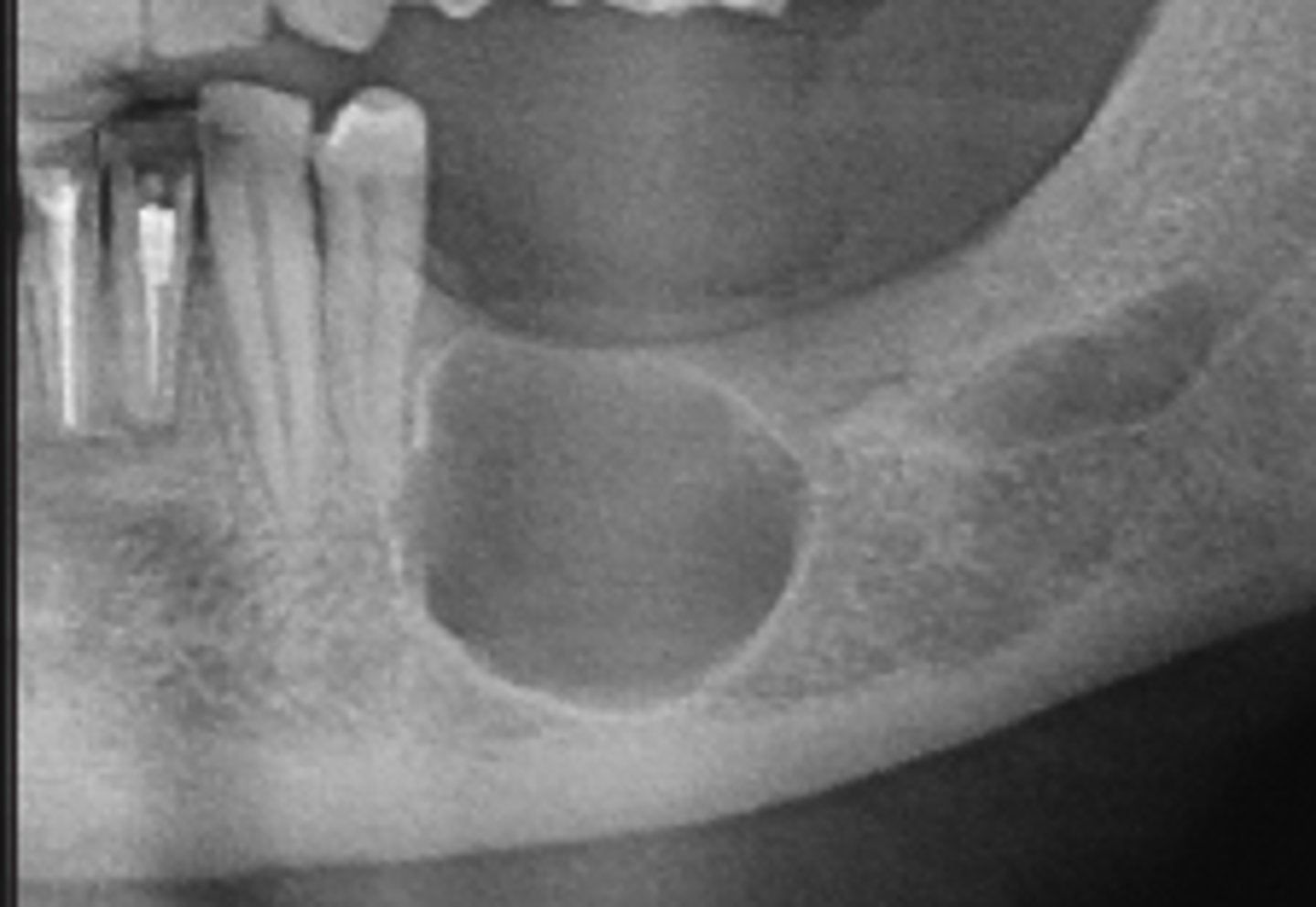
odontogenic
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Residual cyst
extracted
Residual cysts are associated with ____ teeth
Residual Cyst
ID the cyst:
Residual Cyst
•Well defined radiolucent lesion
• Can be Sclerotic or corticated borders
•Located apical to an extraction site
•Usually a radicular cyst left behind after extraction of a tooth
Dentigerous cyst
•Well defined and corticated periphery
•radiolucent
•Pericoronal (associated with crown of unerupted tooth)
•Usually envelops the crown symmetrically
•Usually unilocular
•Displacement of teeth/adjoining anatomical structures
•Displaces associated tooth in an apical direction
•Osseous expansion- of outer cortical boundary of the involved jaw
odontogenic
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Dentigerous cyst
vital
Dentigerous Cyst are associated with ____ teeth
Dentigerous cyst
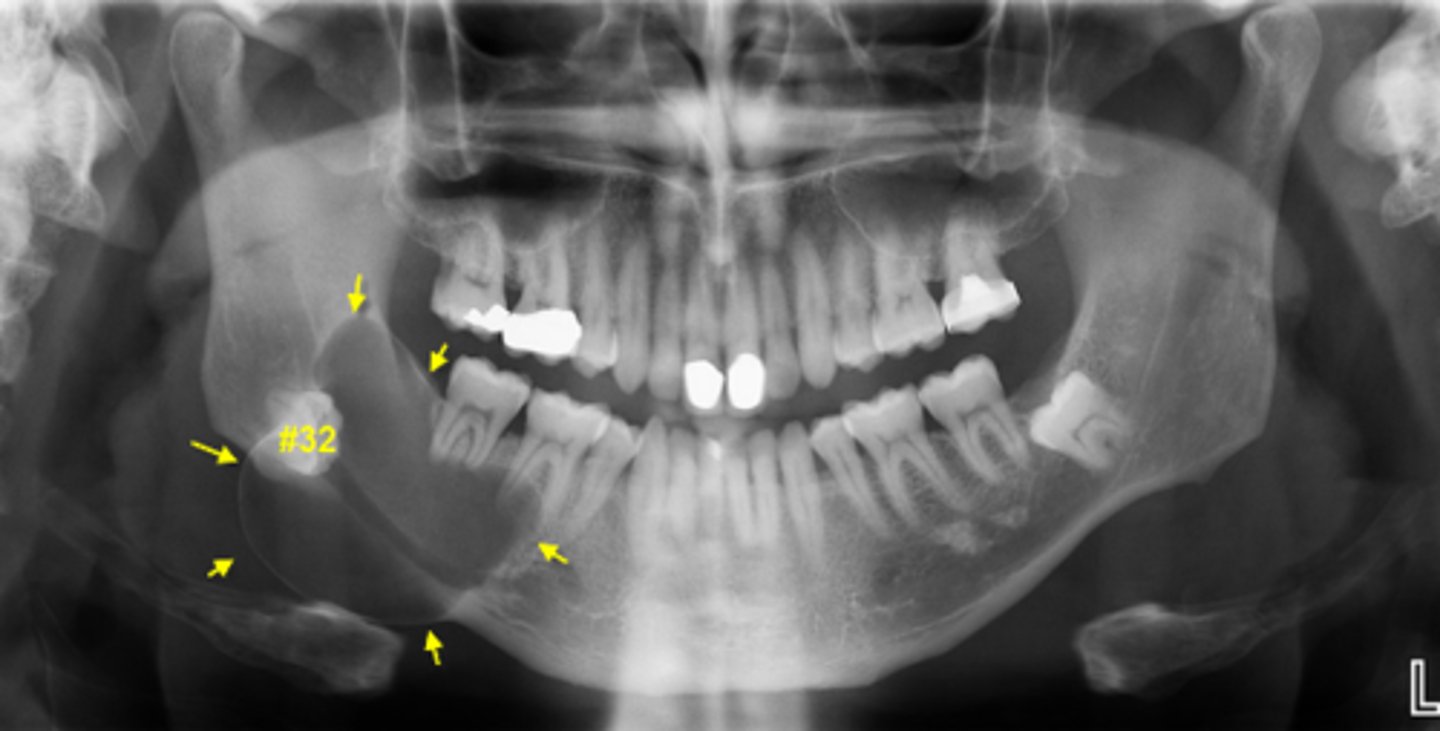
ID the cyst:
Dentigerous cyst
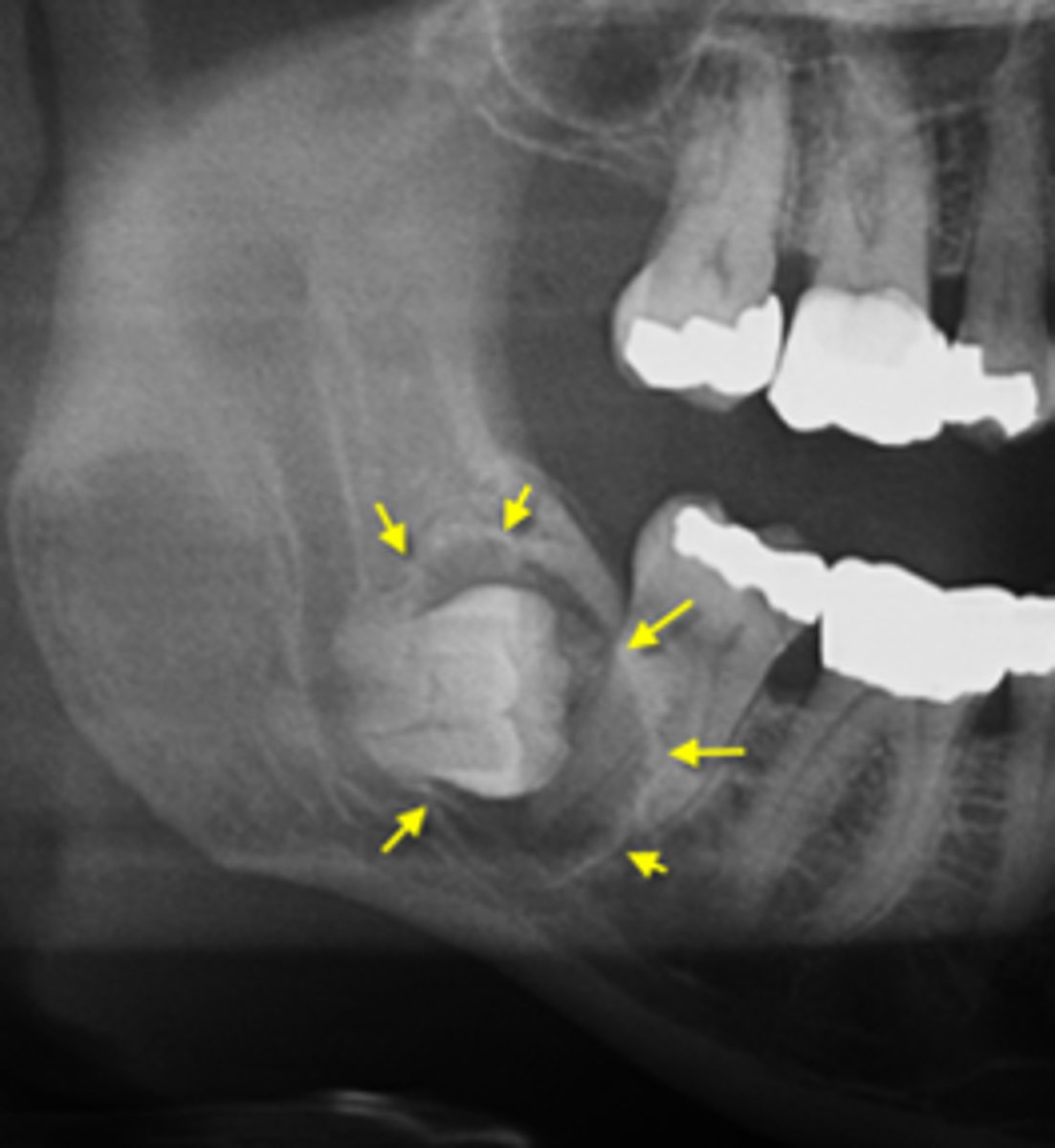
ID the cyst:
Dentigerous cyst
ID the cyst:
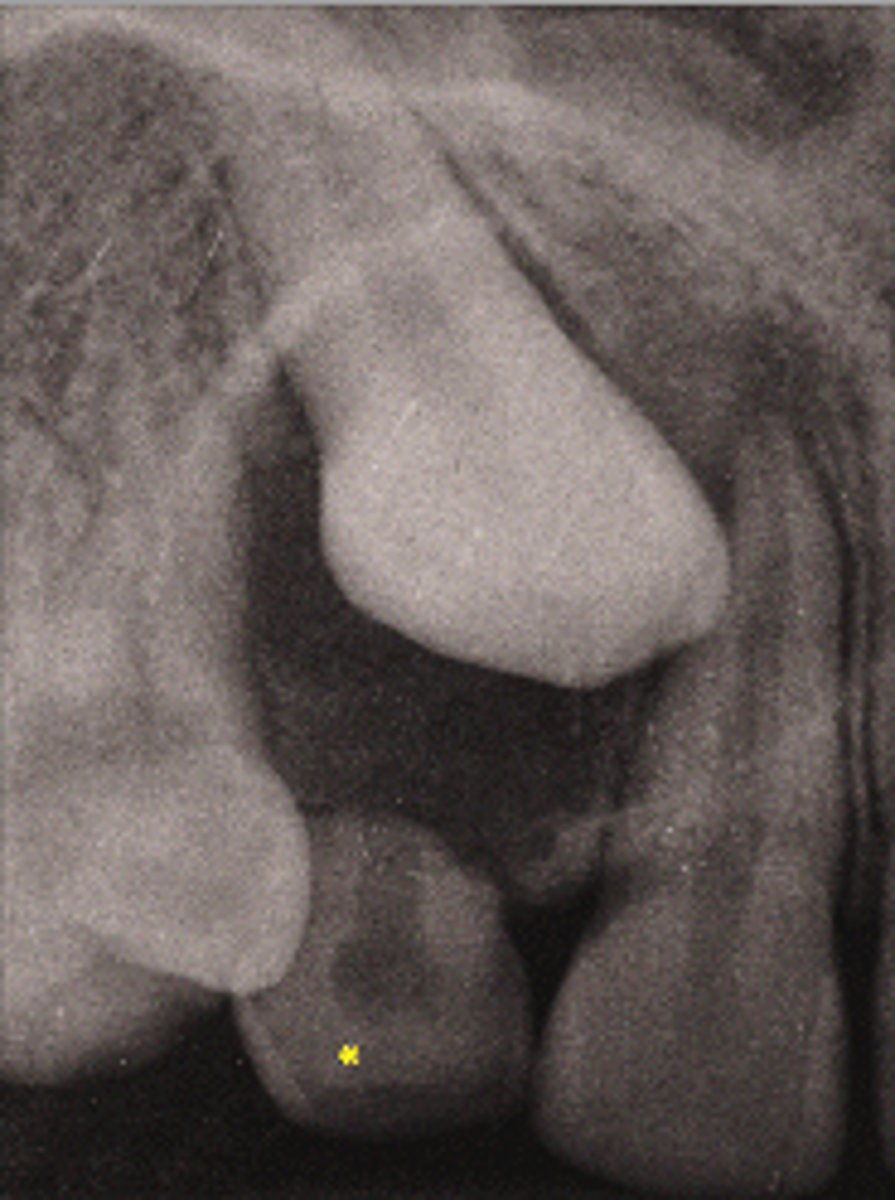
This images follicles measure less than 5mm from crown to follicle border
how can you tell that this is a developmental sac and not a dentigetous cyst?
vital
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KOT)/Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC) are associated with ____ teeth
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KOT)/Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC)
ID the cyst:
•Well defined corticated periphery
•Undulating/scalloped borders
•Radiolucent interior
•Multilocularity (internal septae) is typically noted, but may be unilocular
•Minimal expansion and thinning of cortices
•Displacement of IAN canal inferiorly
•Displacement and resorption of teeth may be seen
odontogenic
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KOT)/Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC)
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KOT)/Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC)
OR
Dentigerous cyst
DDX (differential diagnosis) for the cyst:
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KOT)/Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC)
OR
Lateral radicular cyst
OR
Lateral Periodontal Cyst
DDX (differential diagnosis) for the cyst:
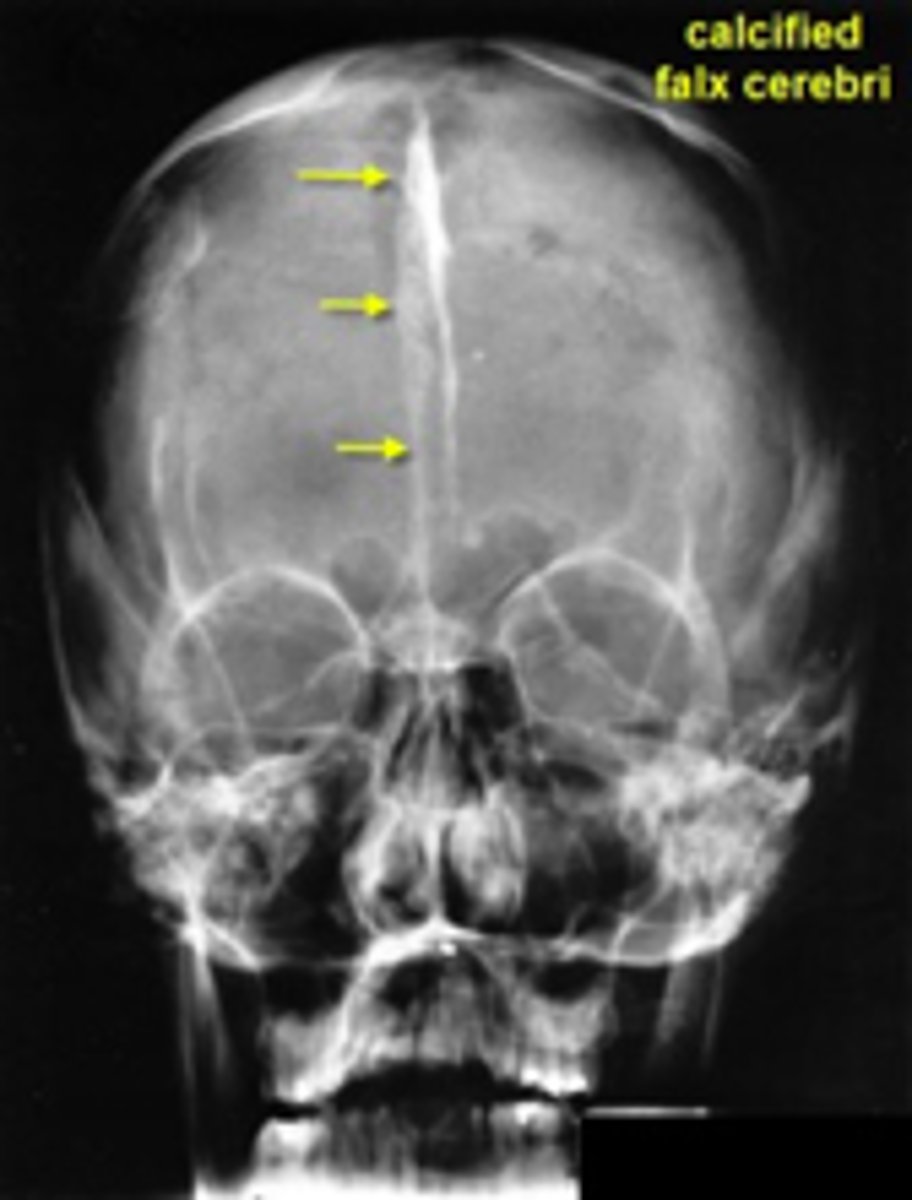
Gorlin Goltz Syndrome/Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
ID the condition:
•Multiple OKCs/ KOTs in multiple locations of both jaws
•Other findings:
•Basal cell carcinoma
•Skeletal anomalies- bifid ribs
•Calcification of falx cerebri
Gorlin Goltz Syndrome/Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Basal cell carcinoma is associated with what type of cyst?
Gorlin Goltz Syndrome/Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Bifid ribs are associated with what type of cyst?
Gorlin Goltz Syndrome/Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Calcification of falx cerebri is associated with what type of cyst?
Gorlin Goltz Syndrome/Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
ID the cyst:
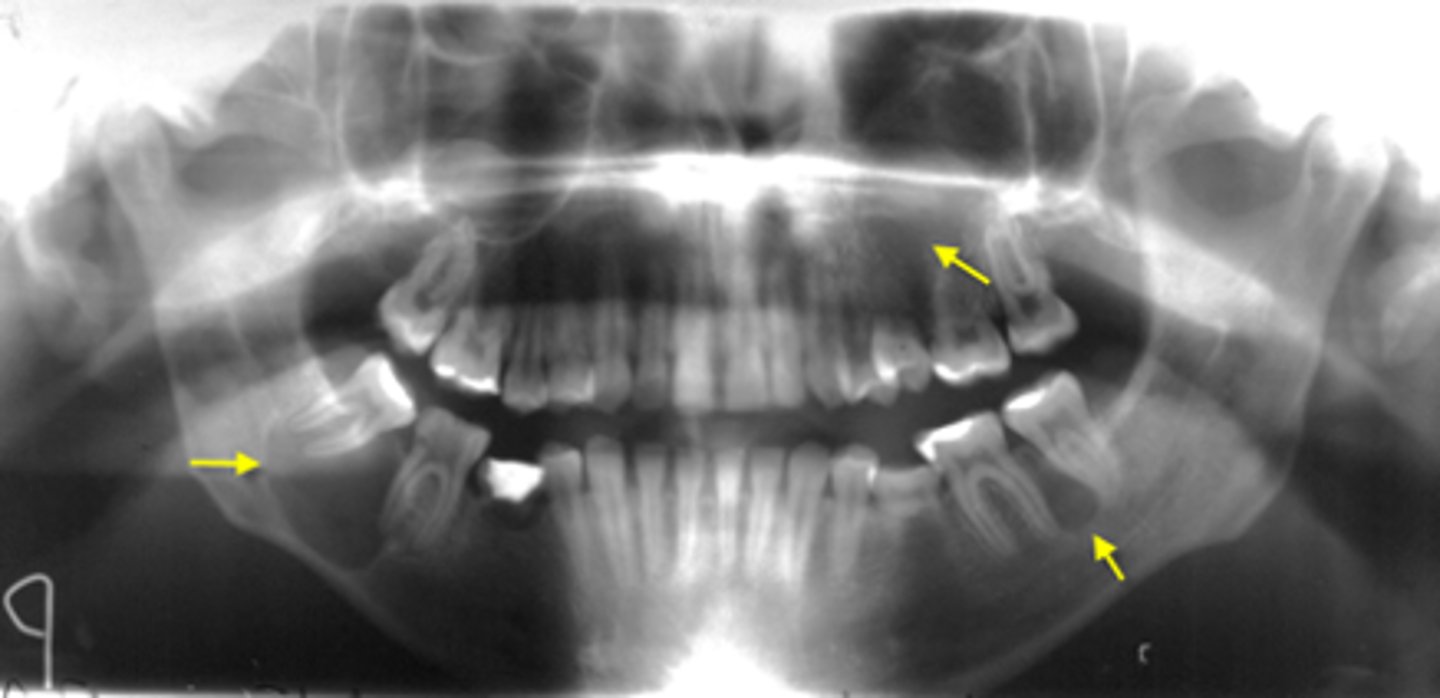
Lateral Periodontal Cyst
•Radiolucent lesion
•Well defined corticated periphery
•Round/oval
•Located between cervical margin and apex
•of adjacent roots
•Typically in contact with root surface
•Vital teeth
Lateral Periodontal Cyst
ID the cyst (tooth is vital)
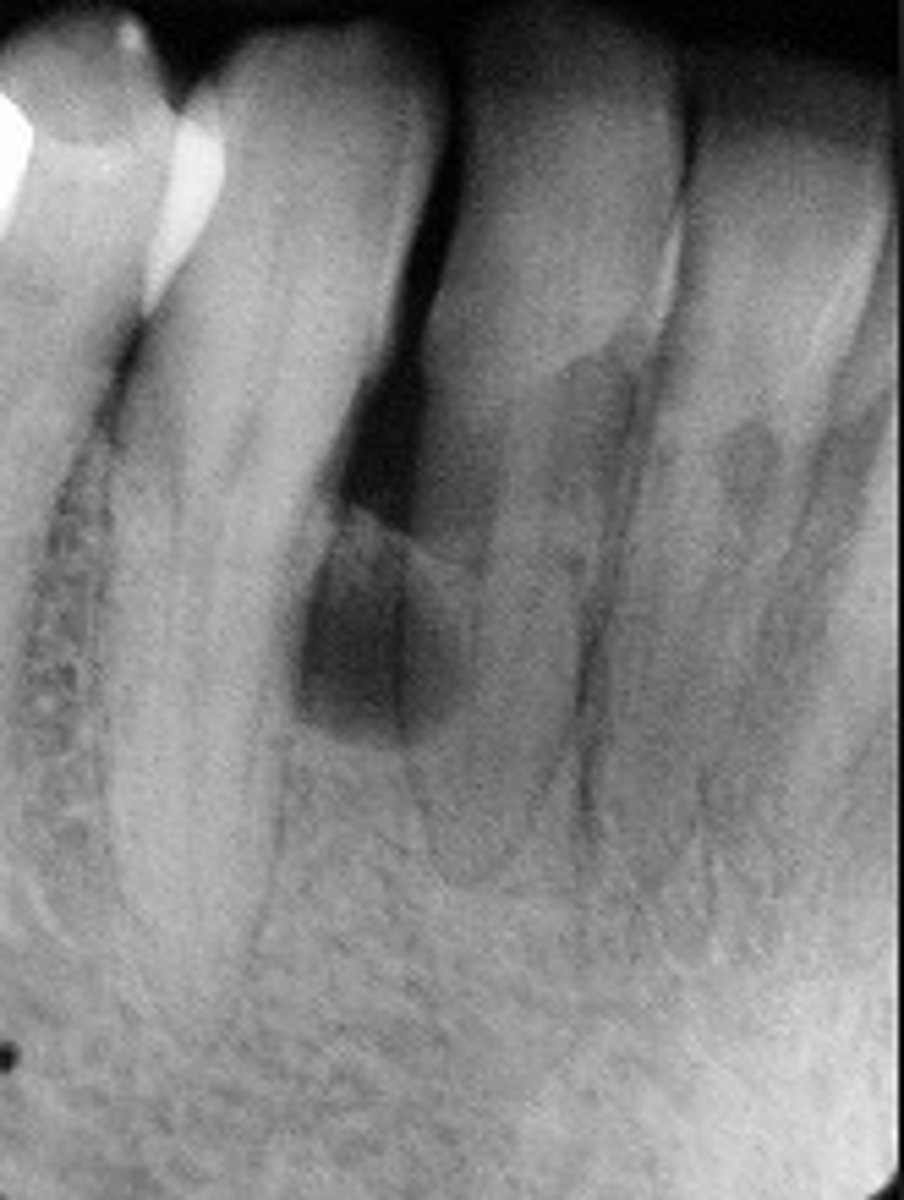
Lateral Periodontal Cyst
ID the cyst (tooth is vital)
odontogenic
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Lateral periodontal cyst
vital
Lateral Periodontal Cyst are associated with ____ teeth
canine-incisor area
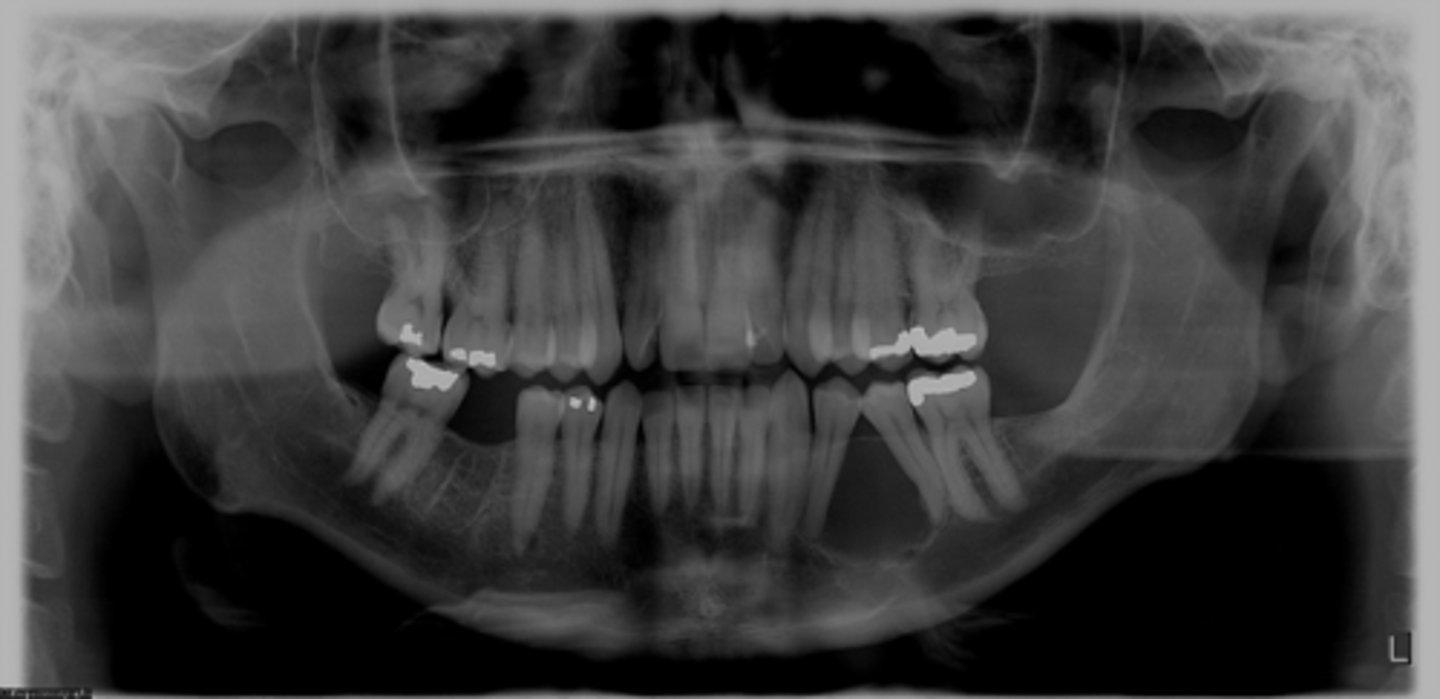
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Cyst (CEOC/Gorlin Cyst )Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor (CCOT) commonly present in what region?
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Cyst (CEOC/Gorlin Cyst )Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor (CCOT)
ID the cyst:
•Mostly in canine-incisor area
•Well defined corticated periphery, maybe ill defined
•Internal aspect- Radiolucent periphery w/ mixed density (mixed radiolucent-radiopaque)
•Maybe associated with unerupted tooth (impeding eruption)
•May cause displacement, resorption of roots, cortical perforation
odontogenic
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Cyst (CEOC/Gorlin Cyst )
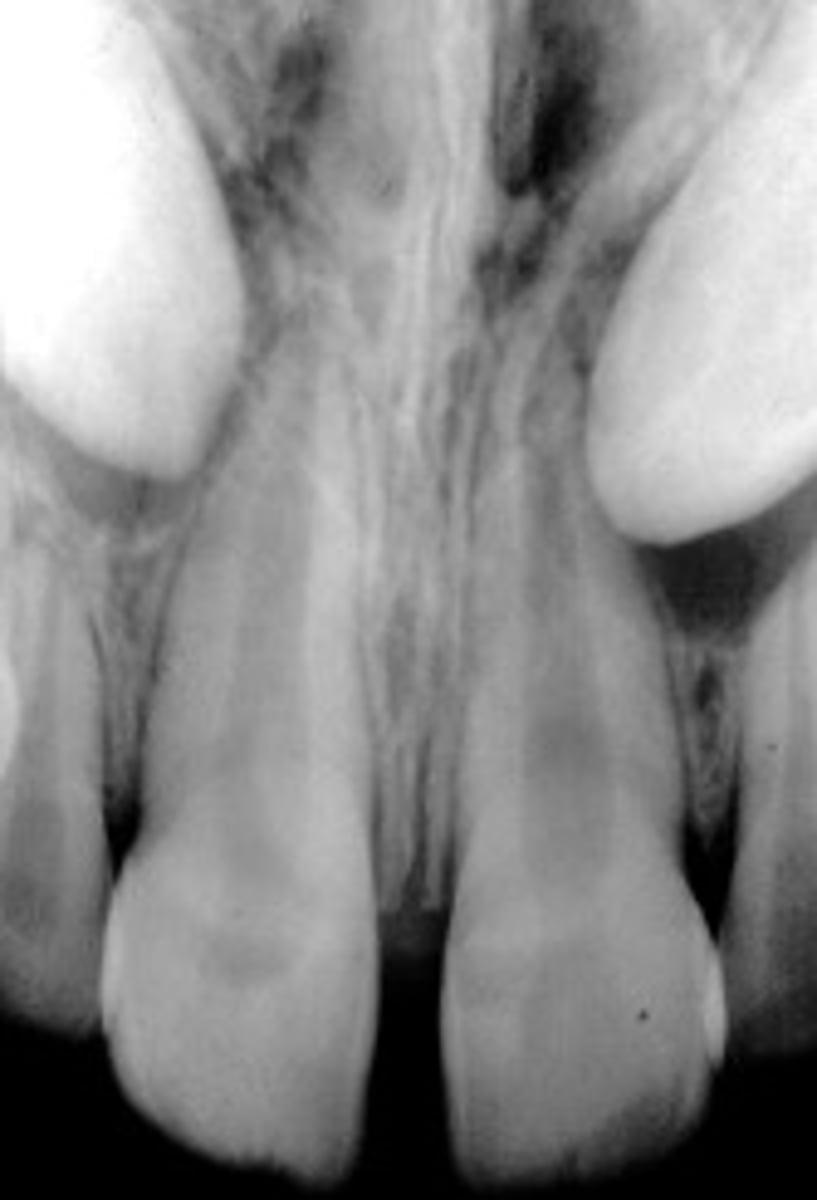
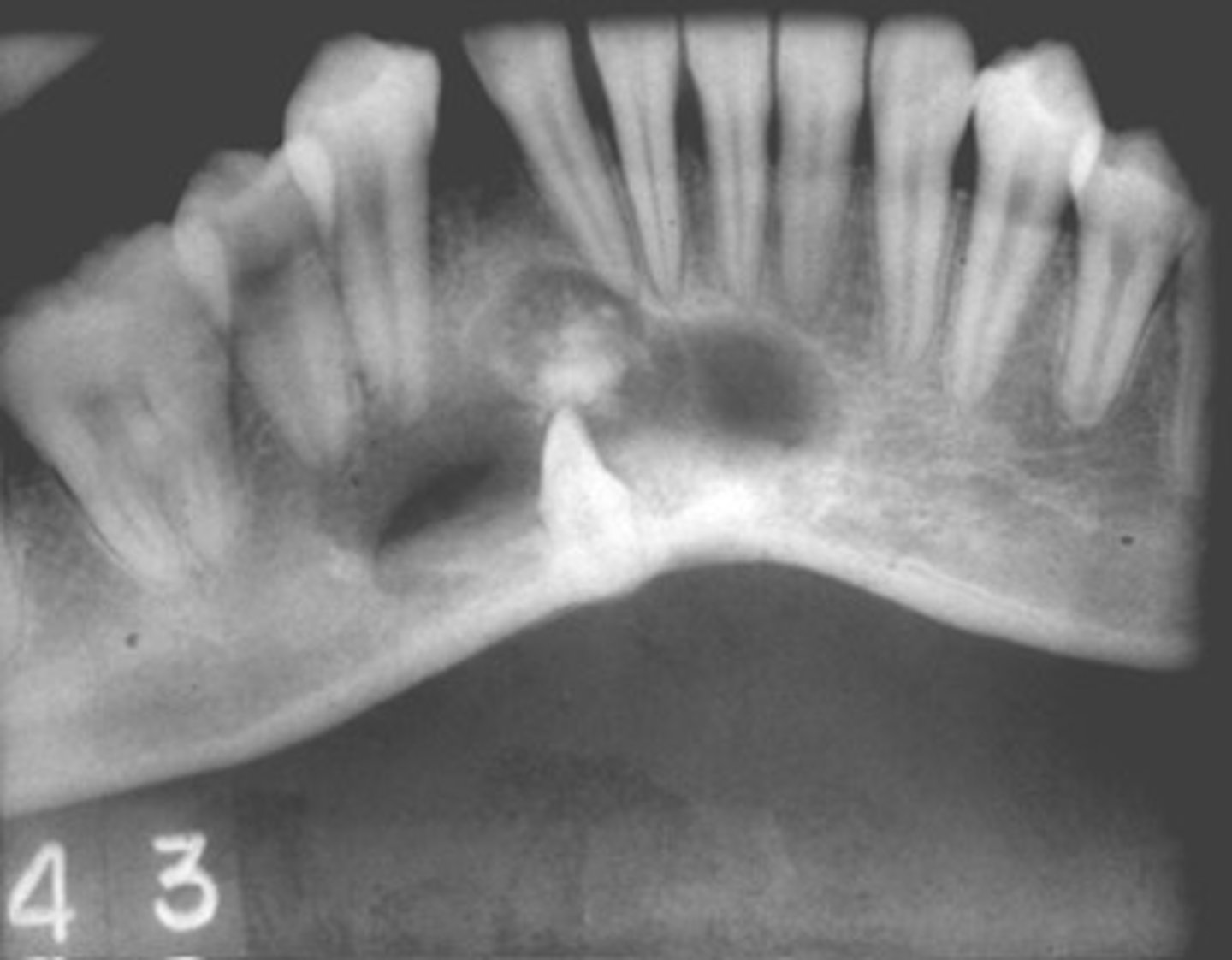
Nasopalatine duct cyst
ID the cyst:
•Well defined corticated periphery
•radiolucent
•Involves nasopalatine canal and incisive foramen
•Lesion is palatal to the teeth
•Maybe 'heart-shaped' due to superimposition of anterior nasal spine
•Lesion is superimposed over the apices of maxillary central incisors
•No changes in apical structures of these teeth (lamina dura, PDL)
•Vital teeth
•May displace these teeth
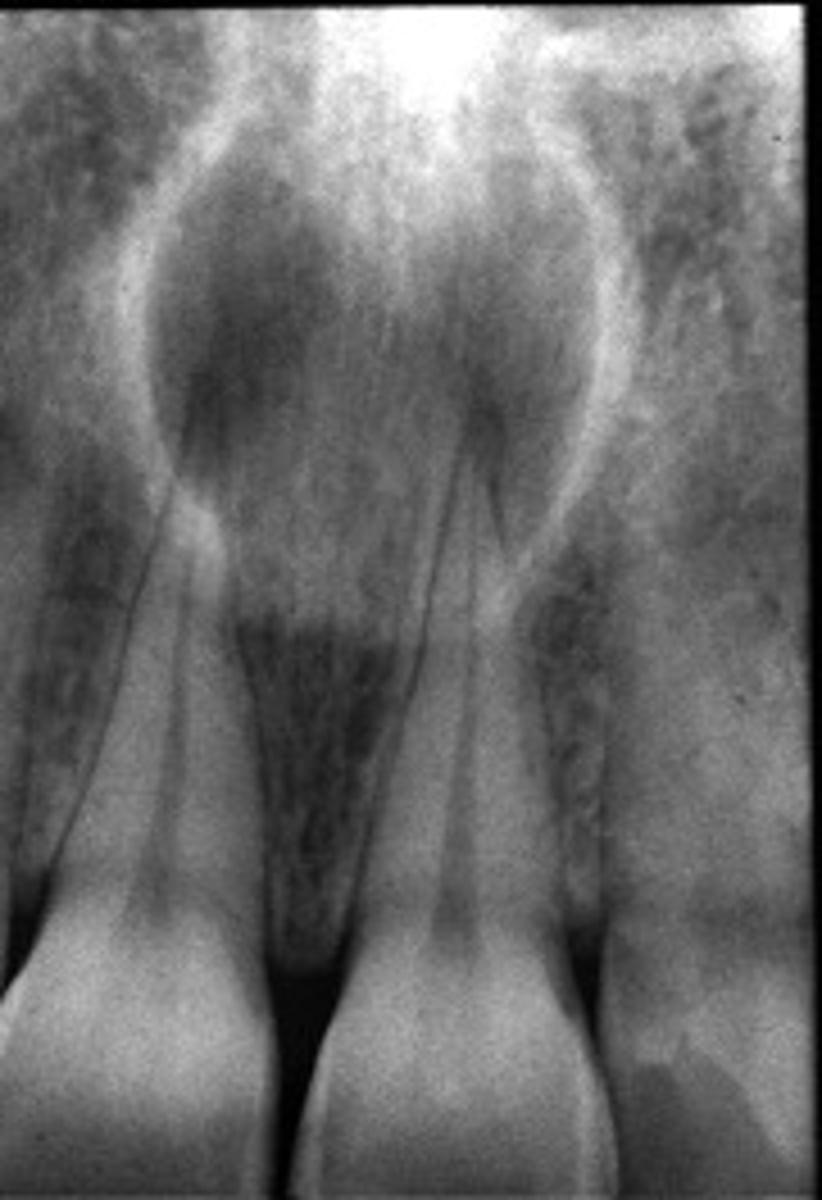
non-odontogenic
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Nasopalatine duct cyst
Nasopalatine duct cyst
ID the cyst:
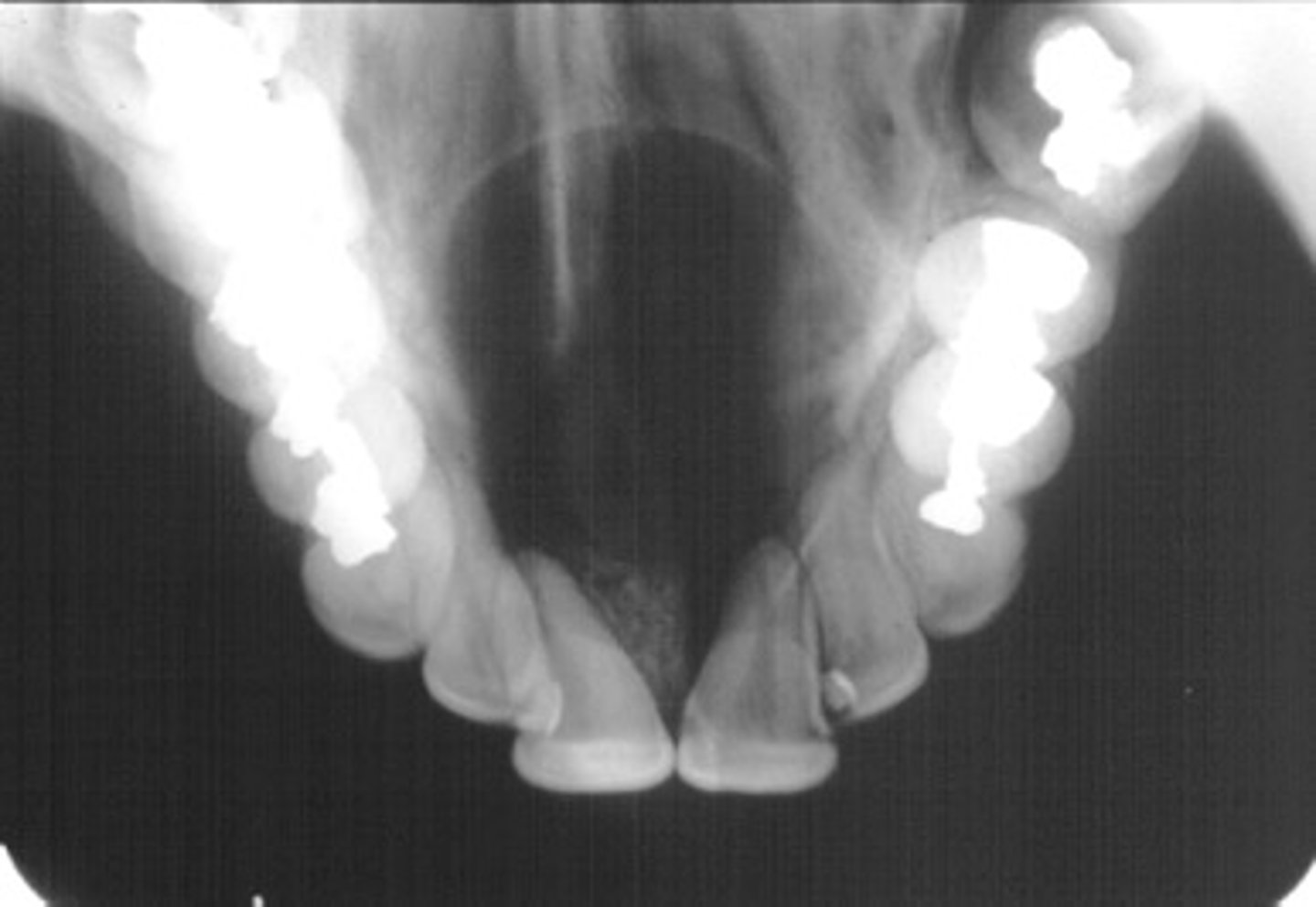
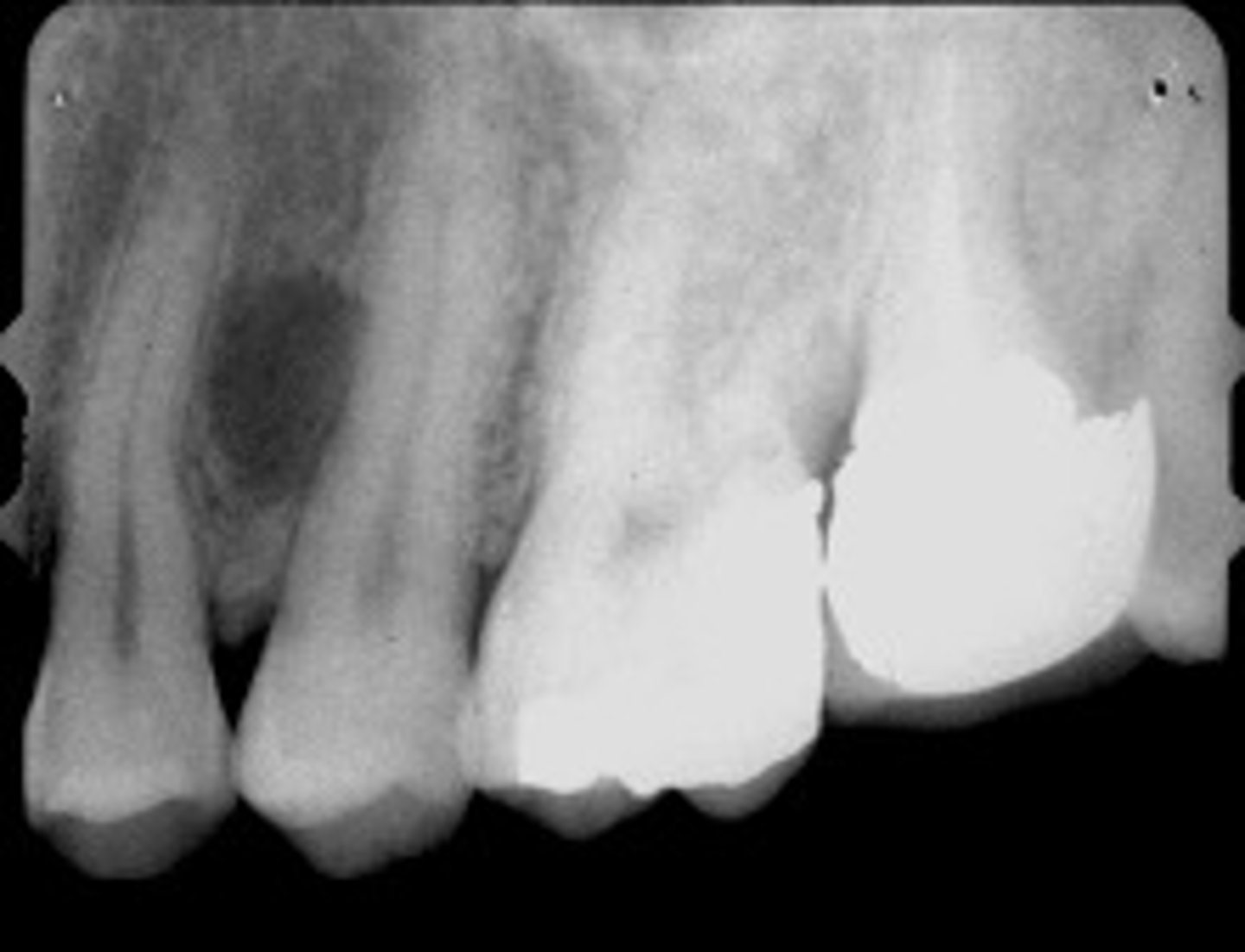
This image shows widening of PDL and Lamina dura disrupted, and is NOT on the midline
How do you know this is NOT a Nasopalatine duct cyst?
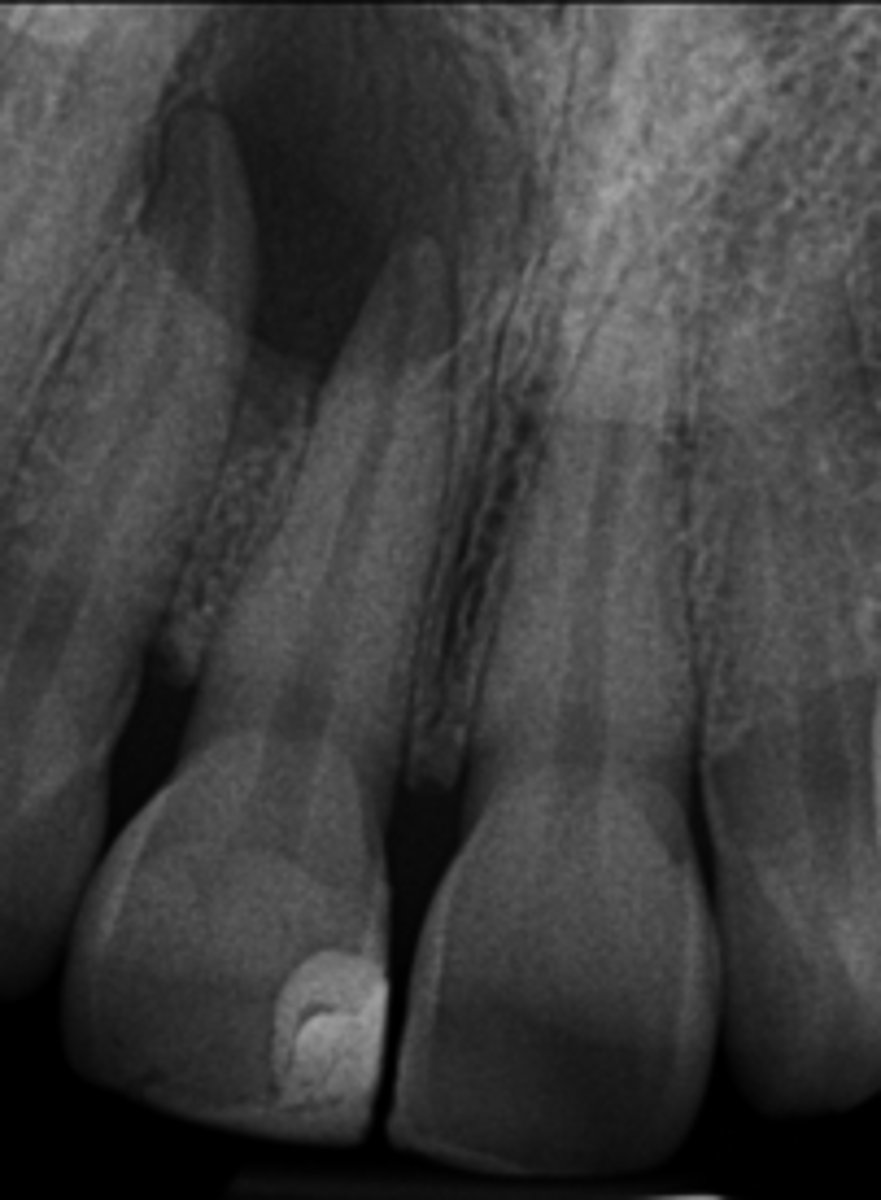
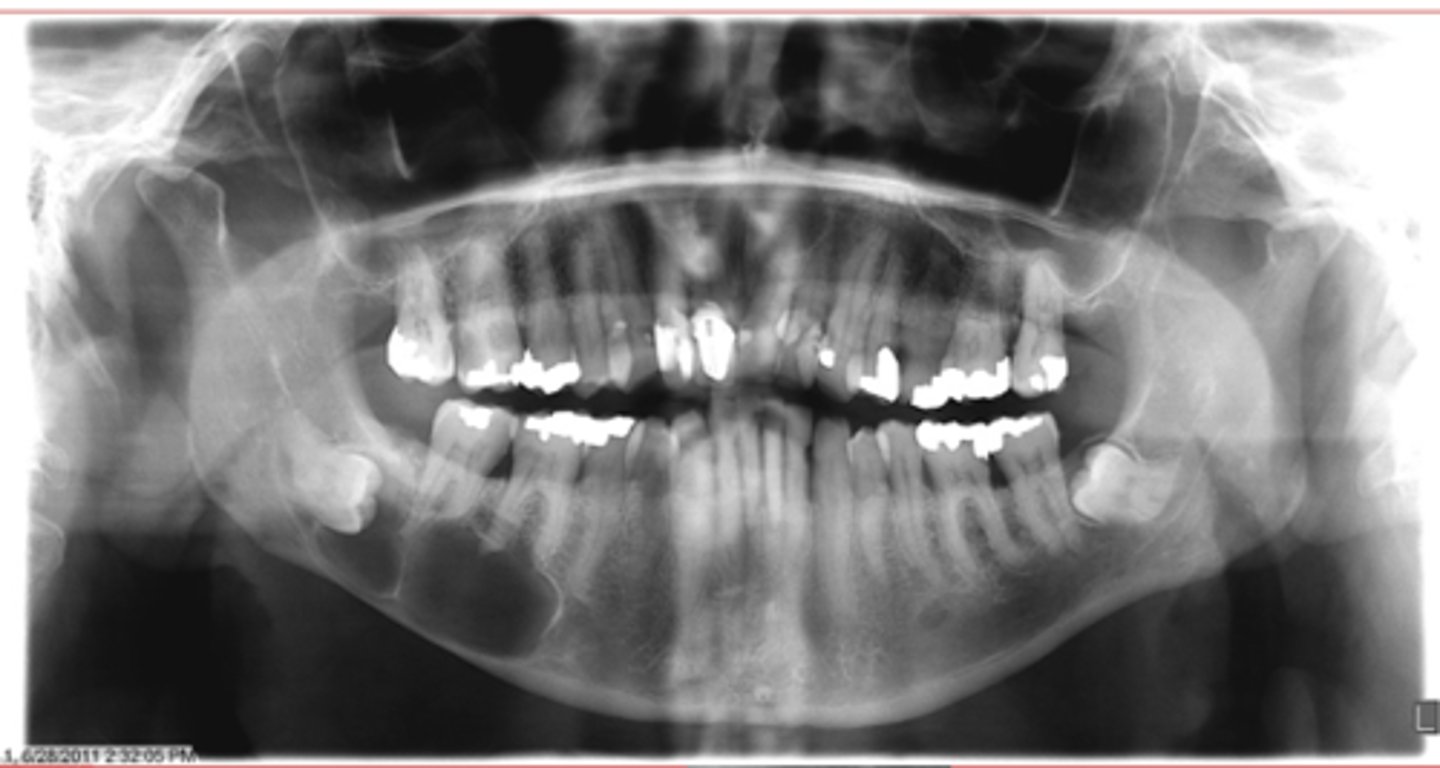
Simple Bone Cyst/Traumatic bone cyst
ID the cyst:
•Radiolucent lesion
•Moderately to well-defined borders
•Unilocular or multilocular
•May create scalloping between roots of involved teeth
•Does not resorb or displace tooth roots
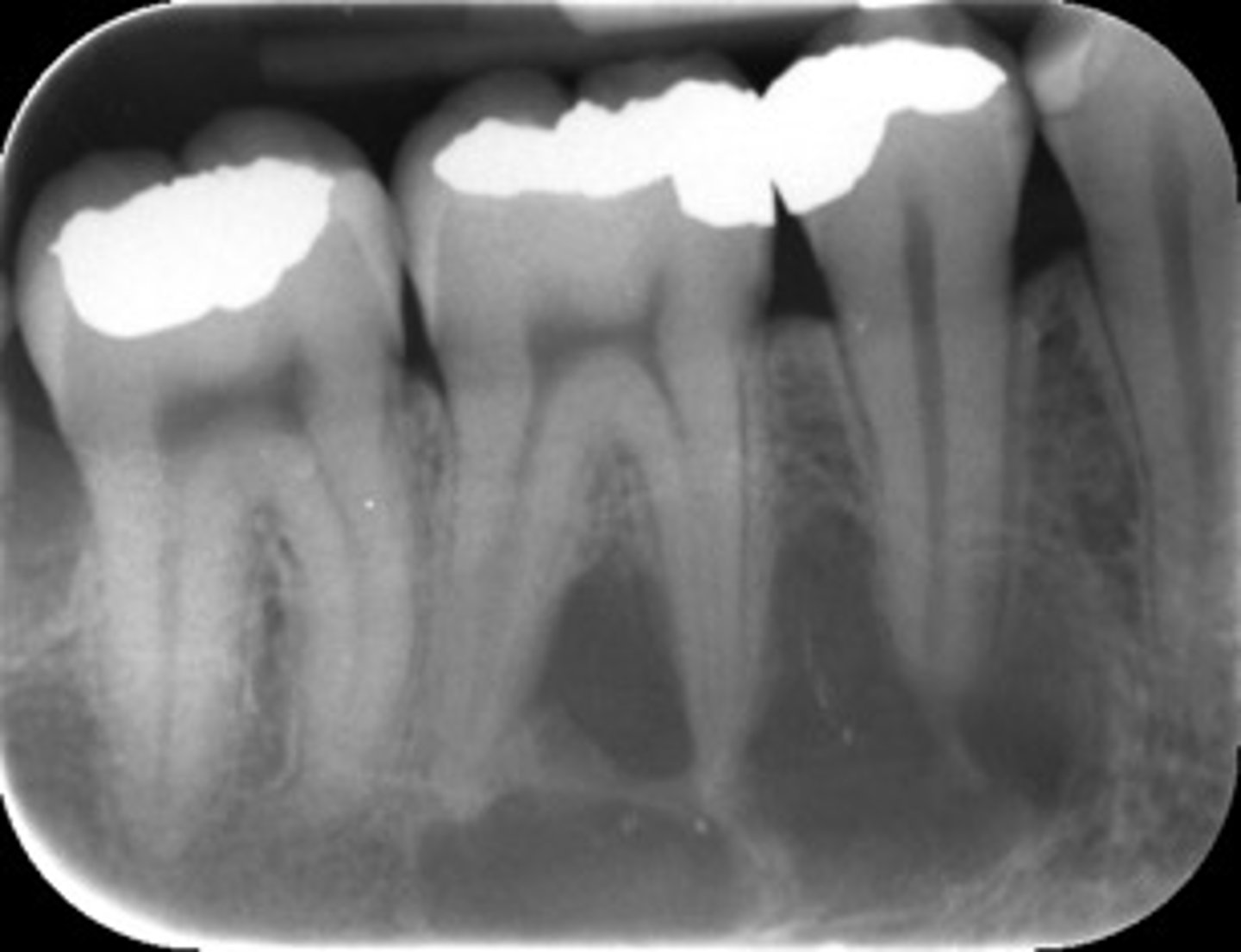
cyst-like
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
simple bone cyst
Simple Bone Cyst/Traumatic bone cyst
ID the cyst:
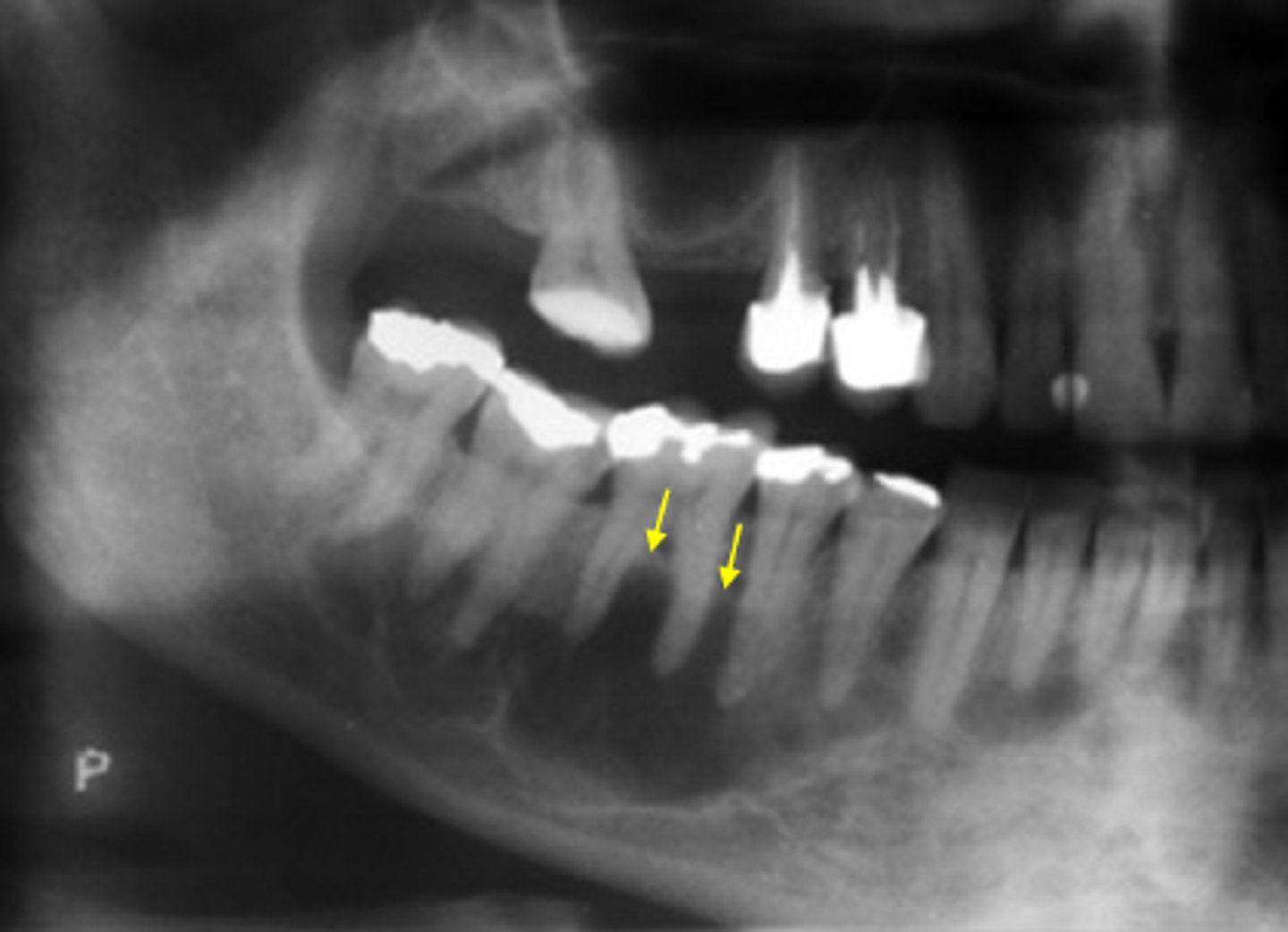
This cyst has obvious effects on surrounding structures, expansion and displacement of roots
how do you know this is NOT a Simple Bone Cyst/Traumatic bone cyst?
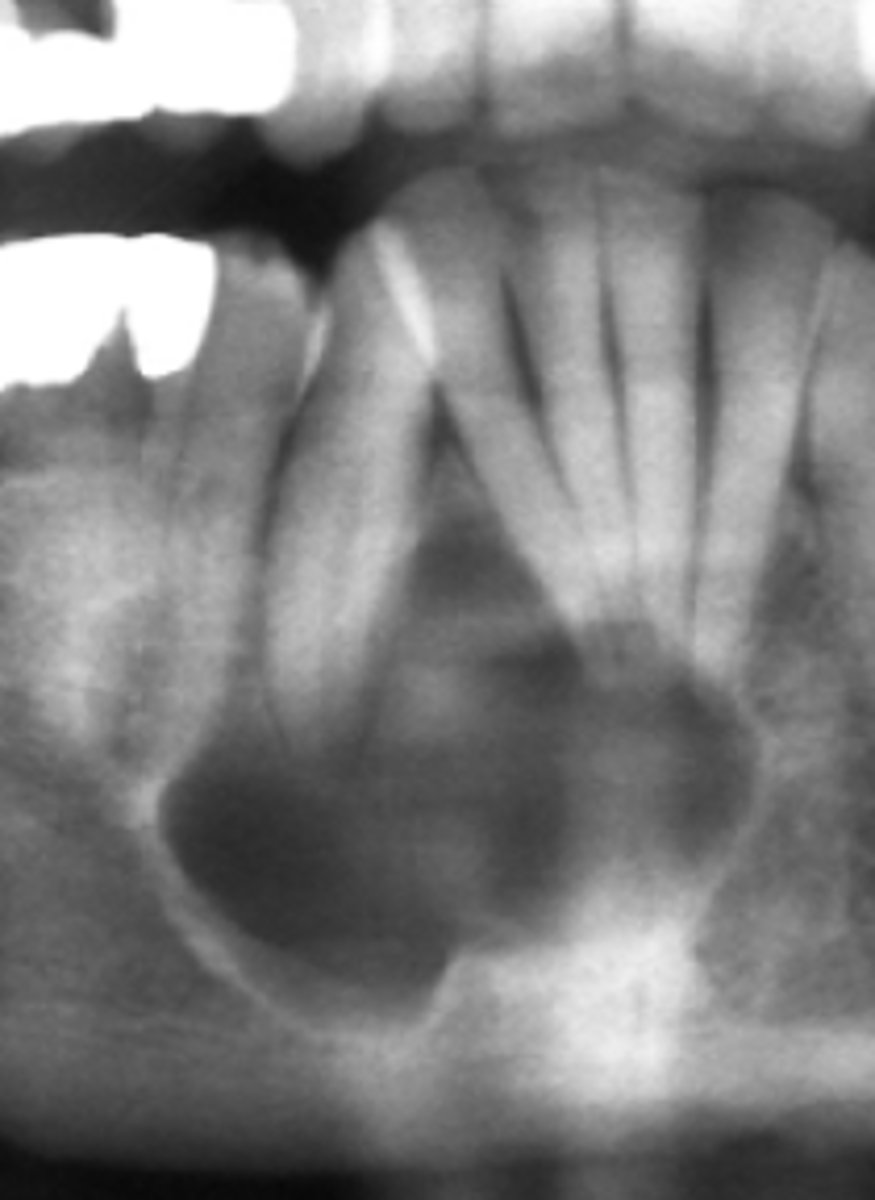
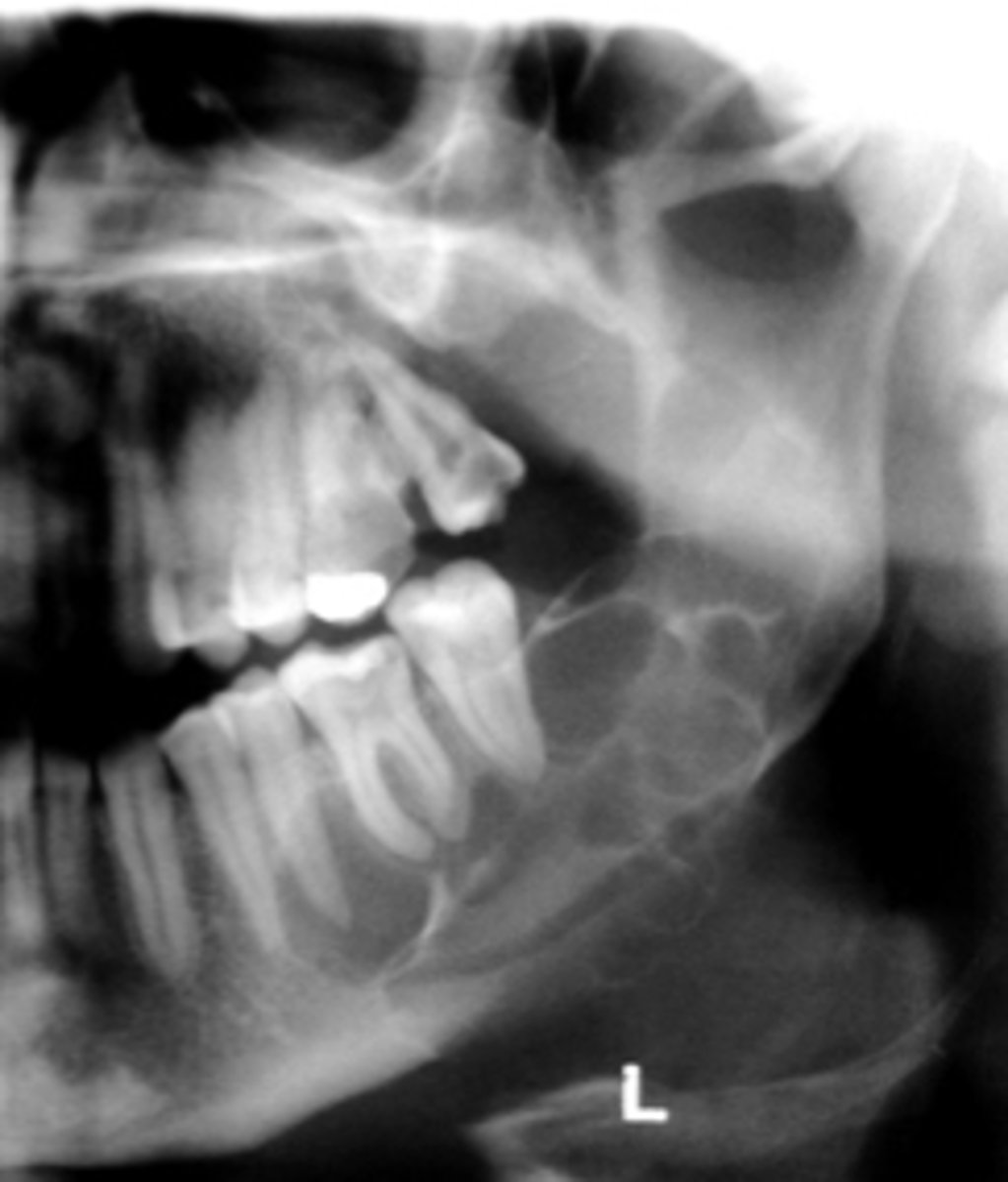
Stafne defect
•located between inferior alveolar nerve canal and inferior border of mandible
•oval/round/elliptical shape
•well-circumscribed radiolucency
•Dense sclerotic corticated (radiopaque border) usually on the superior aspect
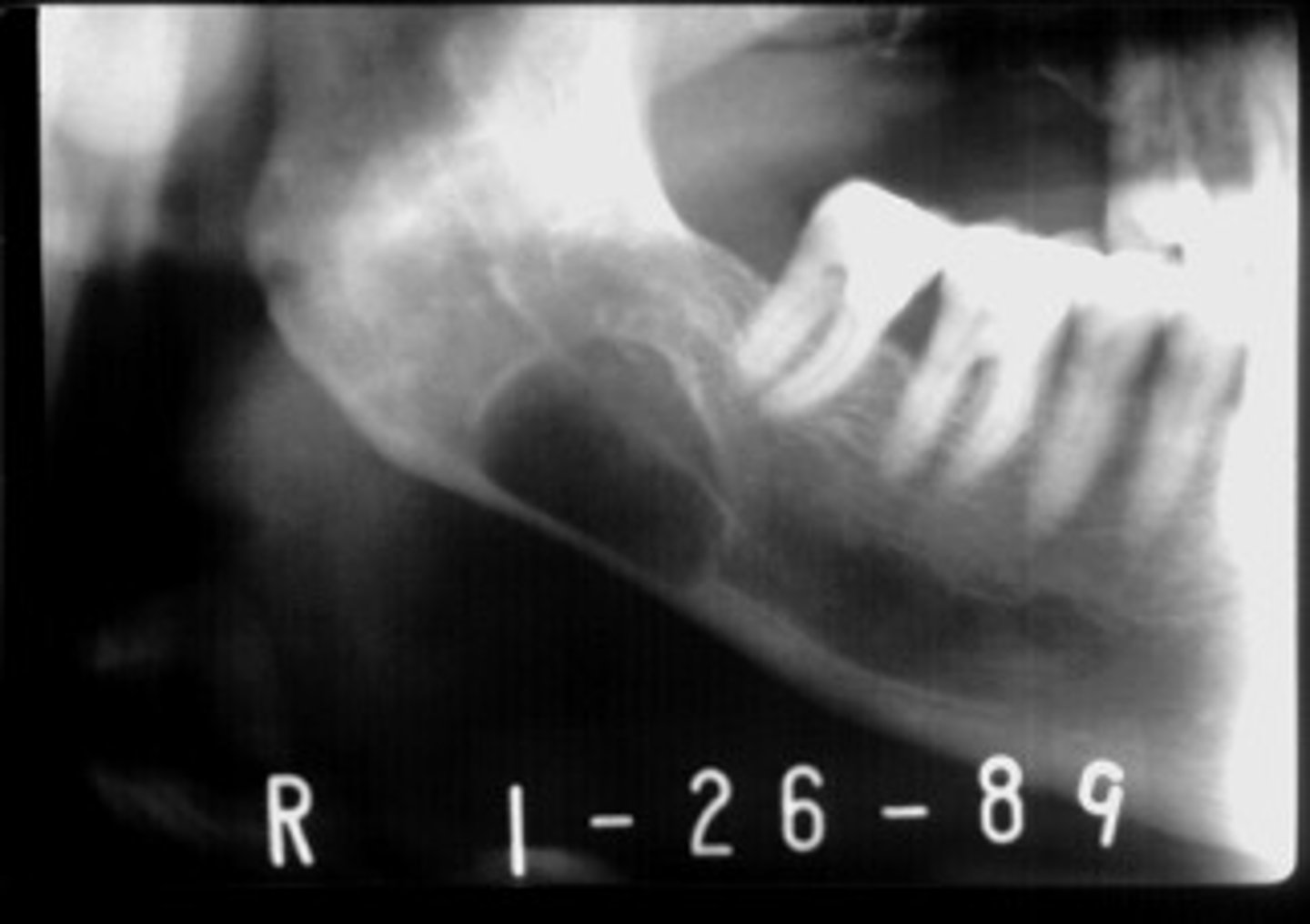
cyst-like
Odontogenic, Non-odontogenic, or Cystlike lesion:
Stafne defect
Stafne defect
ID the pathology:
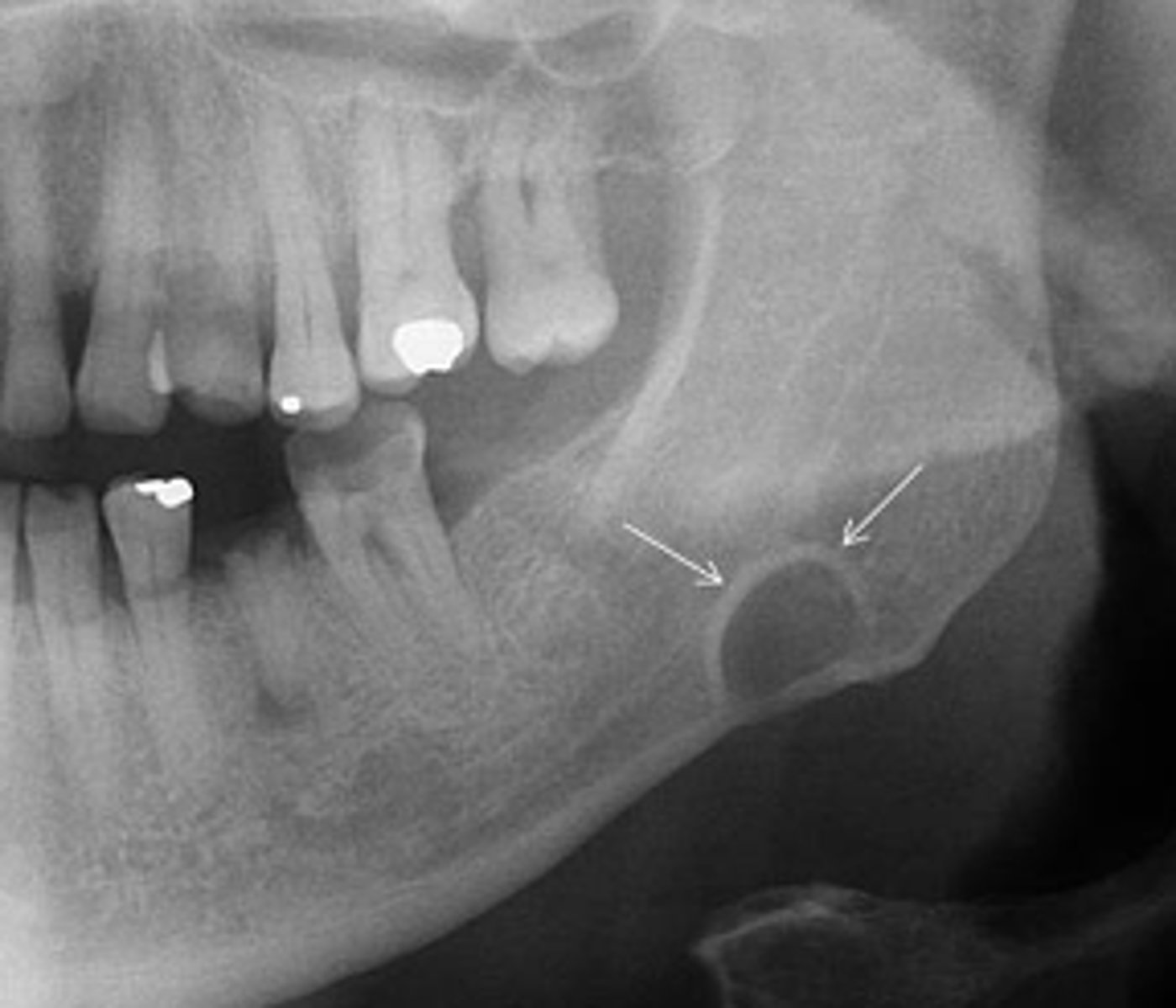
below
In relation to the IAN canal, where do Stafne defects present?
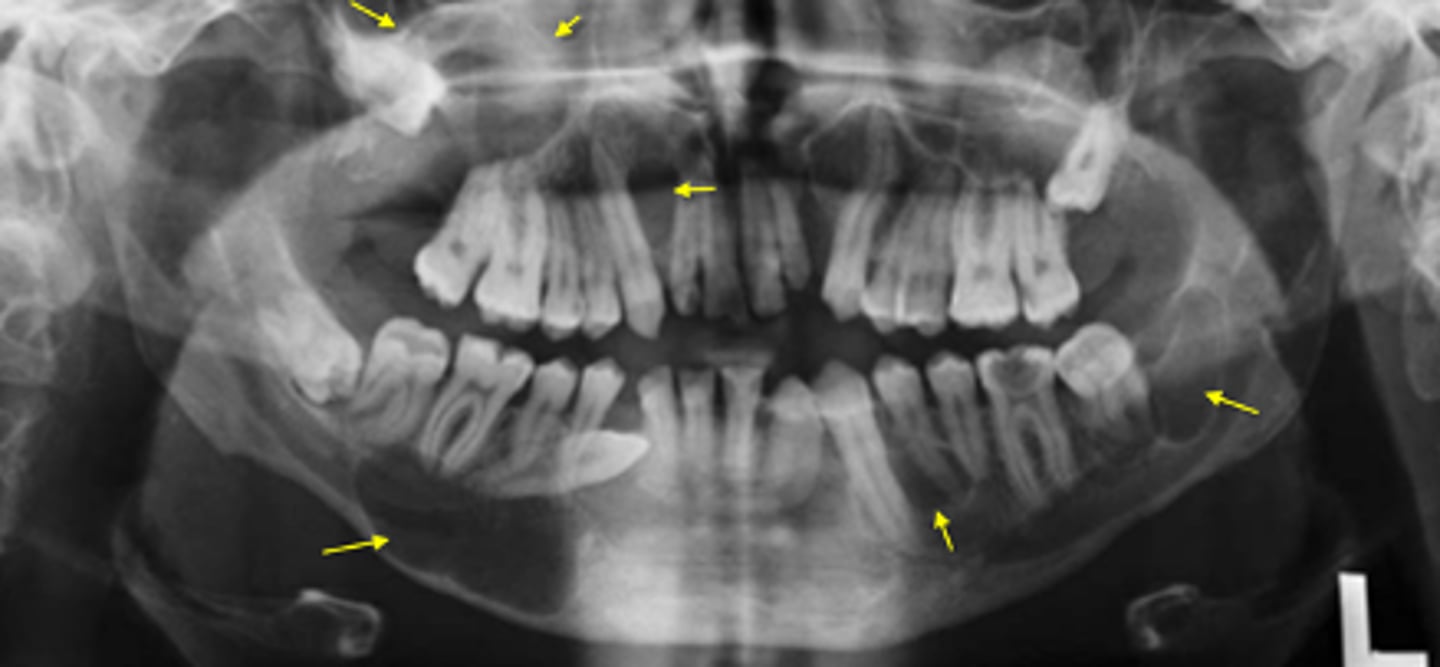
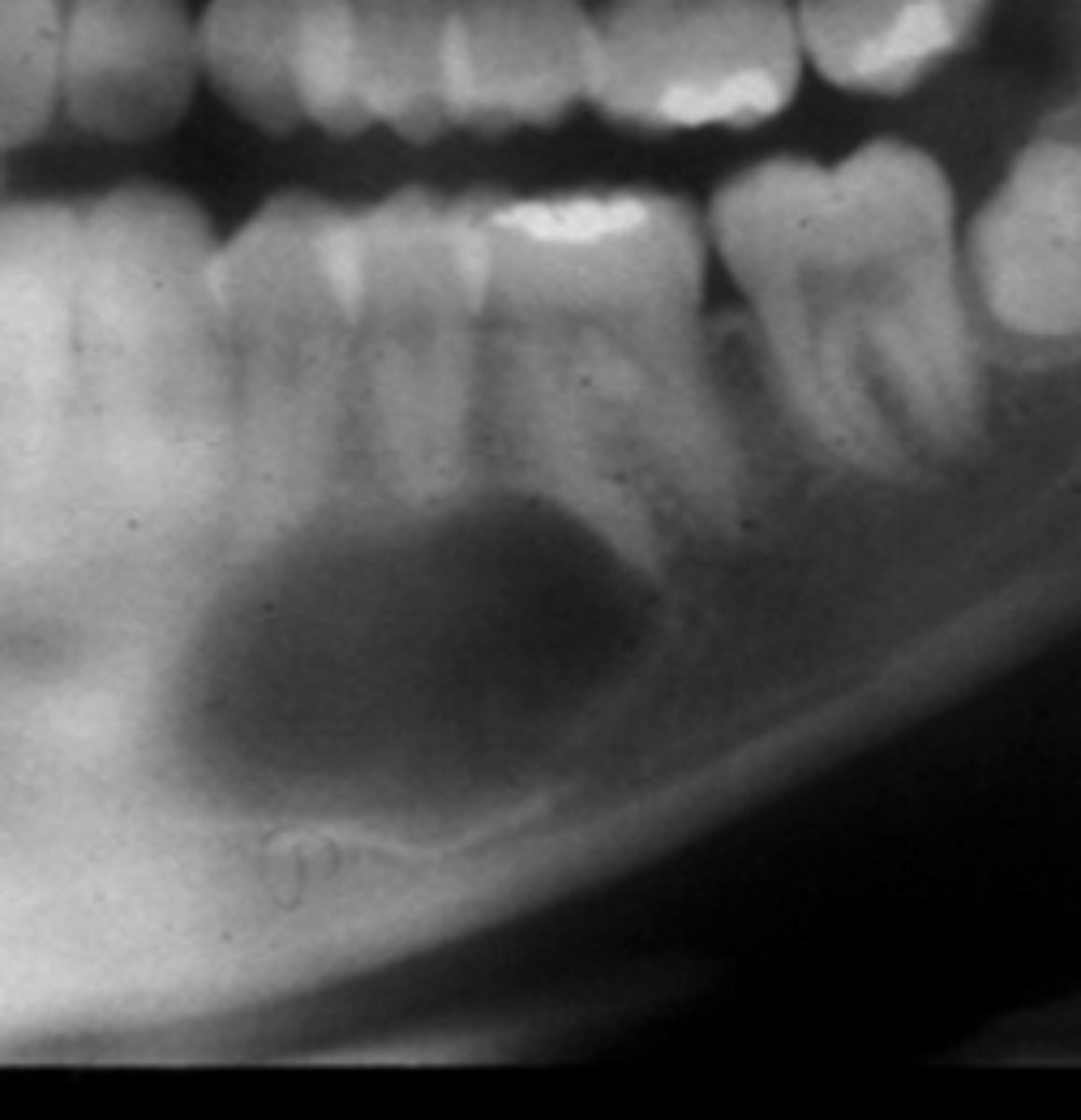
This image has an IAN canal that is inferiorly displaced and roots resorbed
How do you know that this is NOT a Stafne defect?
Mucus Retention Pseudocyst
•Not a true cyst
•Obstruction or dilatation of the duct of sero-mucous glands in sinus resulting in submucosal accumulation of secretions
•Radiographic feature :
•Relative radiopacity on the floor of sinus
•Well-defined, not corticated
•Dome-shaped
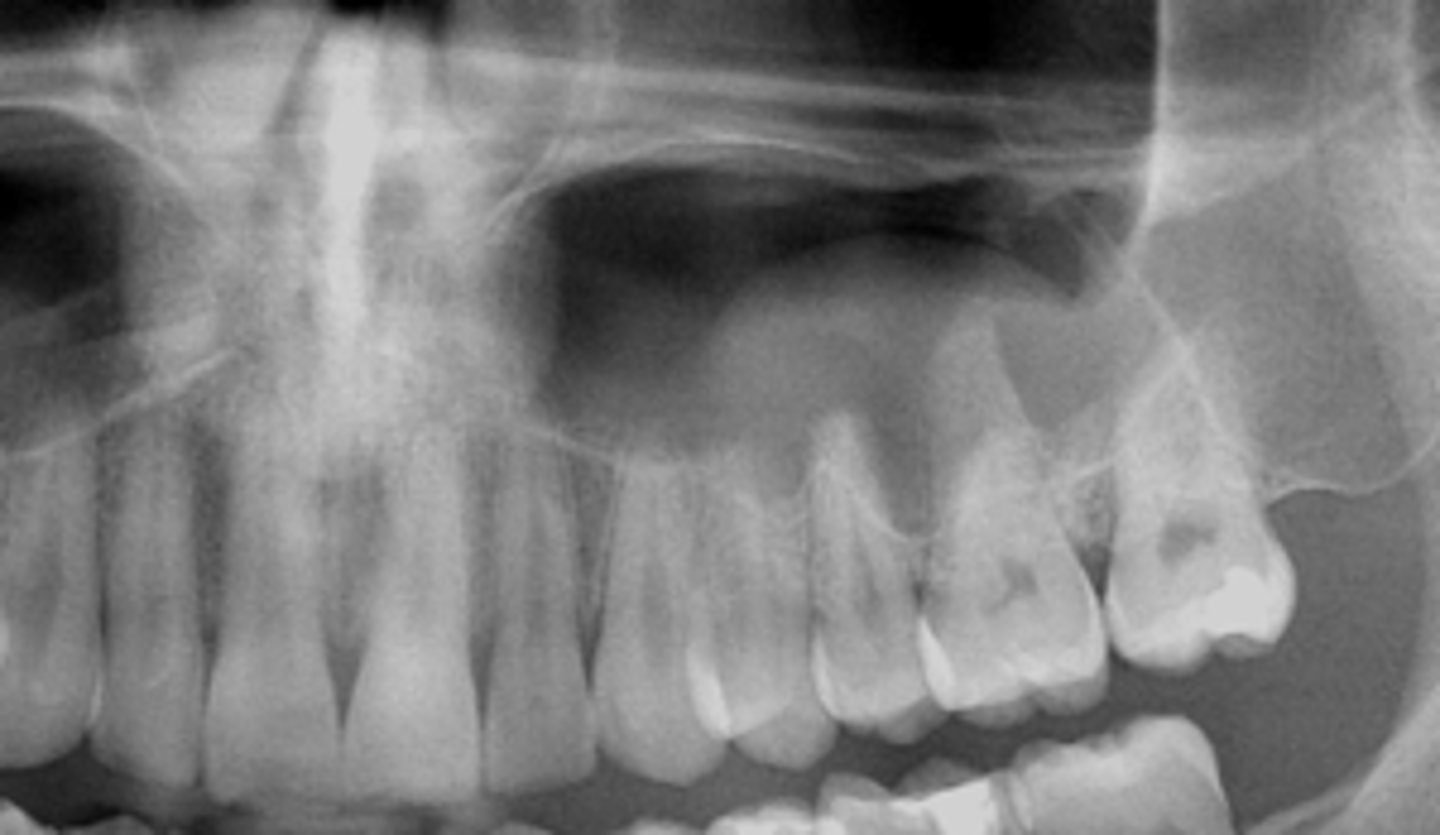
Mucus Retention Pseudocyst
ID the cyst:
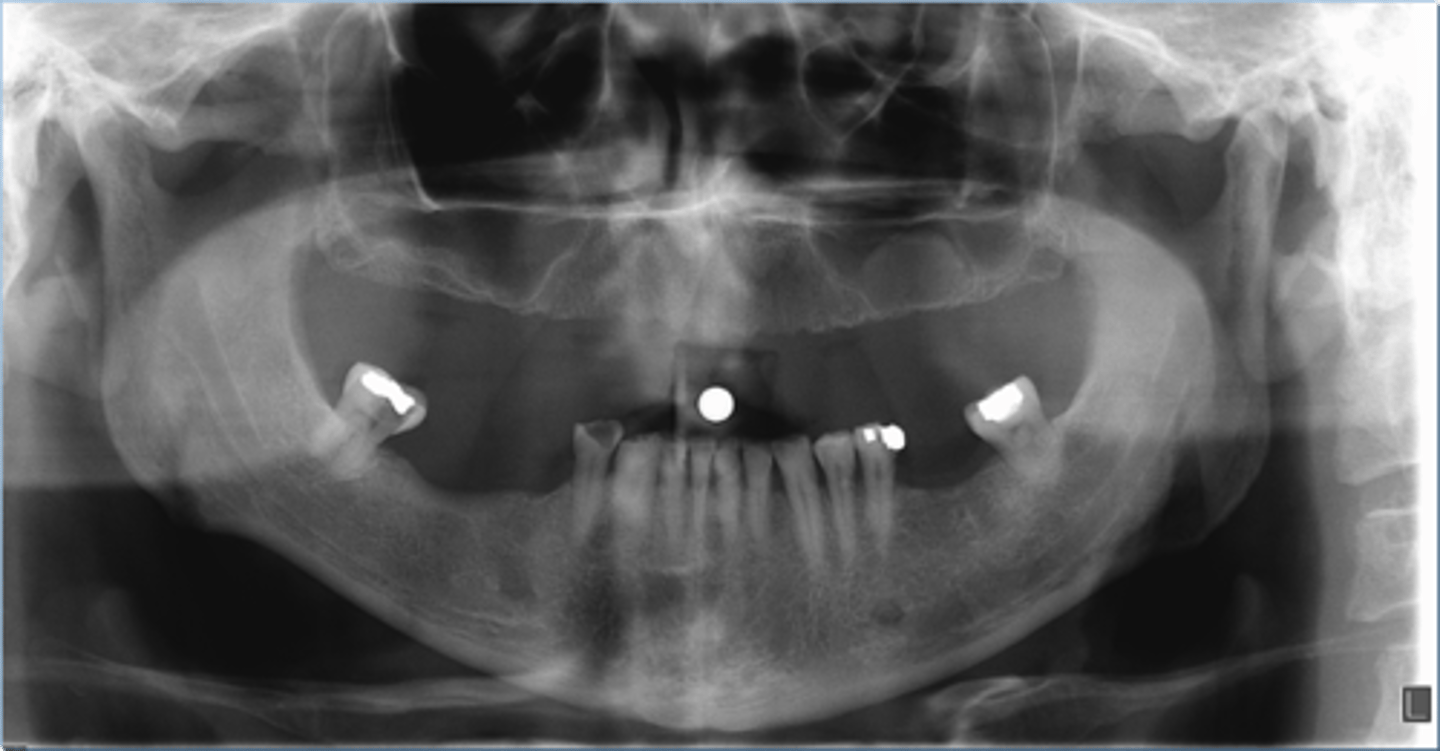
Mucus Retention Pseudocyst
ID the cyst:
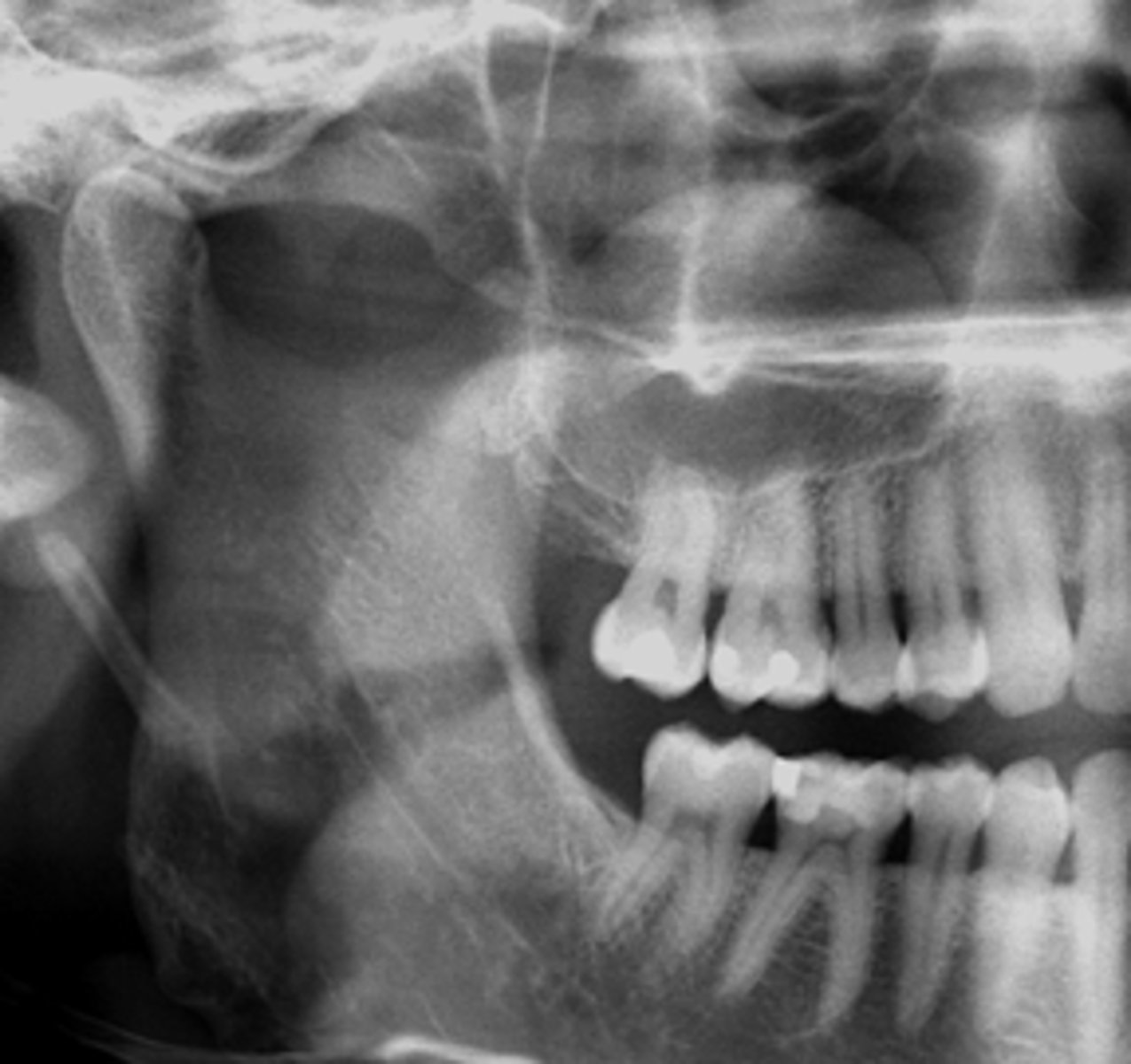
This lesion is corticated
How do you know that this is NOT a Mucus Retention Pseudocyst?