microbio 2125 unit 5 (part 6) Streptococcal Diseases – Long-term Complications / Sequelae
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
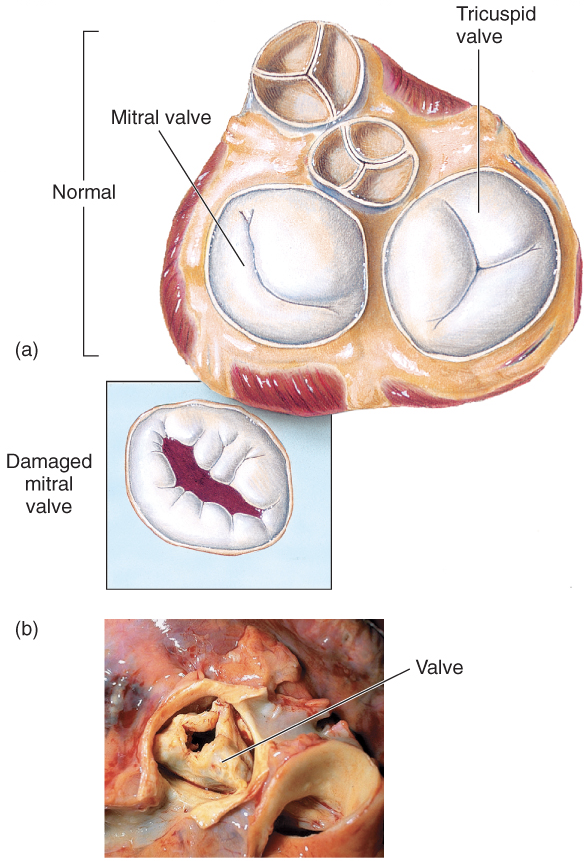
Rheumatic fever
follows overt or subclinical pharyngitis in children or scarlet fever, lasts 3 - 6 months, can lead to carditis with extensive valve damage possible, degree of damage not apparent until middle age
Acute glomerulonephritis
nephritis, increased blood pressure, occasionally heart failure; can become chronic leading to kidney failure
Etiological Agent:
Streptococcus pyogenes (post-infection immunological response)
Distinguishing characteristics of etiological agent:
Usually arranged in chains or as diplococci
Non-spore forming, non-motile
Form capsules and slime layers
β-hemolytic on blood agar
Strict parasite
Inhabits throat, nasopharynx, occasionally skin
Most serious streptococcal pathogen
Virulence Factor(s):
C-carbohydrates and M-protein
the others might show up maybe Hemolysins, C5a protease, Hyaluronic acid, & Erythrogenic toxin in some instances
Predisposing Factors:
Untreated or recurrent strep throat infections
Genetic susceptibility (rheumatic fever)
Children ages 5–15 (most at risk)
Transmission:
Not directly transmissible — these are immune-mediated complications following infection) but…
contact, droplets, food, fomites
Syndrome (signs + symptoms): Rheumatic fever
can cause arthritis, chorea, fever and nodules under skin
migratory arthritis, carditis, chorea, subcutaneous nodules, erythema marginatum
Syndrome (signs + symptoms): Acute glomerulonephritis
hematuria (“cola-colored urine”), edema, hypertension, proteinuria
can become chronic leading to kidney failure
Affected body region/system:
Heart, joints, kidneys, CNS
Treatment:
No treatment for rheumatic fever and acute glomerulonephritis once developed, must treat preceding infections to avoid these conditions
Recommend long-term penicillin prophylaxis for people with history of rheumatic fever or recurrent strep throat
Prevention:
Timely and complete antibiotic treatment of strep throat
Long-term prophylaxis in rheumatic fever patients to prevent recurrence
Other notes:
Rheumatic heart disease can lead to lifelong cardiac issues… rheumatic fever can lead to carditis with extensive valve damage possible, degree of damage not apparent until middle age
Glomerulonephritis usually resolves but can lead to chronic kidney disease in rare cases
Sequelae
are long-term or delayed complications that occur after the resolution of an initial disease or infection.
for example Rheumatic fever is a sequela of untreated streptococcal pharyngitis.